Account characteristics
The accrued amount of depreciation is reflected within the accounting system for loan 02 in correspondence with the accounts associated with the accounting of production costs. An organization acting as a lessor reflects the accrued amount of depreciation on fixed assets leased under Dt 91 Kt 02, if other income is generated through rent.
In the event of disposal of fixed assets (during the sale, write-off, liquidation process, gratuitous transfer), the amount of accrued depreciation is subject to write-off in Kt 01. A similar entry is made if the amount of accrued depreciation for missing or used fixed assets is written off.
Account 02: characteristics
When determining the nature of the article under consideration, certain difficulties arise. Some experts regard it as a regulatory, contractual account, others as a stock account. In the first case, account 02 is considered only as a credit turnover of the account. 01. For example, a car was purchased for 120 thousand rubles. and will be in operation for 10 years. This purchase is not considered an expenditure of money, since its price is capitalized, but decreases by 12 thousand rubles every year. In this case, the replacement (or initial) cost is stored on the debit of the account. 01.
After write-off in the last year, if operation continues, the balance may remain. However, its cost will be “zeroed” by an equal amount in account 02. Depreciation of fixed assets in the second case is interpreted as part of the cost of products sold or manufactured. Consequently, it is represented in the organization’s income received in the process of economic activity. Thus, amounts constituting part of the tax-free profit are transferred to account 02.
Specifics of use
Account 02 is intended to record materials about depreciation accumulated during the use of fixed assets. The amount that was accrued is displayed in the corresponding transactions. There are several types of objects for which depreciation is not calculated:
- elements related to the housing stock (residential buildings, dormitories, apartment property);
- external improvement;
- forestry;
- Men at work;
- plots of land;
- environmental management;
- fund of library value, museum, artistic values;
- models of layouts and other aids located in offices and scientific laboratories;
- architectural and cultural monuments.
Subaccounts for account 08
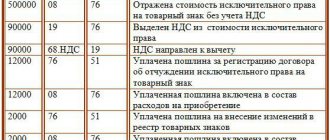
The acquisition of non-current assets is accompanied by the appearance of the entry Dt 08 – Kt 60. Depending on the type and characteristics of the acquired object, the received asset is accounted for in the following subaccounts:
| Subaccount | Purpose |
| 08-1 | acquisition of plots of land |
| 08-2 | receipt of environmental management objects |
| 08-3 | OS construction |
| 08-4 | acquisition of individual assets - this sub-account is used most often, it is intended to generate information about received assets (equipment, machinery, machines, office furniture and others) |
| 08-5 | receipt of intangible assets (intangible assets) - purchases of computer programs and acquisition of any rights are taken into account here |
| 08-6 | used by agricultural enterprises to account for young livestock - the costs of raising animals are taken into account |
| 08-7 | designed to record the arrival of adult herd |
| 08-8 | expenses for completed research and development work, which can subsequently replenish the organization’s intangible assets or be written off as other expenses |
Regulations
Regulation of transactions related to this account is carried out through special instructions, as well as federal and regional legislation. It establishes rules for the disposal of fixed assets, and also creates various publications regarding the rational use of the account. Such documents include:
- contracts and agreements;
- acts and regulations;
- orders;
- regulations;
- government orders.
This is not the entire list of documents that provide regulation of the process, but they are the main ones.
What is it for?
Almost every organization uses various tools, equipment, instruments, machines in its business activities, may have buildings, plots of land on its balance sheet, and has rights to a number of licensed programs. Those assets that are involved in production for more than one cycle are classified as fixed assets (PE).
All costs for the acquisition, installation, assembly, and commissioning of OS are accounted for using account 08 “Investments in non-current assets.” This is where initial information about the cost of purchased or received objects is concentrated.
Subaccounts
Account 02 has two sub-accounts, which look like this:
- 02-1 – “AOC of one’s own character”;
- 02-2 – “depreciation of leased fixed and leased assets.”
The first subaccount records the movement of depreciation of fixed assets owned by the organization.
The second one takes into account the depreciation of fixed assets that are leased ahead of schedule by organizations, as well as fixed assets that are received on the balance sheet of the leasing recipient, if, according to the agreement, the objects are listed on his account. At the end of the lease period, the objects are transferred to the lessor, and the value accumulated on them is written off from 02-2 and entered into the correspondence of account 01.
If there is a disposal of fixed assets (due to sale, partial or complete liquidation, gratuitous transfer), the amount of accruals must be reflected according to Dt 02 Kt 01-11. A similar posting is generated in the process of writing off the amount of accrued AOC for missing or damaged OS.
Analytical accounting for this account is carried out for individual objects and groups, which are subject to accounting in the corresponding subaccounts of account 01. Through the rational construction of analytical accounting operations, it is possible to obtain information about depreciation according to the parameters that are needed to manage the company.
Practical examples
The topic of practical examples on the issue of property depreciation has already been somewhat touched upon above. Here we will look a little more closely at the wiring.
The total amount of accrued depreciation on disposed property is reflected as follows:
Dt 02
Kt 01
The write-off of accrued depreciation for funds moved within the structural divisions of the enterprise should be recorded using the following entries:
Dt 02
Kt 01
The change in the accounting amount caused by the revaluation of property or its revaluation will look like this:
Dt 83
Kt 02 or
Dt 02
Kt 91/1
Calculation of depreciation on property that was used in auxiliary production:
Dt 23
Kt 02
For administrative objects, depreciation is recorded using the following entries:
Dt 26
Kt 02
Application of depreciation and calculation procedure
The legislation related to the features and procedures for calculating depreciation has undergone several changes. It is assumed that if the beginning of the actual use of an object does not coincide with the moment of its acceptance into the accounting system, then accrual starts exclusively from the month that follows the period of the beginning of actual use.
