Accounting for reserves for future expenses in the balance sheet
These are reserves created by the organization for the upcoming payment of vacations, for the payment of remunerations at the end of the year, for warranty repairs and maintenance, for the repair of fixed assets, etc. The same account records reserves for contingent facts of economic activity, for discontinued activities (reserve for repayment obligations, for payment of severance pay, etc.).
The reservation of amounts is reflected in the credit of account 96 in correspondence with the accounts for recording production costs (selling expenses - for trading organizations). The expenditure of the created reserve amounts is reflected in the debit of account 96.
The decision to form reserves and (or) to refuse to form reserves must be recorded in the accounting policy.
Please note: the amounts of estimated reserves are not reflected on line 650 of the balance sheet. The balance of the accounts for valuation reserves (14 “Reserves for impairment of material assets”, 59 “Reserves for impairment of financial investments”, 63 “Reserves for doubtful debts”) is not reflected as a separate amount in the balance sheet. The balances on them are taken to reduce the corresponding indicators of the balance sheet asset:
- the balance of account 14 reduces the indicators in lines 211 “Raw materials, supplies and other similar assets” and 214 “Finished products and goods for resale”;
- account balance 59 reduces the indicators on lines 140 “Long-term financial investments” and 250 “Short-term financial investments”;
- account balance 63 reduces the indicators on lines 230 and 240 “Accounts receivable”.
The balance of account 82 “Reserve capital” is also not reflected on line 650. Line 430 of Section III of the balance sheet is intended for it.
Typical accounting entries with account 96
In accounting, account 96 belongs to the passive category - the balance on it is formed only in the credit part of the balance sheet. There are a number of standard account transactions - the following operations are presented in the Accounting Regulations:
| Debit correspondence | Loan correspondence | the name of the operation |
| 96 | Reserving money for vacation pay | |
| Accrued social benefits | ||
| 76 | Writing off the amount of warranty service as a reserve | |
| The unused amount of reserve stock was included in other expenses | ||
| 08 | 96 | Money intended for investment in construction work or in VNA |
| (23, 29) | Costs of main production included in the reserve | |
| (26) | Reserved amounts are included in the company's general expenses | |
| Reserve inventories included in selling expenses |
The amount that exceeds the reserve may be written off against operating expenses. The vacation reserve is allowed to be carried forward to future periods. In the balance sheet, reserve amounts are reflected on line 1540.
reserves for future expenses asset or liability
NThe maximum amount of temporary disability benefits (with the exception of temporary disability benefits due to an industrial accident or occupational disease) paid from the Social Insurance Fund for a full calendar month cannot exceed 16,125 rubles.
NIf an employee has worked less than 6 months out of the last 12 calendar months, PVNT (except for cases of incapacity for work due to an industrial injury) is paid in an amount not exceeding the minimum wage for a full calendar month.
N To pay for temporary disability - the average daily earnings are determined for the 12 calendar months preceding the month of the onset of disability by dividing the amount of actually accrued wages and other payments by the calendar number of days.
N To pay for vacations and pay compensation for unused vacations, the average daily earnings are calculated for the last 12 calendar months by dividing the amount of accrued wages by 12 and 29.4 (the average monthly number of calendar days). If the employee has not fully worked the pay period, then the number of calendar days in those months that have not been fully worked is determined by multiplying the actual days worked by a factor of 1.4.
Payment for work outside the normal working hours (40 hours per week), as well as payment for work under special working conditions, is made at an increased rate. The amounts of additional payments cannot be lower than those established by regulatory legal acts. Time not worked is paid based on average earnings.
N Incentive payments.
Labor relations of all employees and employers are regulated by the Labor Code of the Russian Federation (LC RF). In accordance with the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, organizations independently determine the type, remuneration system, tariff rates, salaries, bonuses and other incentive payments. Wages are remuneration for work depending on the qualifications of the employee, complexity, quantity, quality and conditions of the work performed, as well as compensation payments.
Accounting for settlements with personnel for wages
The Russian Federation has established a system of state guarantees for remuneration of workers:
ü The amount of the minimum wage (minimum wage);
üTerms and order of payment of wages;
üLimitation of the list and amount of deductions from wages, as well as the amount of taxation of income from wages;
üMinimum duration of annual basic paid leave, etc.
