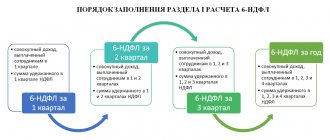
Concept
Article 102 of the Labor Code defines a flexible schedule.
It is defined as a mutual agreement between the parties about the beginning, end and duration of the working day. The Code gives maximum freedom in wording; the employer and employee can vary working hours at will. The main condition is mutual agreement.
In HR practice, there are three types of flexible scheduling:
- Sliding work schedule. In the employment contract, an employee working on such a schedule has standard working hours. He works the same hours as his colleagues. The difference here is the variable opening hours. Example: a person may arrive two hours earlier than the usual start time, but also leave two hours earlier.
- Free. It would be a particularly good solution for musicians, artists, and journalists. Some activities are extremely difficult to regulate and measure in standard ways.
- Shift. The concept of “shift schedule” is a type of organization of working time familiar to everyone. Example: night shifts in hospitals.
Attention!
The provisions on irregular working hours are regulated by another article of the Code -
101 Labor Code of the Russian Federation
.
Although the last paragraph briefly mentioned positions for which flexible work arrangements are generally suitable, for a better understanding, below is an expanded list of examples and their detailed descriptions.
An employment contract with a sliding work schedule, extended to all regular positions, incl. office.
Marketers, secretaries, managers.
The main question will be the feasibility of introducing such a schedule.
If it suits the employee and the employer, then a sliding schedule can be organized for almost any position. It will be especially useful for employees who have other important matters besides work.
Namely: study, part-time work elsewhere.
Shifts: fundamentally there is nothing new. Shifts were introduced at the dawn of capitalism, when factory owners wanted production to work around the clock and constantly produce products, but their desire rested on the physiological characteristics of a person.
That's why such a system was invented. It is widely used in factories, emergency services (hospitals, rescue services), as well as in the private sector (convenience stores).
Free schedule: on the one hand, we have very poorly regulated by standard methods - creative activity. On the other hand, there is the need to conclude a formal relationship between the employee and the company.
An employment contract with a flexible work schedule is the best way out of this difficult situation. Designers, artists, musicians, writers, trainers, this type of working relationship is very suitable for them.
Options
Despite the greater degree of freedom with a flexible schedule, control and recording of working time is required.
There are three main types:
- Daily - a specific number of working hours is established, they must be worked within one day.
- Weekly - if it is not possible to ensure time control within one day, then the standard hours for one week are established.
- Monthly - it is preferred if it is impossible to control working time using the previous two methods.
The accounting period in some cases can be increased, for example, to “quarterly” reporting.
The responsible party for organizing working time, basic principles and methods of accounting is the employer.
The HR department is responsible for recording working hours.
To fill out, use the standard “T-13” form; this is a standard working time sheet.
When is it not suitable?
In some cases, flexible scheduling will not be a good solution. These include: enterprises that have special safety conditions, if the enterprise has weak labor discipline.
In addition, often in the public sector. service, the introduction of a flexible schedule is not possible due to bureaucratic “sluggishness”. Private firms have more opportunities in this regard.
The constituent elements are:
- fixed time - the time when an employee is required to be present at the enterprise;
- variable time - a period of time when the employee has the right to determine the beginning and end of the working day;
- food break - Article 108 of the Labor Code establishes the employee’s right to a break, food and rest. Minimum - half an hour break.
Elements can be supplemented with clarifications and subparagraphs.
What is the procedure for establishing this operating mode?
1. First of all, it all depends on who is the initiator of this process, if it is an employee who is already working at the enterprise. He submits an application to the HR department or boss, in which he voices his request and the reason why he needs a flexible work schedule.
For example:
To the Director of Lepestok LLC
Luzan A.I.
From programmer Sage P.R.
Statement
Due to the need to care for a sick family member, I ask you to set me a flexible work schedule for the period from 03/31/2017 - 12/31/2020 from 10 am to 3 pm, and fixed hours from 3 pm to 6 pm.
