The Tax Code of the Russian Federation allows business entities, within certain limits, to independently choose the taxation system. This primarily applies to individual entrepreneurs. When starting a business, a person must make a responsible decision - choose the optimal taxation system . The future of the entrepreneur largely depends on the correctness of this choice.
The task facing us is the choice between one of two simplified taxation systems (USN or “simplified tax system”) and a single tax on imputed income (UTII or “imputed tax”). It is not very easy to answer the question: imputation or simplification, which is more profitable for individual entrepreneurs. The first step to making the right choice is to find out which simplified tax system and UTII systems can be applied to your case. For, for example, retail trade, if an entrepreneur works alone or has few employees, then it is possible to use any of the above systems.
A significant advantage of both “simplified” (USN) and “imputed” (UTII) is the ease of document management for accounting income and expenses, as well as the preparation of reports to the Federal Tax Service. In all these systems, you do not have to pay VAT (except in certain cases), income tax and property tax, but if an entrepreneur uses the simplified tax system, then it is necessary to maintain a ledger of income and expenses.
Cancellation of UTII for retail trade in 2020: everything you need to know
The fact that the “imputation” will cease to exist in 2021 has already been decided and there is no need to expect any postponements this time. The Ministry of Finance announced this on July 10, 2020. But, for some businessmen, UTII will end even before this deadline.
In addition to the abolition of the special regime in some regions, Law No. 325-FZ of September 29, 2019 makes changes to the Tax Code that define the new concept of “retail trade for UTII purposes.” This means that all trade that does not meet the requirements of the new edition is automatically deprived of the right to apply the “imputation” in 2020.
What does legislation now mean by “retail trade for UTII purposes”:
Firstly, trade based on retail sales contracts;
Secondly, the sale of only permitted goods and products.
Let’s look in a little more detail at what trade is based on retail sales contracts, who can enter into them, and whether everything is so clear. It is generally accepted that wholesale implies large volumes of sales. But the legislation does not have a clear numerical expression for determining the wholesale batch. For example, the sale of 50 units of goods to different buyers will be assessed differently by tax authorities.
As a rule, retail trade is carried out to the end consumer for their personal use through stationary trade points (shops, pavilions). The seller issues a cash receipt without indicating the buyer's name. In this case, the retail sales agreement is considered concluded.
Tax authorities consider wholesale trade the sale of products for legal entities or individual entrepreneurs with the conclusion of a written sales contract and the execution of registered invoices, invoices, etc. Such goods are usually used in the future for consumption in business activities or for the production of their own products. In this case, the payment method (cash or bank transfer) does not matter.
But there are exceptions here. If an entrepreneur bought a product for himself personally, without completing all the documents, then such a sale also applies to retail. It must be borne in mind that if the tax authorities have doubts about the category of the transaction, they will have to challenge it in court, as always.
In accordance with Art. 346.27 of the Tax Code, retail trade for the purposes of UTII also does not include the sale of goods in catalogs through online and television stores, including delivery by mail.
Now, in more detail about those goods, the sale of which in 2020 is completely prohibited for “imputed” people.
Features of the online store and UTII
The legislation of the Russian Federation does not clearly indicate what an online store is considered to be. But in reality, there is an intuitive understanding that an online store can be considered a website containing catalogs of goods where you can place an order.
In accordance with the provisions of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the online store and UTII are incompatible. But nevertheless, there is an option in which it is possible to pay taxes on UTII for owners of online stores. If the store, in addition to the virtual part, has a stationary or mobile point of sale, then the website acts as a showcase, and the sale itself is executed on the premises.
Since using UTII is impossible, the entrepreneur is faced with a choice between a simplified or basic taxation system. The final choice depends on who is the supplier and who is the client, what the company’s turnover and expenses are - all this is important for the formation of VAT. If a store serves large customers who use the basic tax system (OSNO) and have an interest in receiving VAT, then using OSNO will be more profitable.
