In this lecture we will cover the following topics:
- Introduction
- Account characteristics 04.
- Accounting for receipt of intangible assets (Accounting for the purchase of intangible assets, Creation of intangible assets, Receipt of intangible assets free of charge).
- Accounting for the disposal of intangible assets (Sale of an intangible asset, Write-off of obsolete intangible assets, Gratuitous transfer of intangible assets)
- Depreciation of intangible assets
INTRODUCTION
Intangible assets are those assets that are capable of bringing economic benefits without having a tangible form, and are used for more than 1 year.
For example, these are assets such as:
- Web site
- Patents
- know-how
- Computer program for ownership (not 1c).
- Database.
- R&D that gave a positive result.
- Business reputation. (When purchasing an organization if the value of the assets is less than the purchase price)
The most important regulatory document for accounting for intangible assets (INA) is PBU 14/07 (read this PBU, if not as a primary source). Instructions for using the chart of accounts for accounting for intangible assets include account 04. (more on this account later).
To accept an asset as an intangible asset, the following condition must be met:
- An asset can bring economic benefits (for example, you created a website and your sales increased).
- The asset will be used for more than one year.
- The firm does not plan to sell this asset within 12 months.
- The asset does not have a material form (For example, it cannot be touched).
- Documentary confirmation of the presence of intangible assets.
- The cost can be determined.
Intangible assets are registered at their original cost. what the initial cost . The initial cost of an intangible asset is all acquisition costs (purchase) + the price of the intangible asset.
These are expenses such as:
- Amount paid to the supplier of intangible assets
- Fees
- Non-refundable taxes.
- Consulting services.
- Also other costs for the acquisition of intangible assets.
If the company created the intangible assets itself, then the following expenses:
- Accrued expenses for the contractor (for performing work).
- Wages for employees involved in the creation of intangible assets
- Salary insurance premiums.
- Other expenses.
Depreciation is calculated on intangible assets. That is, the cost of intangible assets is transferred to production costs (account 20, account 26, etc.), to sales costs (account 44). Crediting account 05.
PBU provides the following methods for calculating depreciation:
- Linear method.
- Reducing balance method.
- Proportional to the products produced.
We will consider these methods in the following lessons. Depreciation begins to accrue from the first day following the month of commissioning of the intangible asset, and ends from the next month after the month of disposal of the intangible asset. The depreciation charge will be reflected through account 05.
Amortization of intangible assets: postings, calculation methods, account
Intangible assets have their original cost for which they were acquired. They also participate in the creation of the company’s commercial product and have a limited service life, as they are subject to moral and technical obsolescence. Therefore, intangible assets should be subject to the rules on depreciation, as well as fixed assets of the company.
Concept
Working intangible assets, although they do not have physical expression, but participate in the creation of company profits, transfer part of their value to the product produced by the company. Therefore, they should be taken into account in the cost of production in the form of depreciation charges according to a scheme similar to deductions from fixed assets.
According to PBU 14/2007, intangible assets are required to be registered with the company. An accounting card is created on them, and depreciation deductions begin from the next month after this.
What is amortization of intangible assets, this video will tell you:
Features and tasks of accounting
Depreciation of intangible assets is somewhat different from fixed assets in some respects:
- Repayment of the value of intangible assets occurs during the period of useful use.
- This period is determined by the period over which the company expects to use this asset to generate profit.
- If the determination of this period is not accepted, the intangible asset is considered to have an indefinite useful life period and depreciation is not charged on it.
Carrying out
For each asset registered by the company, depreciation is calculated monthly according to the relevant standards.
Depreciation rates
Depreciation rate is a percentage of the cost of an asset included in the cost of the entire commercial product produced by the company, at regular intervals over the full life of its use. The company sets this standard independently in accordance with the company’s method of calculating full depreciation on intangible assets.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=anTbWYiD0_E
Postings and accounting when calculating depreciation for an intangible asset are discussed in this video:
Methods of calculation and procedure
The rules for accounting for intangible assets define three methods for calculating depreciation:
- Linear method . In the case of which the initial price of the asset is evenly distributed over the entire period of active use (analogous to the scheme for the company’s fixed assets).
