Articles on the topic
power of attorney to the personnel officer for the right to sign personnel documents for the director and resolve personnel issues. Read tips on what to write in a power of attorney for signing personnel documents.
A power of attorney to sign personnel documents for the director and to resolve other personnel issues is needed to delegate to the personnel officer the authority to conclude employment contracts, dismissal and other issues within the framework of labor relations.
If you do not transfer the authority to the HR officer by power of attorney to sign personnel documents, in the absence of the director he will not have the right to hire, fire or impose penalties. When the director returns, the time frame for processing these decisions may already have expired.
Articles on the topic
The only thing that gives legal force to any document drawn up in an organization is the signature of the manager. But there are times when a manager cannot physically sign documents. From this article we will learn what a power of attorney is and whether it is possible to issue a power of attorney to sign personnel documents. What conditions must be met for this, how to correctly draw up a power of attorney and its validity period.
From this article you will learn:
- Is it possible to transfer the right to sign personnel documents;
- what is a power of attorney and in what cases is it necessary;
- features of the execution of a power of attorney for the right to sign documents;
- sample of a power of attorney for the right to sign personnel documents.
Do I need a power of attorney to sign personnel documents and how to issue it?
As part of the work of every organization, there is a constant need to prepare some documents. Hiring, dismissal, receipt of wages, business trips, transfers, vacations, sick leave - all this is important to document in order to be able to protect both the work of the organization and the employee himself. Among other things, it also avoids responsibility to the state. But the most important thing in any document, without which it will not be valid, will not have force and cannot be implemented, is the signature of the manager or any responsible person. Without a signature, it will be just paper.
Read more: Extraordinary meeting of the council to re-elect the chairman
Don't miss: major changes in HR
Why will GIT fine personnel officers?
How is the signature of an authorized person drawn up?
Let us separately dwell on the peculiarities of the execution of the documents themselves, endorsed by an authorized person.
When a representative acts under a power of attorney, the “header” of the civil law contract is drawn up as follows. The principal organization is indicated as a party to the agreement, and then it is stipulated that a representative acts on its behalf under a power of attorney. In this case, the details of the power of attorney (date, number, if any) are entered into the text of the agreement.
Detailed information about the authorized person (date, place of birth, place of residence, etc.) may not be indicated in the contract. But sometimes it's better to do it. For example, if we are talking about large transactions or real estate transactions that are subject to registration. Information about the authorized person is entered into the contract in strict accordance with how it is indicated in the power of attorney.
Limited Liability Company "Lazurit-FS" represented by Dmitry Anatolyevich Nikolaev (if necessary, indicate his passport details, date and place of birth, etc.), acting on the basis of a power of attorney dated September 16, 2019...
Representation is formalized somewhat differently when an authorized person signs unilateral documents on behalf of the principal, for example, statements, claims, etc. In this situation, the inscription “representative by proxy” is written directly next to the signature and the details of the power of attorney are displayed.
As for personnel documentation, here too the procedure for signing the authorized representative depends on the type of document. Thus, when drawing up employment contracts, exactly the same approach is used as when drawing up civil law contracts. That is, the header of the employment contract indicates that it was concluded by a legal entity on whose behalf an authorized representative acts.
And in order for an authorized person to sign other personnel documents (for example, orders), you can make appropriate changes to the “signature” attribute of the issued document. That is, such an order will indicate not “Head of the organization”, but “Authorized person”, and will also add fields to reflect the details of the power of attorney.
But you can go another way. As already noted, the Instructions for filling out unified forms directly provide for the possibility of signing such forms not by the manager, but by an authorized person. But at the same time, there are no reservations in the Instructions that in this case it is necessary to change the “signature” attribute of the form itself.
Therefore, we can draw the following conclusion: the authorized person has the right to put his signature in the appropriate column instead of the manager’s signature. That is, no changes need to be made to the form. And the powers of the signatory, if necessary (at the request of the employee, labor inspectorate, court, etc.) will be confirmed by order and power of attorney.
