Therapeutic and preventive nutrition is prescribed for the noble purpose of improving health and preventing occupational diseases of workers in hazardous industries.
It is not possible to fully protect the human body from adverse factors during work processes, although a set of safety measures is being taken.
To increase the protective functions of the skin and internal organs, to enhance the removal of pesticides and toxic substances from the body, this task is performed by special diets developed by nutritionists.
Therapeutic and preventive nutrition - what is it, when is it issued?
Russian legislation provides for various measures to protect people whose work involves conditions that negatively affect human health.
In addition to various payments, increased vacation duration and early retirement, such employees are entitled to therapeutic and preventive nutrition. Therapeutic and preventive nutrition is the provision of certain products and vitamins, intended for people working in harmful and dangerous conditions , which help to minimize the impact of harmful substances on humans and promote the rapid removal of toxins and other toxic substances from the body.
Depending on the type of work performed, therapeutic and preventive nutrition consists of:
- provision of dairy products;
- organizing hot meals according to special rations;
- dispensing vitamin complexes or products enriched with vitamins and microelements.
The need to provide additional free food to workers is outlined in Art. 222 Labor Code of the Russian Federation. It is part of a set of labor protection measures for workers in hazardous and hazardous industries. The list of specialties and positions, diets and rules for the provision of PPP were approved by order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of Russia dated February 16, 2009 No. 46n.
Workers in hazardous and hazardous industries should be made aware of the possibility of receiving supplemental nutrition. To do this, clauses are added to collective agreements and wage regulations that contain detailed information about who is entitled to LPP, how it is provided, as well as the possibility of replacing supplementary nutrition with monetary compensation.
Familiarization with the rules for obtaining personal injury or compensation for it occurs upon hiring, as part of the training on labor protection for employees. In addition, the conditions for receiving supplementary nutrition are also provided for in employment contracts.
To whom and when is therapeutic and preventive nutrition provided?
Order No. 46n provides for the provision of therapeutic and preventive nutrition in harmful (dangerous) working conditions to those employees of the enterprise whose professions (positions) are listed in the order and who perform work in such conditions for at least half of the working day (shift).
In addition, therapeutic and preventive nutrition is provided to:
- workers who one-time perform various repairs, commissioning and other types of work in premises where working conditions are of increased danger to humans;
- employees who are on sick leave due to an acquired occupational disease (outside the hospital) or who have become disabled while working in dangerous conditions;
- employees temporarily transferred from premises with hazardous conditions to other types of work due to health reasons;
- pregnant women and women on maternity leave (up to one and a half years old), provided that they performed work with a higher hazard class.
Those employees who were transferred to another job due to an occupational disease or became disabled in hazardous work are provided with additional food for a period of no more than 1 year.
The employer is obliged to provide his employees with hot meals. As a rule, it is provided in the form of breakfast. However, if this is not possible, in agreement with Rospotrebnadzor or the sanitary service of the enterprise, it is possible to postpone the LPP to lunchtime.
An exception to this rule is made for employees who work in areas of high or low pressure.
In this case, meals are provided after the employee leaves the danger zone.
For workers who work in remote and hard-to-reach areas, a ration is issued, consisting of products provided for in the LPP diet. Disabled people and women on maternity leave also receive PPP at the enterprise. If for some reason they cannot come to work for food, it is delivered to their home.
The delivery of supplementary nutrition is suspended for the following periods:
- vacations;
- days off;
- business trips;
- study;
- performing duties not related to harmful (hazardous) conditions;
- illness not related to working conditions;
- treatment or rehabilitation in specialized institutions.
Organization of special meals for workers in hazardous working conditions
To provide food for employees, LPPs use factory canteens or enter into agreements with catering organizations. Canteen workers prepare weekly rations with a detailed description of daily nutrition, based on the standards for providing food for each employee who is entitled to additional nutrition. These diets must be coordinated with Rospotrebnadzor.
To control the receipt of food at the enterprise, supplementary food coupons are used, which are issued to employees working in harmful and dangerous conditions. These coupons are recorded in a special accounting journal. An employee of the accounting or personnel service is appointed responsible for accounting and issuing coupons, for which a special order is issued.
The order also approves the forms of coupons and logbook, as well as the frequency of reconciliation of issued and used coupons. It is carried out at least once a month.
