Account 55 “Special accounts in banks” is used by legal entities to collect information about transactions in Russian rubles and foreign currency carried out through settlements with counterparties using letters of credit, check books and other means of monetary circulation (with the exception of settlements with bills of exchange).
Account 55 in accounting - collection of information on transactions on current and special accounts of the organization, carried out using letters of credit, check books and special payment documents. Data on settlements in Russian rubles and foreign currencies is displayed here. In addition, account 55 can take into account the receipt and expenditure of targeted financing funds, displayed separately in accounting.
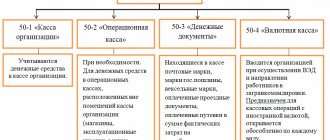
Account 55 is active, the following subaccounts are opened for it:
- 55.01 – payments through letters of credit.
Something to keep in mind! A letter of credit is an obligation of the bank to transfer funds to their recipient (beneficiary) upon fulfillment of the conditions and provision of pre-agreed documentation.The receipt of money for the bank guarantee is displayed by Dt55 in correspondence with the corresponding accounts 51, 52, 67, etc. Funds are written off according to bank statements; as they are transferred, the amounts are displayed according to Kt55. The credit institution returns unused amounts to the accounts from which they were accepted for the letter of credit. Analytical analysis is carried out separately for each opened obligation.
- 55.02 – payments by checkbooks. Debit 55 takes into account the deposit of funds when opening a checkbook in correspondence with accounts 51, 52, etc., and credit – repayment by the bank of the amounts presented for payment of checks. Deposited money that is not issued for repayment remains registered in Dt55.02. Unused amounts are returned to the company (Kt55.02).
Attention! The balance according to 55.02 must fully correspond to the bank statements.Analytical analysis is carried out for each issued checkbook separately.
- 55.03 – accounting for a legal entity’s investments in bank and other deposits. The opening of a deposit is displayed according to Dt55.03 (Kt51.52). The closing of deposits and the return of money to the company is recorded by a reverse business transaction. Analytical monitoring - each deposit separately.
- The amounts of targeted financing received by the enterprise from banks are displayed separately: budget transfers, financing of capital investments, the accounting of which is carried out separately, etc.
- Additionally, sub-accounts are opened to record the receipts and expenditures of money aimed at meeting the current needs of the branches and representative offices of the enterprise.
Something to keep in mind! All mutual settlements expressed in foreign currency must be accounted for separately.
Necessity and significance of position 55
This position is intended to provide synthesis of information on the availability and movement of financial resources on the territory of the Russian Federation and abroad, both in the currency of the Russian Federation and in banknotes of other states, with a letter of credit form of payment, the use of check books and other payment documents on current and other special accounts .
Analytics is carried out using separate sub-accounts opened for accounting:
- check books;
- foreign exchange transactions;
- settlements under letters of credit;
- deposits;
- other payments with the exception of bills of exchange.
The marked position is active. Its debit side reflects the funds accepted for accounting, and the credit side reflects their write-off.
In general, we can say that in accounting 55 position is used to reflect those transactions on bank accounts that differ in nature from settlement services, as well as transit, credit and loan accounts. In addition, it can also be used to account for company funds on electronic wallets.
Typical accounting entries
In practice, the following standard entries are used to reflect transactions on separate accounts:
1) Dt 55
Kt 50 – crediting cash to a special account at a credit institution;
2) Dt 55
Kt 51 – transfer of resources from current accounts to special accounts based on statements;
3) Dt 55
Kt 52 – placement of purchased foreign banknotes on deposit;
4) Dt 55
Kt 60 – return of funds to suppliers to special accounts;
5) Dt 55
Kt 62 – receipt of funds to the bank in a special account as part of the repayment of receivables;
6) Dt 52
Kt 55 – crediting funds from a special account to a foreign currency deposit;
7) Dt 60
Kt 55 – repayment of obligations to suppliers from a special account, etc.
Account 55: special bank accounts. Example, wiring
The balance according to 55.02 must fully correspond to the bank statements.
Analytical analysis is carried out for each issued checkbook separately.
Something to keep in mind! All mutual settlements expressed in foreign currency must be accounted for separately.
Accounting records from check books
To begin with, it should be noted that a checkbook is a document of strict accountability and is issued exclusively by the bank. This document must be filled out carefully, eliminating corrections and errors.
The check consists of a tear-off part and a spine. After filling it out, the spine remains in the book, and the tear-off part is transferred to the bank to receive funds.