As part of the work of every organization, there is a constant need to prepare some documents. Hiring, dismissal, receipt of wages, business trips, transfers, vacations, sick leave - all this is important to document in order to be able to protect both the work of the organization and the employee himself.
Don't miss: major changes in HR
Why will GIT fine personnel officers?
What is a power of attorney and in what cases is it necessary?
As we have already found out, a signature is important in the preparation of any documentation; it gives any document legal force. But there are situations when a responsible official cannot sign a document for one reason or another, for example, when a large amount of documentation is required for signature and the increased busyness of management slows down the process of implementing documents. It is in such cases that organizations try to delegate the right to sign personnel documents to other people.
Read more about signing personnel documents here:
In addition, personnel documentation also applies to more important documents, such as employment contracts or dismissal documents. What to do in this case so that the document is signed and there are no problems with employees?
In this case, the following conditions must be observed:
- it is necessary that the organization’s statutory internal documents indicate that in the absence of the manager, a deputy or authorized person can sign personnel documents;
- availability of a power of attorney on behalf of the head of the organization in the name of the deputy or any other authorized person to sign personnel documentation.
So, in order to understand how to issue a power of attorney for the signature of another person, first, you need to understand what a power of attorney is in general. A power of attorney is a written confirmation that one person has authorized another person to sign documents to represent a third party. For serious documents, in some cases, the power of attorney is notarized.
Read more about the power of attorney for signing documents in the new article.
How to transfer the right to conclude employment contracts to the head of the HR department
It must be canceled by order of the manager. Give the employee written notice of the cancellation of the power of attorney. Inform interested third parties about this, for example, representatives of government agencies with whom the employee interacted (Art.
188, paragraph , art. 189 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation). If the power of attorney of a dismissed employee is not revoked, he will retain the right to act on behalf of the former employer (Article 188 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation). Enshrine in a local act the obligation of employees to return terminated powers of attorney to the structural unit responsible for their preparation, recording and issuance .
Usually this is the legal department, which maintains a special log of powers of attorney. In it, employees sign for receipt and return. If the employee did not return the canceled power of attorney, draw up a report about this in any form. Have the employee sign it.
If he doesn’t want to, make a note about it in the act and certify it with the signatures of two or three witnesses. Regulatory framework Document will help you Articles , , Labor Code of the Russian Federation Conclude an additional agreement on empowering the employee to sign personnel documents Art. 185, art. 185.1, clause 1, art. 186 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation Include in the power of attorney the mandatory details of Art.
188, paragraph , art. 189 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation Cancel the employee’s power of attorney1.
If you instruct an employee to sign personnel documents, enter into an additional agreement to his employment contract, determine the scope and amount of payment for such work.2. Based on the additional agreement, issue an order for the organization and issue the employee a power of attorney for the right to sign personnel documents.
For the power of attorney to be valid, do not forget to indicate the date of issue.3.
If an employee resigns, cancel the power of attorney issued to him by order.
Otherwise, he will retain the right to act on behalf of his former employer. Zvezdaza correct answer Incorrect Correct! If the power of attorney does not indicate its validity period, it is: void; valid for a year from the date of issue; valid for three years from the date of issue.
Power of attorney to perform personnel actions on behalf of the employer (sample sample)
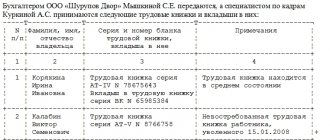
Subject of the document: Text version file: 3.6 kb Save the document: Address: 000 000, Moscow, Telephone deadlock Komunizma, 13 February eighteenth Moscow two thousand and eleven Limited Liability Company "Atoll", registered at the address: .
Moscow, deadlock Kommunizma, 13, represented by General Director Yuri Pavlovich Yakovlev, acting on the basis of the Charter, authorizes Boris Aleksandrovich Adeenko, born December 21, 1972, passport series __ N ________ issued by the Department of Internal Affairs __________________________________________, May 00, 0000, department code 000 -000, registered at:
Moscow, st., holding the position of head of the personnel department, perform legally significant actions on behalf of the employer as part of the performance of their official duties, namely: 1. Sign personnel orders for personnel. 2. Sign orders related to the production activities of the enterprise as they relate to personnel.