If an online store does not need to deduct VAT, many use simplified taxation schemes (STS). Under the simplified tax system, the number of store employees should not exceed 100 people, and there should also be no branches.
If these conditions are met, the owner of the online store can choose one of two types of simplified tax system - “income” or “income minus expenses”. The second option is more often used, which, although it has more complex calculations, is nevertheless more profitable if the store needs to purchase goods.
The simplified tax system “income” option is the simplest and most understandable. With it, all funds received into the account or cash desk will be taxed at 6%. But it will be optimal only if the costs do not constitute an impressive part or are difficult to confirm.
Otherwise, when the markup of the goods is small, it is better to use the income-expense simplified tax system. In this case, a tax of 15% will be charged on the amount received after calculations. In some areas of the country the rate may be lower.
Who else was banned from using imputation in 2020
At the moment, local legislators can maintain or prohibit “imputation”. For example, in 2020, the authorities of the Perm region decided to abandon the special regime ahead of schedule. In Moscow, UTII has been abolished since 2014. In addition, regional authorities can independently change the list of acceptable types of activities for “impossible” people.
Therefore, to find out for sure whether you can apply UTII in 2019, you need to study the local regulations in your region. This information can be found on the tax website nalog.ru in the “Features of regional legislation” section. Perhaps in 2020 new restrictions by region will be adopted.
In general, the Tax Code provides for the following possible types of activities:
- Household and veterinary services;
- Car repair shops and car wash services;
- Parking services;
- Passenger Transportation;
- Hotel services;
- Trade through retail chain facilities;
- Advertising services;
- Leasing of retail space and others specified in clause 2 of Article 346.26 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
In addition, the law establishes restrictions:
- by the number of employees no more than 100 people;
- participation of other organizations no more than 25% (for legal entities);
- activities must be conducted outside of simple partnership and trust management agreements;
- “largest” taxpayers cannot apply UTII. To do this, the tax office must send a notification of receipt of such status. Before receiving such a notice, the taxpayer may be imputed, even if according to his indicators he is one of the “largest”;
- for catering and retail, the area of sales floors is no more than 150 m²;
- For carriers, the vehicle fleet should not contain more than 20 vehicles.
UTII: fixed amount of taxes
The single tax on imputed income is paid quarterly. The amount depends on the volume of retail space, the number of employees and transport, but does not depend on the actual volume of profit. UTII is used for certain types of activities, which include trade. The main disadvantage of UTII is the inability to file a zero return: even if you have not made a profit, you will still have to pay taxes.
For LLCs and individual entrepreneurs there are the same restrictions on the use of UTII:
- Staff up to 100 employees;
- The area of the sales area does not exceed 150 square meters. m.;
- The share of another organization in the LLC charter does not exceed 25%;
- Not subject to agricultural tax or patent;
- UTII is allowed in the subject of the federation.
With UTII, individual entrepreneurs and LLCs can reduce the tax by up to 50% due to insurance premiums paid for employees. When making payments to customers, the use of cash registers is not yet necessary - it is enough to issue a sales receipt.
How to be fully prepared for changes before 2020
If in 2020 you still plan to sell goods prohibited for UTII or wholesale, then you need to choose a different tax regime in advance. It should be noted right away that switching to a patent will not work. For PSN in 2020, the same restrictions are established as for “imputation”. Therefore, only OSNO and simplified taxation remain (6% or 15%). What is the difference?
OSNO is a general system on which individual entrepreneurs pay:
- Personal income tax 13%;
- VAT 20%, 10% or 0% (depending on the type of product);
- Property tax for individuals – from 0.1% to 2%.
Organizations pay:
- Income tax – 20%;
- VAT 20%, 10% or 0% (depending on the type of product);
- Corporate property tax up to 2.2%.
In addition, OSNO will have to keep more detailed records of all business transactions. But in case of losses, they can be carried forward to subsequent periods, and there is no need to pay taxes on profits and income. This system is more suitable for large and medium-sized businesses and those who are interested in paying VAT.
