The concept of inheritance by adopted children and adoptive parents
The legislator equated adopted children with any type of relationship based on origin. Inheritance by adopted children and adoptive parents is carried out in a general manner, and such persons are considered priority heirs.
The rules of kinship apply not only to adoptive parents and children, but also to their offspring, including children adopted at a later date. According to legal norms, the determination of priority is based on the general principle that is inherent in children and parents related by blood.
Adoption by adoptive parents deprives the adopted child of the right to inherit from biological parents, as well as other relatives related by common origin.
There are a number of circumstances that allow an adopted child to maintain ties with blood relatives, which gives him the opportunity to be the bearer of inheritance rights in the future. As a result of this, the adopted person will be able to become an heir both for adoptive relatives and for relatives of his former family.
When inheriting, attention is drawn to the question of confirming the kinship of adopted children. In practice, there are cases when the difficulty of proving kinship arose in relation to both the relatives and the adoptive father and mother.
Inheritance rights of the blood parents of an adopted child
Based on the provisions of paragraph 2 of Art. 137 of the Family Code, the parents of an adopted person by origin, upon adoption, lose any property rights in relation to him. Thus, according to paragraph 2 of Art. 1147 of the Civil Code, along with all property rights, they also lose the opportunity to inherit by law after the death of the adopted person. Together with them, all their family members, who are, to one degree or another, heirs of the adopted person, also lose this right.
Attention
However, the legislator allows for the possibility of preserving for one of the parents and his relatives the relations accompanying the preservation of property rights and obligations between the specified subjects of inheritance. If such relationships, according to a court decision, are maintained, then such a parent and his relatives may inherit in the event of the death of the adopted person or one of his descendants (clause 3 of Article 1147 of the Civil Code).
At the same time, a literal interpretation of family law suggests that maintaining a relationship with a parent of origin is permissible only in the case where adoption is carried out by only one person, and only if the genders of the adoptive and natural parent with whom the relationship is maintained are different (p 3 Article 137 SK). There are other features, in particular:
- In the event of the death of the mother or father of an adopted person by origin, his grandparents may apply for the preservation of personal property and non-property relations with them and other relatives of the deceased . Such decisions are made in court. With their help, the inheritance rights of grandparents by descent can be preserved.
- According to the provisions of paragraph 1 of Art. 143 of the Family Code, in the event of cancellation of adoption, the mutual rights of the adopted person and his adoptive mother or father that arose as a result of this legal relationship are canceled . Moreover, the mutual rights of parents by origin and their children, if this does not conflict with the interests of the minor and he returns to his former family, are restored again.
- Based on the above, in the event of cancellation of the adoption and return to the previous family, the inheritance rights of the mother and father by origin are subject to restoration , as a result of which they will again be able to inherit from their son or daughter by law. However, in this case, prohibitions on inheritance based on their unworthiness may again begin to apply to them (clauses 1, 2 of Article 1117 of the Civil Code).
Inheritance rights of adopted children, adoptive parents and blood relatives
Heirs who are adopted children or adoptive parents are given equal rights of inheritance.
The rights of adopted children who received such status before 1996 must be confirmed by a resolution issued by the district or regional administration. The new Family Code established a judicial procedure for adoption, thus the fact of adoption can be confirmed by presenting a court decision.
The presence of one of these documents, the form of which is determined by the date of adoption, entitles the adopted person to the full range of rights and obligations that are provided for natural children.
Adopted children are also the primary heirs of the parents who acted as adoptive parents. The current and future descendants of the adoptive parents for the adopted are blood members of the family, which establishes for them and in relation to them equal rights regarding inheritance.
The provisions of the Family Code have determined the general rule according to which an adopted child is deprived of rights in relation to blood parents and relatives from the moment of actual adoption. This indicates the impossibility of accepting the inheritance left by biological parents and relatives. The rule has a number of exceptions.