3. Sign additional agreements to employment contracts. 4. Sign notices of changes to the basic terms of the employment contract.
5. Sign agreements between the employee and the employer on changes to the basic terms of the employment contract.
We recommend reading: How long are maternity benefits paid?
6. Sign contract agreements with citizens of the Russian Federation, with foreign citizens who arrived in the Russian Federation in a manner that does not require a visa and have the right to carry out labor activities in the Russian Federation. 7. Sign appendices, additions, acts of completed work to the contracts specified in clause.
6 of this power of attorney. 8. Certify entries in work books when dismissing employees. The power of attorney was issued for a period of 1 (one) year. The powers under this power of attorney cannot be transferred to third parties. I certify the signature of Boris Aleksandrovich Adeenko ______________. General Director of Atoll LLC ___________________ Yu.P.
Yakovlev
- (Rich Text Format)
Registration of a power of attorney to sign personnel documents
All powers of attorney regarding the signing of personnel documentation within the organization can be executed within the organization.
As a rule, the validity period of a power of attorney cannot exceed 3 years. If the validity period of the power of attorney is not specified in the power of attorney itself, it is limited to one year from the date of execution.
Once the power of attorney has been executed, the authorized person can sign documents, but he must indicate his position and the basis for the signature.
Read more: Purchase and sale agreement for the share of the sole participant of the LLC
It is worth noting that in the case of transferring the right to sign to a deputy, this right must be indicated in the regulatory documents. If this does not happen, then a power of attorney alone will not be enough to legally enforce the signed documents and transfer the right to sign.
In addition, it is important that not only the deputy manager, but also any other authorized employee can sign documents under a power of attorney. However, before this, all procedures provided for by the Labor Code of the Russian Federation must be followed. First, you will need to conclude an additional agreement to the employment contract with this employee and issue a corresponding order. In addition, there must be written consent from the employee to perform additional work. This agreement must indicate the timing, scope and content of the work, as well as the amount of additional payment for additional work.
Registration of an order to prepare a power of attorney in an order (instruction)
A power of attorney certified by the employer is considered valid within the organization and outside it if the authorized person is an employee of the enterprise. Upon dismissal, the document loses force, as do the powers granted.
Can an employer certify a power of attorney to an employee?
A person authorized to sign and certify documents is any employee who is entrusted with the obligation to sign. This can include the following:
- owner of the organization;
- director or his deputy;
- Head of HR Department;
- Chief Accountant;
- full-time manager.
A trust document executed at the place of work terminates in the event of the death of the responsible parties, as well as in the event of:
- expiration of the document;
- unilateral refusal of written authority;
- termination of the activities of a legal entity;
- dismissal of an employee authorized by obligations.
We suggest you familiarize yourself with: Power of attorney maximum validity period for issuing goods
With the termination of the power of attorney, the power of attorney also loses its force.
The relevance of the information is confirmed by the MinCredit service.
We will begin our study of the issue of cases and the procedure for using powers of attorney for representation in relations regulated by labor legislation by considering the use of powers of attorney in labor relations.
In order to determine whether representation on the basis of a power of attorney is possible in such relations, let us turn to the legal (that is, enshrined in law) definition of the concept “employment relationship”.
Document fragment. Article 15 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
So, the analysis of Art. 15 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation shows that two parties are involved in labor relations - the employer and the employee. Accordingly, our task is to determine whether the law allows each of the designated parties to issue powers of attorney to represent interests in labor relations, and if such a possibility exists, to establish the content of these documents and the procedure for their issuance.
Question on topic. Is it possible to transfer the rights and obligations of an employer on the basis of a power of attorney?
The Civil Code of the Russian Federation is not classified as a regulatory legal act regulating labor relations. This is understandable: labor relations are regulated by another code - the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
We note that by virtue of Part 3 of Art. 11 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, all employers in labor relations and other directly related relations with employees are obliged to be guided by the provisions of labor legislation and other acts containing labor law norms.
