Trade is subject to the laws of the market, and the market is a dynamic, living and constantly changing factor. Therefore, to conduct business in the trade sector, additional levers are needed to increase the efficiency and stability of market processes.
One of these tools for interaction between manufacturers, suppliers and sellers is the system of retro bonuses, which is widespread in the West and is gradually taking root here.
Let's consider the features of the domestic application of a retrospective discount, the intricacies of its tax and accounting, as well as registration rules, and introduce the latest legislative innovations in this area.
The meaning of retro bonuses
Any broad trading activity is based on the mutually beneficial cooperation of three key participants:
- manufacturer;
- distributor;
- retailer.
Each participant in this chain is maximally interested in “presence” on the market, that is, exercising influence and establishing favorable conditions. Therefore, a tool that provides benefits equally to all participants will be effective and in demand, and will increase business productivity and efficiency.
It is beneficial for manufacturers that their products are in demand from distributors; suppliers want sellers to purchase goods at favorable prices, and they, in turn, strive for profitable sales. If the latter is successful, then each participant benefits.
That’s why a system of retrospective discounts on goods, or in common parlance, retro bonuses or rebates, was invented.
The seller was able to sell a sufficient quantity of goods or earn a certain amount for it, which means he has the right to return part of the funds, receive additional goods, provide a free service, or provide a discount.
The bonus bonus is provided “from top to bottom” - by manufacturers to suppliers or distributors to retail distributors. Thus, distributors may find themselves in the position of both receiving and providing retro bonuses.
REFERENCE! The word “bonus” is translated from Latin as “good”, “to deserve”; in the field of marketing, this term means an incentive bonus, bonus, reward beyond what was expected. A retrospective discount on a product in Russia is more often called a “retro bonus”, and in Western practice the English word “rebate” is more commonly used, meaning a discount or concession.
Accounting: bonus
Having provided a bonus, two business transactions must be reflected in accounting:
- discount on previously shipped goods, work performed or services provided;
- sale of goods, works or services against the resulting accounts payable to the buyer.
Reflect the first business transaction in the manner prescribed for reflecting the discount.
On the debt incurred, charge VAT on the advance payment. After all, money that was received earlier cannot be considered payment for goods that have already been shipped. In essence, this is an advance payment (letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated August 31, 2012 No. 03-07-15/118).
In accounting, reflect the recognition of recovered accounts payable in advance and the sale of goods against this advance with the following entries:
Debit 62 subaccount “Settlements for shipped products” Credit 62 subaccount “Settlements for advances received”
– the amount of the restored debt is recognized as an advance received against a future bonus delivery;
Debit 76 subaccount “Calculations for VAT on advances received” Credit 68 subaccount “Calculations for VAT”
– VAT is charged on the prepayment amount, that is, the recovered debt.
After shipping a bonus shipment of goods, performing an additional amount of work or services, make the following entries:
Debit 68 subaccount “Calculations for VAT” Credit 76 subaccount “Calculations for VAT on advances received”
– VAT accrued on prepayment is accepted for deduction;
Debit 62 subaccount “Settlements for shipped goods” Credit 90-1
– revenue from the sale of bonus goods (works, services) is reflected;
Debit 90-3 Credit 68 subaccount “VAT calculations”
– VAT is charged on proceeds from the sale of bonus goods (works, services);
Debit 90-2 Credit 41 (20)
– the cost of sold bonus goods (work, services) is written off;
Debit 62 subaccount “Settlements for advances received” Credit 62 subaccount “Settlements for shipped goods”
- prepayment has been credited.
What can they provide a retro bonus for?