- Reducing balance method . Here, annual depreciation is calculated from the residual price of the intangible asset using a coefficient that takes into account the remaining useful life.
- The write-off method is proportional to the total volume of production . In this case, the procedure for calculating depreciation determines the expected volume of products to be produced throughout the entire useful life of the asset. And the write-off of part of the cost of intangible assets occurs in proportion to the share of actual monthly production in the expected volume.
Depreciation methods
Reflection by records
Depreciation charges must be reflected in the appropriate entries in the accounting documents:
- Debit to accounts 20, 23, 25, 26, 44 and 97.
- Credit to account 05 using the cumulative method of writing off depreciation amounts.
- The account has 04 for direct debit.
After the asset price has been fully paid off, no depreciation is charged, and the asset is recorded with a conditional valuation.
Account and deadlines
As can be seen above, two accounts are used for depreciation:
- 05 – passive balance sheet account with a credit balance to reflect accumulated deductions.
- 04 – account for direct depreciation write-off.
The validity period of an asset is determined in two ways:
- According to the validity period of the company’s rights to intangible assets.
- According to the expected period of time for the company to receive benefits from the positive use of the asset.
Therefore, the task of accounting for intangible assets is to determine the degree of its influence on the cost of the company’s products. Why, when an intangible asset is registered, an Acceptance Certificate is filled out for it, which indicates:
- Price.
- Validity.
- Depreciation rate.
- Details (if any) that contribute to the uniform accrual of depreciation of this asset.
Postings
When depreciating intangible assets, the following entries are used:
- Dt20/Kt04(05) – in relation to the main production.
- Dt23/Kt04(05) – in relation to auxiliary production.
- Dt25/Kt04(05) – in relation to general production costs.
- Dt26/Kt04(05) – in relation to administrative (household) expenses.
- Dt29/Kt04(05) – in relation to service departments.
- Dt44/Kt04(05) – in relation to product sales.
- Dt97/Kt04(05) – in relation to expenses for future periods.
You will find even more useful information on such depreciation in this video:
Source: https://uriston.com/kommercheskoe-pravo/buhgalteriya/vneooborotnye-aktivy/nematerialnye/amortizatsiya-pri-uchete.html
ACCOUNT 04
Account 04 is provided for accounting for intangible assets.
Account 04 “Intangible assets” - This account is purely active. That is, the balance is always debit. This account is similar in characteristics to 01 account.
The debit of this account reflects:
- Initial cost
The credit of this account reflects:
- Disposal of intangible assets in value terms.
- Write-off of accumulated depreciation
The debit balance (at the beginning and at the end) shows the value of intangible assets at their original cost.
In the balance sheet, Account 04 (account balance) is reflected in the item “Intangible assets” minus accrued amortization on account 05. Section 1 “Non-current assets” Balance sheet asset. For example, the balance at the end of the account is 04-150000 rubles, the balance at the end of the account 05 is 50000 rubles. Under the intangible assets item, the balance sheet will reflect the amount of 100,000 rubles (150,000-100,000).
Schemes 1:
Comments:
Balance at the beginning of 200,000 rubles - Shows that on the reporting date we have intangible assets with an original cost of 200,000 rubles.
The debit turnover of 750,000 rubles (300,000+450,000) shows that intangible assets were received during the reporting period in the amount of 750,000 rubles.
The loan turnover of 300,000 rubles (250,000 +50,000) shows the amount of intangible assets retired.
Calculation of the ending balance for account 04 = 200,000 (beginning balance) + 750,000 (debit turnover) - 300,000 (credit turnover) = 650,000 rubles. This balance shows how much intangible assets are available at the end of the period.
