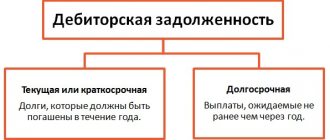
The bankruptcy estate is the totality of all funds, movable and immovable property of the debtor, at the expense of which the claims of creditors are repaid.
The task of creditors and the bankruptcy trustee is to replenish the bankruptcy estate as much as possible by challenging the debtor’s transactions and collecting receivables. The debtors' goal is to achieve exclusion from the bankruptcy estate of property that cannot be foreclosed on.
A bankruptcy lawyer can help both. He will provide assistance to creditors in challenging suspicious transactions of the debtor and returning property, and to debtors in drawing up petitions to exclude property from the bankruptcy estate.
Bankruptcy estate in bankruptcy of individuals
All property of a citizen available on the date of the decision of the arbitration court to declare the citizen bankrupt and introduce the sale of the citizen’s property, as well as identified after this date, constitutes the bankruptcy estate, with the exception of property that cannot be foreclosed on.
In particular, the bankruptcy estate may include the property of a citizen, constituting his share in the general property.
Attention! Property owned by the debtor and his spouse (former spouse) under the right of common ownership is subject to sale in accordance with the general procedure. However, the proceeds are distributed between the spouses in proportion to their shares. But if a spouse believes that the sale of common property does not take into account his interests and the interests of his minor children, he has the right to apply to a court of general jurisdiction with a demand for the division of the common property of the spouses before its sale as part of the bankruptcy procedure. In this case, the common property of the spouses cannot be sold within the framework of bankruptcy until the specified dispute is resolved.
Many debtors are concerned about the question: is it possible to exclude from the bankruptcy estate property that can be foreclosed on, but is insignificant in value? Contact a lawyer, he will help you draw up a reasoned petition to the arbitration court, which has the right to satisfy it.
Attention! The total value of a citizen’s property that is excluded from the bankruptcy estate cannot exceed ten thousand rubles.
What is not included in the bankruptcy estate of bankrupt citizens
Property that cannot be foreclosed on is excluded from the bankruptcy estate:
- residential premises that are the only one and are not under a mortgage;
Attention! On April 26 of this year, the Constitutional Court adopted Resolution 15-P, which allowed the courts to include the only housing of the debtor, whose characteristics exceed the reasonable need for housing, in the bankruptcy estate, and in exchange for this residential premises, the citizen may be purchased or provided by the creditor with another premises within the social norms, but in the same locality. There are no unambiguous criteria for “luxury” housing, so contact a lawyer who will help defend your only home from sale.
- land plots on which a residential building is located;
- items of ordinary home furnishings, personal items (clothing, shoes, etc.);
- property necessary for the professional activities of a debtor citizen, but not more than ten thousand rubles;
- animals used for personal purposes and outbuildings for their maintenance;
- seeds needed for the next sowing;
- food and money for a total amount not less than the established subsistence level of the debtor himself and his dependents;
- special transport for disabled people.
Your lawyer will help you draft a request to exclude such property from the bankruptcy estate.
Bankruptcy estate
First, a regulatory rationale:
Article 131 of the Federal Law “On Insolvency (Bankruptcy)” (quote):
1. All property of the debtor available on the date of opening bankruptcy proceedings and identified during bankruptcy proceedings constitutes the bankruptcy estate.
2. Excluded from the debtor’s property, which constitutes the bankruptcy estate, are property withdrawn from circulation, property rights associated with the debtor’s personality, including rights based on an existing license to carry out certain types of activities, as well as other property provided for by this Federal Law.
As part of the debtor's property, the property that is the subject of the pledge is separately taken into account and subject to mandatory assessment.
In cases established by federal law, the property of the debtor constituting mortgage coverage, which, in accordance with Federal Law of November 11, 2003 N 152-FZ “On Mortgage Securities” (hereinafter referred to as the Federal Law “On Mortgage Securities”), issued bonds with mortgage covered, is excluded from the debtor's bankruptcy estate, and the claims of creditors - owners of mortgage-backed bonds are satisfied in the manner established by the Federal Law “On Mortgage-Backed Securities”.