The form of coupons and magazine is developed by the company independently, based on its own needs. The coupons have serial numbers; they indicate to whom the coupon was issued, on what date, and the type of ration. The coupon includes the signature of the manager and the seal of the enterprise.
The log records:
- Full name and position of the employee who received the coupons;
- date of issue, number of coupons issued and their serial numbers;
- date and reason for returning unused coupons.
Reconciliation of coupon records is carried out according to the journal data and the actual return of used coupons from the canteen. Based on the results of the inspection, a report is drawn up, which is stored along with the journal. The storage period for used coupons, journals and reconciliation reports is at least 5 years.
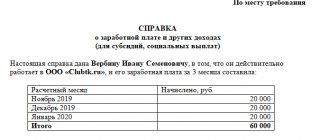
An example of filling out a coupon and journal for obtaining BOB
Ticket:
Series and document number: 4658LD
Voucher for additional food according to diet 3
Source: https://delatdelo.com/organizaciya-biznesa/lechebno-profilakticheskoe-pitanie.html
Food for hazardous working conditions for pregnant women
A pregnant woman should be transferred to a job where her body will not be affected by harmful production factors. If there is no such workplace, the woman is freed from work altogether, while receiving an average salary.
Even after being transferred to another job, the pregnant woman will receive special food until the end of maternity leave for a child up to 1.5 years old.
If the employer has received a certificate from the company’s health service or from Rospotrebnadzor about the need to deliver special equipment. food at home, food will be brought to the employee’s home. Sending is carried out even if the woman’s place of residence is remote from the enterprise.
What products are included in therapeutic and preventive nutrition?
What does therapeutic and preventive nutrition include?
Therapeutic and preventive nutrition is prescribed for the noble purpose of improving health and preventing occupational diseases of workers in hazardous industries.
It is not possible to fully protect the human body from adverse factors during work processes, although a set of safety measures is being taken.
To increase the protective functions of the skin and internal organs, to enhance the removal of pesticides and toxic substances from the body, this task is performed by special diets developed by nutritionists.
Therapeutic and preventive nutrition
First of all, it must be emphasized that only a specialist can determine the degree of physiological norms for the body. Nutrition is called therapeutic with a special meaning, which is aimed at limiting satiety.
Excess, overeating, even healthy foods, is unacceptable. Metabolic disorders, which are caused by harmful factors, are also determined by the doctor; his responsibilities include the rational prescription of biological active substances according to the necessary needs.
What are the rules for issuing milk and providing special meals to employees?
Milk and special food at work sites are provided in strict compliance with the standards of a number of regulatory documents. Among them:
- Government Decree No. 168 dated March 13, 2008, which sets the standards for products issued and the assignment of compensation payments when replacing special food with monetary compensation;
- Order No. 45n dated February 16, 2009, issued by the Ministry of Health and Social Development, which stipulates the conditions for the free provision of dairy products;
- Order No. 46n dated February 16, 2009 (author of the document is the Ministry of Health and Social Development), providing a list of positions and areas of activity for which there is an obligation to provide medical or special dietary nutrition to personnel.
IMPORTANT! The decision made by the company's management about the presence of harmful factors at work must be confirmed by the conclusions of a special assessment of workplaces.
Those employees whose work is accompanied by exposure to harmful factors on the body can apply for dairy products free of charge. When working conditions deteriorate and workers move into the category of workplaces with particularly harmful factors, instead of milk, personnel should be provided with complex nutrition for therapeutic or preventive purposes.
If an employee wants to replace food products with monetary compensation, he has the right to make such a request to the management of the enterprise in writing. An additional requirement is that such a possibility must be stipulated in the employment agreement with a specific employee. The exception to the rule is specialists working in particularly hazardous conditions. They can receive special food only in natural form.
In the case of a dietary menu or diet that has a medicinal effect, all products must be drunk and eaten by employees at the employer’s facilities in specially designated areas. If harmful production conditions are identified, dairy products can be supplemented with pectin (2 g of pectin, which is included in other foods). This standard is provided for specialists who periodically come into contact during their work with inorganic compounds in products made of non-ferrous metals. With regular contact with these substances, milk is replaced with fermented milk products or a dietary diet.
NOTE! Products containing pectin must be given to employees before the start of their shift; liquids in the form of milk or fermented milk drinks must be consumed during work.