03.20.17 Sage P.R.
2. If the initiative comes from the employer, the process will increase slightly, since the employee must be notified no later than two months in advance and an agreement must be signed with him.
3.Then an additional agreement is drawn up in two copies, a schedule is drawn up
4. An order is issued on a new regime for this employee, where it is also necessary to specify when working hours are fixed, and when the employee can apply how many attendance systems
How is flexible working time established?
Compliance with the work and rest regime, taking into account the current legislation, is carried out on the basis of the PVTR. The local document is drawn up not only taking into account the current legislation, but also other legal acts containing labor law norms, collective agreements, agreements (Article 100 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
The work and rest schedule of certain employees may differ from the general one, which is established in the organization for the entire team, therefore:
- differing conditions are reflected in the TD, taking into account the second part of Article 57 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation;
- to avoid discrepancies, the employer has the right to establish a uniform work and rest schedule for employees;
- special work procedures should be set out separately; they will apply only to certain categories of employees in accordance with the instructions in the PVTR.
Question from practice
Answered by Nina Kovyazina, Deputy Director of the Department of Medical Education and Personnel Policy in Healthcare of the Russian Ministry of Health.
In the “Working and rest hours” section, indicate:
- the start and end time of a working day or shift, the duration of the working day and working week, the number of shifts per day (Article 100 of the Labor Code);
- time of the lunch break and its duration (Article 108 of the Labor Code);
- duration and...
Answer from the article “How to draw up internal labor regulations”
The work and rest schedule in Russia is established taking into account the specifics of the enterprise’s activities. PVTR are a guide to action. The local document must take into account working days and weekends. Based on Article 111 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, days off are usually granted consecutively.
Due to the peculiarities of the organizational and technological process, days off can be distributed for different groups of workers during the week, and not just on Saturday and Sunday. Lunch breaks are established taking into account Article 108 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. The duration of the lunch break varies from 30 minutes to 120 minutes.
We invite you to read: Is it possible to enter into an inheritance using a general power of attorney?
Employees working under irregular working hours are provided with additional leave on the basis of Articles 101 and 119 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. When drawing up the PVTR, take into account Article 105 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, which specifies the procedure for dividing the working day into parts. When recording working hours in aggregate, the work and rest schedule for employees is drawn up on the basis of Article 104 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
In accordance with Article 212 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the employer is responsible for providing its employees with safe working conditions. Therefore, the total duration of a shift or working day is determined by the employer himself. Find out what inspectors are currently checking at PVTR. The editors of the magazine “Personnel Affairs” have collected the main mistakes, according to GIT.
Normal working hours are 40 hours per week, 8 hours per day. For certain categories of workers, longer shift durations may be established. Quite strict standards apply in relation to the length of the working week.
The day shift is regulated at the legislative level only for employees performing their duties in difficult, dangerous areas, for minors and disabled people (Article 94 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). The duration of the shift is established at the legislative level for vehicle drivers.
For the remaining employees, the employer has the right to establish a work and rest schedule that differs from the general one specified in the PVTR. It can be fixed in an employment contract or changed by written agreement of the parties.
Conclusion
The work and rest schedule is established taking into account the specifics of the enterprise’s activities and is fixed in the PVTR. For some categories of employees, you can establish a routine that differs from the general one used in the organization, indicate it in the employment contract and, if necessary, change it by drawing up a written agreement between the parties.
According to Article 104 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, with a flexible schedule, a summarized record of actually worked time is kept, for which one of the methods is selected:
- daily - standard hours of labor per calendar day;
- weekly - norm per week;
- monthly - number of hours of work per month.
Establishing an accounting period of more than 1 year is prohibited by the same article of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
Recording and recording of each employee’s working time is carried out by specialists from the HR department or timekeeping service using the T-13 form based on the data received. The collection of information about the start and end times of employees’ working day is organized by the management of the enterprise in the form of:
entries of watchmen in the log of arrivals and departures;- electronic access system;
- video recording by surveillance cameras;
- submission of data by employees themselves.
