Sheet Contents
With the entry into force of Rostrud Order No. 655 dated November 10, 2017, special GIT checklists for 2020 became mandatory for inspections by the State Labor Inspectorate; they are questionnaires devoted to certain aspects of the organization’s activities.
Currently, 133 GIT tables have been approved to assess the correctness of personnel records management and compliance with the rules and requirements of the Labor Code in terms of occupational health and safety. Initially, 107 sheets were approved, and from 10/05/2018 an additional 26 pieces were put into effect (Rostrud order No. 201 dated 04/11/2018). Both questionnaires devoted to general issues and checklists on labor protection during scheduled inspections by the labor inspectorate have appeared, including sheets that allow you to determine compliance with:
- requirements for the procedure for formalizing financial liability and concluding student agreements;
- guarantees for individual workers (from the sports creative sphere, the coal industry);
- labor safety rules at some manufacturing enterprises and when working in public catering organizations.
Each form contains:
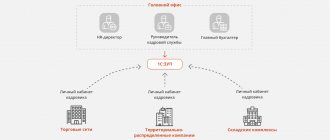
- general information about the employer: name of the legal entity, type and category of risk of activity;
- information about the audit: basis, location and audit credentials.
The list of control questions that the checklist contains when conducting a scheduled inspection of the State Information Inspectorate is presented in the form of a table consisting of three columns:
- question;
- an indication of the normative act that establishes the mandatory requirements being verified;
- answer.
All about the GIT 2020 checklists
This article will be useful for you if you work in any organization.
Whether you are an ordinary worker or the chief director of the entire enterprise. We will talk about labor protection - such an important and rather subtle aspect of the work process. And, of course, which is monitored from time to time by higher inspections.
Consequently, everyone concerned should be familiar with the rules of compliance and all other nuances of labor protection. After all, to be protected means to be confident in yourself and in your environment, and therefore in the future, in the success of your business.
How to figure all this out?
The very phrase “inspection authorities,” and even in combination with “inspection,” usually frighten employers; they begin to get nervous and hastily prepare, which later very often leads to failure.
Below we explain that this is not scary and is more of a plus than a minus.
Yes, from time to time inspection bodies conduct audits of employers for their compliance with labor safety standards using checklists.
In order, so to speak, to be “fully armed” before the inspecting authorities, it is worth familiarizing yourself with the basic concepts of labor protection. The official portal of Rostrud (https://www.rostrud.ru/) can help with this.
The site is free and open 24 hours a day.
By answering the control questions of the checklists there, you can understand whether your organization has any violations in the field of labor law and find out advice on eliminating each of them separately.
Do not worry. When checking independently, there are no negative consequences in the form of sanctions. Consider this so-called training. Checklists can apply punishment during inspections directly by the inspecting authorities.
But there is a nuance - having successfully passed the “test” you should not be 100% confident in the future successful completion of the real test. The specifics of the work of the inspecting authorities include an inspection of the entire enterprise, as well as a detailed study of documents. Well, it can be compared to studying the symptoms of a disease on the Internet and actually going to a specialist doctor.
Therefore, in order to improve their work, employers are recommended to hire professionals specializing in occupational safety issues into their organization.
Statistics show that visits by inspection authorities occur at varying frequencies. Inspections can be carried out either once every two years or once every six years.
On the above-mentioned website you can also find out how often your organization will be checked. Obtaining such information is important so that you will know when and which supervisory authorities will conduct an audit. You will be able to competently resolve personnel issues.
GIT checklists (from the English “checklists”) are a table of 3 columns with questions with the help of which audits are carried out for compliance with the rules of the Labor Code.
In addition to the questions, the table also contains answer options (“no”, “yes” or “not relevant”) and legislative documents establishing the standards being verified.
When, how much and why?
Last year, GIT checklists became one of the main innovations in state regulatory inspections of labor inspectorates.
Since the law on occupational safety checklists was enacted, they have been improved and new ones developed. And this year, 2019, 133 of them are already used in regulatory audits.
There are 3 types of current checklists: checklists on personnel issues, on wages and labor safety issues.
These sheets can check aspects such as:
– the correctness of the process of hiring employees on a permanent basis;
– compliance with generally accepted rules for establishing work hours and recording working hours;
– compliance with generally accepted rules for setting and issuing wages;
– compliance with standards for regulating the labor of children, foreigners, etc.;
– compliance with labor safety rules when working in chemicals. laboratories and many others.
Here is an example of a number of some leading questions from checklist No. 8 “On checking compliance with the requirements for regulating the labor of minors”:
1. Availability, on behalf of an employee who is not yet 14 full years of age, of an employment agreement signed by parents (guardians).