Personnel are provided with a therapeutic type of diet subject to a set of requirements:
- working conditions are recognized as particularly harmful;
- the employee was at the workplace for at least half of the standard shift duration.
Special food is also provided to persons who have received an occupational disease that has caused temporary loss of ability to work (provided that hospitalization was not required).
There is no need to provide the employee with special meals on days when:
- the person is not present at the workplace;
- the employee is on vacation;
- the employee went on a business trip;
- the specialist was on study leave or attended educational courses outside of work;
- the employee was involved in work at other sites where working conditions are not particularly harmful;
- sick leave was issued.
Meals with therapeutic or preventive effects are provided to employees before the start of their shift. Necessary products must be included in the hot breakfast menu. An exception is possible if free meals are transferred from the morning to the lunch break. To implement such changes, it is necessary to obtain the consent of the medical and sanitary authority of the enterprise (if there is no such service in the organization, then this initiative must be addressed to the territorial office of Rospotrebnadzor).
BY THE WAY, if an employee, for objective reasons, cannot receive special food in a designated place on the employer’s premises, the management of the enterprise is obliged to ensure delivery of food to their home. In order to take advantage of this opportunity, an employee must provide the employer with a certificate from the company’s health authority or a conclusion from Rospotrebnadzor.
If the procedure and rules for providing staff with special food or dairy products are not followed, penalties are applied to the employer. The powers to control this area of labor relations are vested in:
- labor inspections;
- Rospotrebnadzor;
- trade union structures.
The law does not provide for the possibility of providing employees with milk while simultaneously providing these same persons with special food. One employee can apply only for dairy products or only for a hot breakfast with a specialized diet.
Standards for issuing products
If there are personnel involved in working at facilities with hazardous conditions, the employer is required to purchase dairy products for employees. Milk is given to employees for each shift, provided that the time worked accounted for more than half of the working day. The daily dispensing rate for dairy products is set at 500 ml.
REMEMBER! It is not allowed to replace milk with sour cream products or butter.
Pectin-containing products can be given to employees in the form of jelly or marmalade. They can be replaced with fruit juice or vegetable drinks with pulp. The volume of the drink cannot be less than 300 ml. When a person has daily contact with inorganic types of compounds in non-ferrous metals, the employer has an obligation to provide such employee with free fermented milk products in a volume of 500 ml (liquid norm). The standard volume of cottage cheese is 100 g, cheese - 60 g. If a specialist is engaged in work on the production of antibiotics, he must receive liquid fermented milk products, necessarily enriched with probiotics (norm - 500 ml).
When replacing a special ration with cash compensation, you must adhere to the following rules:
- the initiative to switch to cash payments belonged to the employee, as evidenced by his written statement;
- the collective agreement and employment agreement with the employee indicate a norm that allows you to replace food with cash payments;
- the conversion of natural meters into cost ones should be carried out in relation to retail prices for the product being replaced;
- compensation transfers to employees must be made monthly;
- the amount of payments is subject to indexation.
Regulations on the issuance of therapeutic and preventive nutrition
Therapeutic and preventive nutrition (special food) is issued on the basis of the Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of March 13.
2008 N 168 On the procedure for determining the norms and conditions for the free issuance of therapeutic and preventive nutrition, milk or other equivalent food products and making compensation payments, which approved the following, agreed with the Ministry of Health and Social Development of the Russian Federation:
– a list of industries, professions and positions in which work gives the right to free medical and preventive nutrition in connection with particularly harmful working conditions;
– diets for therapeutic and preventive nutrition;
– standards for free distribution of vitamin preparations;
– rules for the free distribution of therapeutic and preventive nutrition.
Special food is issued to employees of the Novoposelkovaya Secondary School who perform work (in the canteen) in order to improve their health and prevent occupational diseases. The distribution of therapeutic and preventive nutrition must be carried out in strict accordance with these Regulations.
Therapeutic and preventive nutrition is provided free of charge only to those employees for whom the provision of this food is provided for by the list of industries, professions and positions in which work gives the right to receive free therapeutic and preventive nutrition in connection with particularly harmful working conditions.
Therapeutic and preventive nutrition is given to employees on the days they actually perform work, provided they are employed at the specified job for at least half of the working day, as well as on days of illness with temporary loss of ability to work, if the disease is occupational in nature and the sick person is not hospitalized.
