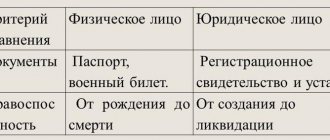
Individual entrepreneur: concept and difference from a legal entity
To understand whether an individual entrepreneur is an individual or an organization, it is important to refer to the terminology itself.
Attention! From an economic point of view, an individual entrepreneur is an individual who owns his own enterprise.
The activities of an individual entrepreneur, which are strictly regulated by law, are aimed at obtaining monetary profit.
It is important to understand that an individual entrepreneur differs significantly from a legal entity according to several criteria:
- Amount of state duty and taxation;
- Unlike legal The individual entrepreneur is not involved in the preparation of the statutory document;
- The individual entrepreneur has full control over the income received from the enterprise;
- An individual entrepreneur is one person, while a legal entity can be two or more people;
- The individual entrepreneur company cannot be sold, as it is the permanent property of the founder.
A special feature is also the status of individual entrepreneur, which is determined by government authorities before registration. The type of status received depends on the intended activities of the enterprise.
Investments
Investments? In IP? Seriously? The most you can count on is a cunning loan agreement under which the entrepreneur will take money for development. More often - a bank loan. And loans and credits need to be repaid.
An individual entrepreneur has nothing to offer an investor; he cannot “share” part of the business. It is easier for a legal entity: it is enough to issue additional shares (in a joint stock company) or increase the authorized capital (LLC). And now there is something to grow on.
What rules should an individual entrepreneur follow?
The founder of his own business is obliged to obey the laws of the state in whose territory the company is planned to be opened. As a rule, each individual entrepreneur acts on the basis of what is prescribed by law:
- Choice of activity or specialization of the enterprise (however, there are some restrictions on this depending on the region).
- Independently setting prices for goods sold or services provided.
- Concluding employment contracts with employees.
- Determination of personnel wages.
- The ability to freely analyze the economic market, highlighting the most profitable segment.
- In legal matters, an individual entrepreneur can act as a plaintiff or defendant in legal proceedings.
- He also has the right to complete control over the expenses and income of the enterprise.
In addition to rights, legislation provides for the existence of responsibilities for an individual entrepreneur. These include the following:
- Compliance with the rules and regulations of the state in which the enterprise is located.
- Payment of taxes.
- Maintaining documentation not only on economic indicators, but also on employment contracts.
- Availability of valid licenses and government permits (for example, patent).
- Mandatory official employment of employees.
Individual entrepreneur enters into employment contracts with employees
What are the main advantages of being an individual entrepreneur?
• Easy creation, that is, registration of an individual entrepreneur. Liquidation of activities is no less easy; • Distribution of funds at our own discretion without any control; • Lack of payment of taxes on property involved in business activities; • No need to keep accounting records; • Making various decisions no longer necessarily requires drawing up a written contract; • There is no tax on dividends.
The main disadvantages of an individual entrepreneur
• An individual entrepreneur is responsible for his obligations with all his property; • It is prohibited to conduct activities that require licensing. This applies to the sale of alcoholic beverages or certain medications; • Practice shows that most large customers refuse to conduct common activities with individual entrepreneurs; • An individual entrepreneur cannot be involved in running a common business; • An individual entrepreneur is his own director, so he must independently monitor the entire process of activity and ensure its proper order.
Who can become an individual entrepreneur?
All citizens of the Russian Federation who have reached the age of majority fall under this category. Foreigners can also apply for this role, but only on condition that they have a residence permit in the Russian Federation, or have a permit for temporary stay in the territory.
Liability of an individual entrepreneur before the law
An individual entrepreneur in his actions is based on the status confirmed by the state. This status is confirmation of registration; an official document regulating the rights, duties and responsibilities of the founder. Whether an individual entrepreneur is an organization or not is unimportant in legal matters, since they take into account all possible situations as much as possible.
Attention! This certificate, securing the responsibility of the individual entrepreneur, presupposes his compliance with civil, administrative and criminal codes.
Civil law
From the point of view of legislation, an individual entrepreneur is liable with his property. This is due to the fact that, as an individual, an individual entrepreneur owns a full package of documents for the enterprise. In the event of any emergency situations (business risks, claims, etc.), the founder will pay from the company’s income or, in a worse situation, its property.
Bankruptcy deserves special attention. The fact is that if the company is closed due to bankruptcy, the owner will not be able to evade paying debts. Thus, he will be forced to pay claims and bills from his own funds, which include private property.