The basic rights and obligations of the employer are established in Art. 22 Labor Code of the Russian Federation. Their list can be supplemented and specified in other regulatory legal acts containing labor law norms, agreements concluded in the field of social partnership, collective agreements, local regulations of the organization (hereinafter also referred to as LNA) and employment contracts with specific employees.
Finally, according to Part 6 of Art. 20 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the rights and obligations of the employer in labor relations are exercised by: management bodies of a legal entity (organization) or persons authorized by them in the manner established by the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, other federal laws and other regulatory legal acts of the Russian Federation, laws and other regulatory legal acts of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation , regulatory legal acts of local government bodies, constituent documents of a legal entity (organization) and local regulatory acts.
Thus, in the Labor Code of the Russian Federation we are talking specifically about the implementation in a complex of both the rights and obligations of the employer by the management bodies of the organization and the persons authorized by them. This is understandable: after all, the rights and obligations of the employer are closely related to the rights and obligations of employees (for example, Art.
21 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation) and the transfer of the employer’s rights separately from duties (non-fulfillment or improper fulfillment of which entails liability) in practice would be fraught with possible violations of the interests of employees as participants in labor relations.
Moreover, neither in the above norm of Part 6 of Art. 20, no other articles of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation mention a power of attorney as a basis for the transfer of rights and obligations. Moreover, even in the norms of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation in relation to civil legal relations, it is emphasized that on the basis of a power of attorney only the rights to carry out any legally significant actions are granted; no obligation can be assigned to the representative by a power of attorney.
It seems correct to draw the following conclusion from the above norms of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation: the rights and obligations of the employer in labor relations with employees in a particular organization can be exercised by persons authorized and acting in the manner established by the constituent documents of this legal entity, as well as LNA (if the procedure for exercising such rights and responsibilities are not established by regulatory legal acts of the Russian Federation, constituent entities of the Russian Federation and local governments, which is rare in practice).
The main judicial act concerning the procedure for applying the norms of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation - Resolution of the Plenum of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation dated March 17, 2004 N 2 (as amended on September 28, 2010) “On the application by the courts of the Russian Federation of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation” - contains the following explanation: by the representative employer is a person who, in accordance with the law, other regulatory legal acts, constituent documents of a legal entity (organization) or local regulations, or by virtue of an employment contract concluded with this person, is vested with the authority to hire employees, since it is in this case that upon the actual admission of the employee labor relations arise from work with the knowledge or on behalf of such a person (clause 12).
As can be seen, in this act, a power of attorney is not mentioned as a basis for transferring the powers of the employer. After all, for example, the relationship between a person applying for a job and an official who signs an employment contract with him, who is in this regard a representative of the employer, is not civil, but refers specifically to labor relations.
We invite you to read: Employee versus employer in court
Therefore, in these relations, the grounds confirming the availability of appropriate powers for representation may be constituent documents (usually the charter) and LNA (for example, internal labor regulations, personnel regulations, regulations on a branch or representative office, other separate division of the organization, job description and so on.).
It seems that the above analysis of legal norms allows us to conclude that the head of an organization, who is its governing body and at the same time an official (CEO, director, president, etc.
), does not have the right to issue powers of attorney to other persons with the authority to conclude (sign) employment contracts, issue personnel orders, or perform other legally significant actions within the framework of labor relations with the company’s personnel.
However, let us immediately make a reservation that there is also a point of view opposite to that expressed by the author of this article. Thus, many experts on this issue are of the opinion that in the cases under consideration it is possible to use a power of attorney to delegate the rights of the employer.