Therapeutic and preventive nutrition is also provided:
a) employees of other structural divisions of the Municipal Budgetary Educational Institution “Novoposelkovaya Secondary School” performing research or other work and working full time at the research reactor;
b) disabled people due to an occupational disease who used special food immediately before the onset of disability due to the nature of their work, until the cessation of disability, but not more than one year from the date of disability;
c) employees who have the right to receive free special food and are temporarily transferred to another job due to the initial symptoms of an occupational disease due to the nature of their work, for a period of not more than one year;
d) women employed before maternity leave in particularly hazardous working conditions, giving the right to free medical and preventive nutrition - for the entire duration of maternity leave.
If pregnant women, in accordance with a medical opinion, are transferred to another job in order to eliminate contact with harmful production factors before maternity leave, special food is given to them for the entire time before and during the leave period. When women with children under the age of one and a half years are transferred to another job for the specified reasons, therapeutic and preventive nutrition is given to them until the child reaches the age of one and a half years.
The issuance of therapeutic and preventive food for the past and monetary compensation for special food not received in a timely manner is also not permitted.
The catering organization where special food is issued must, in its structure and content, fully comply with current sanitary standards and rules.
The preparation and distribution of therapeutic and preventive nutrition is carried out in strict accordance with the approved diets, in accordance with the list of products provided for in the therapeutic and preventive nutrition diets, menu layouts are compiled for each day.
If the cost of food increases, it is necessary to promptly increase the cost of the daily ration.
Special food for employees of the municipal budgetary educational institution "Novoposelkovaya Secondary School" is issued according to the working time sheet signed by the head of the structural unit.
Responsibility for the correct completion of the work time sheet rests with the head of the structural unit.
Familiarization of workers using therapeutic and preventive nutrition with the rules for free provision of food should be included in the mandatory induction training program on labor protection.
Control over the organization of the distribution of therapeutic and preventive nutrition to workers engaged in work with particularly hazardous working conditions is carried out by state examinations of working conditions of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation, bodies and institutions of the state sanitary and epidemiological service of the Russian Federation, the labor protection department of the Municipal Budgetary Educational Institution "Novoposelkovaya Secondary School" and the trade union committee MBOU "Novoselkovaya Secondary School".
Responsibility for providing workers and students with therapeutic and preventive nutrition and for compliance with these Regulations rests with the Responsible for Labor SafetyDeputy. Director of Water Resources _____________________
Receiving monetary compensation for supplementary nutrition
Labor legislation provides for the replacement of LPP with cash payments as agreed between the employer and the employee who is entitled to the benefit. An employee writes a statement to the head of the enterprise requesting payment of money instead of issuing food. This statement must be agreed upon by representatives of the trade union committee or other body protecting the interests of workers.
The employer may refuse to replace supplementary nutrition with monetary compensation, since issuing money instead of food is not the employer’s responsibility.
In addition, it is prohibited to replace LPP with money for workers in particularly hazardous industries.
It is necessary to agree on replacing meals with compensation in advance, and not after receiving coupons for supplementary meals. For example, coupons are issued at an enterprise once a month. The employee needs to write an application before receiving monthly coupons, then he will be able to replace the LPP with a payment.
Unused coupons will not be compensated with money. The only exception is the situation when the employee was unable to receive additional nutrition due to the fault of the employer. For example, an employer uses the services of a third-party catering organization. At the end of the contract, a new one was not signed on time, which is why there was no LPP for several days. In such a situation, workers can count on receiving monetary compensation for those days when they were not provided with food.
In addition, the fact of failure to provide LPP can be revealed by the results of an inspection by regulatory authorities (labor inspectorate or Rospotrebnadzor). In this case, employees who did not receive meals due to the fact that the employer did not notify them or did not organize it, are entitled to a compensation payment for the entire time when they were supposed to receive LPP.
Such actions by the employer are interpreted as a violation of labor laws and entail penalties.
The right of workers to free therapeutic and preventive nutrition
Home Articles Labor relations at the enterprise JOB CERTIFICATION
The provision of therapeutic and preventive nutrition to employees is regulated by the following regulations approved by Resolution No. 4/P-1:
? A list of industries, professions and positions in which work gives the right to free medical and preventive nutrition in connection with particularly harmful working conditions (according to the text - the List); ? rations of therapeutic and prophylactic nutrition and standards for the free distribution of vitamin preparations (in the text - rations);
? Right-handers of free distribution of therapeutic and prophylactic nutrition (according to the text - Rules).