Attention! After declaring bankruptcy, at least 5 years must pass before the bankrupt individual can file and register to conduct business again.
In the event of financial collapse, the individual entrepreneur may file for bankruptcy
Administrative legislation
Administrative law assumes that an individual entrepreneur is an official who can be held accountable in the following cases:
- violation of trade rules;
- attracting foreigners without a patent and migrants to work in companies without the appropriate documents;
- inappropriate advertising (also regulated by the law on advertising activities);
- non-payment due to administrative violations.
Administrative legislation itself contains two basic rules:
- an individual entrepreneur is a legally responsible person;
- Special sanctions may be imposed on individual entrepreneurs.
Criminal Code
In cases where there are violations in the field of criminal law, the individual entrepreneur himself may be held accountable as an individual. Thus, only one person is responsible for the company’s illegal actions, who, as a rule, is the founder of the company.
Individual entrepreneur is responsible for illegal actions under the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation
Attention! Criminal punishment will be borne by the person in whose name the business is registered, but not by employees or trustees. This is due to the fact that an individual entrepreneur is an indivisible enterprise (it cannot be transferred to relatives, friends or shareholders of the company).
Liability of a legal entity
Well, let’s create a company, get loans, pay ourselves profits, and liquidate the company? Not certainly in that way. Limited liability also has its limitations (pardon the pun).
Firstly, only civil liability is limited. And there is also, at a minimum, criminal law, which is not limited. Let's take, for example, an ordinary situation. Vasilek LLC took out a loan from a bank and used the loan to buy Aeron chairs for the employees and a Maserati for the director. There is no money, there is nothing to repay the loan with.
The bank contacts law enforcement agencies. It has grounds: “intentional failure to fulfill contractual obligations,” that is, concluding a transaction without the intention of fulfilling it - this is Article 159.4 (in the future - 159) and several years behind barbed wire. We do not have criminal liability for legal entities, which means that, at a minimum, the director of Vasilka will answer. Perhaps the company's members will also join him - if they contributed to the crime.
As they say, in the skillful hands of an investigator, a startup can easily turn into a group of persons by prior conspiracy.
Secondly, even civil liability can be shifted to the participants. Let's say, if they brought the company to bankruptcy. At the same time, the court has the right to return the money for all suspicious transactions for three years (it will not be possible to transfer the property to the mother-in-law). The real owners can be found even if they did not hold any positions in the company. If you don’t believe me, read how 75 billion rubles were recovered from Sergei Pugachev for Mezhprombank’s debts.
Thirdly, although the liability of society is limited, the responsibility of managers to society has not been canceled. That is, if director Petya (who is also a 50% shareholder of the company) withdrew a million rubles from the company to his wife’s account, the remaining shareholders can force him to return the money with interest (and then contact law enforcement agencies).
Fourthly, there are a number of situations when the company’s participants are liable for its debts. Let's say Vasya registered a company, indicated 100 thousand rubles as capital, but did not deposit it into the account. The company went bankrupt within a month. Vasya must give the creditors this 100 thousand from his own money.
So, everything is more or less clear regarding the liability of a legal entity. It is limited, although not unlimited. In the situation “we just bought AvtoVAZ when Elon Musk became the Minister of Transport” (that is, in a situation of unintentional bankruptcy), a legal entity will save you. If you deliberately get into debt, defraud business partners, or cheat with counterparties, liability is inevitable.
What about IP?
Individual entrepreneur: documents for opening and closing an enterprise
It follows from the legislation of the Russian Federation that an individual entrepreneur is obliged to prepare all the necessary documents for running a business. These official papers are equally important for opening and closing a business.
What forms do you need to fill out to open a company:
- Registration application P21001.
- Notification on the simplified tax system (it is better to prepare 3 copies).
You also need to have a receipt confirming payment of the state fee, and a copy of your passport. You can find out how much it costs to pay the state duty on the government services website or directly at the tax service, MFC.
Attention! Regardless of who submits the documents, you must provide either originals or notarized copies.
Otherwise, the application will not be considered.
To create an individual entrepreneur you will need a minimum of paperwork
Closing a business is easy. To do this, you only need a statement of desire to close the company (form P26001), a tax certificate of no debt, a copy of the Taxpayer Identification Number (TIN), and a check for payment of state duty. In terms of time, the liquidation of a company takes no more than one week, if there are no legal proceedings or problems with the tax service.