3. In order to properly maintain records of the debtor’s property, which constitutes the bankruptcy estate, the bankruptcy trustee has the right to involve accountants, auditors and other specialists.
In relation to bankrupt citizens, slightly different conditions:
Clause 1 of Article 213.25 of the law: all the property of a citizen available on the date of the decision of the arbitration court to declare the citizen bankrupt and to introduce the sale of the citizen’s property and identified or acquired after the date of the said decision constitutes the bankruptcy estate.
Paragraph 4 of the same article: the bankruptcy estate may include the property of a citizen, constituting his share in the general property, which may be foreclosed on in accordance with civil law and family law. The creditor has the right to make a demand for the allocation of a citizen’s share in the common property in order to foreclose on it.
The bankruptcy estate does not include:
Clause 3 of Article 213.25: property that cannot be foreclosed on in accordance with civil procedural legislation is excluded from the bankruptcy estate.
In this case, the law refers to Article 446 of the Civil Procedure Code of the Russian Federation, which provides a list of property for which immunity is established:
- an apartment, house, other residential premises (or part thereof), if for the debtor citizen it is the only premises suitable for permanent residence (with the exception of a mortgaged dwelling);
- a plot of land on which the only residential building is located (except for mortgages);
- items of ordinary home furnishings and household items, personal items (clothing, shoes and others), with the exception of jewelry and other luxury items;
- property necessary for the professional activities of a debtor citizen, with the exception of items the cost of which exceeds one hundred minimum wages established by federal law;
- used for purposes not related to business activities, breeding, dairy and working cattle, deer, rabbits, poultry, bees, feed necessary for their maintenance before pasture (going to the apiary), as well as outbuildings and structures necessary for their maintenance;
- seeds needed for the next sowing;
- food and money for a total amount not less than the established subsistence level of the debtor citizen himself and his dependents;
- fuel necessary for the family of a debtor citizen to prepare their daily food and heat their living quarters during the heating season;
- means of transport and other property necessary for the debtor citizen in connection with his disability;
- prizes, state awards, honorary and memorable signs awarded to a debtor citizen.
To paraphrase the words of the law, which are difficult to understand, we can simply say: the bankruptcy estate is everything that can be taken from the debtor
. This is money (cash and in accounts), this is earnings, a car, a dacha, a plot of land, shares in an LLC, securities, etc., down to the smallest detail.
See also a case from practice about how one kopeck was included in the bankruptcy estate for a whole month and they paid 30,000 rubles for it.
Now we will give several examples of judicial acts on the formation of the bankruptcy estate, for a better understanding.
Judicial acts on inclusion in the bankruptcy estate:
Link: text of the decision on the website of the arbitration court
Link: text of the decision on the website of the arbitration court
judicial acts on exclusion from the bankruptcy estate:
Text of the decision on the website of the arbitration court
Text of the decision on the website of the arbitration court
The main requirement for inclusion in the bankruptcy estate is that the property must belong to the debtor by right of ownership. In essence, disputes about exclusion from the bankruptcy estate come down to proving the fact that the debtor does not own the property.
A separate case is the exclusion of part of the money for personal needs from the bankruptcy estate (as in the last example given from judicial practice).
Here the proof is slightly different. As a rule, the minimum subsistence level approved in the relevant region is taken into account. The living wage is for the debtor; if there is a child, then another for the child.
If the wife is a legal dependent (for example, until the child’s 3rd birthday) - then on her.
This amount can be increased if there are additional expenses that the court recognizes as justified (for example, treatment expenses confirmed by medical documentation and checks, in some cases - expenses for renting an apartment, etc.).
The highest courts have spoken about the possibility of saving part of their earnings for personal needs: Resolution of the Plenum of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation No. 45 of October 13, 2015 (paragraph 39), Resolution of the Constitutional Court of the Russian Federation of July 12, 2007 No. 10-P.
Disputes regarding the formation of the bankruptcy estate, the inclusion of any property in its composition or its exclusion from it are resolved in court.