The industries where workers should receive therapeutic and preventive nutrition include: chemical production (inorganic products, organic products, varnishes and paints (chemical reagents, as well as mining and chemical-pharmaceutical production); - non-ferrous metallurgy production;
? ferrous metallurgy production;
? electrical and radio engineering production;
? work with radioactive substances and sources of ionizing radiation;
? work on loading and unloading apatite in sea and river ports;
? work in conditions of high atmospheric pressure;
? food industry production.
Therapeutic and preventive nutrition is also provided by:
? workers engaged in construction, construction and installation, repair and construction, commissioning work, working full time in existing production
with particularly harmful working conditions;
? workers cleaning and preparing equipment for repair or conservation in a workshop (site), for whose workers the provision of therapeutic and prophylactic nutrition is provided;
? disabled people due to an occupational disease who used therapeutic and preventive nutrition immediately before the onset of disability caused by the nature of their work - until the cessation of disability, but not more than 6 months from the date of its establishment;
? workers who have the right to receive free medical nutrition and are temporarily transferred to another job due to the initial signs of an occupational disease caused by the nature of their work - for a period of no more than 6 months;
? women employed until maternity leave begins in industries, professions and positions that give them the right to free medical and preventive nutrition.
The right to receive therapeutic and preventive nutrition is available only to those workers whose profession and positions are provided for in the relevant sections of the List, regardless of which area of the economy these productions belong to, in jobs with particularly hazardous working conditions, classified by the Hygienic Classification of Labor according to hazard indicators and the dangers of factors in the working environment, the complexity and intensity of the labor process, no less than class 3, hazard degree 3, regardless of the time the employee was employed in these conditions. This must be confirmed based on the results of workplace certification for working conditions.
At enterprises, based on the List and based on the results of certification, a list of industries, professions and positions is compiled, work in which gives the right to free medical and preventive nutrition in connection with particularly harmful working conditions (approved as an annex to the collective agreement).
Therapeutic and preventive nutrition is issued to employees on the days of actual work in industries, professions and positions provided for in the List, as well as in other cases provided for by the Rules.
Preparation and distribution of therapeutic and prophylactic nutrition and vitamins are carried out in accordance with the diets. In order to properly organize therapeutic and preventive nutrition, it is necessary to conclude an agreement with a catering establishment that complies with sanitary and hygienic standards and rules.
After concluding an agreement, enterprises submit orders to canteens for a certain number of breakfasts according to separate rations. They are prepared at a specified time for each shift, delivery is organized using special coupons (subscriptions) of the established form.
Therapeutic and preventive nutrition is provided in the form of hot breakfasts before starting work.
As an exception, in agreement with the medical and sanitary service of the enterprise, and in its absence, with the local sanitary and epidemiological station, it is allowed to provide therapeutic and preventive food during the lunch break.
Persons working in high pressure conditions (in caissons, medical pressure chambers, diving operations) are given therapeutic and preventive food after release.
It is not allowed to give therapeutic and preventive meals home.
Moreover, it is not allowed to issue products intended for the preparation of therapeutic and preventive nutrition, even if the right to receive therapeutic and preventive nutrition is retained for the period when the employee is not actually working (except for receiving them by the sick, disabled due to an occupational disease, or nursing mothers).
The issuance of therapeutic and preventive nutrition for the past period and the payment of monetary compensation are also prohibited.
If the work is traveling, the employee is paid monetary compensation for the purchase of therapeutic and preventive nutrition under the conditions provided for by the collective agreement (Article 7 of the Law on Labor Protection).
Therapeutic and preventive nutrition is not provided in: ? non-working days; ? vacation days;
? days of business trips;
? off-the-job training days;
? days of work in other areas of the enterprise where therapeutic and preventive nutrition is not established;
? days for performing state and public duties;
? period of temporary incapacity for work due to general diseases;
? days spent in a hospital or sanatorium for treatment, as well as during the period of stay in a dispensary.
Employees receiving free therapeutic and preventive nutrition are not provided with additional milk or other equivalent food products.
Responsibility for providing therapeutic and preventive nutrition and compliance with the Rules for issuing therapeutic and preventive nutrition rests with the heads of enterprises.
