Calculation rules
The parties entering into contractual legal relations must know how to calculate the penalty under the agreement in the event of failure of one of the parties to fulfill its obligation.
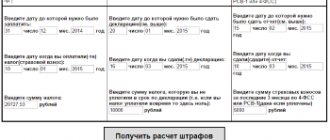
Attention! First you need to know the following indicators that may be needed to calculate penalties:
- the amount of funds from which the penalty should subsequently be calculated (this amount can be either part of the funds contributed by the counterparty or the amount that was not paid);
- the amount of interest, which is established by agreement of the parties, applied in case of violation of obligations;
- the period of time for which the penalty is calculated.
If the above data is available, each party will be able to calculate the fine amounts.
https://youtu.be/iSmIWmQBoa0
When are penalties charged?
Often, when concluding agreements, their participants are subject to additional penalties in case of failure to fulfill their obligations. For example, if a person fails to timely pay interest when using someone else’s money, then such persons may be subject to a fine or penalty.
List of cases of imposing financial liability measures:
- untimely transfer by the developer of the facility for operation;
- untimely delivery of goods;
- violation of tax payment deadlines;
- violation of deadlines for transferring alimony;
- untimely payment of alimony;
- late payment of interest on the loan.
Collection of penalties
The collection of penalties is associated with the fact that a party has violated the terms of the transaction and the presence of losses is not a determining factor. For this reason, the injured party does not need to prove the occurrence of adverse consequences in the form of damage; it is enough to only record the fact of violation of the terms of the agreement. However, in order to avoid problems with the collection of penalties in practice, a legally competent and clear definition of the conditions, amount and procedure for its payment is of great importance. At the same time, it is necessary to avoid ambiguous and vague formulations, which can lead to controversial situations in the event of non-compliance with the terms of the contract.
A penalty can ensure the fulfillment of any condition stipulated by the contract. It is recommended to take into account that the choice of the type of penalty: fine or penalty, depends on the nature of the obligation, which is thus secured. So, for example, for failure to fulfill the terms of an agreement that are urgent in nature (payment, delivery), it is advisable to provide for the collection of a penalty, since the longer the violation lasts, the more significant the measure of liability will be. In such situations, it will be more profitable for the violator to quickly fulfill his duties. And in case of improper fulfillment of the terms of the contract, penalties may be in the form of a fine.
What formula is used to calculate
The penalty increases daily by the amount established by the refinancing rate of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation.
Attention! The rate is taken into account for each period of untimely fulfillment of an obligation:
P = (Z * D * SR) * 1/300, where:
- Z – amount of unpaid funds;
- D – number of days of delay;
- SR – Central Bank rate.
Please note that the interest is not charged for the year, but for a specific period of delay.
Formula for calculating penalties under an equity participation agreement
For entrepreneurs and legal entities, there is the following formula for calculating penalties: N = Price as agreed * number of days of delay * Rate established by the Central Bank of the Russian Federation
For individuals there is the following formula: N = Cost under agreement*number of days of delay*Central Bank rate
An example of calculating the amount of a penalty when concluding an agreement on shared construction
When the cost of the object is $3 million, the number of days of delay is 100, and the Central Bank rate is 8%.
Penalty for individuals: 3000*100*8/100/150= 160 000
Penalty for individual entrepreneurs or organizations: 3000*100*8/100/300 = 80 000
At the refinancing rate
Important! The refinancing rate is the percentage of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation transferring loans to commercial banks. If this rate changes, then its data in the above formulas should be replaced.
At the bank rate for individuals
For individuals, the penalty is determined:
- in accordance with the law;
- in accordance with the provisions of the loan agreement
When the penalty is calculated on the basis of an agreement, the calculation is carried out as follows:
P = Overdue amount*% penalty*number of days/360.
Attention!
Calculator for calculating penalties (penalties) in shares of the Central Bank key rate (1/300, 1/150, 1/130).
Calculator for calculating a penalty (penalty) in double the amount of the Central Bank key rate.
Calculator for calculating interest on contractual penalties (fixed penalty percentage).
When a penalty is provided for by law:
P = Overdue*% Central Bank refinancing rate*number of days/360.