RECEIPT OF NMA:
The disposal of intangible assets is recorded on account 91. The debit of account 91 reflects the amounts of the residual value of intangible assets, expenses incurred as a result of the disposal of these assets, as well as the amount of VAT on assets sold. The credit to account 91 includes proceeds from the sale or other income from the disposal of intangible assets. Ultimately, the debit (loss, expense) or credit (profit, income) balance in account 91 is written off to subaccount 91/9 “Balance of other income and expenses”, and subsequently to account 99 “Profits and losses”.
Disposal of an intangible asset occurs in the following cases: 1) termination of the organization’s right to the result of intellectual activity or a means of individualization; 2) transfer under an agreement on the alienation of the exclusive right to the result of intellectual activity or to a means of individualization; 3) transfer of the exclusive right to other persons without an agreement (including in the order of universal legal succession and when foreclosure on this intangible asset); 4) termination of use due to obsolescence; 5) transfers in the form of a contribution to the authorized (share) capital (fund) of another organization, a mutual fund; 6) transfers under an agreement of exchange, gift; making contributions under a joint venture agreement; 7) identifying shortages of assets during their inventory; in other cases.
2) transfer under an agreement on the alienation of the exclusive right to the result of intellectual activity or to a means of individualization; 3) transfer of the exclusive right to other persons without an agreement (including in the order of universal legal succession and when foreclosure on this intangible asset); 4) termination of use due to obsolescence; 5) transfers in the form of a contribution to the authorized (share) capital (fund) of another organization, a mutual fund; 6) transfers under an agreement of exchange, gift; making contributions under a joint venture agreement; 7) identifying shortages of assets during their inventory; in other cases.
Before writing off an intangible asset as unusable, an organization must determine that it can no longer be used. For this purpose, by order of the head of the organization, a commission is created, which includes the chief accountant (or accountant). The commission must establish the reasons for writing off the asset (in particular, obsolescence, long-term non-use of the asset for production), drawing up an appropriate act about this. Next, the act is transferred to the organization’s accounting department and, on its basis, a note is made on the disposal of the asset in the inventory card (form No. NMA-1).
Most often, the disposal of intangible assets is associated with the expiration of their useful life . Typically, intangible assets have a limited life. So, according to Art. 1363 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, the validity period of exclusive rights to an invention, utility model and industrial design and the patent certifying this right is calculated from the date of filing the initial application for a patent with the federal executive body for intellectual property and, subject to compliance with the requirements, is: 20 years - for inventions ; 10 years - for utility models; 15 years - for industrial designs.
If the useful life of an intangible asset is not established by law or it is impossible to determine it, then such an asset is considered an intangible asset with an indefinite useful life. No depreciation is charged on such assets.
Upon expiration of the useful life, this intangible asset is written off from the balance sheet of the enterprise. In accounting, such an operation is reflected similarly to the write-off of intangible assets due to their unsuitability.
When writing off intangible assets, the following entries are made:
Dt 05 Kt 04 - write-off of accrued amortization of intangible assets
Dt 91/2 Kt 04 - write-off of the residual value of intangible assets
Dt 99 Kt 91/9 - loss identified
Intangible assets, if sold, are written off from the organization’s balance sheet. Moreover, sales can occur not only under sales and purchase agreements. So, according to Art. 1367 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, a license agreement may be concluded to grant the right to use an invention, utility model or industrial design. Under such an agreement, one party - the patent holder (licensor) grants or undertakes to provide the other party (licensee) with a patent-certified right to use an invention, utility model or industrial design within the limits established by the agreement.
An agreement on the alienation of a patent, a license agreement, as well as other agreements through which the exclusive right to an invention, utility model or industrial design is disposed of, are concluded in writing and are subject to state registration with the federal executive body for intellectual property. Otherwise they are considered invalid.
When selling intangible assets, the following entries are made:
Dt 05 Kt 04 - write-off of accrued amortization of intangible assets
Dt 91/2 Kt 04 - write-off of the residual value of intangible assets
Dt 62.76 Kt 91/1 – sales value or revenue
Dt 91/2 Kt 68/VAT – VAT calculation
Dt 91/9 Kt 99 - profit revealed
Dt 99 Kt 91/9 - loss identified.