The salary of each employee consists of:
nPayment for actual time worked;
nPayment for unworked time;
nStarting January 1, 2005 At the expense of the Social Insurance Fund, benefits are paid starting from the 3rd day of illness, the first 2 days of incapacity are paid by the company. Since January 1, 2006, Federal Law No. 255-FZ of December 29, 2006 “On the provision of PMT, maternity benefits for citizens subject to social insurance” has been applied.
nSynthetic accounting of settlements with personnel for remuneration is maintained on passive account 70 “Settlements with personnel for remuneration”. The credit reflects the accrual of wages, vacation pay, bonuses, and personal income tax; the debit reflects the amounts of deductions and payments. The credit balance shows the amount of wages owed by the enterprise to employees.
Salary deductions can be divided into three groups
⇐ Previous12345
Date added: 2014-01-07; ; Copyright infringement?;
Property of the organization - assets and liabilities
Attention: The liability side of the balance sheet records the entire amount of lease payments that the company must pay during the lease term. Rental income is reflected in the liability side of the balance sheet Reserves and funds Reserves and funds. As part of the section “Long-term liabilities”, funds and reserves that have the nature of debts can be created through deductions from pre-tax profits. These include: enterprise pension funds; long-term employee deposits; reserve for paying bonuses to staff, etc. Debt in pension payments arises if the enterprise has a pension fund. The source of formation of the enterprise pension fund are periodic contributions by the employer and employees.
https://youtu.be/HNSTrfHibtw
The fund's funds are used to pay pensions, disability benefits, or in the event of the death of an employee. Value added tax on acquired assets is an account designed to summarize information about the amounts of value added tax paid (due for payment) by an enterprise on acquired assets. Short-term financial investments - short-term (for a period of no more than one year) financial investments of an enterprise in income-generating assets (stocks, bonds and other securities) of other enterprises, associations and organizations, funds in time deposit accounts of banks, interest-bearing bonds of state and local loans and etc. - are the most easily realizable assets.
Account 96 in accounting
The following amounts were included in the reserve:
- for management personnel - 450,000 rubles;
- for employees involved in production - 280,000 rubles;
- for sales employees - 320,000 rubles.
In its accounting, the organization will reflect the following entries for the accrual of the reserve:
- Dt 26 Kt 96 - reserve for vacations of management personnel 450,000 rubles;
- Dt 20 Kt 96 - reserve for vacations of production employees 280,000 rubles;
- Dt 44 Kt 96 - reserve for vacations of sales department employees 320,000 rubles.
As employees go on vacation, the reserve is written off.
Account 96 “reserves for future expenses”
PBU 8/2010):
- as a result of past economic events, the organization has an obligation, the fulfillment of which cannot be avoided;
- the organization is likely to decrease the economic benefits necessary to fulfill the estimated liability;
- the amount of the provision can be reasonably estimated.
If such conditions are met, the estimated liabilities reflected in account 96 may include, in particular, the following liabilities:
- on the upcoming payment of employees' vacations;
- on upcoming expenses for repairs of fixed assets;
- on upcoming costs for warranty service of goods;
- on judicial proceedings;
- on the upcoming restructuring of the organization's activities.
How account 96 is formed and written off Account 96 “Estimated liabilities” is a passive account.
Normative base
Accounting account 96 reflects estimated liabilities. The definition of this concept is given in PBU 8/2010 “Estimated liabilities, contingent liabilities and contingent assets”. From paragraph 4 of this document it follows that an estimated liability is an obligation of an organization with an uncertain amount and deadline, arising as a result of legislative acts, court decisions, contracts, as well as based on business customs or as a result of the organization’s actions that indicate to other persons that that she has undertaken certain obligations that she will subsequently fulfill.
Clause 8 of PBU 8/2010 states that estimated liabilities are reflected in account 96 “Reserves for future expenses.”
It should be noted that paragraph 3 of PBU 8/2010 states that this provision may not be used by organizations that have the right to use a simplified method of accounting. This is a right, not an obligation of the organization. Thus, simplifiers independently determine whether to create reserves for upcoming expenses, and if so, for which expenses, and be sure to reflect their decision in their accounting policies.
Postings to account 96 - reserves for future expenses
Attention
If the actual amount of vacation pay exceeded the amount of reserved amounts, then there are 2 options for reflecting the write-off of the reserve. Example 3 In this example, let’s take into account the business operations of Examples 1 and 2.
In the 2nd quarter of 2020, vacation pay amounted to:
- for management personnel - 80,000 rubles;
- for employees involved in production - 40,000 rubles;
- for sales employees - 280,000 rubles.
The wiring will be as follows:
- Dt 96 Kt 70 - vacation pay for management personnel 80,000 rubles;
- Dt 96 Kt 70 - vacation pay for production employees 40,000 rubles;
- Dt 96 Kt 70 - sales department holiday pay 270,000 (320,000 - 50,000) rub.;
- Dt 96 Kt 69 - insurance premiums.