In case of bankruptcy on a loan
Based on the analysis of judicial practice, it follows that the arbitration court has the right to impose on a person the obligation to pay a penalty, but after the lapse of time he may be declared bankrupt.
Calculation of alimony
Financial debt is calculated from the date the debt arises until its repayment.
Remember! Penalties are calculated:
- in case of payment of alimony based on an agreement;
- by decision of a judicial authority (its amount is 0.5% of the debt amount);
A statement of claim for the imposition of liability measures is filed at the place of residence of the plaintiff in the magistrate's court.
The following are attached to the claim:
- penalty calculation method;
- writ of execution on the basis of which alimony is calculated;
- agreement (when alimony is paid voluntarily).
Please note that the bailiff cannot independently assign a fine. Its collection occurs after a court decision is made.
Watch the video.
How to calculate the penalty for late delivery of a house? Regarding wages
One of the employer’s responsibilities is the timely payment of wages to individuals. When the payday falls on a holiday or weekend, payment must be made the day before.
Please note! In the event of a delay in wages on the basis of labor legislation, the employer may be required to pay compensation, which is calculated using the following formula: number of days of delay*amount of debt*StB/100/300
The company's chief accountant or manager may be subject to a separate measure of responsibility.
How to calculate the penalty?
Calculating the penalty is relatively simple. If the penalty is legal, you take a percentage, multiply it by the cost of the goods, the amount of insurance compensation, the price of the share participation agreement, etc. - depending on what is established by a specific law - and then multiply by the number of days of delay in fulfilling the obligation.
If the penalty is determined by agreement of the parties, then you follow the algorithm described above. With fines it is even simpler: it is either a fixed amount that does not need to be calculated, or a percentage multiplied by the cost of the contract (for example, the amount of freight charge under a contract for the carriage of goods).
For greater clarity, we present the formula for calculating the penalty: percentage * contract price * number of days of delay. In the case where it is established by law, instead of the contract price, place in the formula the amount with which the fine or penalty will be calculated.
Things are more complicated with interest under Article 395 of the Civil Code. If during the delay the Central Bank refinancing rate did not change, then simply substitute its three-hundredth part in place of interest in the formula given above. But if there were changes, then the amount of the penalty will first be calculated separately for each indicator. Then you need to summarize the results. From time to time, the Central Bank issues information letters about changes in the rate, which can be easily found on the Internet.
Example: the delay began on November 5, 2020 and ended on July 28, 2020 with the fulfillment of the obligation. During the specified period, the key rate changed 3 times: from 7.50 to 7.75, then again to 7.50, and the current rate is 7.52 percent. The dates of changes are respectively: December 14, 2020, June 14, 2020 and July 26, 2020.
You must calculate how many days the delay lasted from November 5, 2018 to December 14, 2020 and multiply by the current key rate at that time (7.50%), and then do the same with the remaining indicators, and add up the results. This will be the total amount of the penalty.
Penalty determined by agreement or law
The penalty takes the form of a penalty or fine. The fine must be collected once. It may take the form of a fixed amount or a percentage of the amount of the person’s unfulfilled obligations.
Penalties are accrued daily until the day the obligation is fulfilled. In some types of legal relations, the amount of the collected penalty is determined by the law (for example, when it comes to legal relations related to the payment of insurance compensation under compulsory motor liability insurance).
Please note that when the law establishes that for certain types of legal relations the collection of a penalty is allowed, then it is collected even if it was not provided for by the agreement concluded by the parties.
When the procedure for collecting a penalty is not legally established, the parties independently determine the procedure for calculating it and the procedure for resolving the dispute.
When the parties have not provided for the possibility of imposing financial liability in the event of improper fulfillment of obligations or their non-fulfillment and its imposition is not provided for by law, then it is not subject to recovery from the violator.
Remember! When considering a dispute, the court has the right to reduce the amount to be recovered.
Along with this, there is a list of disputes in which the court does not have the right to independently reduce the amount of the penalty (for example, when it comes to the accrual of penalties in connection with late payment of alimony).
Penalty for late payment under the contract
A fine is a type of liability for late payment. It may also be provided for by the contract in the amount that the parties consider reasonable at the time of signing the contract. It is established in the form of a one-time payment and can be the second form of liability for the violator along with penalties. Law enforcement practice does not consider the simultaneous use of both a fine and a penalty as a double liability of the debtor, therefore indicating two types of liability in the contract is legal.