What taxes does an individual entrepreneur pay?
In Russia, every citizen must pay taxes regardless of their position in society. The same applies to owners of corporations and small businesses.
Attention! Taxation for individual entrepreneurs is divided into several categories: personal, labor, production.
Each of them represents the foundation of the relationship with the tax office.
Personal payments
These include pension and health care contributions. In total, the amount will not exceed 50,000 rubles. This is only relevant for an entrepreneur who uses his own physical capabilities when running a business.
Also, as an additional payment, the individual entrepreneur is obligated to make an annual contribution of 1% if the company’s income exceeds 300,000 rubles. This is a particular example of a business tax.
Employment taxes
Employee wages are also taxed. Recruitment of employees can occur on the basis of an employment or civil law contract.
In addition to the obligation to officially employ a citizen, the individual entrepreneur must take responsibility for withholding personal income tax (13% of staff income). This amount is later transferred to the tax office. The same applies to insurance premiums.
The legislation establishes tax payment systems for individual entrepreneurs. Among them, the following are relevant: OSN (general tax system), simplified tax system (simplified), UTII (temporary profit tax), PSH and Unified Agricultural Tax (patent and agricultural tax, respectively).
Attention! In addition, there is a special tax - NAP, which provides for payments from professional income.
Individual entrepreneurs pay a number of taxes and contributions
Production
This type of tax is relevant for the trading industry. This includes taxation on the sale of goods and services, production and exploitation of natural resources by the company (oil, gas, uranium ores, etc.).
If you have special licenses and patents, it is also important to make payments for the maintenance of animals, the exploitation of biological resources and minerals. The latter includes:
- Water resources borrowed from reservoirs;
- Land resources;
- Wildlife.
Attention! All payments must be made on time, otherwise penalties will be charged.
In case of prolonged neglect of the duties of the tax inspectorate, a claim may be filed.
Which individual entrepreneur to open or the pitfalls of individual entrepreneurship
It may seem that such a life is easy and relaxed: there is no boss who tells you what to do, you yourself recruit employees for your staff and partners with whom you will work, plus a stable income. But only those who are far from entrepreneurship can look at all these things.
Business in Russia is a very labor-intensive, responsible business that requires having a large start-up capital and often taking risks. People who got on the “wave”, which turned out to be happy for businessmen of the nineties, are now having a hard time staying in their place. What does it say about those who are just starting to develop their business?
Therefore, think very carefully about which IP to open . At first glance, it may seem that it is not worth taking on all this. But, as they say, if you are afraid of wolves, do not go into the forest. Many people are now hearing about quite a few young entrepreneurs who have quickly risen up in the business sphere. It is worth considering that if you want your business to become successful, then you need to take it seriously and approach it wisely.
You will ask yourself: “Which IP should I open?” The sales sphere is always relevant, whether there is a crisis in the country or a stable financial situation, people always buy what they need for life. Resourceful and enterprising people always turn to sociologists in such matters, who carefully examine the consumer market and come to a conclusion.
Advantages and disadvantages of individual entrepreneurs
IP has its advantages and disadvantages. To understand exactly what the pros and cons of individual entrepreneurship are, it is worth studying not only the regulations, but also the reviews of the company owners themselves.
The advantages of IP include the following factors:
- Easy and affordable business registration. Opening an enterprise will take about 3 days, during which it is possible to draw up documents and obtain signatures from government authorities. To do this, you need to prepare an application in advance, filled out in accordance with form P21001, pay a tax of up to 1,000 rubles and receive a tax number.
Attention! When completing documents online, you do not need to pay a tax fee.
Individual entrepreneurs do not have to stand in long lines to receive a package of documents; just download the form in your personal account.
- Financial independence. The individual entrepreneur not only manages the cost of goods and services, the amount of wages, but also the financial support of the company. Also, the manager can withdraw funds from the company’s account through the terminal at any time.
- Simple reporting form. An individual entrepreneur is not required to maintain the same amount of documentation that is maintained by a representative of an LLC. They may be limited to quarterly and insurance reports.
- Fines and closure. An individual entrepreneur can be closed within one week by submitting an application to government authorities, in particular, the tax service. The amount of fines will also please the entrepreneur, since it is several times lower than that of the owners of an LLC or other legal entity.