2. Availability of written permission of one of the parents (guardian) and written consent (permission) of the guardianship and trusteeship authority to conclude an employment contract with persons who are not yet 15 full years old.
3. Labor agreements have been concluded with persons who are not yet 16 years old to perform light work that does not harm their health.
4. Compliance by the employer with the ban on signing employment contracts with foreign citizens and stateless persons who are not yet fully 18 years old.
5. Compliance with the terms of the employment contract concluded with a person under 14 years of age with the permission of the guardianship and trusteeship authority.
Are you violating?
If non-compliance with any labor safety rules is detected, you will face a penalty. The consequence of repeated non-compliance with the law may be the forced interruption of the organization’s activities.
How to “stay with clean hands”
If the issue of labor protection has been neglected by you, then the labor safety checklists
Unfortunately, in this area, violations of standards by employers are very common. This happens either unintentionally, or because some entrepreneurs do not have the funds to pay for the costs of hiring specialists in the field of labor protection and believe that they can handle it themselves.
And if you are ready to hire a labor protection engineer, it is difficult to find one, because today this profession is not in demand among Russians, because its wages are insufficient.
There is also a risk of hiring a negligent specialist who will only cause harm.
Summarize
Compliance with the rules regarding labor protection is a complex process for the employer. But it is a very important aspect in the activities of organizations, since it guarantees the safety of workers and ensures the successful process of all activities.
The current GIT 2019 checklists can be viewed for free at any time of the day or night on the official portal of the Federal Service for Labor and Employment. The results of the answers to the questions on the checklists will help you better understand the field of labor protection and successfully manage employees.
In general, the innovation simplifies the entire audit procedure. It is a structured list of all necessary labor protection standards.
How to avoid fines?
In order to avoid fines, you can independently check your company for compliance with labor laws or order an occupational safety audit from our company.
Just call 8 (499) 179-66-45 and our specialists will advise you on any controversial issues. We also regularly conduct training seminars on new labor safety requirements.
Source: https://www.ukkmosdor.ru/yuridicheskaya-pomoshh/proverochnye-listy-git-2019/
Filling rules
In the table, regarding control questions, in column 4, the inspector notes the employer’s compliance with the legal requirements, which are specified in the details of the regulatory act establishing the employer’s obligation.
If the legal requirement is met, the appropriate mark is placed in column 4. If a violation is detected, column 4 is not filled in, and the corresponding value is entered in column 5.
The “Does not apply” column, which Rostrud checklists contain, is filled out in special cases - only if the item is not related to the employer. For example, checklist No. 1 contains a list of questions regarding the conclusion of employment contracts with athletes (since athletes are subject to separate labor law standards and a separate procedure for carrying out mandatory labor protection measures). Accordingly, if a company is being evaluated that does not have athletes on staff, then “Not applicable” is indicated in column 6.
What list of checklists is accepted by the State Transport Inspectorate?
Questionnaires are published in accordance with specific topics. The total number of GIT checklists is 107. Here are some of them, as an example:
- issues of termination of an employment contract (sheet No. 4);
- salary issues (sheet No. 7);
- issues of conducting a special assessment of working conditions (SOUT) (sheet No. 21);
- training on occupational safety issues (sheet No. 28).
The full list of questions can be found by studying Order No. 655, and all documents can be downloaded from the link at the end of the article.
Test questions look like a table divided into several columns:
- the first of them contains item numbers;
- the second reflects the content of specific requirements;
- in the third - regulations governing the relevant obligation;
- in the fourth - answers to the question posed (yes, no, does not apply).
Let's give an example. The questionnaire, which is contained in Appendix No. 5 to Order No. 655, is intended to make it possible to check whether the working hours and recording of working hours are observed in the audited company or individual entrepreneur. An example question looks like this:
| № | Questions | Legal entity details | Answers on questions | ||
| Yes | No | Not applicable | |||
| 1 | Are working hours established? | Part 1 art. 100 Labor Code of the Russian Federation | |||
To be prepared for the test, you need to study the content of specific questions in advance and answer them. If everything is complied with, then there will be no grounds for prosecution.
Self check
All approved GIT checklists for 2020 are publicly available on the Rostrud website.
The employer has the right to use these documents both for preliminary independent preparation for a meeting with the State Labor Inspectorate, and for assessing the correctness of the current conduct of personnel records.
Each sheet is devoted to a separate procedure or block of personnel registration and labor protection. With their help, it is assessed whether the job registration is carried out correctly, whether the employment contract is drawn up correctly, a checklist on labor protection will help determine whether the requirements for labor protection for workers, payment of wages, protection of personal data, etc.
The questions cover all articles of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. The number of questions in each table is different and depends on the specifics of the topic.
The functionality for assessing knowledge and quality of accounting online is available on the Rostrud website in the “Electronic Inspector” section. Here is a test that will identify weak and strong points.
