In this article, we will analyze the methods of filling out documents intended to reflect the inventory of fixed assets in the 1C 8.3 Accounting 3.0 database, including the procedure for recording the results of the inventory of fixed assets in the form of step-by-step instructions.
The Accounting Law requires mandatory inventory of fixed assets (hereinafter referred to as fixed assets). During the inventory, a shortage of OS or, in some situations, a surplus may be discovered.
Any discrepancies found between accounting data and the actual number of fixed assets should be registered in accounting (hereinafter referred to as accounting) and tax accounting (hereinafter referred to as TA) during the period when discrepancies are identified.
1C Accounting 8.3 allows you not only to draw up documents for conducting an inventory of fixed assets, but also, based on its results, write off shortages or capitalize identified surpluses.
What is it - an inventory of fixed assets (fixed assets) at an enterprise
First of all, this is a recalculation of the assets that the company has. With this action, it becomes possible to keep the company's property unharmed. Its main task is to compare real and virtual balances by checking the data specified in the accounting records. This is how money, equipment, buildings, debt obligations and much more are considered.
Using the census, you can monitor the correctness of information reflected in the organization’s accounts. Corrections are made as necessary to keep the reporting current.
Business Solutions
- shops clothing, shoes, groceries, toys, cosmetics, appliances Read more
- warehouses
material, in-production, sales and transport organizations Read more
- marking
tobacco, shoes, consumer goods, medicines Read more
- production
meat, procurement, machining, assembly and installation Read more
- rfid
radio frequency identification of inventory items More details
- egais
automation of accounting operations with alcoholic beverages Read more
During the inventory, determine:
- are there actually objects that are indicated on paper and in the program;
- How correctly are inventory numbers assigned?
- Are accounting records maintained correctly?
- volumes of shortages/surpluses.
Terms, rules, frequency of inventory of fixed assets
According to the law, an inspection should be carried out at least once every 3 years at the enterprise. Library collections will not have to be counted and checked so often - once every five years. This is established on the basis of the Methodological Instructions.
Each company determines specific data for itself. This is usually done before the start of the annual report. But according to the law, there are cases when this should be done more often:
- as a result of an emergency;
- if reorganization or liquidation has begun;
- the property is going to be rented out or completely sold;
- The MOL or manager will change soon;
- annual reporting will be prepared soon;
- facts of theft, damage to property or abuse of authority were identified.
It is worth noting that if team members demand, then such a reconciliation is also carried out in the case when more than half of all participants in the contract leave.
By order of the owner or director of the organization, this can happen suddenly, at any time. There is a continuous inventory, when everything that is in the company is counted, and a selective inventory, when they count the assets in one division, branch or even office.
Required by law
The mandatory nature of this procedure is approved by the federal legislation of our country. Entrepreneurs are required to regularly take inventory of their own, stored or leased property and their financial obligations by two regulatory documents:
- Federal Law of December 6, 2011 No. 402-FZ “On Accounting”;
- Methodological recommendations for inventory of property and financial obligations (approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated June 13, 1995 No. 49).
What is an inventory of fixed assets
This is a count of objects that are constantly used during production or for administration needs. This may include machines, equipment, equipment, including computers, various household equipment, livestock and plants.
The recount can be natural - when inspectors or authorities walk around the company and check the actual presence of assets. Another option is documentary, when they are reconciled only using accounting registers.
Legally, all this is formalized depending on what supporting documents were developed within the enterprise and secured by accounting policies through an order. A statement is a document that will be drawn up in 2 identical forms, because one is sent to the accountant, and the second remains with the MOL.
Surplus fixed assets during inventory in 1C 8.3
Capitalization of surplus fixed assets discovered as a result of inventory:
- If, based on the results of the inventory, a surplus is found, then such an object will be taken into account in accounting at the current market value by posting Dt account 01 - Kt account 91.1 as other income.
- In tax accounting, the cost of fixed assets found during inventory is taken into account as non-operating income by virtue of clause 20 of Art. 250 Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
An enterprise can depreciate fixed assets discovered as a result of an inventory. In this case, it is necessary to establish the useful life from the Classification of fixed assets included in depreciation groups.
Step 1. Creating a document Acceptance of fixed assets for accounting and filling out the document title
To create the document “Acceptance for accounting of fixed assets” in 1C 8.3, use the Create on the basis button - then Acceptance for accounting of fixed assets:
Fill in the title of the document Acceptance for accounting of fixed assets:
- In the Number field – the document number automatically generated by 1C 8.3;
- In the From field – day, month, year of the document;
- In the Organization field – filled in automatically from the OS Inventory document;
- In the field MOL - responsible person, set according to the directory Individuals. If this field is not filled in, then the document will display fixed assets for all responsible persons;
- In the Fixed assets location field – the department where the detected fixed asset will be taken into account;
- In the OS Event field, an event related to acceptance for accounting is entered. Filled in automatically by the Acceptance for accounting with commissioning event:
Step 2. Filling out the tabular forms of the document Acceptance for accounting of fixed assets
The document Acceptance for accounting of fixed assets contains five tabs: Fixed assets, Non-current assets, Tax accounting, Accounting and Bonus depreciation. Within the framework of this article, we will not examine in detail the procedure for accepting fixed assets for accounting.
Let's study which fields of the document are filled in when entering based on the OS Inventory.
Fill out the Non-current asset tab
- The Operation type field is automatically filled in with the value “Based on inventory results”;
- The Cost field reflects the cost of the fixed asset from the Asset Inventory document;
- You should indicate the item of income and expenses, including the cost of the object in tax accounting:
Fill out the Fixed Assets tab
The document table displays the name and inventory number of fixed assets identified as surplus based on inventory results:
On the Tax Accounting and Accounting tabs, you need to enter the parameters for calculating depreciation. The depreciation bonus cannot be applied in this situation, so the Depreciation bonus tab is not filled in.