The powers to dispose of the bankruptcy estate belong to the bankruptcy trustee (in relation to citizens undergoing bankruptcy proceedings - the financial manager).
Bruskov P.V.
Source: https://bankrotstvo.legal/articles/konkursnaya-massa/
Bankruptcy estate of legal entities
All property of the debtor, accounts receivable, property rights, funds (with some exceptions) that were available on the date of opening bankruptcy proceedings or were identified during bankruptcy proceedings are included in the bankruptcy estate.
Its size largely determines how fully the claims of registered creditors will be satisfied. You can read about inclusion in the register of creditors' claims in the article.
The capacity of the bankruptcy estate largely depends on the activity of bankruptcy trustees and creditors. The arbitration manager is obliged to find all the property of the debtor and take all measures to collect the debt owed to him.
In addition, both the manager and creditors can challenge the debtor’s transactions, both on the grounds specified in the bankruptcy law and on general grounds of invalidity of transactions. An experienced lawyer specializing in bankruptcy cases will draw up a statement, help collect evidence and enforce the judicial act, because the main goal of challenging transactions is to return everything illegally received by the counterparty to the debtor's bankruptcy estate.
If the property cannot be returned in kind , the acquirer must compensate the actual value of this property at the time of its acquisition, as well as losses caused by subsequent changes in the value of such property under the rules on unjust enrichment (Article 61.6 of the Bankruptcy Law). Your lawyer will take care of this too.
In order to repay the creditors' claims in the order established by law, the insolvency practitioner must sell the debtor's property included in the bankruptcy estate at auction. We have already written about how auctions are conducted during the bankruptcy of legal entities and citizens.
In addition to filling the bankruptcy estate, the creditor must monitor its expenditure, since it is used to pay off not only the register, but also current claims, as well as the costs of the bankruptcy procedure. If the bankruptcy trustee abuses his rights and unlawfully spends the debtor’s property, complain to a self-regulatory organization or to court and demand compensation for losses. A bankruptcy lawyer will also help you draft a complaint or statement.
What is not included in the bankruptcy estate of legal entities
The following are excluded from the debtor's property, which constitutes the bankruptcy estate:
- property withdrawn from circulation,
- property rights associated with the personality of the debtor (for example, based on an existing license).
Collateral property is taken into account separately , since funds from its sale are used to repay the claims of the secured creditor (70% of the proceeds or 80% for loan obligations, but not more than the amount of debt and interest), the rest - to creditors of the first and second priority, for repayment legal expenses, payment of remuneration to the bankruptcy trustee and the persons involved by him.
The property transferred by the debtor for deposit to the escrow agent is also taken into account separately. The escrow agent transfers the deposited property to the beneficiary in order to fulfill the debtor's obligation despite his bankruptcy. But if the grounds for the transfer of property specified in the agreement did not arise within six months from the date of commencement of bankruptcy proceedings, then such property is also subject to inclusion in the bankruptcy estate.
Procedure for selling property in case of bankruptcy of individuals
Content
1. In what cases is the sale of a citizen’s property provided for?
2. What property can be sold
3. Property immunity
4. Do you want to get rid of all your debts?
5. How does a financial manager evaluate property?
6. Procedure for settlements with creditors
7. Deadlines for the sale of the debtor’s property
Sometimes a debtor’s decision to declare insolvency is prevented by the fear of losing all of his personal property. However, if there is nothing to pay off debts, there is no other choice. Experts say that if a bankruptcy case is handled correctly for individuals, part of their assets can be saved. Let's consider what actions allow you to write off debts and not end up on the street.
When filing a bankruptcy petition with the court, the debtor must include a complete description of everything he owns. Not only accounts, apartments, cars are taken into account, but also shares or shares in the authorized capital of an LLC. The list even includes property that is not subject to sale in bankruptcy.
During the first meeting of the arbitration court, a decision is made:
- on the commencement of bankruptcy proceedings;
- refusal on the basis that the plaintiff could not prove his insolvency;
- about leaving the application without progress;
- about the start of restructuring or sale of your assets.
