The concept of staff turnover
Personnel turnover demonstrates the level of employee dismissal activity. This indicator allows you to understand how effective the company’s personnel policy is.
Personnel turnover is the ratio, expressed as a percentage, of the number of persons who have broken their contract with the employer to the average number of hired subjects (hereinafter abbreviated as TC). When determining this index, a specific period is taken as a basis, for example, a calendar year. TC can be clearly demonstrated through a coefficient that is calculated using a special formula.
The frequency of personnel changes is an indicator of the general condition of the company. At the same time, the following positions are important for analyzing the reasons for turnover:
- intensity of layoffs and hiring;
- period of employment of the employee (how long the person worked at the enterprise).
Determination of staff turnover
Important. There are no strict normative values to which the TC indicator must comply. This index is neutral. For each organization, the optimal turnover is calculated individually, taking into account a number of factors, such as industry specifics or production scale.
https://youtu.be/hky4JsGejqY
Types of staff turnover
There are many reasons why busy workers take payroll. Depending on the reasons that led to the renewal of personnel, several types of turnover are distinguished.
Table No. 1. TC classification:
| Criterion | Place of subsequent employment of the dismissed person | Structural unit by which the calculation is carried out | Initiator of termination of labor relations | |||
| View | Inside the company | External organizational | Absolute (for the enterprise in general) | Relative (by one department, division, by age, gender of those being dismissed) | Active – at the request of the employee | Passive - on the initiative of management |
If a person does not change employer, but only receives a promotion or moves to another department, we are talking about rotation within the organization. Registration with another employer indicates that there has been an external organizational turnover.
Certain types of staff turnover
Absolute turnover is determined according to generalized data for the entire company, and relative turnover is determined according to a separate criterion within one company, for example, for a specific department, according to a certain characteristic of those being dismissed (experience, position, gender, age).
An active labor contract is formed in connection with the termination of employment relations, which is formalized according to the will of the employee. For example, a person wants to get a job with a higher salary or moves to another city and is forced to change jobs. Passive turnover is associated with dismissals initiated by management. An example in this case would be the termination of a contract with an employee due to inadequacy of his position.
Important. Renewal of the team can be natural when cases of removal of individual employees and the infusion of new professionals have a positive effect on the conduct of business. Excessive turnover threatens material losses and general instability of business processes.
An integrated approach to solving personnel management problems
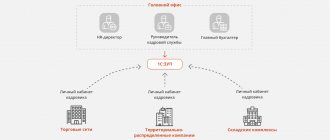
One of the main goals of the personnel management system is to increase the efficiency of using the potential of employees in production processes. To solve this problem in the “2P-Kadry!” system Three interconnected modules have been implemented: “Business Process Modeling”, “Personnel Accounting” and “Work Planning”, which form several logical contours of personnel performance management. Let's consider the diagram of the system information centers:
A business process model contains a sequence of actions necessary to implement a business task. The model is built in the IDEF0, IDEF3 notation, while the performers and the required set of competencies are determined for all elementary actions. Thus, already at the design stage of the process, its availability of human resources is determined.
The connection of the business process model with the organizational structure and personnel allows us to obtain answers to important questions for any business about the quantitative and qualitative composition of personnel for a given or planned production volume. In fact, the business process model is the rationale for various personnel management procedures, such as: changing the organizational structure of an enterprise, recruiting new employees, developing employee competencies, etc. On the other hand, changes in the management structure, staffing and the real competencies of employees directly affect the business processes of the enterprise and must be taken into account in the model.
A serious problem with the use of business process models is the constant change of business processes themselves in response to external and internal influences. Operational information about business processes can be obtained from department calendar plans. In the “2P-Personnel!” system The “Work Planning” module has been implemented, in which the formation of employee calendar plans and control of their implementation are carried out. Plans are drawn up based on business process models, but can be changed within wide limits (composition and sequence of tasks, labor intensity, performers) taking into account the current production situation. Moreover, changes are possible both at the planning stage and during the implementation of the plan. Work planning is carried out both in the context of structural divisions and in the context of business processes. The “Business Process Modeling” module displays summary information about the actual performance of work on the process, based on which the model can be adjusted. Thus, the model is as close as possible to the process, which significantly increases the accuracy of forecasts, and on the other hand, makes it possible to identify critical points of the process.