Step 3. Posting the document Acceptance for accounting of fixed assets
Clicking the Post button will create the following transactions:
Commission for Inventory of Fixed Assets
The tasks of these people include inspection and verification of the correspondence of virtual balances to real ones. They record all the differences in the statement they have, write down inventory numbers, and monitor the characteristics.
They receive all relevant documents before starting their study. Who will be part of the inspectors fits into IVN-22. Financially responsible persons must mark that they hand over everything accountable.
Not only accounting sheets are subject to study and reconciliation, but also:
- information according to which it is possible to determine ownership of objects;
- technical passports;
- availability of documentation for natural resources owned by the company.
Rules for implementing the procedure
The procedure for conducting an inventory of the organization's property and liabilities is actually determined by regulatory documents and established requirements. Therefore, before the event begins, during its implementation and even after its completion, specific steps must be taken. We highlight 5 main stages:
- Formation of a group of company employees who will be responsible for the process.
- Preparation and collection of necessary documentation.
- Direct inventory of existing property.
- Reconciliation of received data and accounting reports.
- Familiarization of management with the results.
The decision about what the procedure will affect, whether any measures will be taken, are made only after all the steps have been completed, even if the deficiency becomes obvious much earlier. Let us consider all the stages of conducting a property inventory in more detail.
Order on audit
First of all, an internal company document must be prepared, which indicates where, when and in relation to which material and technical means the inspection is carried out. It can be prepared in the form of a written order, resolution or other legal act.
Private enterprises usually get by with a simple order, while public enterprises are guided by other documents. In addition to the information already mentioned above, this includes information about the persons responsible for the event.
Inventory service commission
The composition of the group of employees who are responsible for taking an inventory of the enterprise’s property is always homogeneous, since it is regulated by the norms and requirements established by the state. It includes:
- Representatives of the administration, for example, the deputy director.
- Chief accountant or person performing his duties.
- Heads of structural units in which the inventory will be carried out.
- Specialists working in the organization. They must have sufficient qualifications to confirm the quality of a particular property and determine the difference between two similar types of goods.
- Independent experts or invited auditors.
Each member of the commission is registered in the order before the procedure begins. It is unacceptable to carry out an audit in the absence of at least one of them, and replacement is possible only with the preparation of new documentation.
Persons officially responsible for the safety of material and technical means are not allowed to participate. This eliminates the possibility of falsifying results or concealing important information.
Preparation for an inventory of material and technical assets
Since the inventory of property is carried out by the institution in accordance with available documents, even at the preparatory stage, receipts and expenditure acts, previous reports and other papers must be prepared to fully present the picture of the existing property, funds, and liabilities. They are handed over to the commission members for review.
After receiving the papers listed above, a receipt is taken from the responsible persons stating that the necessary documentation was provided in a timely manner and in full. This allows you to determine the presence of all properties in respect of which the inspection is being carried out.
Thus, a group of responsible employees determines a list of assets that must be inspected, since an audit order has been issued in relation to them, and documents have confirmed that the things are in good order, are in a specific location or are used for their intended purpose.
Purpose and reasons for conducting an inventory of fixed assets
There are several reasons to perform such a study of warehouses and operating systems:
- it is possible to speak with certainty about the presence or absence of certain objects on the territory;
- it becomes easy to compare the actual data with those indicated in the accounting registers;
- it is allowed to correct the accounting document in accordance with the information revealed in fact.
When an inspection is carried out unscheduled, this usually happens due to discovered theft, the consequences of an emergency, or a change in management.
Nowadays it is allowed not to use strict reporting forms, but to develop your own accounting documentation. The main thing is to have all the details and positions. If you don’t have time to develop such templates, you can use standard examples in the program.
It is important that the software completely covers all tasks that arise in the enterprise. If this does not happen, then you can seek help from professionals, for example, at.
Thus, you can effectively check an enterprise’s OS using the “OS Inventory” software product.
This software allows you to use an information collection terminal with a built-in barcode reader to reconcile company fixed assets.
Each OS comes with a unique barcode label that can be printed using the driver. A standards-compliant, 100% readable barcode is automatically generated by the software based on the accession number.
The software allows you to upload information about the availability of a particular material from the 1C database, and then use the device to collect barcodes of real positions of fixed assets and balances and then load the received real information into “Inventory of fixed assets” or into “Entering balances of fixed assets and intangible assets” and for receiving availability and discrepancy reports.
The software also supports accounting by materially responsible persons (MRO) and departments.
SURPLUS AND SHORTAGE WHEN INVENTORYING OS
In many cases, the commission discovers unexpected results from the asset inventory - a shortage or absence of property that is listed on the balance sheet. Sometimes it is possible to immediately detect the reason - the equipment may be stored in another warehouse, and this must be documented. Otherwise, the shortage is grounds for an official investigation.
A situation that is the opposite of a shortage is possible - in the process of conducting an inventory of fixed assets, assets are discovered that are not on the balance sheet. In this case, the main thing is to find out where this or that remedy came from. It can be obtained either legally, in the form of a gift agreement, unaccounted profits from previous years, or illegally - if employees are engaged in activities that are not within the scope of their duties or there are other violations of the law. The discovery of unaccounted funds may also lead to an internal investigation. If fixed assets are obtained legally, then they are added to the company’s assets, together with the determination of their market value, regardless of whether they cost a ruble, a thousand or more.
REFLECTION OF SURPLUS AND SHORTAGES IN ACCOUNTING
Shortages or surpluses lead to a change in the state of the objects taken into account. To reflect this in accounting, postings are used.