- by analogy with the law. In this regard, we note that the analogy of the law is applied in the case when certain relations are not regulated by law that is subject to direct application to them. In our case, the rights and obligations of the employer in labor relations are regulated by the norms of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the possibility of their implementation by representatives of the employer is established by Part 6 of Art. 20 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation with reference to specific documents, including constituent documents and LNA, among which powers of attorney are not mentioned. In addition, there is also no basis for vesting the employer’s representative only with rights without responsibilities in the Labor Code of the Russian Federation;
- as norms of “other federal law” mentioned in Part 6 of Art. 20 Labor Code of the Russian Federation. However, as we have already said, the norms of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation are among those regulating labor relations in Part 1 of Art. 11 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation are not specified. It is also important that in Art. 185 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation does not provide for the possibility of extending its effect to the transfer of powers of the employer in labor relations;
- due to the fact that the execution of a power of attorney by the employer in labor relations is not expressly prohibited. But in contrast to the general approach “everything that is not prohibited” that is characteristic of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, for the Labor Code of the Russian Federation and the labor relations regulated by it, the approach “is prohibited is that which is not permitted” is used due to more detailed regulation in the law of issues related to labor relations , in comparison with civil ones, due to the desire of the legislator to protect the interests of the economically weaker party in the relationship - the employee. At the same time, let us once again draw your attention to the fact that confirmation of the powers of the employer’s representative with a power of attorney is not provided for in the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
Due to the fact that the issue of the legality of the head of an organization issuing a power of attorney to officials to exercise the powers of the employer is controversial in the opinions of various authors, judicial practice on this issue is of interest.
The position of the Plenum of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation, which we mentioned above, boils down to the fact that a power of attorney is not included among the documents formalizing the transfer of the employer’s powers in labor relations.
Let's imagine this situation. The head of the HR department signed an order to dismiss the employee at the initiative of the employer, while his authority to issue such an order is certified by a power of attorney issued by the organization and signed by its general director.
The employee goes to court and challenges the legality of the dismissal on the grounds that the dismissal order was signed by an unauthorized person. What decision can the court make when considering such a labor dispute?
October 18, 2010 Moscow N 106/01.2-10
Samples of powers of attorney for signing personnel documents
So, in order to issue a power of attorney to sign for another person, you must indicate the following information in the document:
- name of company;
- legal address of the organization and all its data;
- name of the document - Power of Attorney;
- the name of the person giving the power of attorney and the one who receives the power of attorney indicating his passport details;
- listing the types of documentation that an authorized person can sign;
- signature of the person who received the power of attorney and the director.
The power of attorney is issued in simple written form. In the case, for example, of signing employment contracts by power of attorney, this fact must be indicated when signing with the number and date of the power of attorney.
It is very important to draw up the power of attorney correctly and take care of this issue in advance, so that it does not turn out that all the documents drawn up during the absence of the manager turn out to be invalid.
We recommend
Types of papers for which powers are delegated
The specifics of signatures, the rights to which are delegated by a power of attorney, may vary. The right to sign can be transferred to personnel documents, shipping documents, cash register documents, etc. However, since this point is not strictly regulated by law, the content of these documents does not change much from one type to another.
The main things that must be included in all types of powers of attorney are:
- Signature of the manager (Part 4 of Article 185.1 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
- Date (if the document does not indicate a validity period, then by default it is considered equal to one year) (Part 1 of Article 186 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation)).
- The power of attorney must contain an exhaustive list of documents that the attorney will have the right to certify with his signature.
The powers of the attorney must be clearly regulated: wording that can be interpreted in two ways is not allowed in order to avoid undesirable consequences associated with the abuse of powers by the attorney.
Personnel
To the above list of required items, you need to add a record that the principal trusts the attorney to sign personnel documents (in a separate line, at the top of the document, after the word “power of attorney”).
If you have many employees, then you can draw up a template for a power of attorney to delegate the right to sign personnel documents and store it, adjusting and using it as necessary.
Shipping
The main points of the power of attorney are indicated above and below in the article. In this particular case, after the word “power of attorney,” you need to add a sentence stating that the principal trusts the attorney to sign the shipping documents.
Note! The tax authority may require a power of attorney delegating the right to sign documents.
Who can you trust to sign personnel documents?
In practice, it has developed that the head of the company acts on behalf of the company without additional confirmation of authority. His powers are enshrined in the constituent documents, and all legally significant actions, including signing documents, are carried out without a power of attorney. Although the law provides for the possibility of appointing several persons at once who have the right to act on behalf of the company (Clause 1 of Article 53 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation). But rarely does anyone take advantage of this opportunity when creating a company. And making changes to the constituent documents later is not always convenient; it is easier to write out a power of attorney, transferring certain rights to the selected person.