An organization has the right to transfer intangible assets as a contribution to the authorized capital of another organization or for joint activities. According to Art. 39 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, such a transfer is not recognized as a sale of goods, therefore it is not subject to VAT.
In this case, the following accounting entries are made:
Dt 05 Kt 04 - write-off of accrued amortization of intangible assets
Dt 91/2 Kt 04 - write-off of the residual value of intangible assets
Dt 58 Kt 91/1 – agreed upon cost between the founders
Dt 91/2 Kt 71.76 - costs associated with the transfer of intangible assets are determined
Dt 91/9 Kt 99 - profit revealed
Dt 99 Kt 91/9 - loss identified.
Business reputation of an organization (goodwill). Calculation of the value of business reputation, features of its accounting and amortization
Business reputation is defined as the difference between the purchase price of the organization, as the acquired property value as a whole, and the balance sheet value of all its assets and liabilities.
For accounting purposes, the amount of acquired goodwill is determined by calculation as the difference between the amount paid by the seller for the organization and the amount of all assets and liabilities on the organization’s balance sheet as of the date of its purchase (acquisition)
Goodwill is a price premium paid by a buyer in anticipation of future economic benefits and is accounted for as a separate inventory item.
Dt 04 Kt 60 - positive business reputation reflected
Negative business reputation is a price discount provided to the buyer due to the lack of factors of the presence of stable buyers, reputation for quality, business connections, management experience, etc. are accounted for as deferred income.
Dt 60 Kt 91 - negative business reputation is reflected.
Negative business reputation of the organization in accordance with clause 44 of PBU 14/2007 is attributed to other income:
Dt 98 Kt 91/1
When purchasing privatization objects at an auction or competition, the business reputation of an organization is determined as the difference between the purchase price paid by the buyer and the estimated (initial) cost of the sold organization.
Accounting for the purchase of intangible assets
When purchasing intangible assets, account 08 “Investments in Non-current Assets” is used (the purchase of intangible assets is similar in transactions to the purchase of fixed assets). Before recording intangible assets on account 04, all costs (including purchase price) are collected in the Debit of account 08.
Postings:
- Debit 08 Credit 60-Purchased intangible assets (for example, a patent)
- Debit 08 Credit 60-Consulting services.
- Debit 08 Credit 76- State duty
- Debit 04 Credit 08-Object accepted as intangible asset.
Let's look at an example:
The organization acquired a patent at a contract price of 100,000 rubles. The state duty is 2000 rubles. In accordance with Article 149 (Tax Code of the Russian Federation), a patent is not subject to value added tax.
Solution:
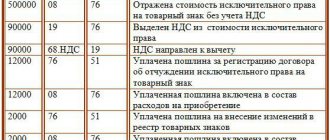
- Debit 76 Credit 51- 2000 rubles – Payment of state duty.
- Debit 08 Credit 60-100,000 rubles - Purchase of a patent.
- Debit 08 Credit 76- 2000 rubles – State duty is reflected as an expense.
- Debit 60 Credit 51- 100,000 rubles - Paid to the counterparty for the patent.
- Debit 04 Credit 08- 102,000 rubles. (100,000+2000) - Patent accepted as intangible asset
Scheme 2: Reflection of transactions on accounts (planes).
Comments: As we can see from the turnover, account 08 is debited for the total cost of purchasing intangible assets of 102,000 rubles, and the loan was written off in one amount of 102,000 rubles.
Creation of intangible assets
When creating intangible assets on your own, all costs are collected on account 08, then written off to account 04.
Postings:
- Debit 08 Credit 60,70,69 itp - All expenses for creating intangible assets are reflected
- Debit 04 Credit 08-(debit turnover on account 08 is written off)-intangible asset accepted as intangible asset.
Let's look at an example:
The organization creates a website on its own:
Creation costs were:
- Employees' salary is 100,000 rubles.
- Insurance contributions from wages - 30,000 rubles (100,000 * 0.3).
- Consulting costs from other organizations 12,000 rubles (including VAT 20%).