If excess is detected:
- DT 01 CT 91-1 – the fixed asset has been capitalized.
Shortage, given that the culprits have not been found:
- DT 02 CT 01 – writes off depreciation for undetected funds;
- DT 94 KT 01 – writes off the residual value;
- DT 91-2 CT 94 - reflects the shortfall in other expenses.
If it was possible to identify the perpetrators, then:
- DT 73 CT 94 – the shortage is written off at the expense of the perpetrators;
- DT 50 CT 73 – the employee repays the amount of debt.
To compensate for the shortfall, funds from the employee’s earnings are withheld, but not more than 20% of it.
DOCUMENTATION OF OS INVENTORY
The following documents need to be completed:
- order to conduct an inventory of fixed assets - form INV-22. Here they indicate the reason, the property that is being inventoried, the timing, the composition of the commission, indicating the position and full name;
- all inventories are entered into the order register - form INV-23. This contains information about the company or structural unit where the inspection is carried out, the persons responsible for the property, information about the property being inventoried, the people who are members of the commission, the actual date of the start and completion of the procedure, the results, the dates of summing up the results and the measures taken;
- the inventory in the INV-1 form records the data that is obtained during the inspection of the property;
- if some equipment is under repair, this is reflected in the INV-10 form. The costs of repairs and their cost are also indicated here;
- in the INV-18 statement, discrepancies between the actual quantity and the accounting quantity are recorded. The document according to the form must be drawn up in two copies - for the responsible person and the accounting department.
RESULTS OF INVENTORY OF FIXED ASSETS
As a result of a correctly carried out procedure, the company receives a clear understanding of what property it has and can manage it more competently to obtain maximum profit. In addition, errors lead to inaccuracies in reporting - if this is discovered by the tax authorities, the company faces fines.
Business Solutions
- the shops
clothes, shoes, products, toys, cosmetics, appliances Read more
- warehouses
material, in-production, sales and transport organizations Read more
- marking
tobacco, shoes, consumer goods, medicines Read more
- production
meat, procurement, machining, assembly and installation Read more
- rfid
radio frequency identification of inventory items More details
- egais
automation of accounting operations with alcoholic beverages Read more
The program supports the simultaneous existence of multiple records on one TSD. In this way, you can conduct a check in several rooms/departments of the organization and then get several results at once in 1C.
How to reflect inventory in accounting
Accounting records are formed based on the established results of inventory reconciliation. Upon completion of an inventory check, either a surplus or a shortage may be identified.
When reflecting the results and drawing up the final entries, the accountant must be guided by clause 28 of Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia No. 34n dated July 29, 1998.
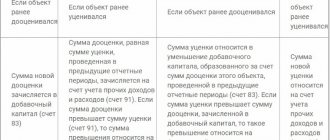
In this case, surplus is understood as a situation where property assets on the date of reconciliation are reflected at the current value of this asset on the market. The identified price relates to financial results, namely: profit included in other income for commercial companies, or income for non-profit organizations.
The shortage identified as a result is of two types:
- Shortage within the framework of natural loss. When it is detected, the monetary value is recorded either as costs or distribution costs.
- Shortage in excess of natural loss. During the reconciliation, guilty employees are identified and such shortages are attributed to specific individuals. However, there are situations when the persons who caused the shortage could not be found, therefore, there is no possibility of collecting debt obligations by court decision. Then the amount of the deficiency is written off as a loss (financial result) for commercial firms. Non-profit organizations write off losses as expenses.
If, during the inspection, the commission discovered unaccounted for property assets, then they should be carried out at the current market value on accounting accounts for fixed assets (clause 36 of the Methodological Recommendations - Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia No. 91n dated 10/13/2013).
Let's present the entries to reflect the results of the audit in the institution in the table:
| Wiring | the name of the operation |
| Surplus | |
| Dt 08 Kt 91.1 | Surplus property assets |
| Dt 10 Kt 91.1 | Excess inventory |
| Dt 41, 43 Kt 91.1 | Surplus of goods, finished products |
| Shortage | |
| Dt 94 Kt 10 | Lack of inventory items |
| Dt 94 Kt 01 | OS shortage |
| Dt 94 Kt 41, 43 | Lack of goods, finished products |
| Dt 20, 25, 44 Kt 94 | The deficiency is written off as part of natural loss |
| Dt 73 Kt 94 | Writing off the shortage to the guilty parties |
| Dt 91.2 Kt 94 | The deficiency is written off as other expenses, since the guilty employees have not been identified. |
gosuchetnik.ru
Required accounting documents
The most relevant papers, without which an inventory of fixed assets (FA) cannot be carried out:
- inventory - INV-1 - here everything that matches or differs in the actual balances from the planned ones is written down, including inventory numbers and violation of operational features;
- INV-22 - an order that is drawn up before the start of the census;
- INV-18 – matching statement;
- INV-23 is a journal in which all recalculations must be reflected.
It is worth remembering that INV-18 must be drawn up in 2 copies, because one is given to the MOL, and the second goes to the accounting department.
Shortage of fixed assets during inventory in 1C 8.3
During inventory, a shortage of an OS object may be identified. In this case, in 1C 8.3 Accounting 3.0 it is necessary to enter an operation to write off a fixed asset.
Step 1. Formation of the document Decommissioning of OS
The document Decommissioning of OS in 1C 8.3 is created by clicking the Create button based on:
Fill out the OS write-off document:
- In the Number field – the document number automatically generated in the 1C 8.3 database;
- In the From field – day, month, year of the document;
- In the Organization field – filled in automatically from the OS Inventory document;
- In the Reason for write-off field – indicate the reason for writing off the fixed asset;
- In the Fixed assets location field – the department where the fixed asset was accounted for;
- In the OS Event field, enter the “Write-off” event;
- In the Write-off account field – enter an account to record expenses for writing off the fixed asset;
- In the Expense Item field, enter an item to account for expenses related to write-off of fixed assets.