Adoptive parents are blood relatives of the adopted person from the moment of adoption. On the same day they are given the right of inheritance to the adopted person. The same rights arise for relatives of adoptive parents. The order of acceptance of inheritance is determined in a general manner, depending on the degree of relationship.
Rights of adopted children to inheritance according to law
In accordance with Art. 1147 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, the adopted person and the adoptive parent, from the moment the court decision on adoption enters into legal force, are endowed with all legal mutual rights and obligations, like those of a blood family. Including the right to inherit each other. In this situation, we are talking exclusively about inheritance by law. Since for inheritance under a will, the presence of a family connection does not matter.
Let's consider what nuances the law provides for inheritance by adopted children.
From adoptive parents
The court decision equates the adoptive parent and adopted child with natural parents and children. If a child was adopted by a married couple, then he receives a relationship with other relatives of the adoptive parents. That is, the adopted child inherits the property of his adoptive parents, along with his natural grandchildren, and they can claim his property in the event of his death.
The situation is more complicated if the child was adopted by only one person.
For example, the mother's new husband. In this case, he loses all rights in relation to his father’s relatives and acquires new ones in relation to the adoptive parent.
If the only adoptive parent (a single woman or a single man) adopts, then the inheritance situation is resolved by him independently. The adoptive parent may retain the property and personal non-property rights of the second parent or exclude a record of him from the child’s birth record. In this case, the relationship is considered terminated, and the adoptive parent is considered a single parent. And the child loses the right to inheritance from both parents.
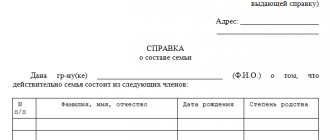
Reference! The adoptee is not required to present a certificate of adoption to the notary. In the Russian Federation there is such a thing as the secrecy of adoption. Therefore, the heir has the right not to disclose such information to anyone, including a notary.
From blood parents
Preservation of rights to inheritance from blood parents directly depends on the court's decision on adoption. The law provides for the following possibilities:
- Exclude natural parents from the birth record. In this case, the child loses rights to the property of his biological mother and father.
- When adopting a child left without parental care, the adoptive parent may leave a birth record and, accordingly, retain his property and personal non-property rights in relation to the child.
In this case, the child retains the rights to the inheritance of the blood parent. Example. Masha's mother was deprived of parental rights, and her father died. Irina decided to adopt Masha. The woman asked the court to exclude information about the mother from the child’s birth record and leave the father’s information. Thus, Masha retained the right to the inheritance of her late father. - When adopting with the consent of the second parent (intrafamily adoption), the parent who gave consent fully retains the rights in relation to the child.
Accordingly, the child has the right to his inheritance. Example. Vanya's mother entered into a second marriage. Her husband decided to adopt Vanya. After the court decision entered into legal force, Vanya received the right to his stepfather’s inheritance, but lost the rights to his blood father’s property.
From blood grandparents
The law protects the rights of grandparents of adopted children. If the child’s parents died and the grandparents are unable to obtain guardianship due to health reasons, the court may retain their property and personal non-property rights with their grandchildren.
That is, after adoption, the child receives the right not only to the inheritance of the adoptive parents and their relatives, but will also retain the rights to the inheritance of their blood grandparents.
Take the survey and a lawyer will share an inheritance action plan in your case for free
You might find it useful:
State duty calculator for inheritance
Samples of inheritance documents
Consultation with a lawyer on inheritance
Peculiarities of inheritance by adopted children and adoptive parents
The procedure for inheritance by adopted children and adoptive parents is determined by the Civil Code of the Russian Federation. It is no different from the procedure that is provided for biological relatives. The reason for this is the rule according to which adopted children and adoptive parents, from the moment of adoption, are considered to be related by blood.