Read more: Is teaching experience suitable for a teacher of additional education?
With the expansion of staff, the volume of personnel documents, the signing of which is entrusted to the head of the company, increases significantly. As the business develops, the manager reserves the solution of strategic tasks, shifting part of his powers to his subordinates. This also applies to the document flow, which bypasses the manager, so the right to sign all or the least significant part of personnel documents is entrusted to an individual employee.
The choice of an authorized employee depends on the company structure. If it has a separate division involved in personnel work, then personnel documents are assigned to be signed by the head of this division. If the staff simply provides for a separate position within which the employee is engaged in personnel work, then the right to sign documents issued by him is not always trusted to him. One of the deputy managers may be authorized to deal with this issue.
There is no direct prohibition in the legislation on the delegation of authority to sign personnel documents of a company by a person who does not work there. Therefore, it is possible that, for example, an agency agreement will be concluded with a person, and he will be given a power of attorney to sign personnel documents.
Who can sign primary documents?
In general, the right to represent a company (to act on behalf of the company), including signing primary accounting documents, without a power of attorney or any other documents, belongs to the sole executive body of the company - its director or a person who has received such functions under a contract (for example, a manager ).
If so, who can sign primary documents? After all, it may turn out that the manager is absent from the workplace, is on sick leave or on vacation, or the organization’s document flow is too large and it is unrealistic for one person to cope with such a volume of work. What to do in this case? Is it possible to transfer the right to sign documents to other persons?
The list of persons who have the right to sign primary documents is determined by the head of the company by order or other administrative document. The manager has the right to issue a power of attorney for the right to sign relevant documents for both the head of the organization and its officials.
Which document will confirm the right to sign primary documents - an order or a power of attorney? Both documents can confirm a citizen’s authority to sign primary documents. What is the difference between these documents? Let's figure it out.
Signing primary documents by power of attorney
The founder of the company, shareholder, and other citizens are not the sole executive body of the company and do not have the right to act on behalf of the company. However, they can represent the interests of the company on the basis of a power of attorney issued to them.
In addition, a power of attorney to sign primary documents (a sample text of the document is given below) can be issued to a citizen with whom the company does not have an employment relationship, that is, he is not an employee of the company.
If a company has issued a power of attorney to an individual, then the citizen becomes its authorized representative and has the right to sign primary documents on behalf of the company.
Thus, if a company needs to give a citizen the right to sign primary documents, it is necessary:
- issue a power of attorney from the company (represented by its general director) for the right to sign primary documents for the relevant officials;
- indicate in a separate agency agreement the citizen’s obligation to timely submit documents for registration in accounting registers, as well as his responsibility for the accuracy of the transmitted data.
The sample, officially approved, does not have a power of attorney for the right to sign primary documents. It is compiled in free form. The header indicates the name of the company, the power of attorney number, and the date when the power of attorney was issued. The main part of the document will look like this:
“Lyudmila LLC, represented by General Director D.V. Nazarov, acting on the basis of the charter, with this power of attorney grants the founder of the limited liability company “Lyudmila” Daria Vladimirovna Volnina (it is necessary to indicate full passport data and place of residence) the right to sign contracts (agreements, contracts).
The power of attorney was issued for a period from September 2, 2020 to September 2, 2017.”
Next comes a sample signature of the authorized representative and the signature of the general director.
Order for the right to sign primary documents
The order is issued by the manager to certain officials working in the company, and is valid as long as they are employees of the company. Thus, several differences between a power of attorney and an order can be identified:
- the power of attorney is issued to a specific individual, and not to an employee holding a certain position in the company;
- a power of attorney is usually issued for a specific period (for example, a year);
- a power of attorney can be issued to an individual who is not in an employment relationship with the company, while the order applies to employees of the company.
The form of the order for the right to sign primary documents is not approved by law; the company can draw up this document independently. It is advisable to include the following information in the order:
- Full names of employees;
- positions of employees who are given the right to sign documents;
- the order may contain a specific list of documents.