Penalty under the contract
Depending on the legal relationship the parties entered into, penalties may be imposed on either one or both participants. Next, we will consider the most common cases of imposing a penalty.
Sales and purchases
The purchase and sale agreement may provide for a penalty for late delivery of the goods purchased by the buyer. The penalty is calculated based on the value of the goods to be transferred.
On the other hand, the buyer, in case of late payment for goods, may also be subject to financial penalties. The amount of the penalty is provided for in the agreement.
Supplies
Delivery is a type of legal relationship related to purchase and sale. In this regard, the rules established for purchase and sale agreements apply to such legal relations.
The only difference is the accrual of a penalty for late delivery of the next batch to the buyer.
Contract
Important! The penalty is payable by both the customer and the contractor.
The customer may be held liable in case of untimely completion of work or a separate stage. The contractor is subject to financial liability in case of violation of the deadlines for delivery of a certain stage of work.
To hold the contractor accountable, the agreement must provide for specific deadlines for the completion and delivery of the work. For this purpose, specific deadlines must be established in the contract.
Attention! Our qualified lawyers will assist you free of charge and around the clock on any issues. Find out more here.
Loan
The possibility of charging a penalty is permitted by law. On the other hand, in order to calculate the amount of the financial penalty, it must be indicated by the parties in the agreement or receipt for the receipt of borrowed funds.
Equity participation
If the developer violates its obligations to deliver new residential premises on time, possible sanctions that are permissible for application are specified by law.
For each day of late delivery of residential premises, 1/300 of the refinancing rate is provided.
When the debtor is an individual, the penalties can be doubled. This means that the penalty amount is 1/150. The accrual base is the amount of the cost of the residential premises, which is specified in the construction agreement.
Procedure for calculating penalties
The procedure for calculating the penalty depends on its nature and is determined either by law or by contract.
The basis for calculating a penalty is the failure of the debtor to fulfill an obligation on a specific date provided for by the contract/law. When such an event occurs, the party in whose favor the penalties are paid has the right to demand their payment if the specified circumstances have already occurred and all conditions for its objective calculation have been met: the execution deadlines have passed, the full period of delay is known.
The party whose rights are violated by non-performance or improper performance has the right to demand voluntary repayment of the penalty. To do this, it is necessary to send a written claim to the debtor with a calculation of the amount to be repaid and a demand for its payment. If reasonable deadlines for making the specified amounts have passed or the violating party refuses to voluntarily repay the debt, it is recommended to file a claim in court to enforce collection.
How to correctly calculate the penalty
Calculation of fines and penalties must be carried out based on the requirements of the contract or law and depending on the form in which such fines and penalties are established. This may be a fixed amount, a percentage of the contract value, or a penalty in the amount of damages caused.
Since violations of contractual obligations are often associated with delay in their fulfillment, the penalty is tied to the amount of the obligation and the duration of the delay. To calculate it, you need to define three key metrics:
- The basis for calculating penalties and penalties. This may be the value of the contract, the outstanding part of the obligation, the amount of losses.
- The rate at which the calculation occurs. It is determined as a percentage or fraction thereof. In some cases, the law may provide for the mandatory application of the Central Bank key rate.
- Length of delay. The final period for which the penalty is accrued is calculated based on the contractual and actual performance deadlines. Within the specified period, the rate may be applied for each day/week/month of delay, depending on the requirements of the law/contract.
Formula for calculating penalties under a contract
To calculate the penalty according to the described parameters, the standard formula is used:
Good to know
calculation base * penalty rate * number of full days/weeks/months of delay
Let's look at the calculation using the example of an indemnity agreement. Let's say they provide for a penalty from the debtor in the amount of 1% of the balance of the debt for each overdue day. The balance of the debt is 150 thousand rubles, the overdue period is 3 months. The calculation is made as follows:
- 1) 150 thousand rubles * 1% = 1.5 thousand rubles
- 2) 3 months (June, July, August) = 30 + 31 + 31 = 92 days
- 3) 1.5 thousand rubles * 92 days = 138 thousand rubles.
Calculation of penalties under Article 395 of the Civil Code
If borrowed funds are used (for example, in connection with a loan agreement), failure to repay them on time means the possibility of imposing financial sanctions on the debtor. The amount of interest to be paid is determined by agreement or by law.