The correctness of time recording during a flexible schedule is controlled by the head of the organization or the head of the personnel department.
Important! An employee with a flexible schedule can change the start and end dates of daily work, its mode, but the total number of payable hours in the accounting period used by the employer remains constant.
According to the employment contract, the employee is obliged to follow all the rules established in this agreement. GDV (flexible work schedule) is a form of organizing the duration of the working day, during which the employee independently determines his working day, which must first be agreed with the manager.
The main point in this mode is the implementation of a complete time plan for a set period.
A floating work regime is established without a time limit or for any period agreed with the manager.
If the schedule is established by agreement of the parties, according to the rules of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, then the employee can make his own choice. During discussions, it is possible to establish the details of the regime and wages according to a flexible schedule.
The need to establish a flexible operating procedure arises during certain downtime due to improper organization of the labor process. The specifics of companies may include night shifts, therefore, in some cases, there are long periods of free time from duties, but the employee still remains at the workplace, and the volume of tasks performed will not increase.
It is in such a situation that a flexible work arrangement would be appropriate, since it allows you to alternate between work and rest, which may be longer than usual.
The peculiarity of such activities is the ability to use long breaks or not work for a full period (week), but fulfill the work norm, according to Article 91 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
GDV should be introduced when, according to the working conditions, it is impossible to determine a working day of normal duration. The establishment of GDV is necessary to take into account the interests of employees and employers, as well as to create conditions for them that will influence the increase in the efficiency and productivity of the work process.
The legislation does not contain a list of positions that must work under GDV, but there are regulations that indicate the possibility of GDV.
For large enterprises, accounting is usually carried out using a special time sheet. Small organizations often prepare a statement.
There are several types of accounting:
- Daily.
- Weekly.
- Summarized.
Day accounting is best used if the employee’s working hours are constant.
For example, he works 6 hours every day.
Overworking of a given norm on one day cannot be compensated by shortcomings on another day.
Because, in fact, this can become a flexible schedule, requiring a different way of accounting.
Weekly - used if the number of working hours/week is determined. The method is a little “wider” in use. An employee can work a different number of working hours per day, the main thing is the established norm per week.
For example, the standard is 30 hours and a five-day week. In this accounting system, an employee can work 2 days for 3 hours each, and the remaining 3 days for 8 hours each. The norm cannot exceed 40 hours.
Summarized accounting of working time in an employment contract is the best solution for those types of work where, due to the conditions of the work process, it is impossible to comply with/determine daily or weekly time standards.
To put it another way, measuring the exact number of hours per week is too difficult because the production cycle is very long. It lasts for many weeks or even months.
In this case, it is recommended to use summarized accounting. The main article in the summary recording of working time is Article 104 of the Labor Code.
Now a few words about how to apply summarized accounting and implement it in an enterprise. First, determine the reporting period - it can be a week, month, quarter, year.
A period of more than a year cannot be set. For enterprises with hazardous conditions it is less - 3 months. A one-day period is also prohibited, since in fact this will already be a daily accounting.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with: Lease agreement - sample form 2019
After determining the period, the standard hours for the selected period of time are established.
For example, per quarter you are entitled to 120 slaves. hours.
Then an order is issued and included in the collective agreement or wage regulations.
Accordingly, new employees are familiarized with the payment method in the form of an annex to the employment contract.
Compensation for overtime and shortcomings is permitted only within a specified period.
If overtime was recorded during the period, then they are paid as overtime according to the general rules.
What is the difference between a flexible schedule and others?
In order to answer the question posed in the title, you need to understand what graphs there are and what mode they imply. We have already mentioned that an applicant can get a job with the following regime:
- Regular is the most popular work schedule. For example, five days a week, eight hours a day, Saturday and Sunday are days off.