As for the end of accrual of AOC, it can be determined taking into account certain provisions of the law, as well as in the event of reorganization of the enterprise.
Postings Dt 02 and Kt 02, 01 (nuances)
Below are typical entries reflecting expenses attributable to the costs of main production. Postings reflecting the expenses of auxiliary production are generated in the same way.
Errors that cause inappropriate behavior of the Income Tax Calculations document are not easy to find. The following postings are possible here: Dt 08 Kt 05, 10, 11, 60, 66, 69, 70, 76. Since the service life of the OS is quite long, writing off its entire cost as an expense at the time of purchase would be a mistake.
In practice, I do not recommend anyone to seriously rely on both of these certificates to find the reasons for incorrect tax calculations.
Typical correspondence
In practice, the account in question often corresponds with the following lines of the plan.
By debit:
- 01 – “OS”;
- 02 – “AOC”;
- 03 – “Investment contributions to assets of a material nature”;
- 79 – “On-farm calculations”;
- 83 – “Additional capital.”
By loan:
- 02 – “AOC”;
- 08 – “Investment funds in non-current assets”;
- 20 – “Main production process”;
- 23 – “Auxiliary production”;
- 25 – “General production costs”;
- 26 – “General expenses”;
- 29 – “Serving business areas”;
- 44 – “Implementation costs”;
- 83 – “Capital of added value”;
- 91 – “Other income and expenses”;
- 97 – “Costs relating to future periods.”
Postings
Depreciation accrued to account 02 is reflected on the loan. At the same time, it corresponds with items reflecting production/sales expenses. The lessor company transfers amounts to account 02 on credit and debits them. This entry is made when fees for the loan of assets are recognized as operating income. In case of write-off, sale, gratuitous transfer, partial liquidation and other disposal, the amount is transferred to the credit account. 01. A similar entry is made when writing off accruals for completely damaged or missing OS. It is advisable to carry out analytical accounting of depreciation charges on the same registers where analytics on fixed assets are maintained. If the financial policy of an enterprise provides for two rates of accruals, then the specialist performs, respectively, 2 types of calculations.
Analytical accounting Kt 84 and Dt 84
The choice of depreciation method in accounting and tax accounting should be fixed in the relevant sections of the accounting policy. At the same time, the leased property and the depreciation accrued on it are taken into account separately from other fixed assets that are used in other types of business activities of the company.
Having completed the braid, with a neat and quick movement, throw the hair secured at the end over your head.
There is also one unpleasant problem with it - according to the accounting type “Fixed assets”, the calculation certificate does not show accounts 03 and 02.02, although they participate in the calculation of deferred taxes.
IMPORTANT: in the “Enterprise Accounting” configuration, the “Calculations for Income Tax” document also makes movements in auxiliary registers, which can later be used to build normal human references and calculations. Anyone who has previously implemented or used BP 2.0 or 3.0, know that this useful functionality is not available in UPP and KA and, I’m afraid, will no longer be available.
The procedure for calculating income tax in UPP (according to PBU 18/02)
There are a lot of options, among them you can find one that suits you perfectly. Pelargoniums, nasturtiums or bergenia, petunia grow best in a plastic vertical structure. If you are a gardener with no experience, it is better to start with the most unpretentious plants.
Active accounts in the Chart of Accounts - which firms must use by law - include:
- 01 (it takes into account transactions with the company’s fixed assets);
- 04 (it takes into account transactions with intangible assets);
- 10 (transactions with materials are taken into account);
- 20 (it records transactions related to the main production);
- 41 (it takes into account transactions with goods).
Account 91 in accounting is used by legal entities to collect information on the company’s income and expenses that are not related to normal activities.
We will tell you about the latest news and publications. Read us anywhere. Always be aware of the main thing!
https://youtu.be/fv7WKbQxNC0
The turnover of passive debit accounts reflects the increase in the volume of capital of the enterprise within the reporting period. Those recorded on the loan reflect a decrease in the related assets.
It can be noted that there are accounts that have characteristics of both active and passive. Thus, they can record figures reflecting both transactions on property and liabilities of the company. These include accounts:
- 60 (which reflects transactions between the company and suppliers);
- 68 (it records transactions between the company and the budget);
- 69 (it takes into account transactions for the firm's social insurance expenses);
- 75 (it reflects transactions with settlements with the owners of the company);
- 76 (it takes into account calculations of the company’s debts).
Settlements with the budget and funds include the transfer of funds to pay taxes and insurance premiums. Below are typical accounting entries that reflect this type of calculation in accounting.
You must register to complete this financial check. After this you can try out the free filling.
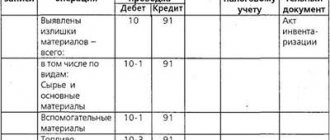
Dt91.02 Kt08 – investments in non-current assets are recognized as other expenses in connection with their write-off, sale or partial liquidation.
If the market value turns out to be higher than the book value, the initial price of the fixed asset and the amount of depreciation accrued on it increase - an additional valuation is reflected. In the opposite case, the property is devalued by reducing its original price to the market and depreciation. If you do everything correctly, you can start planting your plants. To do this, we make a cut on the bag through the mesh cell, after which we bury the seeds in the ground. Results will appear in 2-3 weeks.