The conditions for providing a rebate should always be specified when concluding an agreement, since they can vary greatly. The system of retrospective discounts for goods is a flexible system that allows you to find the optimal implementation option in each specific case. Most often, the conditions under which distributors or sellers can count on bonuses are based on fulfilling or exceeding the following obligations:
- the sales plan indicators have been achieved - if the agreed volume of goods is sold or the stipulated amount is received for it, this indicates activity in the market; using this method, it is more convenient to regulate the sales of specific types of goods or these processes in a certain market segment;
- impeccable monetary discipline - when all the terms of the transaction are met “without a hitch”, including payment and delivery deadlines, an additional bonus may be offered for this;
- good distribution indicators - for which suppliers or manufacturers can reward their counterparties when they promptly and in the required quantities supply goods to retail chains; Other criteria for the quality of suppliers’ work are also possible;
- new customers - expanding the distribution network is beneficial not only to the distributors themselves, but also to manufacturers, and additional bonuses can be provided for this.
Promotion does not change the price
If the incentive does not change the price, then the income tax basis does not need to be adjusted. Incentives of this kind must be taken into account as part of non-operating expenses in relation to:
- goods - on the basis of subclause 19.1 of clause 1 of Article 265 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation;
- works, services - on the basis of subparagraph 20 of paragraph 1 of Article 265 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
A similar point of view is reflected in letters of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated July 23, 2013 No. 03-03-06/1/28984, dated December 19, 2012 No. 03-03-06/1/668, dated September 27, 2012 No. 03 -03-06/1/506, dated April 3, 2012 No. 03-03-06/1/175.
When using the accrual method, expenses in the form of incentives provided to the buyer are taken into account when calculating income tax in the reporting (tax) period to which they relate. This is established in Article 272 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
When using the cash method, expenses in the form of incentives provided to the buyer are taken into account when calculating income tax in the reporting (tax) period in which:
- paid the buyer a premium;
- transferred goods provided as a bonus or gift, but only if it was paid to your supplier;
- at the time of debt forgiveness, if a discount is provided that does not reduce the price. All other discounts reduce the price.
This follows from the provisions of paragraph 3 of Article 273 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Document the provision of incentives to the buyer in a deed.
Types of retro bonus rewards
A retro bonus honestly earned by a supplier or distributor of retail chains can be received in various forms, pre-fixed in the text of the concluded contract or additional financial agreements.
There are several main options for providing retro bonuses:
- Monetary equivalent. The counterparty, as it were, receives back part of the amount received by him for the goods delivered or sold to the final consumer. In this case, additional conditions are stipulated:
- the time during which goods are sold and, accordingly, bonuses are paid;
- volume or amount upon reaching which the reward is due;
- cash return percentage.
- Preferential purchase price. The distributor or seller receives the right to purchase goods at a more favorable price, under special conditions, which must be documented. This bonus is usually valid for a limited time.
- Additional item supplied free of charge. This is a convenient and easy-to-account method of retrospective discounting. An important point that needs to be taken into account is the emerging VAT obligations of the distributor and the need to take into account the gross income of the recipient.
- Preferential or free delivery of goods. This bonus service also includes additional tax obligations for both parties.
- Option . This is a method of mutual payment in non-monetary form, for example, goods or the provision of reciprocal services. The terms of the contract or agreement must specify the deadlines for fulfilling bonus obligations, their form and, if necessary, deferment.
IMPORTANT! To avoid the risk of trouble with the tax authorities, the size of any retro bonus should not exceed 10% of the amount or volume of the transaction.
Promotion changes price
Accounting for the calculation of income tax using the accrual method depends on when the incentive that changes the price was provided - in the same reporting (tax) period in which the sale took place, or in subsequent ones.
So, if the incentive was provided in the same period, then adjust the basis for calculating income tax in the current reporting (clause 7 of Article 274 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
If a decrease in the price of goods affects the seller’s tax obligations for income tax in past reporting (tax) periods, then you can do one of the following:
- submit updated income tax returns for previous reporting (tax) periods;
- do not submit updated returns, but recalculate the tax base and the amount of tax for the period in which the incentive was provided, and reflect this in the tax return for the same period;
- do not take any measures to adjust the tax base (for example, if the amount of overpayment is insignificant).