- Irregular - this regime is notable for the fact that the boss has the right to call the employee to work before the start of the working day or, conversely, to detain him after. In this case, additional time is paid, but the employee can only perform his duties required by his position.
- Shift work - this mode of work is used by companies whose employees must be away from home for a long time, living in rotation camps. For example, during the construction of a highway in the Arctic.
- A flexible work schedule allows an employee to independently regulate the beginning, end and duration of the work day so that the total amount is the number of hours or volume of work agreed upon with the employer.
- Shift work is a regime according to which an employee has the right to work two, three or four days and rest for the same number of days. Such a schedule is provided for in companies whose operating hours exceed the daily norm established by the Labor Code.
- Split working day - most often this schedule involves dividing the working day into two equal parts with a two-hour unpaid break.
Setting up a flexible work schedule
The main question for an employer is how to properly draw up an employment contract with a flexible schedule? The specifics and conditions for this agreement are contained in the labor laws of the Russian Federation. If the employment contract is drawn up incorrectly, the organization faces a fine and suspension of activities.
A package of documents when registering a GDV is formed depending on the status of the employee - hiring for a position or already an employee of the company.
In the first option, the terms of GDV are included in the text of the working agreement and detail the working time. The order to hire an employee must be executed in form T-1 and contain the conditions for starting work on the GDV.
To specify the operating mode and method of accounting, approximately the following is added to the contract:
- The employee is assigned a summarized accounting method. The accounting period is one month.
- The employee works in flexible working hours.
The following points are described in detail. For a flexible schedule, a standard, fixed work time, and rest schedule are established.
The daily work and rest schedule is set out in the Internal Labor Regulations. The local act is developed by the employer. The approval is carried out taking into account the opinion of the trade union or other representative body of workers. Taking into account Article 190 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the document can be considered as an annex to the collective agreement.
The employment contract with the employee establishes the work and rest schedule, if it differs from the general one established for all employees of the enterprise. If the routine does not differ from that generally accepted in the company, then, taking into account the second part of Article 57 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, there is no need to include it in the TD. All personnel are introduced to the PVTR upon signature.
If the employer is an individual, the work schedule is determined by agreement of the parties and is prescribed in the TD with employees. For employees of religious organizations, the corresponding regime must be enshrined in the internal Charter.
A fine for violating the work and rest regime, that is, for violating PVTR, is not provided for by labor legislation. An employee can be punished for causing material damage to an organization on the basis of Article 238 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. If the PVTR is violated, the employer has the right to bring the employee to disciplinary liability in the form of a reprimand or reprimand on the basis of Article 192 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
For repeated violations, when labor regulations are not systematically observed, the employee may be fired at the initiative of the employer. Experts tell us how to fill out the section “Responsibility for violation of labor discipline” of the organization’s PVTR.
In order to draw up an employment contract, in the section “Conditions and nature of work” you need to indicate “Flexible working hours” and supplement the section with clauses regulating the main elements of the schedule.
A change to an existing contract, for example, a transfer to a “Floating work schedule”, must be agreed upon by both parties. This is impossible unilaterally.
Sample wording for this section might look like this:
- employee “X” is given a “flexible working time regime” with a total amount of time of 30 hours per week;
- for employee “X” a six-day work week is established, the days are determined by the employee himself;
- the break is scheduled between 12.00 and 12.30;
- a “weekly” type of accounting period is established.
The Labor Code includes a vague concept of flexible hours. According to Article 102 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the end and beginning of a work shift, its duration are established by mutual agreement between the employee and the employer. Wages are calculated based on the number of hours worked.
Article 102. Working in flexible working hours
When working in flexible working hours, the beginning, end or total duration of the working day (shift) is determined by agreement of the parties.
The employer ensures that the employee works the total number of working hours during the relevant accounting periods (working day, week, month and others).
In practice, three types of flexible scheduling are used:
- sliding (floating) - for a specific employee, the start and end times of the working day are shifted while maintaining its duration.