In the document table, the inventory number and name of one or more fixed assets to be written off are automatically entered:
Step 2. Posting the document Decommissioning of OS
Clicking the Submit button will do the following:
- Additional depreciation was accrued for the month of write-off of fixed assets (posting Dt of the cost account - Kt 02.01);
- The depreciation of the missing object was written off (entry Dt 02.01 – Kt 01.09);
- The cost of the missing object was written off (posting Dt 01.09 – Kt 01.01);
- The residual value of the missing object is written off (entry DT 94 – Kt 01.09):
If the culprits are not found, then in the future the shortage of fixed assets in the NU is classified as non-operating expenses, and in the accounting system it is included in Dt 91.02 “Other expenses”.
If the perpetrators are identified, then the shortage is included in Dt 73.02 “Calculations for compensation for material damage.” These operations are documented in 1C 8.3 with the document Operation entered manually.
The features of performing OS accounting operations in 1C 8.3 were studied in more detail in the course on working in 1C Accounting 8.3 ed. 3.0 in the module Acquisition and movement of fixed assets.
For more information about the rules for conducting inventory, see our video lesson:
Please rate this article:
Registered users have access to more than 300 video lessons on working in 1C: Accounting 8, 1C: ZUP
Registered users have access to more than 300 video lessons on working in 1C: Accounting 8, 1C: ZUP
I am already registered
After registering, you will receive a link to the specified address to watch more than 300 video lessons on working in 1C: Accounting 8, 1C: ZUP 8 (free)
By submitting this form, you agree to the Privacy Policy and consent to the processing of personal data
Login to your account
Forgot your password?
What is the documentation of inventory accounting for unusual fixed assets (FPE)?
There are several situations in which actions will be slightly different from usual:
- if the inventory was under repair at the time of repair, then an INV-10 should be drawn up, which will reflect the total cost along with the costs of correction;
- for those objects that were leased, you will have to draw up your own documentation with confirmation from the counterparty;
- separate papers are needed for those materials that cannot be used further in business activities, and it is impossible to restore them - they are written off with an indication of the reasons.
In addition, if the material has changed its purpose after repair, it is important to enter updated, current data. This is especially true in cases where, after such reconstruction, the book value changes, which has not yet been reflected in accounting.
Postings for displaying the OS inventory: example
Below we offer a sample of exactly what write-offs that occur due to the fault of employees and as a result of breakdown should look like.
- table
| Dt | CT | Amount, thousand rubles | Rationale | Documentation |
| When there are no guilty parties | ||||
| 01 (select) | 01 | 53 | The original price of the machine is written off | Write-off act |
| 02 | 01 (select) | 15 | Depreciation costs | Buh. certificates |
| 94 | 01 (select) | 38 | Remainder price | |
| 91 | 94 | 30 | Losses after write-off | |
| When there are culprits | ||||
| 01 (select) | 01 | 350 | The original price of the car is written off | Write-off act |
| 02 | 01 | 250 | Depreciation costs | Buh. certificates |
| 94 | 01 (select) | 100 | Remainder price | |
| 73 | 94 | 100 | The shortages were attributed to the culprit E.S. Erokhin. | |
| 73 | 98,4 | 25 | Difference between residual and market price | |
| 70 | 73 | 125 | The cost of the car was withheld from the salaries of E.S. Erokhin. | |
How to conduct an inventory of fixed assets: draw up an order
Each census begins with this document, which is prepared by the head of the organization. You can use the INV-22 form or create your own standard template for these purposes.
Certain points must be specified:
- Business name;
- the date on which the process will begin and end;
- who will be the chairman and members of the commission;
- how comprehensive the inspection will be (selective or complete);
- for what reason is it initiated;
- When should the documentation be submitted to the accounting department?
The executed order must be registered in the INV-23 journal, and then handed over to the chief inspector.
Before you start, you should check if you have:
- technical certificates for all objects;
- accounting cards;
- documents if the OS is leased.
How to fill out a statement
How to make an inventory of fixed assets - count them and record all the different parameters. It is worth remembering that this is necessary not only to establish the correspondence of the number of units actually and according to plan. Other characteristics that must match the data on the card are also compared:
- performance;
- inventory numbers;
- what is it intended for;
- what it looks like externally, level of depreciation;
- presence/absence of defects.
When inspecting buildings, it is important to pay attention to:
- number of floors;
- year of construction;
- the material from which the room was built;
- total area and the share of useful space from it.
If a natural deposit is being studied, then its depth and probable length are of interest. For existing plants and trees, age and their presence on the site matter.
Why do you need a matching statement?
All this is recorded on a sheet, compared and approved. All detected deviations will be entered into accounting. This allows you to understand how much the enterprise in its reporting corresponds to what it actually is. You can work with up-to-date data and plan the further development of the organization.
How to draw up an act based on the results
We have discussed in what cases an inventory of fixed assets is carried out. It is important to decide in what cases the document is drawn up. It is issued when it is discovered that a certain object no longer meets the required characteristics or does not work properly. In some cases, a write-off is made because the material is not available due to mis-sorting, theft or damage.
You must specify:
- MOL;
- the composition of the commission that revealed the inaccuracy;
- dates of statements, their numbers, comparative inventory data;
- when the census was started and completed.
All papers are attached to it, which reflect the discrepancy between accounting and the real picture.
Highlights ↑
The inventory procedure is an integral part of the activities of many enterprises. This means that you need to figure out what it means and what the purpose of it is.
What it is
A fixed asset is property that is used by a company to conduct business (necessary in production), is included in the company’s balance sheet and has a useful life of one year.