USN (simplified) is a simpler system for accounting and reporting. In addition, simplifiers are exempt from paying personal income tax, income tax, and VAT. But this special mode has its limitations:
- No more than 100 employees;
- For income no more than 150 million rubles. in year;
- The residual value of fixed assets is no more than 150 million rubles;
- Participation of other companies is no more than 25% (for organizations).
In the simplified version, you can choose a rate of 6% (Income), in which case the tax will be calculated based on the volume of all income. Or 15% (Revenue minus expenses) - tax is calculated on the difference between revenue and expenses. But, if the tax is calculated to be less than 1% of all income, then you need to pay a minimum tax of 1%.
When choosing a system, you also need to take into account the peculiarities of regional legislation, because local authorities can set lower tax rates under the simplified tax system, in some cases up to 0%.
In addition, when assessing future job prospects, you need to be prepared for an increase in the tax burden. Since, if the right to UTII is lost, taxes will no longer depend on physical indicators established by the state, but on real profit. So, with high turnover, the tax burden in 2020 for some may increase to 80%.
For individual entrepreneurs who sell their own products without hired personnel in 2020, it is possible to switch to the special “Professional Income Tax” regime. This is an experimental project for micro-businesses, which provides for minimal reporting and low tax rates of 4% (on income from citizens) and 6% (on income from individual entrepreneurs and organizations). But it can only be used by residents of Moscow, Moscow, Kaluga regions and Tatarstan.
Why is it important to resolve the issue of the future taxation system by the end of 2020? You can switch to the simplified tax system only from the beginning of the year. In this case, you must submit a notification to the inspectorate before December 31, 2020. If this is not done, the tax office will automatically transfer the taxpayer to the general system. This means that you will have to work on it for a whole year.
Regardless of whether you continue to work on another system or decide to close your business, you will need to deregister as a UTII payer.
Differences between simplified tax system and UTII
| simplified tax system | UTII |
| Under the simplified tax system, the tax depends on the amount of income or on the difference between income and expenses. Regions have the right to reduce the tax rate. Tax on the simplified tax system “Income” is paid only if the enterprise had income. The tax on the simplified tax system “Income minus expenses” is always paid, even if there is a loss, and then it is 1% of the enterprise’s revenue. | With UTII, the tax is paid in any case, regardless of the profitability of the enterprise, and is a fixed amount. The tax rate is 15%, and the base for calculating the tax depends on the implied profitability of the type of activity and the coefficients established by federal and municipal authorities. Therefore, UTII tax must be paid, even if the enterprise was operating at a loss. |
| In the simplified version, you will have to use cash register equipment in most cases. | When selling goods and providing services to the public, it is often enough to issue a sales receipt or a strict reporting form. Check the requirements for your type of activity. |
| Under the simplified tax system, the tax period is a calendar year, the declaration is submitted once a year until March 31 (organization) or April 30 (individual entrepreneurs). But advance tax payments are made quarterly within 25 days after the end of the quarter. | With UTII, the tax period is a quarter, the tax is paid within 25 days, and the declaration is submitted within 20 days after the end of the reporting quarter. |
| The simplified tax system can be applied from the beginning of the calendar year. | You can apply or refuse UTII in any month. |
How to withdraw from UTII correctly, not forget anything, and why this is so important
If you switch to a different tax system, this does not mean that you will automatically be removed from the “imputation”. The inspectorate can remove a taxpayer from UTII registration only upon application of UTII-3 (organizations), UTII-4 (entrepreneurs). Such an application must be submitted no later than five days after the termination of activities at the imputation.
Since the whole country will be on vacation at the beginning of the year, such an application should be submitted no later than January 15, 2020. It is sent to the tax office where the individual entrepreneur or organization is registered under UTII. Then, within five working days, the tax office deregisters the taxpayer for UTII. After this, you will need to submit the latest tax return and pay tax.