- Free - due to the specifics of the profession, the employee independently determines the time and mode of work.
- Shift work - employees perform job duties in alternating shifts - day and night, morning and evening.
The given flexible work modes are suitable for students combining work responsibilities with studying at an educational institution; women on maternity leave or leave to care for a young child; people of creative professions who work “by inspiration”.
For individual specialists, it is important to complete work tasks within a certain time frame, which changes daily. These are sales managers, programmers, designers, sales and advertising agents, and other similar categories of employees; for them it would be correct to establish a flexible schedule.
The Appendix to Order No. 112 of September 8, 2003 of the Ministry of the Russian Federation contains a list of professions in the field of communications and information, the specifics of which make it necessary to introduce flexible working hours.
Important! If an agreement on a convenient schedule is not reached between the employee and the employer, the latter has the right to ignore the employee’s request for a flexible work schedule. The Labor Code of the Russian Federation does not oblige the head of the organization to introduce an individual work schedule.
To streamline the work process, a flexible schedule is divided into elements:
fixed time - daily intervals required to be present at the workplace;
- variable time - determined independently by the employee (convenient starting and ending hours of the working day);
- meal break - the right to food, enshrined in Article 108 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the variability or constancy of the lunch break is based on an agreement between the employer and the employee.
Article 108. Breaks for rest and foodDuring the working day (shift), the employee must be given a break for rest and food lasting no more than two hours and no less than 30 minutes, which is not included in working hours.
The time for granting a break and its specific duration are established by internal labor regulations or by agreement between the employee and the employer.
At jobs where, due to production (work) conditions, it is impossible to provide a break for rest and food, the employer is obliged to provide the employee with the opportunity to rest and eat food during working hours. The list of such work, as well as places for rest and eating, are established by the internal labor regulations.
“The employee is provided with a flexible work schedule with a 5-day work week of 35 hours.”
We invite you to read: The most common violations of labor laws by employers
It is necessary to clearly indicate the time of mandatory presence at the workplace (fixed part), the hours of presence determined by agreement of the parties (flexible part), the time interval of the lunch break, and the accounting period used for remuneration.
The remaining sections of the employment contract with a flexible schedule do not differ from those with a regular work schedule. The place of work, the rights and obligations of the parties, the guarantees provided to the employee, and the period for granting annual paid leave must be indicated.
Legal regulation
A flexible work schedule according to the Labor Code of the Russian Federation is a special case of a work regime in which the time worked is summed up (Article 102 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, Article 104 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation and comments to them). It can be selected both for a specific employee and for the department as a whole. In the latter case, regulation is enshrined not only in the employment contract of each employee, but also in the internal labor regulations and other regulations of the company.
What documents document compliance with the work and rest regime?
The establishment of a flexible schedule in an organization or individual employee is allowed under Article 102 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation by mutual agreement of the parties. Unscrupulous employers and employees take advantage of flexible working hours, not observing the start and end dates of the working day specified in the employment contract.
According to Article 99 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, due to production needs or in the event of an emergency, it is allowed to exceed the number of hours worked by no more than 120 per year. An employer, ignoring the law and forcing an employee to work beyond the time limit established by a flexible schedule, is subject to administrative liability.
For violation of labor legislation under clause 1 of Article 5.27 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation, punishment is provided in the form of a fine of 1,000 to 5,000 rubles for an official, 30,000 to 50,000 rubles for an organization (up to the suspension of activities for up to 90 days).
Article 5.27. Violation of labor legislation and other regulatory legal acts containing labor law norms Clause 1
Violation of labor legislation and other regulatory legal acts containing labor law norms, unless otherwise provided by parts 3, 4 and 6 of this article and article 5.27.1 of this Code:
- entails a warning or the imposition of an administrative fine on officials in the amount of one thousand to five thousand rubles;
- for persons carrying out entrepreneurial activities without forming a legal entity, from one thousand to five thousand rubles;
- for legal entities from thirty thousand to fifty thousand rubles.