Inventory is the procedure for carrying out periodic checks and documenting the presence, condition and assessment of objects.
It is carried out in several stages. The audit is carried out on a certain date by comparing factual information with accounting information.
For what purpose is it carried out?
Before drawing up annual accounting reports, the company must reconcile assets and liabilities with accounting information, that is, conduct an inventory (Article 11 of Federal Law No. 402 of December 6, 2011).
This is necessary to reflect the real facts in the annual balance sheet. The inventory should be carried out in relation to:
- enterprise assets;
- the company's obligations;
- sources of financing;
- debts of the payable and receivable plan;
- other operations that are associated with profits and costs.
Reconciliation can be voluntary or forced. In the second case, you should be guided by clause 27 of Regulation No. 34n of July 29, 1998.
Reason for revision:
- the financially responsible person changes;
- property objects are transferred under a lease, purchase and sale agreement;
- there is theft or damage;
- force majeure circumstances occur;
- the company is to be liquidated or reorganized;
- need to prepare accounting reports, etc.
Purpose of inventory:
- identify the actual presence of objects;
- compare property with accounting information (to identify shortages or surpluses);
- document the existence of objects and responsibilities;
- determine the condition of objects and their assessment;
- check whether the liability is reflected correctly and in a timely manner.
Inventory allows you to:
- control the safety of production stocks to avoid abuse by the person in charge;
- identify and write off shortages;
- obtain information about the real situation in production.
Normative base
We list the legislative acts that you will have to refer to to determine the timing of the inventory and the procedure for conducting it:
| Federal Law No. 129 of November 21, 1996 | — |
| Guidelines for conducting an inventory | Order No. 49 of 06/13/1995 |
| Instructions for budget accounting No. 70 | Order dated August 26, 2004 |
Business Solutions
- the shops
clothes, shoes, products, toys, cosmetics, appliances Read more
- warehouses
material, in-production, sales and transport organizations Read more
- marking
tobacco, shoes, consumer goods, medicines Read more
- production
meat, procurement, machining, assembly and installation Read more
- rfid
radio frequency identification of inventory items More details
- egais
automation of accounting operations with alcoholic beverages Read more
How to draw up the minutes that are drawn up at the final meeting
After the inventory is completed and all documents are filled out, the last council is assembled to sum up the results. A report on the work done is brought to the manager. This is not a mandatory process, but the record of its maintenance can become real evidence in court if a claim is filed for damage to the enterprise.
During the meeting, all changes, shortages, surpluses are read out, explanations from the MOL and expert opinions are listened to.
Finally, documentation is prepared that includes:
- results of the procedure performed;
- reasons why incorrect data was indicated in accounting;
- conclusions adopted by the commission;
- suggestions - how to eliminate all shortcomings and correct errors.
Everyone present signs it, then it is handed over to the manager so that he can make a final decision on all inaccuracies and inconsistencies.
Basic mistakes during inventory
There are several typical violations that many companies commit:
- an order appointing a commission is not drawn up;
- the UP did not specify the timing and order in which the inventory should be completed;
- hired an independent auditor who made errors in reporting;
- the order was filled out incorrectly - incorrect details, wrong full name;
- one of the inspectors was not present at the recount;
- everything was done only on paper, no actual calculations were carried out;
- violations were committed during weighing, measuring, etc.;
- the warehouse became accessible to everyone, and there was a risk of loss;
- A new MOT was chosen, but a census was not carried out before the old one left.
Results
We examined the procedure for conducting and organizing an inventory of fixed assets (FPE), studied the sequence of its stages and documentation. With the help of recalculation, it becomes possible to understand which assets are reflected correctly in the accounts and which ones are not. We recommend that you carry out timely monitoring and complete postings. This is important for any enterprise, since without inspections it is impossible to determine the actual availability and shortage of objects, and this can result in problems, including with the tax service.
Documents for download:
Number of impressions: 955
Application of the GHS “Rent” in an educational institution
On January 1, 2020, the first five federal accounting standards for public sector organizations (hereinafter referred to as GHS) came into force. Some of them will manifest themselves later, and the beginning of the application of the GHS “Fixed Assets” and “Rent” has already been marked by large-scale changes. We’ll talk about what’s new in accounting for rental relations in this article.
Does this apply to us?
The very first question that accountants ask themselves when moving to standards is: do they apply specifically to our institution? The answer lies in the standards themselves.
Here we will make a small digression and note that, in contrast to the existing accounting instructions, the standards are perfectly structured and their structure is identical; the scope of application of any standard is disclosed in Section. I "General provisions".
Directly SGS "Rent"
is used when reflecting in the accounting of objects arising upon receipt (provision) for temporary possession and use or temporary use of material assets
under a lease agreement
(property lease) or
under an agreement for gratuitous use
(
clause 2 of the GHS “Rent”
).
Relations that arise when state (municipal) property is assigned to the subjects of accounting with the right of operational management in order for them to fulfill the powers (functions) assigned to them are not classified as lease accounting objects ( clause 10 of the GHS “Rent”
).
Another clarification on the limitation of the use of the GHS “Rent” is given in Letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation No. 02-07-07/83464
: the provisions of the GHS “Rent” do not apply to relations arising when transferring property for free use without imposing on the user of the property the responsibility for its maintenance.
Such relationships in educational institutions may be the transfer of part of the institution’s space for free use to a medical institution for the organization of the work of a medical office, the transfer of a canteen premises to another organization for the organization of hot meals, while the responsibilities for maintaining the property, including reimbursement of utility costs, are not transferred. Experts from the Ministry of Finance clarify: the standard does not apply in cases of gratuitous transfer of property carried out in order to comply with the established quality standards of the service provided by the institution. For example, in the same educational institutions there are sanitary standards for providing children with food; for this purpose, the premises and equipment of the canteen are transferred for free use. According to the department, such relationships do not fall within the scope of the GHS “Rent”.