At the first court meeting, the candidacy of the arbitration manager is approved. From this moment on, all of the debtor’s property included in the bankruptcy estate will be managed by the administrator. Many debtors try to avoid the restructuring stage and immediately proceed to the sale of property. This will allow you to save 25,000 rubles on payment for the manager’s work - it is charged in stages.
In what cases is the sale of a citizen’s property provided for?
To better understand how the bankruptcy process of an individual proceeds, carefully read Article 213.24 of the Federal Law “On Insolvency”. There you can also find instructions on how to remove property from the bankruptcy estate.
The law prescribes to proceed to the sale of the bankruptcy estate if:
- the debtor did not submit a restructuring plan on time;
- creditors refused to approve the restructuring plan;
- the court rejected the debtor's proposal for restructuring;
- the debtor violated the terms of the settlement agreement, missed the restructuring payment schedule, or otherwise proved his unreliability.
The debtor himself often insists on introducing a procedure for the sale of property. The fact is that during restructuring, the prospect of declaring bankruptcy and writing off debts can be significantly delayed. You will have to pay the loans, albeit according to a softer algorithm. The sale of property is completed faster. The proceeds are transferred to creditors, and any remaining outstanding debts are written off. Once the court officially declares you insolvent, no one will be able to make claims or demand repayment of debts. If you do not have expensive property, then this path becomes the simplest and most profitable. You can apply to skip the restructuring procedure based on your difficult financial situation.
What property can be sold
Expert opinion
Dmitry Tomilin
All property discovered by the financial manager is subject to sale. Exceptions are provided in Article 213.25. You cannot foreclose on personal belongings, equipment necessary for your work, food, or the debtor’s only home. If the apartment is pledged or purchased with a mortgage, then you can sell it too.
All valuable property of the debtor that does not fall under the list of those protected from collection can be included in the list for sale. A list of such property is in Art. 446 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation.
It is especially important to remember that the financial manager has the right to foreclose even on property that is in shared ownership. This also applies to everything acquired together during marriage. You can read about this in the corresponding section of the Family Code of the Russian Federation.
When selling bankrupt property that is in shared ownership, the proceeds are used to pay off creditors' claims. Only if something remains, the difference will be transferred to the spouse (without taking into account the size of the shares). Considering this fact, the sale of property is beneficial to those debtors who do not have valuable property or other real estate other than their only home.
Property immunity
The Federal Law “On Insolvency” uses the concept of property immunity. When bankruptcy is filed, all of your assets are included in the bankruptcy estate. However, the court can then exclude what is not subject to implementation by law. The main thing people are worried about is the only housing that will help maintain property immunity.
An apartment or a share of real estate, a house, a plot of land, or a dacha can be recognized as the only housing, if it is suitable for permanent residence. If the debtor lives in one region, and his only apartment is located in another, property immunity also applies to it. The court recognizes the housing as the only one, even if the person has registered at a different address.
Deductions from the amount of permanent income should leave the debtor with money in the amount of the subsistence level. If you have minor children or dependent parents, then the minimum subsistence level required for them is also taken into account. Immunity extends to personal awards, belongings, household items and pets.
The law allows the debtor to file a petition for additional exclusion from the bankruptcy estate of property for a total amount of no more than 10,000 rubles. The basis for such a decision may be the declaration of property as necessary for work or other vital needs. Lawyers specializing in personal bankruptcy cases will help you draft a petition correctly.
Do you want to get rid of all your debts?
A free consultation with our specialists will allow you to compare risks and take the first steps towards bankruptcy.
Leave a request for our company’s services and we will contact you within 15 minutes
By leaving a request you agree to the processing of your personal data
How does a financial manager evaluate property?
The assessment of the bankruptcy estate is carried out by a financial manager appointed by the arbitration court. First, an inventory of the property is performed. If no financially significant objects are found, then the manager must draw up a report. It is called “On the absence of property subject to sale.” Everything that can be sold is put up for auction to form the bankruptcy estate. Typically, the sale of property lasts 6-7 months.
The following property can be sold to pay off debts:
- specified by the debtor when filing for bankruptcy;
- registered as collateral;
- hidden, but revealed by the financial manager;
- previously sold or donated, if the transaction was completed within the last 3 years and was canceled by the manager.