Why is it important not to miss a deadline? The “imputation” tax is charged regardless of whether the activity is carried out or not. Therefore, if you do not deregister on time, the accrual of tax will not be stopped, and therefore the tax authorities will demand its payment, and in addition you will have to submit returns for the entire overdue period. Accordingly, fines and penalties cannot be avoided.
Advantages and disadvantages of the simplified tax system and UTII
To decide whether to use UTII or simplified tax system for retail trade, you need to know the advantages and disadvantages of these modes.
Advantages of the simplified tax system:
- a wider list of activities to which the simplification can be applied;
- the tax amount is calculated from the money earned;
- non-cash transactions are carried out without any difficulties;
- convenient mainly when income is not large;
- The activity report only needs to be submitted once a year.
Disadvantages of the simplified tax system:
- when a large profit is made, the tax amount increases significantly;
- When engaging in retail trade, the use of cash register equipment is mandatory.
Advantages of UTII:
- the tax amount is fixed, it will not change as profits increase;
- you can write off fixed payments for employees;
- When carrying out retail trade, you do not need to use cash registers.
Disadvantages of UTII:
- some transactions are not subject to UTII tax, and therefore companies have to keep separate records;
- unprofitable when making a small profit;
- reporting must be submitted every quarter;
- There is no opportunity to work in the field of wholesale trade.
From the above pros and cons, it is clear that for some companies it will be more profitable to use the simplified tax system, and for some UTII.
What awaits sane people who violated the ban in 2020?
Since all changes and amendments, including those for labeled goods, are carried out in a very short time, many gaps in the legislation and controversial issues arise. At the moment, there are no specific fines for violating restrictions on the use of UTII.
This situation is regulated by the provisions of clause 2.3 of Art. 346.26 Tax Code. This means that if the tax authorities establish a violation of the retail sales rules for UTII purposes, the individual entrepreneur or organization will automatically be transferred to OSNO from the beginning of the quarter in which the violation occurred. In addition, the taxpayer will have to pay all taxes for this quarter and complete the reporting provided for the general taxation system.
But that's not all. As we have already written, you can switch to “simplified” only from the beginning of the year. Therefore, if the tax office transfers the violator to OSNO, it will have to be applied until the end of the year.
Combination of simplified tax system and UTII
Companies can simultaneously use both UTII and simplified tax system. This is possible, for example, if the company was first engaged in wholesale trade and then switched to retail trade. In this case, they are required to keep separate records for each of the modes of expenses and sales operations.
As soon as a company combines the two modes, it must immediately switch to maintaining separate accounting records. If this is not done, you will have to sort through and retroactively redo a lot of documents.
okbuh.ru
Top questions on UTII for 2020
- Question: An individual entrepreneur sells cigarettes, they are subject to mandatory labeling. Does this mean he won’t be able to apply UTII in 2020?
Answer: In addition to the above three groups of products (medicines, shoes, furs), the following are subject to labeling in 2020: tobacco products, bed linen, tires, etc. However, the ban on labeling does not yet apply to them (if all the conditions for “retail trade” are met) .
- Question: if an individual entrepreneur provides services at the customer’s home and at the same time sells him related products, can he apply UTII in 2020?
Answer: if an entrepreneur goes to the customer’s home to perform work (repair work, hairdresser services, manicure) and sells related products to complete them, then such a sale does not apply to retail, because it was not carried out through stationary retail outlets. Accordingly, UTII cannot be used.
- Question: what to do with the remnants of goods that are prohibited for “imputation” due to mandatory labeling?
Answer: if you are going to switch to a different taxation regime in 2020 and continue to trade in labeled goods, then you need to label the remainder yourself (except for medicines). In the event that you remain on UTII in 2020, then by the end of 2020 you need to sell off all the remnants of such products.
- Question: if a store located in a trade pavilion accepts orders for its goods and payments via the Internet, and then customers pick up such goods in this store, will such activity be subject to UTII?