Other transfer (receipt) of property for paid or free use - an ATM or payment terminal in the lobby of an institution, a pharmacy or a kiosk with office supplies - must be reflected in accounting according to the rules of the standard.
What can be the rent in an educational institution?
All types of lease relationships, including free use, are classified in the standard as operating and financial lease relationships. According to the available explanations, accounting objects, the use of which assumes a long-term nature, comparable to the service life of the property itself, the total amount of lease payments for which is comparable to the value of the transferred property, the transfer of ownership of which occurs upon expiration of the lease term, are objects of financial
rent.
A complete list of features of a financial lease is given in Letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation No. 02-07-07/83464, but even from the listed three it is obvious that an ordinary educational institution created in the form of a budgetary or autonomous institution, with the right of operational management of the real estate and especially valuable property transferred to it movable property simply cannot be the lessor of a financial lease, since it is not the owner of the property. For the same reasons, a state-owned educational institution cannot be a lessor of a financial lease.
The right of ownership and the right to dispose of property have special bodies - departments, property management committees, and educational institutions are not them.
As for the possibility of an educational institution to be a tenant in a financial lease relationship, theoretically it exists, but practically does not occur.
So, let’s make the first conclusion: for an ordinary educational institution, all relations regarding the acceptance and transfer of property for paid or gratuitous use will be relations under an operating lease.
This leads to a second, no less important conclusion: indicators of the analytical group “Investment Real Estate” account 0 101 00 000
The educational institution does not have “fixed assets”.
Let us remind you that this accounting group 0 101 30 000
added to the chart of accounts since 2020 and is described in
the GHS “Fixed Assets”
.
Investment real estate is recognized as a real estate object (parts of a real estate object), as well as movable property that constitutes a single property complex with the specified object, which are in the possession and (or) use of the subject of accounting for the purpose of receiving payment for the use of property (rent) and (or) increasing the value of real estate, but not intended
to fulfill the state (municipal) powers (functions) assigned to the subject of accounting, carry out activities to perform work, provide services, or for the management needs of the subject of accounting and (or) sale.
In other words, property intended exclusively for rental is again managed by property management departments and committees, and only such specialized institutions will generate indicators for account 0 101 30 000
“Investment real estate”.
Operating lease accounting items
GHS "Rent" introduces a completely new type of accounting object - the right to use property, recorded on balance sheet accounts. At the time of writing the article, the revision of Instruction No. 157n
, which would already include these accounts, was not yet available, and for now we will be guided by the available explanations. Let's summarize all the changes in the table.
| Operating lease objects from the lessee | Items under operating lease from the lessor |
| Right to use property: new balance sheet account 0 111 40 000 "Right to use property" | Calculations for rental payments with the user of the property: corresponding analytical accounting accounts accounts 0 205 21 000 “Settlements with payers of income from operating leases” |
| Liabilities to make lease payments: balance sheet account 0 302 24 000 “Calculations for rent for the use of property” | Information about property objects transferred for use (about transferred operating lease accounting objects), namely the corresponding off-balance sheet accounts: – 25 “Property transferred for paid use (rent)”; |
| Depreciation of the right to use property: new balance sheet count 0 104 40 450 “Depreciation of the right to use property” | Expected income from rental payments, calculated for the entire period of use of the property, provided for on the date of conclusion of the agreement (contract): relevant analytical accounting accounts accounts 0 401 40 121 “Deferred income from operating leases” |
| Expenses (liabilities) for contingent lease payments arising on the date of determining their value (usually monthly): – corresponding analytical accounting accounts of account 0 302 00 000 "Obligations"; | Income (calculations) on conditional lease payments arising on the date of determining their value (usually monthly): – corresponding analytical accounting accounts 0 205 35 000 “Calculations of income from conditional rental payments”; |
The new term “conditional rental payments” refers to payments to reimburse the costs of maintaining property leased in the case where the user of the property does not enter into an agreement for the maintenance of the property on his own behalf, but reimburses these costs to the lessor. This accounting object itself is not new, only the name is new.
The lessor's income from conditional rental payments is separated by a new analytical accounting account - 0 205 35 000
“Calculations of income from conditional rental payments”, and the calculation of income uses the new KOSGU code - 135 “Income from conditional rental payments”.
Transition rules
GHS “Lease” is applied from January 1, 2020, and new lease relationships will be reflected in accounting according to the new rules. But what about lease agreements (free use) that were concluded before this date and continue to be valid in 2020? The answer to this question, including a description of all necessary actions, is contained in the Guidelines communicated by Letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation No. 02-07-07/83463
.
Let us consider them in more detail only in terms of operating leases for the reasons stated above.
Actions common to tenant and landlord:
1. Conduct an inventory of property received (transferred) for use in accordance with contracts concluded before January 1, 2020 and valid during the period of application of the GHS “Rent” (under contracts valid both in 2017 and in the year(s) ), next(s) after it).
2. Determine the remaining useful life of operating lease objects (remaining terms of use of the property).
3. Determine the amount of obligations to pay lease payments for the remaining useful life of the objects (starting from 2018 and until the expiration of the terms of use of the lease accounting objects).
How to determine the remaining terms and amounts? From the terms of the lease agreement. For example, an institution entered into a lease agreement on September 1, 2017 for a period of 11 months and a monthly rental amount of 5,000 rubles. As of January 1, 2020, the remaining period is 7 months (11 - 4), and the amount of obligations is 35,000 rubles.
4. Draw up an accounting certificate (f. 0504833) in order to form opening balances for lease accounting objects during the inter-reporting period.