The moment of adoption deprives the adopted person of the right to inherit from his biological parents and relatives. There are exceptional cases that allow an adopted child to be the heir of his own parents. These are the following:
- adoption of a child after the death of both parents. The basis for inheritance is the presence of blood ties that existed on the day the inheritance was opened, because until the moment of adoption the relationship is not terminated;
- situations in which, after the death of a parent, a close relative retains rights even after adoption. Such relatives can be grandparents. As a result, the adoptee may inherit the grandparent's property in place of the parent who died. This rule is regulated by the right of representation;
- adoption of a child by the new spouse of a living parent who is remarried. Property relations between parent and child do not end.
Adoptive parents have a general range of rights to inherit the property of their adopted children. They are also among the priority heirs.
Inheritance rights of adoptive parents
After proper execution of all documents, adoptive parents are legally equal to blood relatives (Article 137 of the RF IC). The rule also applies to descendants of adopted citizens.
The same goes for adopted children. They acquire similar property rights/responsibilities in relation to the adoptive parents.
In the event of the death of an adopted child, the adoptive parents acquire the status of heirs.
What if the testator left a will? If a child assigns property to a brother, sister or third parties, then the adoptive parents are deprived of their inheritance.
The exception is the mandatory share rule. If the adoptive parents have reached retirement age, then they are entitled to a part of the property, regardless of the content of the administrative document (Article 1149 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
Rights of inheritance by adopted children and adoptive parents
The rights of heirs who are adopted children or adoptive parents are equal.
Children who were adopted before 1996 confirm their status with a decree issued by the district or regional administration. Updated family legislation established a judicial procedure for adoption. Since 1996, the act confirming the status has been a court decision.
Adopted children are considered to be the primary heirs of their parents, who are adoptive parents.
Adoptive parents are also considered the primary heirs of their adopted children. All descendants of adoptive parents are blood relatives for adopted children, which indicates the application of general rules and order of inheritance.
The adoptive parent receives the status of a blood relative of the child adopted by him from the moment of adoption. This date is the day when the rights of inheritance for the adopted person arise in the general manner.
How to get an inheritance for adopted children
If at the time of the death of the adoptive parent the adopted child has reached the age of majority, then he carries out all legal actions independently. Emancipated teenagers also do not need a guardian or legal representative. They must first prove their legal capacity to representatives of the guardianship authorities and the court.
The role of the legal representative may be the spouse of the deceased or his other close relative. The scope of powers of the adopted person varies depending on the age of the child:
- Up to 14 years old . At this age, the adopted child is considered incompetent. All actions to obtain a share of the inheritance are carried out by the legal representative.
- 14-18 years old . The adopted person independently accepts the inheritance. The legal representative must notify the guardianship authorities in writing of his consent. The document is certified by a notary.
If an adopted child is left without a representative after the death of his parents, the process of dividing the inheritance is supervised by the appropriate authorities.
Procedure
Stages of acquiring property rights:
- Finding a will executor . The adoptee must find out which notary office is handling his business. Most often, the notary is assigned to the territory (microdistrict, rural district) where the testator lived.
- Submitting an application . After reviewing the application, the adoptee is notified which specialist will handle the transaction.
- Collection of information . The package of documents must be handed over to the notary.
- Payment of duties . The amount includes notary fees.
- Issuance of a certificate . After all formalities have been completed, the heir receives a certificate of ownership.
On the first visit to the notary, the adoptive parent must have with him an identity document and other legal documents. The specialist accepts the application and registers it. If the heir has collected a package of necessary papers in advance, then he can present all the certificates to the notary on his first visit. After this, you must pay all fees and fines (if any). A certificate of ownership is issued 6 months after the death of the testator.
Statement
The adopted person writes a statement of intention to receive a share of the inheritance from the deceased parent. The paper can be drawn up by hand or using technical means (computer, printer). The applicant personally signs the document.
Sample
What should be in the petition:
- Full name of the legal representative and the applicant;
- the applicant's residence address;
- location of the notary office;
- Full name of the specialist supervising the process;
- Full name of the testator, address of his residence (until the moment of death);
- a detailed description of the inherited property;
- list of heirs;
- date of application.