Option 1: expenses not covered by the reserve will be written off as a debit to the account.
We reflect vacation pay according to new accounting rules
Important: We will tell you in our material how to correctly record the created reserve and write it off correctly. What does the score 96 reflect? Which transactions contain debit 96 - credit 96? Results What does the score of 96 reflect? In accordance with the instructions for the chart of accounts, provided for by the order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation “On approval of the Chart of Accounts of Accounting” dated October 31, 2000 No. 94n (hereinafter referred to as the Instructions), Dt 96 - Kt 96 are applied for transactions that will be reflected in subsequent periods associated With:
- payment for planned vacations;
- annual payments for length of service;
- production costs incurred in preparation for seasonal production;
- repair of fixed assets;
- warranty repairs;
- other operations provided for in the Instructions.
At the same time, depending on the specifics of the detailing of expenses to the account.
What are reserves for future expenses and payments? score 96
Creating a reserve for warranty repairs How reserves for future expenses are formed The organization's reserves for future expenses consist of:
- Upcoming costs of paying vacation pay to employees;
- Costs for current repairs of equipment and fixed assets;
- Costs for warranty service and repairs;
- Other expenses of the organization.
An enterprise has the right to independently establish the procedure for calculating the reserve for the payment of vacation pay to employees, indicating in the accounting policy, taking into account paragraphs 15 and 16 of PBU 8/2010: When determining the calculation base of the reserve for the repair of fixed assets or equipment, it is necessary to take into account data on the sale of products in the reporting period, estimated percentage of defects, statistics in the field of warranty repairs, and so on.
How to prepare reports?
Reserves for future expenses may not be reflected in tax accounting, but this circumstance must be specified in the accounting policy of the enterprise. If it is decided that reserves or part of them are taken into account for tax purposes, then one must be guided by the procedure prescribed in Article 324.1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. When preparing your income tax return, they will be included in non-operating income and expenses.
As for the balance sheet, for contingent debts in liabilities, in section IV “Long-term liabilities” a separate line 1430 “Estimated liabilities” is allocated, which collects the credit balance of account 96 in terms of long-term reserves, that is, more than one year. In section V “Short-term liabilities” on line 1540, you can reflect debts for a period of less than a year.
Account 96 in accounting: reserves for future expenses
Example 2 Taking into account the conditions of example 1, in the 1st quarter of 2020 vacation pay was paid:
- for management personnel - 65,000 rubles;
- for employees involved in production - 20,000 rubles;
- for sales employees - 50,000 rubles.
In this regard, the following entries were recorded in the accounting:
- Dt 96 Kt 70 - accrual of vacation pay at the expense of the formed reserve of management personnel 65,000 rubles;
- Dt 96 Kt 70 - vacation pay for production employees 20,000 rubles;
- Dt 96 Kt 70 - vacation pay of the sales department 50,000 rubles.
In addition, it will be necessary to make an entry for the calculation of insurance premiums from the reserve Dt 96 Kt 69. For the calculation of vacation pay, see the publication “Calculation of vacation in 2020 - examples and features.”
Wiring dt 96 and kt 96 (nuances)
The amount of contributions to pension insurance for these vacations is 13200, insurance contributions to the Social Insurance Fund - 1740. Entries for writing off the vacation reserve Dr Kt Amount Description of the transaction 96.1 70 60000 Accrued vacation to employees 96.1 69.2 13200 Accrued contributions to the Pension Fund 96.1 69.1 1740 Accrued contributions to the Social Insurance Fund Entries to write-off of the reserve for repair of fixed assets Fixed assets were repaired in the amount of 56,000 rubles. However, in the balance sheet from 2011, not all provisions will be reflected as provisions. For example, provisions for repairs of fixed assets must now be written off as other expenses.
Therefore, estimated liabilities will be considered expenses for vacation pay for employees and cash bonuses for long service, as well as expenses for warranty service. Creation of reserves for vacation pay The organization has the right to independently establish terms and methods for assessing its own obligations in accounting and consolidate them with the provisions of its accounting policies.
An organization can create reserves based on the approved vacation schedule for employees. Reserve funds can be accrued monthly or quarterly.