The movement of financial resources when performing transactions using checkbooks is reflected in subaccount 55.2. Thus, when a checkbook is issued, a certain amount of funds is deposited, which is reflected in the following entry:
1) Dt 55.2
Kt 51, 52, 66.
Check book funds are debited from the account as checks issued by the organization are cleared by the bank, which is reflected in the following transaction:
1) Dt 76
Kt 55.2
If the checks were returned to the credit institution, the amounts for them are reflected in the following entry:
1) Dt 51 or 52
Kt 55.2.
Subaccount 55.1 takes into account the movement of funds in letters of credit.
Topic 7. CASH ACCOUNTING
Accounting for transactions on foreign currency accounts
Accounting for transactions on special accounts
Accounting for transfers in transit
Accounting for transactions on foreign currency accounts
The implementation of a unified state currency policy is ensured by the Federal Law of December 10, 2003 No. 173-FZ “On Currency Regulation and Currency Control.”
Residents can have accounts in foreign currency with an authorized bank, both in the Russian Federation and abroad. The number of foreign currency accounts to be opened is not limited. Typically, banks open accounts for certain types of foreign currencies.
Based on the bank account agreement, the authorized bank opens 2 currency accounts for the organization simultaneously: current
and
transit.
To summarize information about the availability and movement of funds in foreign currencies in foreign currency accounts in banks in the country and abroad, account 52 “Currency accounts” is used.
Sub-accounts can be opened for account 52 “Currency accounts”:
52.1.
– “Currency accounts within the country”:
52.1.1.
– “Transit currency accounts”;
52.1.2.
“Current foreign currency accounts”;
52.2.
— “Currency accounts abroad.”
Transit currency account
used to identify the receipt of foreign currency in favor of residents and for the purpose of accounting for foreign exchange transactions.
All foreign currency receipts in favor of the resident are credited to the transit currency account in full. The exception is 3 types of income, which are credited immediately to the current currency account:
1) funds received from 1 current currency account of a resident opened with an authorized bank to another transit currency account opened with the same bank - Dt 52.1.2 Kt 52.1. 2
;
2) funds received from the authorized bank in which the resident’s current foreign currency account is opened, under agreements concluded between the bank and the resident;
3) funds coming from the current foreign currency account of a resident to the current foreign currency account of another resident opened in one authorized bank.
The list of transactions for writing off funds from a transit currency account is closed:
1) write-off to a separate personal account - funds in foreign currency for mandatory sale on the domestic foreign exchange market - Dt57Kt52.1.1.
;
2) to the accounts of other persons to pay expenses and payments related to the execution of export transactions - Dt 60, 76 Kt 52.1.1.
;
3) for crediting to a resident’s current currency account opened in this authorized bank or to a current currency account opened in another authorized bank receipts in foreign currency that is not subject to mandatory sale; part of the foreign exchange earnings remaining after the mandatory sale - Dt 52.1.2 Kt 52.1.1
;
4) to return funds erroneously received in favor of a resident - Dt 62 Kt 52.1.1.
Current currency account
is opened to organizations to account for the funds remaining at the organization’s disposal after the mandatory sale of export proceeds and other transactions on the account in accordance with foreign exchange legislation.
Receipts to the current foreign currency account:
1) crediting currency from a transit foreign exchange account, which is not subject to mandatory sale, remained after the mandatory sale of export foreign currency proceeds, received from the sale of foreign currency bills of the same bank: Dt 52.1.2 Kt 52.1.1
;
2) crediting foreign currency purchased for rubles on the domestic foreign exchange market: Dt 52.1.2 Kt 57
;
3) crediting foreign currency not used to pay expenses for foreign business trips, as well as received from the sale of traveler’s checks - Dt 52.1.2 Kt 50
.
Debiting from a current foreign currency account:
1) transfer of funds to a foreign currency account abroad: Dt52.2 Kt 52.1.2
;
2) to pay obligatory payments in foreign currency: Dt60.76Kt52.1.2
(suppliers, transport organization, consulting, insurance);
3) repayment of loans and interest on them received in foreign currency: Dt 66.67 Kt 52.1.2
;
4) for payment for imported goods, works, services - Dt 60 Kt 52.1.2.
5) withdrawal of cash to pay for travel expenses of employees - Dt 50 Kt 52.1.2.