The arbitration manager must visit your apartment to evaluate the property. You can agree on a date and time with him. At the same time, he asks government agencies and banks about what transactions you made in the previous 3 years. If the manager decides to challenge your transactions, then such property will also be sold. If information about hidden property is discovered, it will be searched.
Procedure for settlements with creditors
Expert opinion
Dmitry Tomilin
After your property is sold at auction, the financial manager makes payments to creditors. The payment procedure is established by Article 213.27. First, current payments are made - alimony debts, as well as all expenses associated with the bankruptcy procedure itself. Legal costs and the manager's remuneration are covered.
Then debts to government agencies and housing and communal services debts are repaid, only after which the claims of the remaining creditors are satisfied. These debts are also paid in order of priority. Priority is given to compensation for damage to the life and health of third parties and wages.
Among the remaining creditors, those who have the debtor's property as collateral have priority. When a pledged item is sold, 80% of the proceeds immediately goes to the creditor with whom it was pledged. The remaining debts, even if there is not enough money, can be recognized by the court as repaid.
Deadlines for the sale of the debtor's property
Even if the debtor has no property that can be sold, this stage of bankruptcy lasts 6 months. The time frame may be shorter if the financial manager is prompt, creditors are not stubborn, and the court schedule is convenient. In case of discovery of hidden property or cancellation of completed transactions, the process is delayed.
You should not trust those who promise to complete bankruptcy of an individual in 2-3 months - such a period is completely unrealistic. If you have property with which you can at least partially pay off your debts, then the bankruptcy procedure may be delayed. Selling property during bankruptcy of individuals requires time to evaluate the property and organize auctions.
You can get more precise advice on the timing of the bankruptcy procedure. The service is available through a form on the website or by calling a toll-free number. Contacting experienced lawyers will help you get rid of debts faster, and consultations will be useful at any stage.
Help from a bankruptcy lawyer
We at the law firm “Pravovaya GarantiYa” support the bankruptcy procedure of both individuals and legal entities. “Turnkey” or at individual stages. We are ready to work in any format that is convenient for you.
How much does bankruptcy cost? Read the article!
Competitive weight. What is it formed from?
Creditors receive their money at the final stage of bankruptcy - during bankruptcy proceedings, from the so-called “bankruptcy estate” - a financial reserve that was formed from the debtor’s existing assets during bankruptcy.
The larger the bankruptcy estate, the higher the likelihood that creditors will receive their funds in full.
The bankruptcy estate is collected by the arbitration manager through all open and hard-to-reach channels, namely, it is formed from the debtor’s property owned by the organization at the expense of:
- Collection of accounts receivable
Debtor's receivables are financial assets due to an enterprise from individuals and legal entities and contained in unfulfilled contracts and monetary obligations. Debt collection from counterparties is carried out both pre-trial (through negotiations or filing claims) and in court.
- Reclaiming property from someone else's illegal possession
Property owned by the debtor is not always actually in his hands. Sometimes an organization voluntarily transfers part of its assets for use to counterparties - on the basis of written or oral agreements. In other cases, property is lost due to invalid transactions or as a result of forceful pressure and fraudulent actions of third parties. Such property is subject to return and is included in the bankruptcy estate, and the legal basis for return in each specific case will depend on how the assets were removed from the debtor's possession. In addition, the debtor has the right to demand the return of income received by the illegal holder from the use of other people's assets.
- Challenging previously concluded transactions
Bankruptcy provides an opportunity to challenge and cancel the debtor’s illegal transactions. As a result, all funds and lost property are returned to the debtor and are subject to inclusion in the bankruptcy estate for settlements with creditors. In this case, the burden of proving the absence of grounds to challenge the transaction falls entirely on the defendant.
Almost any transaction can be challenged: purchase and sale, loan, pledge, offsets, and even direct write-off by credit institutions of the amount of debt from accounts. The court recognizes the transaction as invalid or void if it has signs of interest; caused significant property damage to the debtor company or counterparty; was committed with an underestimated value of assets and on other legally established grounds.