Source: https://obuhgalterii.info/?p=1995
Diets
Diet rations
There are the following rations for therapeutic and preventive nutrition for workers:
- Diet 1.
It is intended for those employees whose activities involve radioactive drugs, loparite products and sources of ionized radiation.
This diet includes those foods that contain cystine and methionine. Thanks to them, the resistance of the human body to radioactive drugs increases. Such products are: low-fat fish, hard cheeses and cottage cheese.
- Diet 2.
It is intended for those specialists who work with acids (sulfuric and nitric), alkali alloys, organophosphorus compounds, fluorine and chlorine compounds.
This diet includes the following products: fish, meat, milk (prevent the accumulation of hazardous chemicals in the body); vegetables and fruits (contain healthy vitamins and minerals); vegetable oils (contain polyunsaturated acids).
- Diet 2a.
It is received by those workers who, during their work, come into close contact with chromium and its compounds. This food is designed to affect the nervous and endocrine systems, as well as being hypoallergenic.
This diet includes food containing lecithins, as well as vitamins A, C, P, E (cream, sour cream, liver); products that contain amino acids (milk, berries, vegetables).
- Diet 3.
It is received by those employees who come into contact with lead compounds.
This diet includes fruits, berries, fermented milk products, and juices containing pectin. Ascorbic acid is an addition to the diet.
- Diet 4.
Issued to those specialists whose work involves working with mercury, arsenic, fiberglass, as well as to those employees who work at high atmospheric pressure.
Includes foods with a high content of lipotropic substances (vegetable oils, cottage cheese). For people who directly work with arsenic and mercury, additionally include foods containing vitamins B and C in their diet.
- Diet 4a.
It is intended for those who work with phosphoric acid, phosphorus and phosphorus derivatives.
This diet mainly contains animal proteins and vegetables. Instead of milk, those fermented milk products that help reduce phosphorus absorption should be given.
- Diet 4b.
It is issued to those employees who come into contact with such aggressive chemicals. substances such as dinitrotoluene, animine and toluindine derivatives.
This diet includes vitamins, herbal ingredients and glutamic acid. These substances prevent toxic drugs from entering the body.
- Diet 5.
Issued to specialists working with carbon disulfide, polymer materials, manganese and hydrocarbons.
The basis of this diet is to protect the nervous system and liver from toxic substances. It includes meat, eggs, fish and low-fat cottage cheese - these products are rich in lecithin, complete proteins and polyunsaturated fatty acids.
In what cases are employees provided with free therapeutic and preventive food?
in production, work, professions or positions specified in the list;
cleaning, maintenance, repair, dismantling or conservation of equipment (preparation for these operations) in production facilities where workers receive therapeutic and preventive nutrition. These employees are provided with therapeutic and preventive nutrition, regardless of whether it is provided in the structural unit of the organization in which they are hired;
performing construction, construction and installation, repair, construction and commissioning work at the production facilities of other organizations, if employees of these production facilities, including those engaged in repair work, receive therapeutic and preventive nutrition.
In organizations whose employees receive therapeutic and prophylactic nutrition, menu layouts are compiled for each day, including products included in the rations of therapeutic and preventive nutrition.
In the diet of therapeutic and preventive nutrition, designed for one dose (day), the following deviations are allowed:
in the consumption of products, but during the working week they must be used in full;
indicators of chemical composition and energy value ± 10 percent of the diet.
Ready-made meals prepared on the basis of a therapeutic nutrition diet and (or) vitamin preparations are issued once before the start of the working day (shift) regardless of its duration in public catering facilities.
It is allowed to provide therapeutic and preventive food at other times, but no later than during the lunch break.
On business trips or during the traveling nature of the work, an employee who has the right to free provision of therapeutic and prophylactic nutrition is paid monetary compensation for its purchase under the conditions stipulated by the collective agreement, agreement, or employment contract.
Conditions for providing healthy meals
Preventative nutrition is provided daily before starting work. The employee receives it in the form of a hot breakfast in the enterprise canteen, buffet or other room specially designed for food consumption. It is due not only to those who work full time, but also to those who work at least half a shift. At the same time, issuing meals for past or future shifts is unacceptable. Sometimes a hot breakfast is replaced by a hot lunch. Those whose work takes place under high pressure conditions are given healthy food after finishing the work.
