In Ozhegov's dictionary
TURN, -a, m. I. see wrap, -sya, turn, turn, turn, -sya. 2. Consumption, use. Let into o. commemorative coin. Entered about. new word. 3. A separate part, a separate link, some stage. activities, development of something. (specialist.). O. field crops. O. herd (change in its structure and number over a certain period). 4. A completed cycle of operations performed by means of transportation (for example, moving somewhere with a return to the starting point) (special). O. carriages. 5. Circulation of funds and goods for reproduction and profit. O. capital (its continuously renewed circulation). Annual o. enterprises. Trading o. 6. One circle of circulation around something; turn (in 3 digits). To gain momentum (also translated: about some kind of business, event: to speed up, speed up). 7. Reverse side (of a sheet, page, some kind of image). Inscription on the back of the sheet. Abstract on the back of the title. 8. Bending (one turn) of a spiral, pipe (special). There are four turns in the pipe. 9. transfer A change in the flow or development of something. The case takes an unwanted o. 10. Verbal expression. Wrong o. speech. Participial o. * Take someone into circulation (colloquial) - to exert a decisive influence on someone, to force them to act, to work. || adj. reverse, -th, -oe (to 3, 4, 5, 6, 7 and 8 values). Revolving depot. Recycling of water. Working capital. Reusable packaging. The other side of the coin (also translated: the other, usually negative side of something). * ""E"" is the reverse - the name of the letter ""e"".
https://youtu.be/ElPJTWAv_ZM
Sales tax
Sales tax
Form of mobilization of revenues to the state budget. Under capitalism, N. with o. is the main form of indirect taxation, acts as a surcharge on the price of a product: in the UK, France and Germany it is a value added tax, in the USA it is a sales tax.
In the USSR and other socialist countries, N. with the island. - part of the cash savings (net income) of socialist enterprises (associations), directly converted into state income. Through N. with about. the state mobilizes significant financial resources for the purposes of expanded socialist reproduction and satisfaction of other national needs. N. with o. It is also used as an important economic tool for regulating the profitability of products in the interests of strengthening cost accounting and the main source of balancing republican and local budgets. In terms of its economic content, N. s. is not a tax, because it does not serve as a premium to the price of goods and does not represent a deduction from the wages of workers and employees and other income of workers. It has only external signs of tax payment (obligatory payment, fixed amount, payment on time).
Distinguishing the cash accumulations of enterprises into profit and non-income from the o. and the principles of their collection into the budget were established by the tax reform of 1930. N. with o. are paid by self-supporting state and cooperative (except for collective farms) enterprises and organizations, as well as enterprises of public organizations. The main part of N. with the island. It is sold in the light and food industries. A high share of N.'s income from the island. in these industries is due to the fact that, along with the value of the surplus product created here, part of the value of the surplus product produced in other branches of material production: heavy industry, construction and agriculture is thus realized. For many consumer goods N. with about. not paid (baked bread and bakery products, meat and meat products, sausages, cheeses, milk, lactic acid products, butter, canned food, vegetables, fruits, medicines, book products and many other goods). In heavy industry N. with about. levied in the oil and gas industries, in the electric power industry and for certain types of mechanical engineering products.
N. with o. charged: in the form of the difference between retail and wholesale prices of the enterprise minus trade discounts; at fixed rates (in rubles) per unit of production volume (from 1 ton of petroleum products, bakery products and fermented tobacco, from 1 thousand m3 of natural and associated gas, etc.); as a percentage of turnover (for all goods for which enterprise wholesale prices have not been established). N.'s receipts from the island. in the form of differences in prices, they occupy the main place, their share increased from 74% in 1964 to 80% in 1972, and the share of taxes charged at rates as a percentage of revenue decreased during this period from 12 to 5.8 %.
N. with o. plays an important role in providing the state budget with stable, evenly received payments. The absolute size of its receipts in the state budget systematically increases: in 1960 - 31.3 billion rubles, in 1965 - 38.7 billion rubles, in 1972 - 55.6 billion rubles, although its share in the total amount of money enterprise savings and state budget revenues fall respectively (in%): 48.0, 46.5, 37.8 and 40.7, 37.8, 31.7. Decrease in the specific gravity of N. from the island. due to the increasing role of profit as the main form of cash savings and the main source of generating state budget revenues.
In order to stimulate the growth of production of consumer goods, expand their range and improve quality, manufacturing enterprises are provided with benefits; some of these enterprises are completely exempt from taxes. for goods sold.