An example of making entries for account 96
Table 1. Calculation of the reserve for payment of upcoming vacations
| Job title | Number of unused vacation days | Average daily earnings | Amount of vacation pay as of the date of the period (column 2 * gr.3) | Insurance premium rate in % | Amount of insurance contributions for vacation pay (gr.4 * gr.5%) | Total reserve amount (column 4 + column 6) |
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
| Lawyer | 6,66 | 500,10 | 3 330,67 | 30 | 999,20 | 4 329,87 |
| Accountant | 16,65 | 434,20 | 7 229,43 | 30 | 2 168,83 | 9 398,26 |
| Engineer | 23,31 | 651,32 | 15 182,27 | 30 | 4 554,68 | 19 736,95 |
| HR specialist | 13,32 | 367,45 | 4 894,43 | 30 | 1 468,33 | 6 362,76 |
The total amount of wages and insurance contributions that must be included in the reserve will be 39,827.84 rubles:
- Dt 26 “General business expenses” Kt 96.01.01 “Estimated liabilities for employee benefits” - 30,636.80 rubles for the amount of salary;
- Dt 26 Kt 96.01.02 - 9,191.04 rubles for the amount of charges to the funds.
- Dt 96.01.01 Kt 70 “Settlements with personnel for wages” - a reserve for employees on leave in the amount of 30,636.80 rubles was used;
- Dt 96.01.02 Kt 69 “Calculations for social insurance and security” - a reserve in the amount of 9,191.04 rubles was used for the amount of accrued insurance contributions.
Account 96 “Reserves for future expenses” in accounting
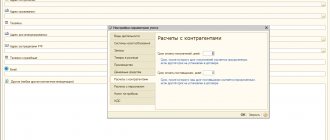
As far as I understand, according to 69.01, the reserve can only be written off and not created. And here it turns out that it is being created. UPP configuration 1.3 https://s008.radikal.ru/i303/1702/15/34b78aaadc58.jpg
TeMochkiN Good people, tell me who can do what)rbcvg (1) What is in the form of calculation on the accounting tab? Amra What, the accounts don’t know? This is the Social Insurance Fund as a reserve for upcoming vacations. If the reserve is not created, then why write off? Bull's heart (0) This is in case the company suddenly wants to fire everyone. TeMochkiN (2) https://s008.radikal.ru/i306/1702/5e/0e67b75a7794.jpg These are all types of calculations that are the calculation base for the TeMochkiN reserve (3), but I have not found information anywhere that the social insurance reserve is formed by posting Dt 69.01 Kt 96TeMochkiN (3) even in the same consultant TeMochkiN or I didn’t search well...Amra (6) (7) Well, you can argue here. In general, yes, usually the posting is Debit of the cost account - Credit 96, both for the vacation reserve itself, and for the insurance from it, but this option is also acceptable, like shuhard (9) the posting is fundamentally incorrect, there should be a cost account in Dt, the presented option is not will reduce income taxAmra (10) I won’t argue, because I myself said that “it seems like” shuhard (11) you won’t =) Mr. PZh (0) it’s all strangeFirst, a reserve is formed at the expense of expenses of type D26 K96, then written off upon the onset of vacation D96 K70, D96 K69
shuhard (13) cm (10) piter3 (5) and their reflections can be seen? In the form of postings from the reflection methods TeMochkiN (15) can I reset the analysis of 96 or in what form should it be? TeMochkiN (15) here is the analysis of the account: https://s020 .radikal.ru/i718/1702/6f/40912a4d2cdd.jpgsonne666 (5) your sick leave is included in the calculation base, hence the posting. I doubt that a reserve should be accrued from sick pay at the expense of the Social Insurance Fund. TeMochkiN (18) I’ll tell the salary calculator tomorrow, thank you for your help! Zlopchinsky on vacation reserves was all detailed in the yellow magazine, and there seems to be an ITS on the disk (in terms of the DS reserve) TeMochkiN deleted sick leave from the calculation database, refilled the reflection - everything was fine. just now what to do with previous periods =/(20) yes, I actually read this article: https://its.1c.ru/db/staff1c/content/33747/zup25
but it didn’t help to understand that there was an error in the calculation base)))
chuckk (0) Subaccount 96.01.2 “Estimated liabilities for insurance premiums” reflects the organization’s obligations for insurance premiums accrued on the amounts of payments in favor of employees. Subaccount 96.01.2 is used to record amounts for upcoming payments to the Pension Fund, Social Insurance Fund and Compulsory Medical Insurance Fund.The account is used to both accrue the amounts of estimated liabilities and transfer these amounts to the budget of the local municipality. Analytical accounting for subaccount 96.01.2 is organized by type of insurance premiums.
plan for the year or quarter
Get your work in order using the 1C configuration “IT Department Management 8”
ATTENTION!
If you have lost the message input window, press
Ctrl-F5
or
Ctrl-R
or the Refresh button in your browser.
The topic has not been updated for a long time and has been marked as archived. Adding messages is not possible.
But you can create a new thread and they will definitely answer you!
Every hour there are more than 2000
people on the Magic Forum.