A sample document can be downloaded from the official website of the Russian Federation. Inheritance.
Documentation
List of documents required to receive an inheritance:
- passport or other identification document of the applicant;
- certificate or power of attorney regarding parental rights;
- a document confirming the death of the testator;
- documents on the right of inheritance (will, adoption certificates);
- address certificate.
What additional documents may be needed?
Additionally you may need:
- report of the appraiser of inherited property;
- payment receipts;
- technical and cadastral passports of real estate.
The applicant pays the costs of the appraiser from personal funds.
Expenses
The cost of all related procedures for entering into an inheritance varies depending on the region of residence of the testator and heir. It may be affected by the type of property being registered and the list of additional services provided by the notary as part of the transaction.
State duty amount
The heir pays the state fee for the certificate of ownership. The specialist evaluates the inherited property and records the amount in the report. The applicant must contribute at least 0.3% of the total value of the property to the state treasury.
Additional expenses:
- filing fee;
- registration of the applicant’s rights as the owner;
- payment for services of specialists (appraisers, notary).
Minor children or incapacitated heirs may be exempt from this expense item. WWII veterans (including concentration camp prisoners) can count on benefits. The maximum amount (regardless of the region) is 100 thousand rubles.
Deadlines
Adopted children are considered heirs of the first priority. Experts do not recommend delaying the submission of documents for property rights; the application must be submitted within 3-6 months from the date of death of the adoptive parent. If the applicant did not manage to enter into rights in time, he must present evidence of entry to the notary.
The heirs have the right to apply to the court with a request to extend the deadlines. The judicial authority may satisfy the requirements if one or more actual heirs did not have time to declare their rights for a good reason (illness, long business trip).
The order of inheritance by adopted children and adoptive parents
Provisions of Art. 1147 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation established the procedure for inheritance by children who were adopted and by adoptive parents.
Inheritance based on law will require proof of adoption. This verification will be carried out by a notary. An adopted person will be able to inherit the property of his adoptive parents, but, according to the law, he will not be able to become the heir of his blood parents. The moment of adoption is the date of mutual termination of the rights of the adopted child and his biological parents regarding inheritance.
The adopted person, acting as the heir of his adoptive parents or relatives, belongs to the order of heirs, which is determined by the degree of his relationship, which is provided for by the general provisions on the order of succession.
Author of the article
Receiving an inheritance from adoptive parents
According to the law, after official adoption, a baby adopted into a new family acquires exactly the same legal, financial privileges and responsibilities that he would have in relation to this family in the case of biological kinship.
Therefore, you can freely talk about the rights of an adopted child to the inheritance that the adoptive father/mother will leave behind. Moreover, this opportunity will be given to him by law, which means that the ability to inherit will not depend on the presence/absence of a will.
In any case, the adopted child will be entitled to a certain part of the property of the adoptive parents. And by right of representation - this or that part of the property of other close relatives related to the new family.
Such property privileges will be received in the future by both the children and grandchildren of the adopted child. That is, they will be able to inherit from grandparents with whom they are not actually connected by blood ties.
Moreover, even if the adopted child still has the right to inherit from his biological relatives, this will not in any way affect his ability to inherit from his adoptive parents and their relatives.
If the fact of adoption is annulled, the child loses the opportunity to inherit from the former adoptive father/mother or members of their family.
At the same time, he automatically regains the opportunity to receive an inheritance from relatives by biological origin.
Inheritance by adoptive parents
In the matter of receiving an inheritance from an adopted child by adoptive parents and their relatives, everything is exactly the same as in matters of inheritance by an adopted child from adoptive parents and their family.
That is, both the adoptive parents themselves and their close relatives can inherit from the adopted child and his descendants - both by law and by will.
If the adoption is annulled, the former adoptive family loses any property rights in relation to the once adopted child.