At the tenant's
The following entries will be made:
| Contents of operation | Debit | Credit |
| The right to use leased objects is recognized (in the amount for the remaining term of the lease agreement) | 0 111 40* 000 | 0 401 30 000 |
| The volume of obligations to pay lease payments has been recognized (in the amount for the remaining term of the lease agreement) | 0 401 30 000 | 0 302 24 000 |
* The analytical account is determined by the type of leased property.
At the landlord's
The following entries will be made:
| Contents of operation | Debit | Credit |
| Receivables are recognized for settlements with property users for rental payments (in the amount for the remaining term of the lease agreement) | 0 205 21 000 | 0 401 30 000 |
| The amount of expected income from lease payments is recognized (in the amount for the remaining term of the lease agreement) | 0 401 30 000 | 0 401 40 121 |
Accounting for rental relations in 2020
For newly concluded lease agreements, the procedure for recognizing lease objects will be approximately the same, and further accounting actions do not differ for old and new agreements.
At the tenant's
The following entries will be made:
| Contents of operation | Debit | Credit |
| The right to use leased objects is recognized (in the amount of the lease agreement) | 0 111 40 351 | 0 302 24 730 |
| Depreciation has been accrued on the right to use the asset (monthly in the amount of lease payments due) | 0 109 00 224 0 401 20 224 | 0 104 40* 451 |
| Contingent lease payments accrued | 0 109 00 000** 0 401 20 000 | 0 302 00 000 |
| The right to use property is terminated upon termination of the lease relationship: | ||
| – in the amount of the contract, if the lease is terminated according to the term | 0 104 40 451 | 0 111 40 451 |
| – in the amount of accrued depreciation, if the contract is terminated ahead of schedule, at the same time, the amount of debt on lease payments that will not be fulfilled due to termination, equal to the residual value of the right of use, is reflected by the “red reversal” method | 0 104 40 451 0 111 40 451 | 0 111 40 451 0 302 24 730 |
* The analytical account is determined by the type of leased property.
** For all types of accepted costs.
At the landlord's
the transfer of property for rent is reflected by an internal transfer operation:
debit of account 0 101 00 310 / credit of account 0 101 00 310
- in the amount of the book value of the transferred property, as well as a change in the financially responsible person (he becomes the head (person authorized by him) of the legal entity that accepted the object for use).
If part of an object, for example a building, is leased, then records of internal movement are not made, but in both cases, information about the transfer of the object for use is reflected in the inventory card for recording non-financial assets (f. 0504031). At the same time, counting indicators increase 25
“Property transferred for paid use (lease)” in the book value of operating lease objects transferred for use.
Many institutions ask the question: how to determine the book value of transferred property if it is part of an inventory item? The guidelines do not contain a direct answer to the question posed, but it would be logical to calculate the value of part of an object in proportion to its total book value, for example, by area, and to consolidate this method of valuation in the accounting policy.
Other operations with the lessor
We will show it in the table.
| Contents of operation | Debit | Credit |
| Future income from granting the right to use the asset is recognized in the amount of lease payments for the entire period of use of the lease accounting object | 0 205 21 560 | 0 401 40 121 |
| Revenues of the current financial year from the provision of the right to use an asset under an operating lease are recognized (evenly and monthly or in accordance with the lease payment schedule) | 0 401 40 121 | 0 401 10 121 |
| Income from conditional rental payments is recognized (income from reimbursement of costs for the maintenance of property transferred for use) | 0 205 35 560 | 0 401 10 135 |
| Previously accrued deferred income from the provision of the right to use an asset in the event of early termination of the lease agreement has been adjusted in the remaining amount of payments using the “red reversal” method. | 0 205 21 560 | 0 401 40 121 |
The end or early termination of the lease agreement also means the return of the property, which requires an inventory. It is carried out by a commission of the party receiving the property, with the participation of representatives of the transferring party. All identified changes in the structural components of the property complex made by the user (tenant) of the property during its use, including inseparable improvements, are subject to reflection in inventory documents.
The return of property will also be reflected by an internal movement transaction, if it was carried out initially, and a decrease in the account indicator 25
“Property transferred for paid use (rent).”
When transferring property into an operating lease, the responsibility for calculating depreciation on it remains with the balance sheet holder, the accounting records of this operation remain unchanged, as well as the chosen method of calculating depreciation and the depreciation rate:
Account debit 0 109 00 271
“Depreciation costs of fixed assets and intangible assets for the manufacture of finished products, performance of work, services” or
account 0 401 20 271
“Depreciation costs of fixed assets and intangible assets”
Account credit 0 104 00 410
"Depreciation"
Accounting for authorization in rental relations
If accounts payable for lease payments are recognized in accounting, this means that obligations (budgetary obligations) must be assumed from the lessee, and for the lessor, deferred income is also recognized as an increase in planned (forecast) assignments for income from operating leases.
Liabilities and income of long-term rental relationships will be reflected in the corresponding analytical accounts:
– 10 “Sanction for the current financial year”; – 20 “Sanction for the first year following the current (next financial year)”; – 30 “Authorization for the second year following the current one (the first year following the next one)”; – 40 “Authorization for the second year following the next”; – 90 “Authorization for other subsequent years (outside the planning period).”
Example.
A budgetary institution rents premises from another budgetary institution. The contract was concluded for two years from March 1, 2020 with a monthly payment of 10,000 rubles. The contract was concluded with a single supplier.