Another control loop relates to the personnel assessment function. The level of fulfillment of production tasks, along with other criteria, serves as an objective assessment of the employee’s potential. Analysis of the implementation of plans serves, among other things, as an indicator of the effectiveness of management procedures (training, motivation, etc.).
What types of dismissal do not affect turnover?
Termination of labor relations occurs due to various factors, but not all of them affect the Labor Code index.
Types of dismissals under Russian law
To calculate the coefficient, dismissals at the employee’s own request, by agreement of the parties, due to violation of labor discipline (absenteeism, ignoring safety requirements) are taken into account. This list also includes failure to pass mandatory certification and transfer to another position.
To determine the indicator, cases of contract termination based on:
- staff or headcount reductions;
- reorganization;
- retirement of a worker;
- changes in management and related personnel renewal.
B-frames
Naturally, both the third and fourth frames can be recorded according to the same principle, that is, formed on the basis of the previous one. However, using only I and P frames for normal video compression is not enough.
Therefore, there is another type of frame, the so-called B-frame. B-frames are the most compressed. It is due to them that the lion's share of the size of video files is saved. The minimum size of a B-frame is achieved due to the fact that it carries a minimum of information and is formed by two adjacent frames.
Let me give you an easy to understand example (Fig. 3).
Figure 3. B-frame.
In the first frame, the black block is in the lower left corner. In the third frame, the black block is in the upper right corner. Between the first and third frame, there is a B-frame. The codec, having detected a B-frame, compares the first and third frames, and calculates the intermediate value between them, thus obtaining the second frame (Fig. 4)
Figure 4. B-frame.
The more B-frames a video contains, the smaller its size. But the likelihood of artifacts associated with errors during calculations is greater.
Reasons for increasing staff turnover
Common reasons for employee turnover
Among the most common reasons that influence the instability of the subject composition of the work team are:
- Insufficient wages - very often this factor is the main lever that forces an employee to look for a new job. Uncompetitive salaries can ultimately lead to a constant outflow of specialists from the enterprise.
- Business line - retail trade and consumer services have a higher personnel renewal rate than, for example, IT or industrial production.
- Lack of promotion - a large percentage of specialists strive for professional development and stable climb up the career ladder. A company that does not meet these needs may continually suffer from a lack of labor resources.
- The actual place of work - in megacities, people often change companies, since a large concentration of competing organizations gives the employee the opportunity to choose. In small towns, people tend to hold on to their jobs due to the lack of other offers.
- Working conditions - climate, risks of industrial herbs, harmful factors affecting the health and general well-being of employees.
- The situation and relationships in the team and with management - employee outflow occurs due to a low level of communication between the manager and subordinates, tense relations between hired entities.
An approximate diagram of the costs of an enterprise when breaking a contract with a worker
The reason for termination of an employment contract can often be determined based on the length of time a person has been employed by a particular company. It is believed that dismissals in the first 6 months of performance signal the shortcomings of personnel selection when hiring. Leaving during the first year demonstrates insufficient adaptation skills of the person leaving, and the high percentage of outflow of employed persons with 3 years or more of experience indicates the instability of the hiring organization.
Formula for calculating staff turnover rate
The staff turnover rate (CTR) is determined using a special formula. For calculations you need to know the following information:
- the period for which the analysis needs to be carried out;
- number of people fired;
- indicator of the average number of employees (ASH) for the reporting period of time.
Calculation of staff turnover (formula 1)
To determine the NPV, it is necessary to regularly maintain statistics of the total number of units hired on a certain date. For example, every month, as of the 1st day, you can note how many people in total occupy their positions according to the employment contract. Some enterprises summarize information for two or three months.