Solution:
- Debit 08 Credit 70- 100,000 rubles - Salaries accrued to employees.
- Debit 08 Credit 69-30,000 rubles - Insurance premiums from salary accrued
- Debit 08 Credit 60-10,000 rubles. (12000/120*100) - consulting costs.
- Debit 19 Credit 60-2000 rubles (12000/120*20) - VAT from consulting services.
- Debit 04 Credit 08-140,000 rubles (100,000 +30,000+10000) - The site is accepted as an intangible asset.
Comments: During the creation of a website, the costs of a domain and hosting for the first month may be included in the initial cost.
Scheme 3 Reflection of transactions for the creation of intangible assets on accounts (airplanes)
Receiving intangible assets free of charge
When receiving an intangible asset free of charge (free of charge), the intangible asset is accounted for at its market value on the date of receipt. Account 08 “Investments in Non-current Assets” is also used to reflect the market value + acquisition costs in the debit of account 08. The market value is recognized as other income and is reflected through account 91 (other income and expenses). To calculate income tax, by means of calculating depreciation, market value does not apply expenses, and expenses for the receipt of intangible assets are recognized as expenses free of charge (in reducing income (tax base)). If these tax accounting expenses are less than 100,000 rubles, they are written off at a time.
Postings:
- Debit 08 Credit 91-01 – Receipt of intangible assets free of charge at market value is reflected.
- Debit 08 Credit 60 -Reflects the costs of assessing intangible assets.
- Debit 04 Credit 08 - The object was capitalized as an intangible asset.
Let's look at an example:
A software product has been received with the right of disposal (ownership of the program) with a market value of 100,000 rubles. The costs of a third-party assessment organization amounted to 20,000 rubles. Depreciation is calculated using the straight-line method (more on this in other lessons). SPI (useful life 2 years)
- Debit 08 Credit 60-20,000 rubles - Consulting services for valuation of intangible assets reflected
- Debit 08 Credit 91-1-100,000 rubles - Other income on intangible assets received free of charge is reflected
- Debit 04 Credit 08-120,000 (100,000+20000) - The intangible asset was accepted at its original cost.
Let's break down the amounts by account (airplane):
We find the ready depreciation amount of 120,000 (initial cost)/2=120,000/2=6000 rubles. We find the monthly depreciation amount 60,000 (per year)/12 (number of months in a year) = 5,000 rubles.
4) Debit 26 Credit 05-5000 rubles (from the next month after the month of acceptance of intangible assets) - Depreciation for the month has been accrued.
Comments:
In tax accounting (accounting for profits, expenses), a gratuitously received intangible asset is not accepted as an expense, i.e. it does not reduce income, but expenses incurred in connection with the free receipt of intangible assets are accepted for deduction (they reduce income, profit) in our example, 2000 rubles immediately written off as expenses (up to 100,000 is written off at a time)
REMOVAL OF INVESTMENTAL MATERIALS:
Documents for writing off intangible assets
The procedure for writing off intangible assets after the expiration of their useful life (USP) is accompanied by the preparation of primary documentation in accordance with Art. 9 of Law No. 402-FZ dated December 6, 2011. The forms can be approved by the head of the enterprise with the entry of all mandatory details, including the reason for disposal.
List of documents for write-off of an asset in connection with the end of the established SPI:
- The act and order for writing off intangible assets - the forms are signed by the head of the company; it is required to indicate the basis for writing off the object. In the case of a special commission, the act is signed by all participants, and the composition is pre-approved by the director of the enterprise.
- Intangible asset registration card - on the basis of the drawn up act, the corresponding entries on the write-off of the object are made in the registration card. Depreciation ceases from the month following the disposal period.
Sale of an intangible asset.
Intangible assets can be sold, the sale is accounted for through 91 accounts “Other income and expenses” (similar to the sale of fixed assets). The debit of 91 accounts reflects all expenses for the sale of intangible assets, and the credit reflects revenue. The debit of account 91 reflects the residual value of the sold intangible assets (Original cost - Amount of accumulated depreciation).