;
6) voluntary sale of foreign currency - Dt 57 Kt 52.1.2.
Accounting for funds in other bank accounts
Cash used separately for its intended purpose is accounted for in special bank accounts.
Investments of funds for specific purposes include
letters of credit
,
check books
,
deposit accounts
and other accounts.
Account 55 “Special accounts in banks”
is intended to summarize information about the availability and movement of funds held in letters of credit, check books, bank accounts, cards, current and deposit accounts, as well as in targeted financing accounts.
Sub-accounts can be opened for account 55 “Special accounts in banks”:
55.1. — “Letters of credit”
;
55.2. - "Checkbooks"
;
55.3. — “Deposit accounts”
.
Subaccount 55.1 takes into account the movement of funds in letters of credit.
Letter of Credit
is a conditional monetary obligation accepted by the bank (issuing bank) on behalf of the payer, to make payments in favor of the recipient of funds upon presentation by the latter of documents that comply with the terms of the letter of credit, or to authorize another bank (executing bank) to make such payments.
The payer submits an application for opening a letter of credit
, which, in the prescribed form, contains the number and date of the letter of credit, the amount of the letter of credit, the payer's details, the details of the issuing bank, the details of the recipient of funds, the details of the executing bank, the type of letter of credit, the validity period of the letter of credit, the method of execution of the letter of credit, the list of documents submitted by the recipient of funds, and requirements for submitted documents, purpose of payment, deadline for submitting documents, need for confirmation (if any), procedure for paying bank commissions.
Letters of credit can be:
1) covered (deposited) and uncovered (guaranteed);
2) revocable and irrevocable.
Covered (escrowed) letters of credit
– letters of credit, upon opening of which the issuing bank, at the expense of the payer, transfers the amount of the letter of credit (coverage) from the current account to the ordering bank of the supplier for the period of validity of the letter of credit.
Uncovered (guaranteed) letter of credit
– a letter of credit, upon opening of which the issuing bank grants the executing bank the right to write off funds from the correspondent account maintained by it within the amount of the letter of credit. Uncovered (guaranteed) letters of credit are opened only if there is a correspondent relationship between the payer's bank and the supplier's bank.
Revocable letter of credit
– a letter of credit that can be changed or canceled without the prior consent of the supplier. If the terms of the contract are not met or the payer's bank cannot guarantee payment under an uncovered letter of credit, the payer usually requests that the letter of credit be cancelled. The payer gives such an order through his bank, which notifies the supplier’s bank about this, and it notifies the supplier organization.
Irrevocable letter of credit
cannot be canceled or changed without the consent of the supplier in whose favor it was opened. If there is no clear indication, the letter of credit is considered revocable.
Closing of a letter of credit is possible in the following cases:
1) upon expiration of the letter of credit;
2) according to the supplier’s statement of refusal to use the letter of credit before its expiration;
3) according to the buyer’s statement about refusal of the letter of credit in whole or in part;
4) in case of incomplete use of the letter of credit, i.e. the amount of the supplier’s invoices turned out to be less than the deposited amount in account 55.1.
In these cases, the supplier's bank sends a notification to the buyer's bank, and the unused amount is credited to the account from which funds were deposited to open the letter of credit.
Covered letter of credit
The write-off of funds for opening a covered letter of credit is documented by accounting entries:
Dt 55.1 Kt 51
— issuing a letter of credit at the expense of one’s own funds from the current account;
Dt 55.1 Kt 52
— issuing a letter of credit at the expense of one’s own funds from a foreign currency account;
Dt 55.1 Kt 66
— issuing letters of credit using short-term loans.
The basis for such accounts are extracts of special bank accounts with documents attached to them.
Payments by letters of credit are carried out in the following order:
The supplier ships the products to the buyer only after receiving notice of the opening of a letter of credit and submits to the executing bank four copies of the register of accounts, shipping and other documents confirming the fact of shipment of the products to the buyer. The executing bank verifies the submitted documents and credits the amount of the letter of credit to the account of the recipient of funds. At the same time, the executing bank sends a notification to the issuing bank about the use of the letter of credit with attached documents confirming the fact of the transaction under the agreement. The issuing bank informs the buyer about the use of the letter of credit and provides him with documents confirming the shipment of goods.
The use of the letter of credit amount is reflected by the entry:
Dt 60, 76 Kt 55.1.
— payment of supplier bills from a letter of credit account.
