Formation of the initial cost of a fixed asset according to primary documents
Example. Situation. The organization late received a document confirming the costs of purchasing a separate piece of equipment that had already been put into operation. The accountant did not include this amount in the original cost of the property.
Example conditions. In January, Paritet LLC put into operation equipment that required installation. According to available documents, the value of the property was 30,000 rubles. (without VAT). Installation cost - 6000 rubles. (without VAT). The organization has established a useful life of 4 years for this fixed asset. The method of calculating depreciation is linear.
The accountant of Paritet LLC prepared the following entries:
Dt 07 “Equipment for installation” Kt 60 “Settlements with suppliers and contractors” - 30,000 rubles. — equipment requiring installation has been taken into account;
D-t 08 “Investments in non-current assets” D-t 07 - 30,000 rubles. — the transfer of equipment for installation is reflected;
D-t 08 K-t 60 - 6000 rub. — installation costs are taken into account;
D-t 01 “Fixed assets” K-t 08 - 36,000 rub. — equipment has been accepted for accounting as part of fixed assets.
Every month, starting in February, the accountant calculated depreciation on this equipment using the following entries:
D-t 20 “Main production” K-t 02 - 750 rub. (RUB 36,000: 48 months) - depreciation has been calculated.
In May, the accounting department of Paritet LLC received an invoice for a separate piece of equipment that was installed during its installation, costing 8,400 rubles. (without VAT). The accountant reflected the cost of this part as part of inventories and wrote it off as expenses with the following entry:
Kit 10 “Materials” Kit 60 - 8400 rub. — the cost of the part is reflected in the inventory;
D-t 20 K-t 10 - 8400 rub. — inventories are written off for production.
The rules for determining the initial cost of fixed assets are established in clause 8 of PBU 6/01, according to which the initial cost of fixed assets acquired for a fee is recognized as the amount of the organization’s actual costs for acquisition, construction and production, excluding VAT and other refundable taxes.
According to Art. 377 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the tax base for property tax (average annual value of property) is formed based on the residual value (Article 375 of this Code).
The accountant of Paritet LLC, when accepting the fixed asset item for accounting, was unable to timely include in the initial cost all the actual costs of its acquisition. An error in assessing the value of a fixed asset led to an incorrect amount of accrued depreciation, and this, in turn, affected the residual value of the property.
Thus, the understatement of the tax base led to an understatement of the amount of tax payable to the budget.
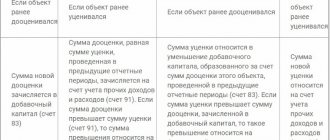
In general, the initial cost of fixed assets accepted for accounting is not subject to change, with the exception of cases of completion, additional equipment, reconstruction, modernization, partial liquidation and revaluation of fixed assets (clause 14 of PBU 6/01).
However, in this example we are not talking about a change in the initial value of the property, because the expense was made not after, but before the fixed asset was accepted for accounting. Therefore, having discovered a document confirming the amount of actual expenses for the acquisition of a fixed asset, the accountant had to correct the initially incorrectly formed initial cost.
If the initial cost of a fixed asset changes, then the accountant must recalculate the property tax base for all periods after putting this property into operation.
So, the error was discovered in May. In the same month, corrections should have been made to the accounting and additional property taxes should have been assessed. But first, the accountant needed to make changes to the initial cost of the main asset put into operation and correct the act of acceptance and transfer of fixed assets (Form N OS-1).
The accountant had to issue corrective entries:
D-t 10 K-t 60 - 8400 rub. — the cost of the part is excluded from the inventory;
D-t 20 K-t 10 - 8400 rub. — the cost of inventories is excluded from the cost structure;
D-t 08 K-t 60 - 8400 rub. — the amount of investments in non-current assets has been increased;
D-t 01 K-t 08 - 8400 rub. — the initial cost of the fixed asset has been increased.
Then the accountant had to recalculate the amount of monthly depreciation charges for this fixed asset, which should have been 925 rubles. [(RUB 36,000 + RUB 8,400) : 48 months].
Thus, for all months of operation, the accountant had to add additional depreciation in the amount of 525 rubles. [(925 rub. - 750 rub.) x 3 months].
The accountant prepared the following entry in this case:
D-t 20 K-t 02 - 525 rub. — additional depreciation was accrued on fixed assets for February - April.
The calculation of the tax base for the first quarter includes the residual value of fixed assets as of January 1, February 1, March 1 and April 1.
Let us assume that before the error was discovered, the average annual value of the property of Paritet LLC, indicated in the calculation of the advance payment for property tax for the first quarter, was 480,000 rubles.
The amount of the advance payment for property tax that Paritet LLC paid to the budget for this period was calculated in the amount of 2,640 rubles. (RUB 480,000 x 2.2%: 4).
After correcting the error, the average annual cost increased by 6169 rubles. ([8400 rubles + (8400 rubles - 175 rubles) + (8400 rubles - 175 rubles x 2 months)] : (3 + 1)), and the tax amount increased by 34 rubles. (RUB 6,169 x 2.2%: 4).
The accountant recorded the following entry for the amount of additional tax payment:
Dt 91 Kt 68, subaccount “Calculations for property tax of organizations” - 34 rubles. — additional assessment of property tax for the first quarter is reflected.
Residual value of property for the reporting period [column 3 Data for calculating the average annual value of property for the tax period Sec. 2 declaration] should have been indicated taking into account the increase:
— on February 1 — by 8,400 rubles;
- on March 1 - by 8225 rubles. (8400 rub. - 175 rub.);
- on April 1 - by 8050 rubles. (8400 RUR - 175 RUR x 2 months).
The average annual value of property (page 150 of the declaration) should have increased by 6,169 rubles. [(8400 rub. + 8225 rub. + 8050 rub.) : 4].
The tax base should have increased by the same amount (page 190 of the declaration).
The amount of the advance payment for property tax is calculated based on the results of each reporting period in the amount of one-fourth of the product of the corresponding tax rate and the average value of property for the reporting period (clause 4 of Article 382 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
In this example, the amount of the advance payment (page 180, column 3, section 2 of the tax calculation for the advance payment for property tax) should have increased by 34 rubles. (RUB 6,169 x 2.2%: 4).
The procedure for forming the value of fixed assets for tax accounting purposes
In the process of carrying out economic activities, organizations regularly acquire property necessary for their normal functioning. This includes quite expensive property with a long service life.
The procedure for recognizing expenses for the acquisition of such property, both in the accounting and tax accounting of an organization, depends on:
- on the functionality of such property,
- property value,
and also on how you plan to use it.
For tax accounting purposes, in accordance with the provisions of Article 256 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, depreciable property is:
- property,
- results of intellectual activity,
- other objects of intellectual property,
which are owned by the taxpayer (unless otherwise provided by Chapter 25 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation), are used by him to generate income and the cost of which is repaid by calculating depreciation.