Article 192 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation provides for disciplinary sanctions for an employee who does not properly fulfill the duties assigned to him, in the form of a reprimand, reprimand and dismissal.
Lateness without a valid reason, absenteeism, violation by an employee of the flexible lunch break period specified in the employment contract are grounds for the application of these measures.
The severity of the offense committed determines the type of penalty imposed.
Important! According to Article 195 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, disciplinary action may be taken against managers at various levels who violate labor laws.
Article 195. Bringing to disciplinary liability the head of the organization, the head of the structural unit of the organization, their deputies at the request of the representative body of employees
The employer is obliged to consider the application of the representative body of employees about the violation by the head of the organization, the head of the structural unit of the organization, their deputies of labor legislation and other acts containing labor law, the terms of the collective agreement, agreement and report the results of its consideration to the representative body of employees.
If the fact of violation is confirmed, the employer is obliged to apply disciplinary action to the head of the organization, the head of the structural unit of the organization, and their deputies, up to and including dismissal.
The introduction of flexible working hours has a negative impact on the environment. Increasing the length of time employees spend at the workplace disrupts the heating and cooling regime of buildings and increases the amount of electricity consumed.
Most managers refuse flexible work schedules for employees due to the inability to control the proper performance of their job duties.
What types of employment contracts are there?
There are several types of employment contracts:
- By duration: they are divided into unlimited and urgent
Indefinite, as a rule, the most common, but fixed-term are concluded for a certain period and cannot last more than five years.
Important!! If neither the employee nor the employer expressed a desire to terminate the fixed-term contract and the employee continues to work, then such a contract becomes indefinite.
- By the nature of the labor relationship
- By the nature of the work, by time: contract for the main place and part-time
Responsibility for non-compliance with a flexible work and rest schedule
The liability of the parties is governed by the general provisions of the Labor Code. By violating an employee’s right to rest and break, the employer risks being fined. The fifth section of the Labor Code covers this issue in detail.
Attention! Article 99 of the Labor Code prohibits exceeding the overtime work norm; it amounts to
120 hours per year
. This also applies to flexible scheduling.
If the employee does not work conscientiously, he also runs a risk. Abuse of flexible scheduling that disrupts work flow may result in contract termination.
Markers of abuse include: violation of fixed time, shortcomings, failure to complete a given amount of work.
Attention! A flexible schedule is not a license to miss company events.
Responsibilities and rights with a flexible schedule
Applicants should not naively believe that working with a flexible schedule (in Moscow, St. Petersburg or another city) provides complete freedom and negligent performance of their duties. Because such a regime also obliges the employee to take the work seriously, responsibly, and cope with it in full within the prescribed time frame. Otherwise, the negligent employee may also be fined or fired.
However, certain requirements are imposed not only on the employee. The boss who officially (with the conclusion of an employment contract and an entry in the work book) employs an employee is obliged to provide him with social guarantees. The so-called social package. Including days off, maternity or sick leave payments, paid vacation after each full year of work.
Setting up a flexible work schedule
Flexible schedule does not apply:
- in conveyor production, where the labor process directly depends on the operation of equipment;
- when staff is employed in 3 shifts;
- with a 2-shift operating mode and no vacancies;
- in organizations with a specific production process;
- in case the employee performs official duties outside the enterprise (business trips, conferences, etc.).
The absence in the organization of a system of accurate accounting and control of time worked, production discipline, and clear organization of work makes the use of a flexible schedule impossible.
Elements of “floating” working time
These include:
- Lunch break . According to Article 108 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, every worker has the right to eat and rest. Lunch time should not be less than 30 minutes.
- Variable time . This is the period of time that the employee can independently choose (determining the beginning and end of the working day).
- Fixed working hours . At this time, the employee must always be at his workplace in the organization.
These elements can be changed and supplemented.