At the time of concluding the agreement, the following entries were made in the records of both institutions:
| Contents of operation | Debit | Credit | Amount, rub. |
| At the tenant's | |||
| Reflects assumed obligations for lease payments of the current period (10 months of 2020) | 0 506 10 224 | 0 502 17 224 | 100 000 |
| Obligations for rent payments for the current financial year have been accepted | 0 502 17 224 | 0 502 11 224 | 100 000 |
| Reflects assumed obligations for lease payments to be fulfilled in the year following the current financial year (calculated for the period from January 1, 2020 to December 31, 2019) | 0 506 20 224 | 0 502 27 224 | 120 000 |
| Obligations for lease payments have been accepted and are due in the year following the current financial year (calculated for the period from January 1, 2020 to December 31, 2019) | 0 502 27 224 | 0 502 21 224 | 120 000 |
| Reflects assumed obligations for lease payments to be fulfilled in the second year following the current financial year (calculated for the period from January 1, 2020 to February 29, 2020) | 0 506 30 224 | 0 502 37 224 | 20 000 |
| Obligations for lease payments have been accepted and are due in the second year following the current financial year (calculated for the period from January 1, 2020 to February 29, 2020) | 0 502 37 224 | 0 502 31 224 | 20 000 |
| At the landlord's | |||
| The projected income of the current financial year is reflected | 0 507 10 121 | 0 504 10 121 | 100 000 |
| Projected revenues for the year following the current financial year are shown. | 0 507 20 121 | 0 504 20 121 | 120 000 |
| Projected revenues for the second year following the current financial year are shown. | 0 507 30 121 | 0 504 30 121 | 20 000 |
If the relationship is terminated before the deadline established by the contract, the authorization transactions are reversed.
Note that liabilities and income for contingent lease payments are also subject to reflection in the authorization accounts, and they will be liabilities and income for the current financial period. And since there are no changes here, we will not provide records of these accounting transactions.
Accounting for relations involving the transfer of property for free use
Despite the fact that the GHS “Rent” is also valid when transferring for free use, the accounting for such relationships is different and is regulated by Section. IV “Features of reflecting lease accounting objects at fair value” GHS “Lease”.
Firstly, the right to use the lease accounting object on preferential terms (including free of charge) is taken into account at fair value, which means the amount of lease payments that could have been made. Recognition of an asset at fair value ( clause 27 of the GHS “Lease”
) involves calculating the amount of the contract at rental rates determined in accordance with the regulations of the executive authorities of the public legal entity.
Receipt of property for free use is recognized as deferred income (future income) from the provision of the right to use the asset and is subject to segregation in the accounts of the working chart of accounts of the accounting entity.
As in the case of paid use, the asset is depreciated over its useful life while recognizing future income as current.
At the borrower
The following entries will be made:
| Contents of operation | Debit | Credit |
| The right to use leased objects is recognized (in the estimated amount of the lease agreement) | 0 111 40 351 | 0 401 40 182* |
| Depreciation has been accrued on the right to use the asset (monthly in the estimated amount of lease payments due) | 0 109 00 271 0 401 20 271 | 0 104 40 451 |
| Income of the current financial year from the right to use an asset received free of charge under an operating lease is recognized (evenly and monthly) | 0 401 40 182 | 0 401 10 182 |
| The right to use property is terminated upon termination of the agreement for gratuitous use: | ||
| – in the amount of the contract, if the lease is terminated according to the term | 0 104 40 451 | 0 111 40 451 |
| – in the amount of accrued depreciation, if the contract is terminated early, at the same time an adjustment is made to deferred income from gratuitous use in an amount corresponding to the balance under the contract, reflected by the “red reversal” method | 0 104 40 451 0 111 40 451 | 0 111 40 451 0 401 40 182 |
* As amended by Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation No. 255n.
Secondly, the lender records income from granting the right to use the asset also at fair value, but at the same time also reflects the expenses that it incurred by providing the property for use free of charge. Both accrual operations - income and expenses - are carried out through account 0 210 05 000
“Settlements with other debtors”, since in relations of gratuitous use, debts that need to be repaid still do not arise.
Operations for the internal movement of property transferred (returned) for free use are reflected similarly to those discussed above with an increase (decrease upon return) of the off-balance sheet account 26
“Property transferred for free use.”
From the lender
The following entries will be made:
| Contents of operation | Debit | Credit |
| Future income from granting the right to use the asset is recognized in the amount of lease payments for the entire period of use of the lease accounting object | 0 210 05 560 | 0 401 40 121 |
| Deferred expenses (lost profits) are recognized when providing property for free use | 0 401 51 241 0 401 51 251 | 0 210 05 660 |
| Income of the current financial year from the right to use an asset transferred free of charge under an operating lease is recognized (evenly and monthly) | 0 401 40 121 | 0 401 10 121 |
| Expenses of the current financial year from the right to use an asset transferred free of charge under an operating lease have been recognized (evenly and monthly) | 0 401 20 241 0 401 20 251 | 0 401 51 241 0 401 51 251 |
| Previously accrued income and expenses of future periods from granting the right to use the asset free of charge in the event of early termination of the contract have been adjusted in the remaining estimated amount of payments using the “red reversal” method. | 0 210 05 560 0 401 51 241 0 401 51 251 | 0 401 40 121 0 210 05 660 |
Let us note that operations for accounting for leased objects when transferring property for free use have not yet been disclosed in as much detail as regular lease relations. Thus, comments and clarifications from the Ministry of Finance are still possible on this issue.
* * *
In conclusion, let us reiterate the main conclusions:
1. In the accounting of the lessee (borrower), a new accounting object arises - the right to use the asset.
2. The right to use the asset is depreciated.
3. The lessor (lender) accrues income from the rental of property not on a monthly basis, but in the total amount of the lease agreement as part of future income with their monthly inclusion in current income.
4. To account for rental relations, new synthetic and analytical accounts have been added, which we will soon see in the updated Instructions No. 157n and Instructions No. 65n.
Kravchenko E., expert of the information and reference system “Ayudar Info”