Order on the right to sign primary documents (sample)
Facsimile signature on primary documents
Some managers believe that it is not necessary to give employees the right to sign documents - you can simply use a facsimile instead of your own signature. According to the Civil Code, facsimiles can be used in cases and in the manner provided for by law, other legal acts or agreement of the parties.
However, the use of facsimiles specifically on primary documents is a controversial issue: regulatory authorities believe that the use of facsimiles when preparing primary documents is unlawful.
Despite the fact that there have been cases when judicial practice proves the opposite point of view on this issue, nevertheless, if you do not want controversial issues to arise, it is better not to use a facsimile.
Source: https://spmag.ru/articles/kto-mozhet-podpisyvat-pervichnye-dokumenty
Form and content of the power of attorney for signing personnel documents
The legislation does not have any specific requirements for the form and content of the power of attorney, through which the authority to sign personnel documents will be transferred. Therefore, the general rules established by Chapter 10 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation apply here. Here are the requirements:
- The power of attorney is issued in writing (Article 185 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation); To sign personnel documents, a notarized power of attorney is usually not required (Part 1 of Article 185.1 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
- The power of attorney is executed with the signature of the head (Part 4 of Article 185.1 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
- The power of attorney must indicate the date of its preparation; without this, it is void. If the power of attorney does not indicate its validity period, then it can be used for exactly one year (Part 1 of Article 186 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
- The power of attorney must list all the names of documents that an authorized person can sign.
In a company with a large staff, it makes sense to develop a sample power of attorney that could be adjusted from time to time. It is convenient to use to transfer the authority to sign personnel documents to a person holding a certain position.
Signing an agreement by proxy from a legal entity
Who has the right to sign documents at the enterprise
Who can sign the agreement instead of the director
If the contract is signed by a representative: consequences
Authority to sign an agreement on behalf of the organization
Who has the right to sign documents at the enterprise
An enterprise may have several persons acting jointly or independently of each other who have the right to sign documents on the basis of current legislation (Part 1 of Article 53 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation). These include:
- Managers whose information is subject to inclusion in the Unified State Register of Legal Entities.
- Chief Accountant.
The status of the head of the company is confirmed by Art. 53 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, the Law “On Limited Liability Companies” dated 02/08/1998 No. 14-FZ and the Law “On Joint-Stock Companies” dated 12/26/1995 No. 208-FZ.
According to the provisions of the Law “On Accounting” dated December 6, 2011 No. 402-FZ, the chief accountant is responsible for the correct preparation of financial documents of the enterprise, as well as financial statements.
Who can sign the agreement instead of the director
You can delegate the powers of the head of an enterprise to another person by drawing up a power of attorney. Sometimes delegation of authority is used through an order from a manager.
Using a power of attorney to confirm authority to sign an agreement is more convenient than issuing an order for the following reasons:
- there is no need to indicate the position of the authorized person in the power of attorney, since the issuance of this document is in no way related to the existence of an employment relationship;
- when confirming the powers delegated by the order, it is necessary to present not only the order itself, but also the order for employment in the organization, and in some cases the job description.
In addition, one should take into account the fact that the order itself is considered an internal administrative document: its effect extends exclusively to the powers of the director within the company and does not apply to relations with counterparties, courts, etc.
IMPORTANT! There is an exception when a person may be authorized to sign an agreement due to the current situation in which he operates (Clause 1 of Article 182 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation). For example, an operator in a bank or a salesperson in a store. These persons do not have a power of attorney to sign contracts, but act on the basis of the order and their job description.
If the contract is signed by a representative: consequences
What are the risks of signing an agreement by proxy? Such an agreement may be declared invalid if the following circumstances exist in total (clause 1 of Article 174 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation):
- The statutory documents or regulations on the representative office (branch) establish restrictions on the powers specified in the power of attorney, which the other party to the agreement knew about.
- The plaintiff is the person in whose interests the specified restrictions are imposed.
In addition, a transaction concluded in the absence of authority may be recognized as concluded by a representative in his own favor, when the represented person, although does not demand that the transaction be invalidated, did not approve it after its conclusion.