All marked indicators are summed up, and the resulting number is divided by the number of months. For example, you need to calculate the NPV for the year worked. In this case, the following algorithm is used:
NFR for the year = (C1 + C2 + C3 + ….. + C12)/12
or
NFR for the year = (C1 + C2) / 2 + (C3 + C4) / 2 + ....,
where C1 is the total number of personnel for January,
C2 - for February and so on.
Correctly calculating the actual CTC is possible only if the true reasons for the departure of each person are identified. Often, in an application, a person indicates the wording “at his own request,” but in fact, the prerequisites for processing the calculation are completely different. In this regard, there is an opinion that the coefficient should be determined in a different way.
Calculation of TC (formula 2)
To understand the real picture of the variability in the composition of the team at a company, it is not enough to simply calculate the CPC. Qualitative analysis involves obtaining answers to the following questions:
- why the specialist quit;
- what was his length of service in the company;
- in which department he held the position;
- what resources should the administration use to compensate for the loss of manpower.
Important. In modern HR management, for a comprehensive assessment of the personnel status of organizations, they use the internal benchmarking method, which consists of comparing CTC for different periods of business activity.
Other indicators for TC analysis
I and P frames
Essentially, a video is a sequence of frames that quickly replace each other. If you decompose the video into successive frames and compare two adjacent frames, you will notice that they differ little from each other (Fig. 1).
Figure 1. Sequence of frames.
In the picture you see a sequence of 9 frames. In the video, frames from which are presented here, all objects are in motion. If you compare the 1st and 2nd frames, it is quite difficult to find the differences between them. More or less, the differences are visible if you compare not adjacent frames, but for example the 1st and 4th.
It is this feature that is used for video compression. Instead of recording each frame individually, the program records only the first frame (I-frame) in its entirety. The next frame (P-frame) is not completely recorded. Instead, information is recorded with reference to the previous frame, as well as information about the changed areas.
To help you better understand what I'm talking about, I'll give you an example.
Suppose there is a video: a black square, which is filmed on a multi-colored background, moves to the right (Fig. 2).
Figure 2. Recording I and P frames
As you can see in the first frame, the black square is in the center, and in the second frame it is shifted to the right.
If you imagine recording the first (I) frame in “human” language, it will look like this:
Block “a1” is red, block “b1” is white…. block “z1” is blue.
This is followed by the second line: block “a2” is blue, block “b2” is blue, .... and so on until the end, until all the blocks are described (in our example there are 64 of them), ending with “z8”.
Now comes the fun part. To record the second (P) frame, it is not necessary to re-record the characteristics of all 64 blocks.
Instead the entry looks like this:
The second frame is a copy of the first, but it has the following changes:
“g4” is red, “e4” is black, “g5” is blue, “e5” is black.
All! To record the second frame, we only needed to describe four blocks that were changed. Agree, this is much less than doing a complete description of all 64 blocks again.
This example is quite primitive. I brought it up only so that you understand the general essence. The bottom line is this: the less the second frame differs from the first, the less information is required to record it.
Standard turnover indicators
In practice, it is considered normal to have a CTC in the range from 3% to 5%. If the index value does not even reach 3%, then there is a risk of falling into a stagnation phase, since minimal personnel renewal is still necessary to improve the company’s overall achievements. It is considered a completely acceptable phenomenon for workers to retire upon reaching retirement age due to relocation and the elimination of insufficiently competent employees.
A coefficient value that exceeds 50% indicates ineffective management and unjustified costs for the constant search and training of applicants for vacant positions.
Important. Each corporation must independently calculate its optimal CPC. To do this, you need to take into account the industry direction, working conditions, salary levels, reward system and other levers of influence.
Table No. 2. Labor Code standards by industry:
| Industry | Standard TC value, % |
| High tech | 8-10 |
| Trade | 30 |
| Production | 12-15 |
| Construction, real estate | 20 |
| Hotel business, tourism | 26 |
| transport and logistic | 25 |
Table No. 3. Standards in terms of job responsibilities:
| Job title | TC norm, % |
| Leaders, top managers | 0-2 |
| Middle managers | 10 |
| Ordinary specialists | 30 |
| Operating personnel without special qualifications | 50 |
Turnover rate by industry