Let's look at an example:
The company decided to sell the trademark with an initial cost of 500,000 rubles, the accumulated amount of depreciation is 300,000 rubles. The state duty for the sale of a trademark is 15,000 rubles. Sale price 840,000 rubles.
Postings for the task:
- Debit 76 Credit 51- 15,000 rubles - State duty paid for registering the agreement.
- Debit 62 Credit 91-1-840000 rubles. Revenue from the sale of intangible assets.
- Debit 91-2 Credit 68/VAT -140,000 rubles (840,000/120*20) - VAT reflected.
- Debit 05 Credit 04-300,000 – The accumulated amount of depreciation on intangible assets is written off.
- Debit 91-2 Credit 04-200,000 rubles (500,000-300,000) - The residual value of the sold intangible asset is written off.
- Debit 91-2 Credit 76-15,000 rubles - State duty is included in expenses.
- Debit 91-9 Credit 99 -385,000 rubles (840,000-140,000-300,000-15,000) - Profit from the sale of intangible assets (trademark) is reflected
Airplanes:
Write-off of obsolete intangible assets
In accordance with PBU 14/07, intangible assets that are not capable of generating income are subject to write-off. Income and expenses on the disposal of intangible assets are taken into account in other income and expenses in account 91. In tax accounting (accounting for determining income tax), the residual value of intangible assets (under-marketed) reduces the income tax.
Let's look at an example:
Know-how (intangible assets) initial cost is 500,000 rubles, the amount of accumulated depreciation is 300,000 rubles. Due to the fact that this intangible asset no longer generates income, it was decided to write off the intangible asset due to obsolescence.
Solution:
- Debit 05 Credit 04-300,000 rubles - Accumulated depreciation is written off.
- Debit 91-2 Credit 04- 200,000 rubles. (500,000-300,000). The residual value of intangible assets has been written off.
- Debit 99 Credit 91-9-200,000 rubles - At the end of the reporting period, the LOSS is written off to the financial result.
Let's break it down according to the charts of accounts (airplanes):
Comments: The residual value in the amount of 200,000 rubles in tax accounting reduces taxable profit. (In accordance with the tax code art. 265 p1. p. 8)
Free transfer of intangible assets
Income tax:
In case of gratuitous transfer in accordance with Article 270 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, gratuitous transfer of intangible assets (as well as costs incurred in connection with the transfer) For accounting for income tax, such expenses do not reduce taxable profit
VAT:
In the event of a gratuitous transfer, VAT is charged, but there is an exception: if the company provides intangible assets for charity, then VAT is not charged.
Accounting:
All transactions for the transfer of intangible assets are carried out through account 91 (other income and expenses).
Let's look at an example:
Company A decided to transfer intangible assets with an initial cost of 150,000 rubles to a charitable organization. Accumulated depreciation is 50,000 rubles.
Solution:
- Debit 05 Credit 04-50,000 rubles - The accumulated amount of depreciation is written off.
- Debit 91-2 Credit 04 – 100,000 rubles. (150,000-50,000).-Residual value of intangible assets written off
Reflection in accounting
In the economic activities of enterprises, there are often cases when intangible assets, for various reasons, become unsuitable for further use in production or for management purposes. An unused intangible asset continues to be registered and the company pays property tax on the residual value of this asset. In order to reduce the company's losses, this intangible asset must be written off.
The write-off of intangible assets due to their unsuitability for further use is carried out on the basis of an act drawn up by a specially created commission and approved by the head of the enterprise.
The act must indicate the initial cost of the intangible asset being written off, the amount of depreciation accrued during operation, the residual value of the object, the reasons why the object is written off from accounting and other data relating to the intangible asset being written off.
The act approved by the manager is transferred to the accounting department of the enterprise, where they make a note about the disposal of the asset and make the necessary entries in the accounting accounts.
Simultaneously with the write-off of an intangible asset, the amounts of depreciation accrued during operation are written off, if it was taken into account on account 05 “Depreciation of intangible assets”