Authority to sign an agreement on behalf of the organization
Powers to sign a contract may include the following rights:
- negotiate;
- enter into and terminate contracts (of a certain type or any, with or without a limitation on the transaction price);
- contact a notary to certify the transaction;
- use an electronic digital signature.
The following persons have the right to delegate powers:
- official representative of the organization without a power of attorney (mentioned in this capacity in the Unified State Register of Legal Entities);
- a person who has been given a power of attorney to perform certain actions with the right of substitution (within the powers of his power of attorney).
The procedure for drawing up a power of attorney is defined in Art. 185–186 Civil Code of the Russian Federation. How to draw up a power of attorney from a company is described in the article “Power of Attorney for concluding contracts from a legal entity.”
In some cases (for example, when concluding an agreement that requires state registration), a notarized form of power of attorney will be required. The notary certifies the specified document, guided by the Methodological recommendations for certifying powers of attorney, approved by the decision of the FNP board of July 18, 2016 (protocol No. 07/16), according to which he checks:
- powers and personality of the manager, legal capacity of a legal entity;
- legality and specificity of transferred powers;
- availability of mandatory information (date of commission, data of the representative and the represented person).
The authority to sign one, several, a series or all possible contracts on behalf of the enterprise can be transferred by proxy. Exceeding the limits of authority by a trustee can lead either to recognition of the transaction as concluded in the interests of the trustee, or to its recognition as invalid.
Source: https://rusjurist.ru/dogovory/zaklyuchenie_dogovora/podpisanie_dogovora_po_doverennosti_ot_yuridicheskogo_lica/
Who is responsible?
Signatures on an organization's papers can have different meanings. To understand who is responsible for the consequences of using the right to sign by proxy, you need to know them.
So the signature could be:
- Legal (binding) is a signature after which the enterprise experiences a change in obligations to counterparties (documents evidencing the facts of the purchase of products).
- Confirming legality - certifies that the content of a business transaction does not contradict the law (accounting reports).
- Informational - indicates that the contents of the paper correspond to the actual parameters of the business transaction (salary statement).
Important! Only the head of the enterprise can issue powers of attorney. As a rule, he is responsible for the consequences of transferring the right to sign the company’s papers.
Individual
- In the case of a binding signature, the responsible person is the enterprise in which the chief manager who issued the power of attorney works. Although in cases of violations, administrative and even criminal measures may be imposed on the manager. But if we are talking about labor relations, then the person responsible is the head of the enterprise himself (Article 5.27 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation).
- Signature confirming the legality of the document. Responsible persons are the chief manager and the company where he works.
- An information signature is the most harmless in terms of legal sanctions for the principal: in the worst case scenario, the documents simply will not be considered. The signatory is not responsible for the contents of the document.
Entity
This situation mainly occurs in matters related to tax and financial reporting. When it comes to financial statements, the responsible persons are the head of the enterprise and the attorney.
- Only those employees who have the appropriate powers under the organization’s charter will sign financial documents.
- When accounting is assigned to the management of a legal entity, the employees of such a legal entity will not sign the accounting papers for the chief manager, even when they have the necessary document.
To understand who is responsible for the signature on fiscal reports and why, you need to know that in all relations between the state and the taxpayer, the person who must pay the tax is always considered a participant in legal relations, whether he acts on his own or through a representative (Letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated October 20 .2005 N 03-02-07/1-274, Letter of the Federal Tax Service of Russia for Moscow dated 05.25.2007 N 20-12/049059 and dated 09.23.2005 N 28-10/67686).
This is true for all cases of legal relations when it comes to paying taxes.
If a legal entity trusts an individual to sign tax returns, then the enterprise itself bears responsibility for the signature.
When an employee is an organization
It happens that the management functions of an enterprise are transferred to a special company. Then, when concluding an act of transferring the right to sign, the responsible persons are the head of the managing enterprise, or the director of a special company (for example, if it is engaged in accounting), sometimes responsibility can be assigned to the employees of the enterprise that delegated the right to sign.