In turn, IP also has disadvantages. These include:
- Mandatory contributions. Individual entrepreneurs must start paying insurance premiums immediately, that is, immediately after opening the company. The minimum contribution amount is constantly changing, so the entrepreneur needs to recheck the data annually. So, in 2020 the insurance premium was about 37,000, and in 2020 – 41,000 rubles.
From the moment of receiving the certificate, the individual entrepreneur is required to make contributions
- Economic responsibility. The individual entrepreneur bears full responsibility in cases where litigation takes place. Even if the company is officially declared bankrupt, the founder of the company is obliged to pay wages to each employee, government agency (taxes, loans, etc.). That is why, before you start working, you should draw up a business plan and take into account all the risks.
Attention! The only apartment or house, furniture and car cannot be used to pay off debts.
- Type of activity. A company that positions itself as an individual entrepreneur can engage in activities in limited areas: trade, tourism, insurance, security, etc.
- Integrity of the company. Individual entrepreneur is a single person, one owner. Therefore, the company cannot be inherited. There should also be no sale of shares to shareholders or investors.
Individual entrepreneurship in Russia: pros and cons
In the modern world, in the era of broad economic opportunities and the development of private property, a person is often faced with such a concept as “individual entrepreneurship.” What is the essence of this type of activity, what are its main purpose and features? What laws regulate private entrepreneurship and how to obtain the status of an individual entrepreneur? We will try to answer these and many other questions in our article.
The concept of individual entrepreneurship
French economists first began to use the concept of “entrepreneurship” in their vocabulary. Among them we can highlight Jean-Baptiste Say. However, we owe the appearance of this term to the Irish entrepreneur and economist Richard Cantillon, who uses it in his work “An Essay on the General Concepts of the Nature of Trade.” Unfortunately, many of the terms about entrepreneurship existing in modern economic sources do not fully reveal the entire essence and multifaceted aspects of its functioning.
The concept of “individual entrepreneur” is understood as an individual (citizen) who carries out personal business on his own behalf at his own expense and at his own risk, who independently makes decisions about the development of his farm and the methods he uses in production processes, the main goal of which is to systematically obtain arrived. [1]
The history of the origins of individual entrepreneurship
First stage
The introduction of possession law in 1721 had a major impact on the development of entrepreneurship. It allowed merchants to acquire villages and peasants to work in their enterprises.
In 1698, Peter I issued a decree according to which merchants could pool their capital and organize joint production. The government provided them with various benefits.
The reforms carried out by Alexander II contributed to the division of Russia into pre-reform and post-reform periods. The manifesto of February 19, 1861 marked the abolition of serfdom, and peasants had the opportunity to become entrepreneurs.
Second phase
In the 19th-20th centuries, entrepreneurship goes through a radical stage of change. Workers in light industry are being replaced by factory owners in heavy industry.
The Ryabushinsky family played a special role. In the middle of the 19th century. they set up textile factories. In the second half of the century, they decided to expand the range of their activities and engaged in credit operations, tried their hand at linen, paper and printing. Let us also remember the names of the following great entrepreneurs and philanthropists: Pavel Tretyakov, who gave the country his art gallery, founded the Savva Mamontov Opera House, Alexander Sibiryakov, who donated money to open a university in Siberia, and others.
Third stage
In the USSR, entrepreneurial activity was completely under the control of the state and was prosecuted by law.
At the end of the 80s, Russia began to actively introduce a market mechanism. A new period begins in the history of the development of Russian private entrepreneurship.
Fourth stage
In 1987, the Law “On Individual Labor Activity” was signed. This act made it possible to become a private entrepreneur in such areas as crafts, consumer services, etc. Gradually, the number of individual entrepreneurs began to grow. [3]
Individual entrepreneurship in the modern world
Individual entrepreneurship has its own characteristics, features that determine its character: the principle of independence, independence of decision-making by participants in economic relations. This principle is based on the goals of the entrepreneur; he independently determines the form and structure of economic activity, taking into account economic benefits. Also, the entrepreneur bears full property liability for all his duties (Article 24 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation) and for his activities to society. Compliance with this principle places the entrepreneur within a fairly strict framework, the violation of which is prohibited by law. Every entrepreneur strives to create something new, putting his own efforts into it. Thus, it ensures the high quality of its products and increased consumer demand. It is also necessary to highlight such a feature as the risk of losing one’s property. The risk of losing one's material resources contributes to the emergence of a spirit of competition and extraordinary thinking, and an increase in efficiency.