Unused funds in letters of credit are restored by the bank to the account from which they were transferred, which is reflected in the accounting records:
Dt 51 Kt 55.1.
— unused amounts of the letter of credit are deposited into the current account;
Dt 52 Kt 55.1.
— unused amounts of the letter of credit are deposited into a foreign currency account;
Dt 66 Kt 55.1.
— unused amounts of the letter of credit are written off to repay the bank loan.
Analytical accounting
according to the score 55.1. is maintained for each letter of credit issued by the organization, the amounts of their use, opening and closing dates.
Uncovered letter of credit
The amount for which an uncovered letter of credit was opened in the account 55.1. not reflected. Off-balance sheet account 009 “Securities for obligations and payments issued” is intended for its accounting.
When opening an uncovered letter of credit, an entry is made to the debit of off-balance sheet account 009:
Dt 009
— an uncovered letter of credit has been opened.
The use of an uncovered letter of credit is reflected by the entries:
Kt 009
— the funds of the letter of credit have been spent;
Dt 60, 76 Kt 51, 52
— settlements with the supplier have been made.
The score is 55.2. "Checkbooks"
, the movement of funds in check books is taken into account. The procedure for making settlements by checks is regulated by the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, as well as the rules of settlements between organizations established by banks.
Check
- this is a security that represents an unconditional order from the drawer to the bank to pay the amount specified in it to the check holder.
To receive payment on a check, you must present it to the bank servicing the check holder.
The issuance of check books by a bank at the expense of the organization’s own funds or short-term loans is reflected in accounting entries:
Dt 55.2. Kt 51
— issuing a checkbook using your own funds from your current account;
Dt 55.2. Kt 52
— issuing a checkbook at the expense of one’s own funds from a foreign currency account;
Dt 55.2. Kt 66
— issuing a checkbook through short-term loans.
Checks used for payment to the bank when purchasing material assets are reflected by the entry:
Dt 60, 76 Kt 55.2.
- the checks used for the purchase of material assets are presented to the bank for payment.
Amounts of unused checks and those returned to the credit institution by recording:
Dt 51 Kt 55.2.
— unused check amounts are deposited into the current account;
Dt 52 Kt 55.2.
— unused check amounts are deposited into a foreign currency account;
Dt 66 Kt 55.2.
— unused check amounts are written off to repay the bank loan.
Amounts for checks issued but not presented for payment remain in account 55.2, which must correspond to the balance on the bank statement of this account.
Analytical accounting
This sub-account is maintained for each checkbook received.
Checks are strict reporting forms (SSR)
and are accounted for in off-balance sheet account
006 “Strict reporting forms”
. Checks are written off from account 006 as they are used.
Dt 006
— checks received from the bank have been capitalized.
Kt 006
— used checks are written off.
Kt 006
— checks returned to the bank are written off.
Investments of the organization's free funds in bank deposits are reflected in account 55.3. "Deposit accounts".
When opening deposit accounts, depending on the terms of reimbursement and conditions for withdrawing money, a distinction is made between
demand deposits
and
time deposits.
For demand deposits, their minimum size and the amount of non-withdrawable balance are not established. For these deposits, the organization has the right to close the deposit account upon request.
The organization's contribution of funds under a term deposit
carried out for the period established by the contract. In the case of long-term withdrawal of funds from the deposit account, the organization loses the percentage of income established by the agreement; Credit institutions charge interest on this deposit as provided for demand deposits.
The organization reflects the transfer of funds on the basis of the deposit agreement and statements from current and other bank accounts:
Dt 55.3. Kt 51
— opening a deposit using your own funds from a current account;
Dt 55.3. Kt 52
— opening a deposit using your own funds from a foreign currency account.
When reflecting the amount of accrued interest on deposits in deposit accounts, the following entry is made:
Dt 55.3. Kt 91.1.
— interest accrued on deposits in deposit accounts.
When a credit institution returns deposits, the following entries are made:
Dt 51 Kt 55.3.
— the deposit was returned to the current account;
Dt 52 Kt 55.3.
— the deposit was returned to the foreign currency account.
Analytical accounting
is maintained for each deposit in accordance with the agreement with the bank, indicating the terms of the deposit and their return.
On separate sub-accounts to account 55, the movement of target financing funds separately stored in the bank can be taken into account; funds received for the maintenance of special institutions from parents and other sources; funds to finance capital investments accumulated and spent by the organization from a separate account.