Similar clarifications are contained in the letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated May 22, 2020 No. 03-03-06/1/29540.
For more information about this, see In what cases you need to file an updated tax return.
As for the cash method, sales income is recognized on it on the date of receipt of money from customers. Accordingly, there will be no need to adjust revenue after the incentive is provided. Even if it is a retro discount, that is, when the price of an already sold product changes. Indeed, in this case, the money received earlier must be reclassified as an advance, and under the cash method it is also taken into account in income. This means that the tax base will not change in any way. This follows from paragraph 2 of Article 273 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation and is confirmed in the letter of the Federal Tax Service of Russia for the Moscow Region dated October 5, 2006 No. 22-22-I/0460.
The costs associated with providing a premium, bonus or gift to offset price changes should be taken into account in the same way as in a situation where prices do not change.
Documentation of rebate
As mentioned above, a retro bonus discount in trade is necessarily regulated by regulatory documents. The main act regulating the “bonus” relationship is an agreement or additional trade agreement on retro bonuses. Key points to be covered in this document:
- the provision of retro bonuses is recorded in the title of the document next to the name of the action (“delivery of goods”);
- the conditions for providing a rebate are specified in the last paragraph stipulating contractual actions, under the title “Financial conditions and settlement procedures”;
- the price of the goods agreed upon by the parties and the method of payment (cash or non-cash) are indicated;
- form, timing, size and features of retro bonus accrual.
FOR YOUR INFORMATION! To reduce possible tax and partner risks, it is recommended to list in detail the groups of goods that are subject to the retrospective discount, or their names, to correctly use the units of measurement of the product (liter volume, packing unit, weight, piece, etc.), and also to describe in detail the retro mechanism itself -bonus.
What are additional retro bonuses and why are they needed?
Despite the fact that the retro bonus has documentary evidence in the form of a legally binding contract, which clearly states the cost of goods, in reality it happens that the price of products already shipped and received by the buyer may be subject to revision downward. So, for example, if a purchase contract was signed in one tax period, and the shipment was made in the next tax period, the supplier has the right to make a post-discount on the price of the goods.
The accounting department carries out this retro discount using a negative invoice. The use of such a document has been legal and legal from the point of view of the law since October 2011. Applying for this discount is not that difficult:
- The supplier issues a correction invoice.
- The seller notifies the buyer of the fact of a price reduction; this is done due to the need to document the recipient’s consent to the change in the price of the product.
- Having carried out the above actions, the supplier has the right to issue a retro discount as a special type of retro bonus.
Retro bonuses: tax and accounting
Taxation on rebates depends on several factors.
- Is VAT charged ? In most cases, bonuses received do not cancel the payment of value added tax on them. If the rebate is immediately increased by tax 18%, the amount will be too significant and unprofitable to return.
- Group of goods – food or non-food (they are subject to VAT differently). The price of food products usually already includes VAT, so when receiving a retro bonus you need to take into account the full cost.
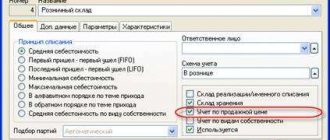
In accounting, retro bonuses can be reflected in different ways:
- be attributed to the cost of production - best regulates pricing policy, the most transparent accounting tool;
- to be attributed to the result is the most convenient method that allows you to systematize monetary transactions, organize them on any basis, and also, if necessary, adjust the value.
Accounting: discounts
Discounts are provided by:
- at the time of sale or thereafter in respect of future sales;
- after the sale - in relation to goods sold, work performed or services provided. These are so-called retro discounts.
If a discount is provided at the time of sale or after it for future deliveries, then for accounting purposes this can be considered a sale at the price agreed upon by the parties. In this case, the established price may be less than what the seller declares under normal conditions. There is no need to reflect such a discount in accounting. You just need to reflect the implementation using standard postings.
Record the fact of implementation with the following entry:
Debit 62 (50) Credit 90-1
– sales revenue is reflected taking into account the discount.