An important role in the development of individual entrepreneurship is played by legislative acts regulating the implementation of entrepreneurial relations. Such an act in the Russian Federation is the Federal Law “On State Registration of Legal Entities and Individual Entrepreneurs” (No. 129-FZ), adopted on August 8, 2001 (last amended on December 31, 2014), which describes the procedures for carrying out state registration and entering the relevant entries in the Unified State Register of Individual Entrepreneurs. Also, paragraph 1 of Article 23 of the Civil Code indicates that a citizen has the right to engage in entrepreneurial activity without forming a legal entity from the moment of state registration as an individual entrepreneur. And clause 1 of Article 25 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation states that an individual entrepreneur who is unable to satisfy the demands of creditors related to his business activities may be declared insolvent (bankrupt) by a court decision. Along with legislative acts on state registration of individual entrepreneurs, there are also acts authorizing the implementation of certain activities. Federal Law of the Russian Federation “On licensing of certain types of activities” (No. 99-FZ), adopted on May 4, 2011 (last amended on December 31, 2014). This law specifies the main purposes, principles of licensing and powers of licensing authorities. They also highlight the Federal Law “On the Protection of the Rights of Legal Entities and Individual Entrepreneurs in the Exercise of State Supervision and Municipal Control” (No. 294-FZ), adopted on December 26, 2008 (last amended on December 31, 2014). [2]
Opportunities for future development of individual entrepreneurship
In the conditions of modern Russia, the question arises: are there opportunities for the development of individual entrepreneurship? It is very difficult to find an answer to this ambiguous question. It is necessary to analyze all the factors influencing business activity.
Firstly, the state policy of the Russian Federation plays an important role in the development of individual entrepreneurship, aimed at supporting entrepreneurs by paying subsidies and issuing loans as financial assistance for starting their own business. But on the other hand, all these cash payments are not enough to cope with the rising prices caused by the corruption of officials in the country.
Secondly, the legal and legislative framework is also important, providing conditions for entrepreneurship. Legislative acts existing in Russia on the registration of individual entrepreneurs and licensing of certain types of activities, as well as laws on the protection of the rights of entrepreneurs, contribute to a clear definition of the operations performed by participants in business relations.
Thirdly, it is also necessary to create “reasonable” tax legislation that does not turn the payment of taxes by beginning entrepreneurs into heavy debt slavery. After all, this only leads to a complete loss of creative initiative by entrepreneurs. Therefore, it is necessary to mitigate the tax burden for beginning individual entrepreneurs.
Comparative analysis of individual entrepreneurship
A) Advantages of individual entrepreneurship:
Firstly, the ability to carry out entrepreneurial activities without large initial capital. Entrepreneurs invest a small amount of money in their own business, and when they receive their first profit, they use it to further develop their activities.
Secondly, the absence of discrimination in the implementation of individual entrepreneurship on grounds such as gender, age, race, language, and social status.
Thirdly, the simplest procedure for state registration and termination of business activity. Therefore, in case of failure and loss of economic benefits, it is easy to stop the activity.
Fourth, independence in making instant decisions. This ensures the development of flexible and extraordinary thinking, as well as an incentive to work more productively only for yourself.
Fifthly, the simplicity of preparing accounting and tax records. An entrepreneur can keep records on his own without spending money on the services of people specially trained for this.
B) Disadvantages of individual entrepreneurship:
Firstly, there are insignificant opportunities and territories for the implementation of entrepreneurial activities, limited by the amount of available capital;
Secondly, bearing full property liability for all one’s obligations and debts;
Thirdly, obstacles in obtaining permits to engage in certain types of activities;
Fourthly, the impossibility of carrying out large-scale production, therefore, limitations in their competitiveness;
Fifthly, the impossibility of using more hired labor due to the limited availability of capital. [4]
Conclusion
Thus, in conclusion, I would like to note that individual entrepreneurship is a significant and serious step in the development of modern entrepreneurial activity. Despite the fact that this organizational and legal form has many pitfalls, this type of entrepreneurship undoubtedly has the right to further existence and improvement.
Literature:
1. https:// www.base.garant.ru/10164072/
2. https://www.consultant.ru
3. Kireev A. A. International economics. - M., International Relations, 1997.
4. Shevchenko I.K. Organization of entrepreneurial activity. Textbook. - Taganrog: TRTU Publishing House, 2004.