It is planned that in the future employers will be able to register through the Unified Identification System. If the employer does not commit violations when answering the questions contained in the labor safety checklists for 2020, he will receive a declaration confirming compliance with the requirements of labor legislation. The declaration will be automatically generated based on the results of the online verification.
After confirming the results of the audit, which uses the State Tax Inspectorate checklists when checking personnel officers, the inspectorate will be able to decide on incentive measures for the relevant employer, which will be expressed in the form of a guarantee of protection from scheduled inspections by the supervisory authority and other benefits. It is expected that such employers will be exempt from scheduled on-site inspections.
There are no penalties for detected online violations - prepare and take the test again.
How to act at the beginning of an inspection and when the inspector can not be allowed in
When an inspector appears on your company's premises, first find out his credentials. But remember that on the employer’s part, not any employee can be present during the inspection, but only those who have been specifically assigned this task.
| The inspector draws up a list of documents that he will request, based on the specifics of the organization and the subject of the inspection The State Tax Inspectorate will notify the employer of the scheduled on-site inspection no later than three working days in advance. The inspectorate will send a copy of the order or inspection order to the company. The document indicates the numbers of the checklists that the inspector will use. Now the inspector selects checklists independently. In the near future, the list of sheets will be generated automatically by the information system based on the type of activity, the size of the organization and other factors. The law does not require the State Tax Inspectorate to develop a list of documents subject to verification using checklists. The order to conduct an inspection in each case includes a different list of documents that are needed to achieve the goals of the inspection. At the same time, Rostrud has developed an approximate list of documents by which the inspector must check whether the employer complies with one or another mandatory requirement from the checklist. A selection of such documents can be viewed on the Rostrud resource “Electronic Inspector” during self-test. |
What should the inspector show to the personnel officer? At the beginning of the on-site inspection, the inspector shows an order or instruction about it and an official identification document (Part 4 of Article 12 of Federal Law No. 294-FZ of December 26, 2008, hereinafter referred to as Law No. 294-FZ). Receive a copy of the order or its second copy against signature and study it (sample below). This way you can challenge the inspection or cancel its results if the order was drawn up with violations. The inspection must be carried out by the controller indicated in the order. Therefore, check the inspector’s full name in this document and his service ID. If there are several inspectors, make sure that all of them are included in the order.
Now the order for a scheduled inspection specifies the details of the checklists by which it will be carried out. There are 107 in total, but the State Tax Inspectorate usually uses sheets numbered 1 to 37 and sheet No. 100. The inspector has no right to ask questions that are not on the checklist. The checklist form provides three possible answers to the questions: “yes”, “no” or “not applicable”. When there are no complaints against the employer on a specific point, the inspector puts Fr. If the company does not comply with one or another requirement, the inspector will mark it and make the necessary explanations in the inspection report. If the item on the checklist does not affect the employer, the inspector will indicate o.
The head of the GIT or his deputy has the right to sign an inspection order. If the document is unsigned or it was signed by an unauthorized person, you have the right not to allow the inspector into the company and write a complaint to the State Tax Inspectorate about his actions or cancel the results of the inspection later in court (Part 1 of Article 20 of Law No. 294-FZ).
At the same time, there are cases when employers needlessly refuse an inspector to check. For example, they don’t let him in, citing the fact that the director is absent and has not left a power of attorney for anyone. Another futile argument: the order did not indicate the actual address, but only the legal one. In these cases, the inspector will draw up a report stating that the inspection cannot be carried out. In the future, he can re-check the company within three months. At the same time, the new check will not be included in the annual plan and the employer will not be notified about it in advance (Part 7, Article 12 of Law No. 294-FZ).
How can a personnel officer confirm his authority? The director can represent the interests of the organization during an inspection without a power of attorney (Part 6 of Article 11, Part 5 of Article 12, Part 3 of Article 14 of Law No. 294-FZ). A power of attorney is issued for another employee, for example a personnel officer (sample below). Mandatory details of the power of attorney - date of issue, information about the principal and representative, powers of the representative and signature of the principal (clause 1 of article 185, clause 4 of article 185.1, paragraph 2 of clause 1 of article 186 of the Civil Code). For representation in the courts, the power of attorney must be certified with the company’s seal, unless the charter indicates that the company has renounced the seals (Parts 2, 3, Article 53 of the Code of Civil Procedure).
GIT inspections in 2020
We remind you that since 2020, a system of risk-based approach has been introduced during inspections of government bodies and their frequency has been established depending on the category:
- high risk category - once every 2 years;
- significant risk category - once every 3 years;
- medium risk category - no more than once every 5 years;
- moderate risk category - no more than once every 6 years;
- the low risk category is not subject to verification.