Accounting for transfers in transit
Transfers on the way
- these are funds deposited at the cash desks of credit institutions, collectors, savings banks or postal mailboxes for the purpose of being credited to the current accounts of organizations, but not yet received for their intended purpose.
During the period of transfer of funds to collectors or directly to credit institutions, savings banks or post offices, the deposited funds are accounted for in the active synthetic account 57 “Transfers in transit”
. The basis for accepting funds for accounting under account 57 is a receipt from a credit institution, savings bank or post office, copies of accompanying statements for the delivery of proceeds to collectors or other similar documents.
By debit
Account 57 reflects funds deposited in banks or post offices for crediting to the organization's current account, and
for a loan
- their receipt to the current account.
Dt 57 Kt 50
– cash deposited with credit institutions, savings banks or post offices.
Then, based on the bank statement (usually on the next banking day), it is necessary to reflect the transfer of money to the organization’s current account:
Dt 51, 52 Kt 57
— the receipt of money into a current or foreign currency account is taken into account.
Recommended pages:
Use the site search:
Making payments by debit card
Let’s imagine that a debit card was issued for the director of an enterprise for making payments during business trips, and therefore funds in the amount of 42,700 rubles were transferred to a special bank account.
During the next business trip, a payment for hotel accommodation was made using the designated card for a total amount of 12,700 rubles.
After the head of the enterprise returned from a business trip and provided a report, the accounting service made the following entries:
1) Dt 55
Kt 51 – 42,700 rubles, transfer of funds to the corporate account of the enterprise;
2) Dt 71
Kt 55 – 12,700 rubles, accounting for advance funds issued;
3) Dt 26
Kt 71 – 12,700 rubles, covering living expenses at the expense of travel allowances.
Credit card payments
Example
In April 2020, an agreement was concluded between Delovoy Profile LLC and Vympel Bank to issue a credit card. According to the bank agreement, a loan of 200,000 rubles was issued, the repayment period is 18 months, the interest rate is 16% per annum. Interest is calculated once a month on the amount actually spent.
In July, an employee of Delovoy Profile LLC was sent on a business trip with an advance payment of 5,000 rubles. Travel and travel expenses were paid by credit card.
Postings
At Delovoy Profile LLC:
| Dt | CT | Operation description | Sum | Document |
| 55 | 66 | Receipt of loan amount (withdrawn amount) | 5000 | Bank statement |
| 71 | 55 | Advance issued to accountable person | 5000 | Statement |
| 71 | Travel expenses included | 5000 | Advance report | |
| 91.2 | 66 | Interest for use written off as expenses (5000*16% /12) | 67 | Agreement with the bank |
| 66 | Payment of interest for using a credit card is reflected | 67 | Bank statement |
Transactions on deposit accounts
Let’s assume that a certain company placed a deposit in one of the banks in April 2020 under the following conditions:
- placement period – 9 months;
- deposit amount – 137,000 rubles;
- interest on deposit – 21% per annum.
The company's accountant made the following entries:
1) Dt 55.3
Kt 51 – 137,000 rubles, transfer of funds to a bank deposit;
2) Dt 76
Kt 91.1 – 21,578 rubles, interest income on deposit;
3) Dt 51
Kt 76 – 21,578 rubles, crediting accrued interest to the company’s account.
Transactions with a covered letter of credit
Example
LLC "Galfind" and LLC "Demiurge" entered into an agreement for the supply of materials in the amount of 1,200,000 rubles. The terms of the contract assume that payment for the delivery of LLC Galfind is made using a covered letter of credit. For this purpose, Demiurge LLC opens a letter of credit in the bank in the amount of 1,200,000 rubles.
The delivery was carried out only in the amount of 1,000,000 rubles. The remaining funds were returned to the settlement account of Demiurge LLC.
For servicing the letter of credit, the bank charged a commission of 0.% of the letter of credit amount.
Postings
At Demiurge LLC:
| Dt | CT | Operation description | Sum | Document |
| 55.1 | The amount of funds for the covered letter of credit is reflected | 1200000 | Bank statement | |
| 10 | 60 | Materials accepted for accounting | 1000000 | TORG-12 |
| 60 | 55.1 | Funds transferred to pay for equipment | 1000000 | Payment order |
| The amount of bank commission is included in costs (1200000*0.05%) | 600 | Bank statement | ||
| 55.1 | The unused balance of the letter of credit was returned to the account | 200000 | Bank statement |