An example of calculating a penalty under OSAGO 2016
Attention! The Federal Law “On Compulsory Civil Liability Insurance” states that the amount of the penalty in case of failure by the insurance company to pay timely insurance compensation is 1% of the amount to be paid.
Penalty due to late payment is associated with the following indicators:
- rates developed by the Central Bank;
- the sum of days of delay;
- the amount of unpaid funds.
Calculation example:
If the company’s debt is 50,000 rubles, 20 days overdue, the rate is 8.5.
The penalty is calculated as follows:
50*0.013 (1/75)*0.085*20=1.105 thousand rubles.
Determination of days of delay
To correctly calculate the amount of the penalty, you should know from what day the debtor became overdue. When the agreement stipulates that the fulfillment of the obligation must be carried out on a specific day, the period of delay begins to be calculated on the next day.
The parties may indicate in the agreement several days during which the obligation must be fulfilled by the party (usually working days). In this case, it is necessary to count the days provided for in the agreement. After the last day, the day of delay follows.
It also happens that the parties do not indicate specific deadlines in the agreement that are allocated for the fulfillment of obligations.
Remember! In this case, it is necessary to act in accordance with the mechanism developed by the legislator:
- the counterparty is sent a written request to fulfill the financial obligation;
- The received request must be considered within no more than a week from the date of receipt of the document. The eighth day is the first day of delay.
The end of the period is the day on which the obligation was fulfilled. Remember that the period of delay includes all calendar days, including holidays and weekends.
Formula for calculating penalties
There are two main types of compensation:
- Penya. Accrued, as a rule, when payment or shipment is late. Its size depends on the size of the payment, the number of days of delay and the discount rate.
- Fine. Occurs due to such violations as the presence of defects, mismatch of product names, shortage of goods, and others.
If information about the amount of sanctions is specified in the agreement, then such a penalty is called contractual. In other situations, we are talking about a legal penalty.
The formula for calculating compensation depends on the type of penalties:
- The fine is assessed on a fixed amount basis.
- The legal penalty is calculated as: Contract amount * Percentage rate * Delay period
- The formula for calculating penalties at the key rate of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation: amount under the agreement * period of delay * key rate of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation / 36,000.
Appeal to a judicial authority
Please note! The statement of claim is filed with the court at the place of registration of the creditor, at the place where the agreement was concluded or its execution.
This means that the creditor has the opportunity to go to court at a location other than the debtor’s place of residence.
The claim must contain the following list of information:
- name of the judicial authority;
- information about the plaintiff indicating his contact information;
- information about the defendant;
- circumstances of the case;
- a list of requirements presented by the applicant;
- a list of documents that a person attaches as evidence of his position.
Remember that the statement of claim is drawn up in accordance with the number of persons involved in the process.
Receiving a penalty
In order for the obligated person to fulfill his obligation to pay funds, it is necessary to contact him with a pre-trial claim. It indicates on what basis the debt arose, the amount of the penalty and the procedure for paying it. It should be noted that filing a pre-trial claim is a mandatory procedure.
If the debtor ignores the received claim, then the creditor has the right to appeal to the court.
Since legal proceedings take a long period of time, it is better to resolve financial conflicts amicably.
Penalty for violation of deadlines under the law and under the contract
A penalty is a certain amount of money that must be paid by one person to another in the event of failure to fulfill or poor performance of any obligation within the agreed period.
As a way to protect the rights of the parties in the event of dishonest fulfillment of obligations under the contract, if not specified in the latter, it is applied in accordance with the rules of law (the law on the protection of consumer rights, the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, legal acts on the transportation of goods and others).
Its legal form can be terminated in the following ways if the main obligation is violated:
- provision of compensation (according to the agreement of the parties, the obligation is terminated by the payment of money or the provision of other property);
- novation (the parties agree to replace the existing obligation between them with another);
- debt forgiveness (when the debtor is released from the obligation by the will of the creditor).
Important! A penalty cannot be demanded from a person if he is not responsible for failure to fulfill or poor performance of any obligation.