If you pay VAT and it is levied on goods (works, services), then simultaneously with the sale, reflect its accrual as follows:
Debit 90-3 Credit 68 subaccount “VAT calculations”
– VAT is charged on the actual sales amount;
Well, when you receive payment into your bank account, make the following entry:
Debit 51 Credit 62
– payment has been received from the buyer taking into account the discount.
This procedure follows from the Instructions for the chart of accounts (accounts 50, 51, 62, 68 and 90), paragraph 6 of PBU 9/99 and is explained in the letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated February 6, 2020 No. 07-04-06/5027.
If a discount is provided on a product, work or service that has already been sold, then reflect it in accounting depending on when the buyer was rewarded:
- before the end of the year in which the implementation took place;
- after the end of the year in which the implementation took place.
The discount was provided in the same year in which the sale took place. Adjust sales revenue for the period by the amount of the incentive at the time it was granted. In accounting, reflect such transactions as follows.
At the time of sale, before the discount is granted, complete the usual transactions:
Debit 62 Credit 90-1
– revenue from sales is reflected;
Debit 90-3 Credit 68 subaccount “VAT calculations”
– VAT has been charged (only post if you pay tax and sales are subject to it).
At the time of discount:
Debit 62 Credit 90-1
– revenue from previously shipped goods, works, and services is reversed in the amount of the discount provided.
After issuing an adjustment invoice to the buyer:
Debit 90-3 Credit 68 subaccount “VAT calculations”
– VAT is reversed from the amount of the discount provided.
This procedure is established by paragraphs 6, 6.5 of PBU 9/99.
The discount is provided in periods following the year in which the sale took place. Reflect it as part of other expenses in the current period as of the date of provision (clause 11 of PBU 10/99).
When identifying expenses from previous years in accounting, make the following entry:
Debit 91-2 Credit 62
– losses from previous years associated with the provision of a discount to the buyer (excluding VAT) were identified.
After issuing an adjustment invoice to the buyer:
Debit 68 subaccount “VAT calculations” Credit 62
– VAT is accepted for deduction from the amount of the discount provided.
This procedure is established by paragraph 39 of the Regulations on accounting and reporting, the Instructions for the chart of accounts (account 91), paragraphs 6 and 6.4 of PBU 9/99 and is explained in the letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated February 6, 2020 No. 07-04-06/5027 .
Providing a discount (including in cash), which does not change the price of the goods under the terms of the contract, should be considered as a sale of property.
In accounting, reflect the provision of such a discount in the form of an additional batch of goods with the following entries:
Debit 62 Credit 90-1
– revenue from the sale of a consignment of goods within the discount is reflected (in the amount of the discount);
Debit 90-3 Credit 68 subaccount “VAT calculations”
– VAT has been charged (only post if you pay tax and sales are subject to it);
Debit 90-2 Credit 62
– the amount of the discount provided to the buyer is included in the cost price (excluding VAT).
This order follows from the Instructions for the chart of accounts (accounts 41, 62, 68, 90).
If you provide a discount in cash, then make the following entries in your accounting:
Debit 90-2 (44) Credit 62
– a cash bonus has been awarded to the buyer;
Debit 62 Credit 51
– premium paid to the buyer.
This order follows from the Instructions for the chart of accounts (accounts 51, 62, 68, 90).
Innovation in the retro bonus system from Russian legislators
On June 24, 2020, the State Duma adopted, and on June 29, the Federation Council approved amendments to the Trade Law “On Amendments to the Law “On the Fundamentals of State Regulation of Trade Activities in the Russian Federation.” As part of this law, the maximum amount of retro bonuses has been halved (from 10% to 5%), and there are changes in the timing of the deferment. The amount of administrative fines for violation of obligations has also been revised.
The consequences of the introduction of the new norm of the law are still unpredictable; it has been accepted ambiguously by the public, suppliers and sellers.