V. V. Dementsev.
Source: Great Soviet Encyclopedia on Gufo.me
Meanings in other dictionaries
- TURNOVER TAX - A tax levied as a share, a percentage of the cost (price) of domestically produced and sometimes imported goods, withdrawn to the state budget as these goods are traded. Economic dictionary of terms
- turnover tax - A tax established under the conditions of state regulation of prices for certain highly profitable products. The tax rate is set either as a percentage of the wholesale price, or as a markup (discount) on the price in monetary terms. Great Accounting Dictionary
- Blog
- Jerzy Lec
- Contacts
- Terms of use
© 2005—2020 Gufo.me
In the dictionary D.N. Ushakova
TURNOVER, turnover, man. 1. Full circle of rotation, circular turn. Wheel revolution. The shaft makes 20 revolutions per minute. | moving back and forth, returning to the original place. Speed up the turnover of wagons. 2. A separate stage, a completed process in a sequential change, movement of such stages, processes (economics). Turnover of field crops. Arable land turnover. Forestry turnover plan. Turnover of capital (the movement of capital from its original monetary form through circulation and production back to this form). Turnover of amounts. 3. Circulation of funds and goods, commercial and industrial operations for the purpose of reproduction and profit. “Freedom of circulation and freedom of trade, this means the exchange of goods between individual small owners.” Lenin. “I’m going to Paris and starting commercial activities.” Pushkin. Put money into circulation. Trade turnover. 4. The amount in these transactions (fin.). Annual turnover. Gross turnover. Calculation of turnover as of January 1. 5. Turning from one side to the other. Formation turnover when plowing virgin soil. 6. The back, reverse side of something, the wrong side. Reverse of the medal. Inscription on the back of the picture. Look on the back (of the page, sheet). 7. ***** bad turn.” Pushkin. “What a strange turn of thoughts you have today.” A. Turgenev. “I’m afraid that my illness will take a bad turn.” Chekhov. 9. Method of verbal expression, phrase. Book turn of phrase. Wrong turn. Participial turnover. (gram.). • Put into circulation (Introduce, involve, etc.) - Put into use. Introduce new materials into scientific circulation. Take someone into circulation ( colloquial · fam.) - to exert a decisive influence on someone, to give someone a severe reprimand, a suggestion for something.
Types of turnover
Company turnover is not an unambiguous term, since it includes many subparagraphs. It can be carried out in one form or another of monetary settlements, calculated for the company as a whole or for a separate area of work. The period for which the data is analyzed also matters. Most often, economists are interested in the company’s annual turnover; a twelve-month distance is considered optimal for assessing the state of things in the business structure.
The types of annual turnover made in cash and non-cash form have a huge impact on modern accounting and reporting in general.
Total turnover in cash
This should include all cash payments, such as financial payments made by companies to their employees. In addition to wages, the form includes the transfer of scholarships, pensions, cash assistance, subsidies, and income from financial systems. Cash payments are widely used for the purchase and sale of goods and services.
How is cash issued? The system provides for the transfer of funds from the organization's current account using checks, the amount and purpose are indicated on them. The total turnover can be calculated even for one day if the funds entering the organization’s cash system are transferred every day to the bank servicing the enterprise. Surely, you have come across situations where organizations leave cash in their cash registers.
Such actions are permitted, but only within the limit established by the bank. This limit is set depending on the turnover and specifics of the company’s work - the question should be answered: how much money must be left in the cash register to ensure uninterrupted functioning, service to clients and users?
Non-cash turnover of a business company
The company's turnover is not only cash, these days, it is rather predominantly non-cash payments. Such transfers go directly from one account to another and have a number of advantages over the cash payments through cash desks described above. Companies do not need to take additional measures to implement the regulatory function of supervisory government bodies; they reduce public costs.
It is known that improving the economic condition of a certain company means accelerating overall turnover, which is achieved mainly through non-cash form. How should non-cash payments be organized? It is important to carry them out in a timely manner, to ensure that the company’s non-cash turnover is under the constant control of responsible persons, and to prevent unauthorized movement of funds.
Increase or decrease row 1210
Every year, every company must submit financial statements, including a balance sheet, which is called Form. The balance is drawn up in accordance with clearly defined instructions, which can be found in PBU 4/99. This document requires the reliability of the information in the report, therefore the “Reserves” item should be collected strictly according to the formula:
Debit 10, 11 – Credit 14 + Debit 15, 16 + Debit 20, 21, 23, 28, 29 + Debit 43 + Debit 41 – Credit 42 + Debit 44, 45 + Debit 97.
Inventories on the balance sheet are a current asset that indicates the company’s financial security. The absence or sharp decrease in indicators in line 1210 of the current assets section, which collects all data on inventories, may indicate a scarcity of resources in the enterprise’s warehouses. On the other hand, there is an option that the process of turning an asset into money occurs so quickly that the company can barely keep up with its marketing service.
Since financial receipts to the company’s accounts depend on the rate of inventory turnover, it is necessary to maintain the proper level of resources by pursuing an effective marketing policy.
Reflection of revenue in the balance sheet: line
VAT is reflected in the income statement; the tax must be shown in assets and liabilities. In assets it is reflected in lines 1220, 1230, in liabilities – 1520.
In line 1220, you can reflect VAT on purchased assets - the amount of the fee that the organization undertakes to accept for deduction in the future. Line 1230 represents accounts receivable. It displays the amount of funds for the fact that buyers underpaid at the time of drawing up the balance, taking into account the fee.
Line 1520 shows the company's accounts payable including VAT. When displaying taxes, accounting entries reflect the fact of sale of goods, work to generate income, entrance fee, and refunded payment.
Collection declarations include a cover page, as well as the amount of the collection to be contributed to the budget or compensation. The document must be drawn up and submitted no later than the 25th day of the month following the end of the quarter.
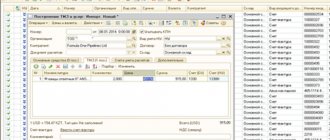
There are some features of recording revenue in accounting in the 1C program. When receiving income from the sale of finished products, you need to create a document. After this, the required fields are entered, products are selected and entered into the table. Information about works and services is entered in the same way.