Penalty and court decision
In practice, the following situation may arise. The court makes a decision in favor of the creditor to collect the principal debt and penalties in the form of penalties and interest. Participants in legal relations may have a question: will the accrual of sanctions be stopped? The answer is no.
Important! The penalty is accrued until the person finally pays the entire amount of the debt. In order to receive it, you must submit a new claim.
To calculate it, you should take into account the period that begins from the day the first claim was filed until the day on which the counterparty fulfilled the debt obligation. In this case, the person should not forget about the statute of limitations, which is three years.
Watch the video. Calculation of penalties for alimony:
Dear readers of our site! Our articles talk about typical ways to resolve legal issues, but each case is unique.
If you want to find out how to solve your specific problem, please contact the online consultant form on the right. It's fast and free! Or call us at :
+7-495-899-01-60
Moscow, Moscow region
+7-812-389-26-12
St. Petersburg, Leningrad region
8-800-511-83-47
Federal number for other regions of Russia
If your question is lengthy and it is better to ask it in writing, then at the end of the article there is a special form where you can write it and we will forward your question to a lawyer specializing specifically in your problem. Write! We will help solve your legal problem.
Features of penalties
Depending on where it is registered, the penalty may be:
- negotiated;
- legal.
Legal is divided into the following types:
- imperative;
- dispositive.
Payment in itself does not deprive the right to claim compensation for damages caused. In relation to them there are:
- Exceptional (when only a penalty is payable);
- Alternative (at the choice of the creditor, either it or the losses are subject to payment);
- Penalty (in addition to this, damages caused are also subject to payment);
- Settlement (the part of the losses caused that is not compensated by the collected penalty is subject to compensation, unless otherwise agreed upon by the parties in the contract).
In practice, mixed types may also occur. For example: the buyer purchased a cabinet and entered into an agreement with the seller for its supply and assembly. The contract only stipulated liability for failure to fulfill the delivery clause. The seller violated its delivery obligations, which led to failure to complete the assembly on time. The consumer may demand both payment of compensation for late delivery and a measure of liability not provided for in the contract for violation of deadlines for completing work in the amount established by law.
How to calculate the amount of the penalty
As a general rule, to calculate the amount of the penalty, you need:
- find out its amount for one day of delay, for which the debt is divided by the total number of days in the year, equal to 360;
- multiply the resulting number by the period of delay (also in days);
- multiply the result by the percentage of responsibility.
According to Article 330 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, it can be accrued up to the moment of actual fulfillment of the obligation. However, its size or accrual period may be limited by laws or contracts. If a court decision is made, its amount is calculated by the court on the day such a decision is announced. Further accrual is carried out either by the enforcement agency (bailiff service) or by other institutions (treasury, bank and others).
If the main obligation is terminated, its accrual is also suspended. Exception: if the contract is terminated, but the obligation remains (for example, a product purchased on credit is not paid for on time, or the buyer during the purchase found defects in the product and returned it, which led to termination of the contract), a penalty is charged.
Download for viewing and printing:
Article 330 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation “The concept of a penalty”
Size is negotiable
When the penalty itself is established in the contract by mutual agreement of the parties, then its size is determined by them. However, its amount is determined in such a way that it should not lead to unjust enrichment of the creditor. If its size significantly exceeds the amount of damage, it may be reduced by the court.
Calculation formula under the Consumer Protection Law
According to the Law on the Protection of Consumer Rights, in case of violation of established deadlines (for example, to replace a low-quality product) or failure to comply with the requirements of a consumer’s claim on a voluntary basis, the seller (manufacturer, other person) is liable in the form of a penalty (fine). Its size is 1 percent of the cost of the goods for each day of such delay.
To determine the size, you need to multiply the cost of the product by the number of days overdue and by 0.01 (1%).
Example
A sofa worth 40,000 rubles was ordered. It was manufactured and delivered to the buyer 10 days later than the agreed upon date.
Thus, the size will be:
- 40,000×10×0.01=4,000, total 4,000 rubles.
The amount of liability is calculated in the same way in case of violation of the deadline for the delivery of prepaid goods and performance of work. In the first case, 0.5 percent of the payment amount is charged for each day of delay, in the second - 3 percent for each day (or an hour for hourly work).
Download for viewing and printing:
Law of the Russian Federation dated 02/07/1992 No. 2300-1 “On the protection of consumer rights”