Answer: In accordance with the clarifications of the Ministry of Finance dated April 1, 2020: the sale of goods through a stationary trade facility (store) both for cash and non-cash payments, in which buyers pick up the goods purchased for non-cash payments, can be carried out on UTII if all other conditions are met. That is, if you have a store, and not a point for issuing online orders, then the activity falls under the “imputation” category.
So, we have analyzed in detail what difficulties “impossible people” will face very soon: the abolition of UTII for retail trade in 2020, a change in the tax regime, mandatory labeling and new requirements. The list is far from complete. For some reason, the government decided to deal with UTII as quickly as possible, so every day our legislation brings new “surprises”.
You need to track these changes every day yourself, and you can’t count on tax inspectors to provide complete, up-to-date, and most importantly correct information. Therefore, be sure to subscribe to our news to always be aware of new requirements. Also, feel free to share information in the comments, it could be very valuable to other entrepreneurs.
Other details and criteria
Conditions of operation
Can UTII taxation be beneficial for retail trade? This is a question many entrepreneurs ask.
The main positive aspects of working on UTII:
- Part of the taxes (“on profit”, VAT) is not paid, so the burden on business is significantly lower;
- the tax is calculated not on the income received, but on the physical indicator;
- UTII can be combined with other taxes;
- there is no need to use CCT;
- voluntary use.
A disadvantage of UTII may be the impossibility of filing a zero declaration if no trading activity was carried out. To stop paying tax, you must deregister with the Federal Tax Service. Also, if there are different types of activities, separate records will have to be kept for each of them, and in case of violation of the UTII payment limits, a complete recalculation will be required.
In accordance with the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, retail trade can be carried out in:
- a stationary retail outlet, which can be with or without premises (up to 150 sq.m.);
- in a temporary retail outlet with an area of 5 sq. m;
- in mobile retail outlets, by delivery trade;
- through vending machines.
Patent nuances
Another method of taxation for private entrepreneurs is the PSN (patent taxation system). The essence of this system is to pay for a patent for a specific type of activity, which replaces the payment of certain taxes.
Unfortunately, PSN is also not suitable for taxation of an online store, since a patent can only be issued for retail trade, which does not apply to the sale of goods via the Internet.
Application principle
UTII can be used to tax business activities specified in Article 346.26 of the Tax Code, and the type of activity must be introduced in the municipal area.
Conditions for using UTII:
- the taxpayer is not the “largest”;
- the regime must be approved by local acts;
- enterprises with less than 100 employees;
- the share of participation in other legal entities must be less than 25%;
- The individual entrepreneur is not involved in the field of education, social security, medicine or public catering;
- economic activities should not be carried out under simple partnership or trust management agreements.
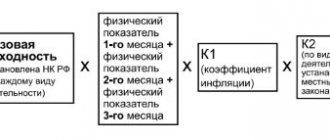
When using UTII reporting, tax is calculated based on the following indicators:
| Estimated yield | This indicator is determined at the legislative level and depends on the specific region and type of activity. |
| Physical indicator | Determined by the area of the retail space, the number of staff, etc. |
| Adjustment factors | Fixed by law. |
| Tax rate 15% | Uniform for all regions and types of activities. |
Selling through networks
The special tax regime gives the entrepreneur many advantages. This is especially true for such a form of special regime as UTII. With it, a businessman is freed from the need to maintain complex tax accounting, gets the opportunity to minimize the burden with high incomes, and is also freed from maintaining cash accounting.
A combination of an online store and UTII may be a tempting opportunity for an entrepreneur, since the law allows for reporting on UTII in retail trade. In this case, an online store is defined as a site that sells products via the Internet.
Users who visit the store's website can create an order for the purchase of a specific product, select a delivery option and payment method, and also pay for the product itself.
The advantage of selling goods via the Internet is that there is no need to hire employees, set up a retail outlet, or rent premises. It is this advantage that makes online trading the fastest growing business. But it also excludes online trading from the list of activities in which UTII can be used.