The daily diet must contain dairy products. However, in some cases, milk is replaced with equivalent products. Replacement is carried out with the consent of the employee himself or the body representing the interests of the work collective. Replacing milk with dietary foods is permitted only with the consent of Rospotrebnadzor.
Milk can only be replaced with an equivalent product. It cannot be replaced with kumiss, ayran, sour cream, condensed milk, butter or curd mass.
If during the course of work a person comes into contact with inorganic compounds of non-ferrous metals (with the exception of Mg, Al, Ca), he should be given daily products containing 2 mg of pectin substances. If work involves constant contact with “harmful” metals and their compounds, milk is replaced with fermented milk products (less often with special dietary products).
Fermented milk products include the following:
- curdled milk (thick sour milk);
- kefir;
- low-fat (up to 3.5%) acidophilus (a product made by fermenting pasteurized cow's milk using acidophilus, kefir grains or lactic acid streptococcus);
- low-fat yogurt (up to 2.5%);
- cottage cheese with fat content up to 9%;
- low-fat cheese (up to 24%).
For those whose work involves antibiotics, milk is replaced with fermented milk products rich in bifidobacteria, or colibacterin, made from milk that has not been subjected to any heat treatment.
An employee receiving dairy products can write a request to replace them with money. The amount in this case must be equivalent to the food products provided. Payment is made at least once a month. At the same time, the amount paid must be indexed annually, because food prices are also rising. Subsequently, payments can be replaced with milk again if desired.
When medical and preventive nutrition is issued, Modern Entrepreneur
Depending on the conditions in which employees work (harmful or particularly hazardous industries), the employer must provide them with free food. The amount of food and its composition is approved by law.
According to Part 1 of Art. 222 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, workers who work in hazardous industries are required to be given special food for hazardous working conditions - milk or other equivalent food products.
The list of harmful production factors, in the presence of which milk or other products should be provided to workers, is given in Appendix No. 3 to Order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of Russia No. 45n dated February 16, 2009.
The list of harmful substances includes almost a thousand items.
Regardless of how long a work shift lasts, the amount of milk that must be given to an employee is half a liter.
If an employee works in hazardous production for less than half of the work shift, the company is not obliged to provide him with food.
Dietary and therapeutic food is provided in canteens or other premises equipped for this purpose. It should also be eaten (drinked) there.
If during the course of work an employee sometimes comes into contact with inorganic compounds of non-ferrous metals (with the exception of compounds of aluminum, calcium and magnesium), then in addition to milk, the enterprise must give him 2 grams of pectin contained in food products (for example, jelly, jam, marmalade, etc. ). These products can be replaced with natural fruit or vegetable juices with pulp in a volume of 0.3 liters.
If an employee constantly works with inorganic compounds of non-ferrous metals, then instead of milk he must be given:
- or fermented milk products;
- or products for dietary nutrition (it can also be therapeutic and preventive nutrition) under hazardous working conditions.
In this case, the enterprise must provide free food to workers as follows: products containing pectin (jelly, marmalade, etc.) before the start of the working day, and sour milk during the working day.
If an employee is involved in the production or processing of antibiotics, then instead of fresh milk the organization should provide fermented milk enriched with probiotics or colibacterin prepared from whole milk.
In some cases, the company may replace the provision of products to employees with monetary compensation. To do this you need:
- a written statement from the employee agreeing to receive compensation instead of receiving products;
- the possibility of replacing products with monetary compensation is provided for in the employment contract.
The implementation of compensation payments is provided for by the procedure approved by Order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of Russia No. 45n dated February 16, 2009. If an employee performs work under particularly harmful working conditions, then in this case it is impossible to replace meals with monetary compensation.
Answers to common questions about food for hazardous working conditions
Question #1: Are there any rules for replacing milk with cash compensation?
Answer: Yes. Compensation amounts are paid at least once a month. In this case, the equivalent cost of milk must be taken into account with the condition that the product contains at least 3.2% fat. The cost assessment should be based on data on the price of milk in retail trade in the region where the organization is located.
Question No. 2: How often should an employer increase the amount of monetary compensation for milk production?
Answer: Compensation payments for milk should be indexed in proportion to and simultaneously with price increases in retail trade.
The exact amount of compensation is approved by entering information into the collective agreement or employment contract with employees. Rate the quality of the article. Your opinion is important to us: