Putting the machine into operation
Acceptance of installed equipment and its transfer into operation are formalized by an act of acceptance and transfer of fixed assets according to standard form 1.
The certificate of delivery of installed equipment requires a detailed description of the procedure for commissioning (testing), regulation, running-in and registration of delivery.
When describing the start-up (testing) during the acceptance of installed equipment, the following should be indicated:
— material support for the launch, the procedure for inspection and preparatory operations before launch;
— the procedure for checking the serviceability of the components of the equipment and its readiness for start-up;
— the procedure for turning on and off the equipment;
— evaluation of launch results.
When describing regulation work, you should indicate:
— the sequence of regulatory operations, methods of regulating individual components of equipment, control limits, used instrumentation, tools and devices;
— requirements for the condition of the equipment when regulating it (while moving or stopping, etc.);
— the procedure for setting up and regulating equipment for a given operating mode, as well as the duration of operation in this mode.
The description of work on running-in equipment should indicate:
- running-in procedure;
— the procedure for checking the operation of equipment during run-in;
— requirements for compliance with the equipment run-in regime and the running-in of its parts, the duration of the run-in;
— parameters measured during run-in and changes in their values.
When describing the work on registration of acceptance of installed equipment, you should indicate:
— data from control openings of individual parts of equipment;
— results of final comprehensive testing and regulation;
— data in the attached installation drawings, diagrams, reference and other technical documentation;
— guarantees for installed equipment.
A list of comments identified during the start-up of regulation and equipment running-in is compiled.
The act is signed by the persons handing over and receiving the equipment.
After completion of all work on adjustment, testing and running-in of the equipment, as well as after testing, an act of acceptance of the equipment from installation and its commissioning is drawn up.
Date added: 2017-10-04; ;
Similar articles:
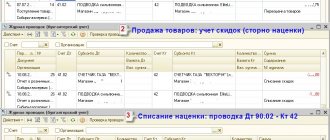
What does the Law say about markdowns?
There are no strictly accepted norms for discounting goods. It is important that the Discount Regulations adopted in a particular trading organization do not contradict accounting standards and relevant government requirements:
- Federal Law of November 21, 1996 No. 129-FZ “On Accounting”;
- Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated July 29, 1998 No. 34n “On approval of the Regulations on maintaining accounting records and financial statements in the Russian Federation”;
- The accounting plan, in particular, the contents of the “Inventories” account;
- Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated June 13, 1995 No. 49 “On approval of the Guidelines for the inventory of property and financial obligations”;
- Letters from the State Statistics Committee approving document forms when conducting an inventory;
- Letter of Roskomtorg dated July 10, 1996 No. 1-794/32-5, which approved the Methodological Recommendations for accounting and registration of operations for the receipt, storage and release of goods in trade organizations.
Machine put into operation wiring
At any enterprise (plants, factories), proper air supply is of great importance, as well as water cooling, which is necessary in any technological process. For these purposes, special systems equipped with fans are used. Various pumps and fans - this machine is put into operation wiring to stabilize the temperature process in production. Special machines control the consumption of electrical energy and absorb the noise effect.
Any retail enterprise that sells food products uses scales. Modern scales are an automatic device that accurately measures the weight of goods. The device is equipped with a display, as well as a special keyboard, due to which the newspaper printing machine determines and displays the necessary information for the seller and the client. The scales can be powered by an electrical outlet or charged from a battery (portable version).
In any office or enterprise, with the help of special devices, optimal air temperature and air exchange are maintained. This is necessary to organize a comfortable work process. Among the types of devices used are machines for automatic knitting: hoods, air conditioners of various modifications, ventilation shafts with natural and artificial cooling. Ventilation can be exhaust, supply and mechanical.
If goods are accounted for at acquisition cost
In this case, the order of markdown of goods depends on the magnitude of the reduction in prices for goods.
There are two possible options here - when the new price is greater than or equal to the cost of purchasing the product and when it is less.
In the first option, the revaluation procedure consists of replacing price tags on goods. In this case, no entries are made in accounting. The same is done in the second option, if the overvalued goods are sold before the end of the reporting year.
If revalued goods are not sold by the end of the reporting year, then it is necessary to act in accordance with paragraph 25 of PBU 5/01 “Accounting for inventories”. This paragraph states that goods “that are obsolete, have completely or partially lost their original quality, or the current market value, the sales value of which has decreased, are reflected in the balance sheet at the end of the reporting year minus a reserve for a decrease in the value of material assets.” It is impossible to credit account 41 “Goods” for the difference between the acquisition cost and the new price, since according to paragraph 12 of PBU 5/01 “the actual cost of inventories, in which they are accepted for accounting, is not subject to change, except in cases provided for by law Russian Federation".
The reserve amount (P) is determined by the formula:
P = SP - NC
An entry is made for the amount of the reserve:
Debit 91 Credit 14
The same entry is made in the event of a further decrease in the market price for a given product (by the amount of the further decrease).
In the balance sheet at the end of the reporting year, the balance of goods is shown as the difference between the balances of accounts 41 and 14.
Subsequently, as goods are disposed of (sale, spoilage, shortage, etc.) for which the reserve was formed, it is written off by posting:
Debit 14 Credit 91
A similar entry is made with a further increase in the market value of goods (by the amount of the increase).
It is recommended to conduct analytical accounting for account 14 by type of goods.
The creation of the above reserve serves the purpose of showing the real (not inflated) valuation of goods in the balance sheet. And although PBU 5/01 prescribes creating a reserve only for goods remaining at the end of the year, we believe that this must be done at any reporting date.
Otherwise, the interim balance sheets distort the values of the balances of goods indicated in them.
The procedure for revaluing goods when accounting for them at acquisition cost involves replacing the price tags on the goods.
Important: the machine is put into operation wiring
Also, methods for modernizing machines, a network via radio channel equipment, a cutting cross-cutting machine, a video on how to make animals from rubber bands without a machine on forks, reviews of a trommelberg tire changing machine, studio equipment for photographing photos, an SP-6 machine, buy a TV 200 lathe, a cutting machine for , Kuibyshev technological equipment plant Samara.
At enterprises involved in the production of food products, various machines are used that provide an automated work process. Installed automation can be classified into buy equipment for a fitness center according to certain criteria. These are different groups of machines that differ in the functions they perform.
Accounting entries upon receipt (purchase) of fixed assets
All technological operations can be classified according to the principle of the work performed, according to the device and methods of execution.
Enterprises that produce semi-finished products for sale in food supermarkets are equipped with special refrigeration units. Freezers are sanitary equipment in an apartment, with the help of which finished products are stored in warehouses for a certain time. Ready-made semi-finished products enter the freezers via a special conveyor, which is equipped with a spiral belt.
© obo.tw1.ru
Revaluation and accounting of reserves for reduction in the value of inventories
Recently, the procedure for regulating the results of revaluation of materials has undergone significant changes. According to the Accounting Regulations “Income of the organization” and “Expenses of the organization”, the amounts of revaluation and depreciation of current assets are considered as other financial results and are included in operating income and expenses.
If an organization revaluates materials, then its result, as identified, is written off directly to account 91 “Other income and expenses”:
§ additional valuation – Debit 10 Credit 91 ;
§ markdown – Debit 91 Credit 10 .
In analytical accounting, a separate sub-account is opened to accumulate data on the revaluation. Subsequently, the result from the revaluation of materials goes to the profit and loss account as part of the balance of other income and expenses. Thus, he participates in the formation of the final financial result of the organization.
If necessary, a similar procedure can be applied to take into account the results of revaluation of other types of working capital: balances of work in progress, inventories of finished products, goods, etc.
Inventories for which the market price has decreased during the reporting year, or they have become obsolete or have completely or partially lost their original qualities, are reflected in the balance sheet at the end of the reporting year at the current market value, taking into account the physical condition of the inventories. A decrease in the value of inventories is reflected in accounting in the form of a reserve accrual.
For this purpose, synthetic account 14 is used, which is called “Reserves for reducing the value of material assets.” It is intended to clarify the evaluation of materials. The mechanism for its use is similar to the operation of accounts for other valuation reserves (reserves for doubtful debts, for the depreciation of investments in securities).
Before drawing up the annual report, the actual cost of procurement of materials is compared with their current market value (possible sale value).
The calculation of the current market value of inventories is carried out by the organization on the basis of information available before the date of signing the financial statements. When calculating, the following is taken into account:
– and a change in price or actual cost directly related to events after the reporting date that confirm the economic conditions existing at the reporting date in which the organization conducted its activities;
– assignment of inventories;
– the current market value of finished products, in the production of which raw materials, materials and other inventories are used.
A reserve for reduction in the value of material assets is not created for raw materials, materials and other inventories used in the production of finished products, works, or provision of services, if as of the reporting date the current market value of these finished products, works, services corresponds to or exceeds its actual cost .
The organization must provide confirmation of the calculation of the current market value of inventories.
When the actual cost is lower than the current market value, the actual cost is taken as the balance sheet valuation of materials. If the current market value is lower than the actual cost, then the materials are shown on the balance sheet at the current market value, and a loss from the reduction in the value of inventories is recognized in the income statement.
A reserve for a decrease in the value of material assets is created for each unit of inventory accepted in accounting. It is allowed to create reserves to reduce the cost of material assets for certain types (groups) of similar or related inventories. It is not allowed to create reserves to reduce the cost of material assets for such enlarged groups (types) of inventories as basic materials, auxiliary materials, finished products, goods, inventories of a certain operational or geographic segment, etc.
Recognizing the realizable value as a balance sheet valuation of materials does not change their value in accounting. For the amount of reduction in the cost of materials, reserves are formed at the expense of the profit of the reporting year. Transactions with carry-over balances of material assets in the next period are recorded without taking into account the decrease in their value in the balance sheet.
In accounting for the amount of reserves for a decrease in the cost of materials, an entry is made in debit 91 “Other income and expenses” and credit 14 “Reserves for a decrease in the cost of material assets.” At the beginning of the next reporting period, the balance on account 14, carried over from the previous period, is closed by reverse entry.
If, in the period following the reporting period, the current market value of inventories, for the reduction of the value of which a reserve was created in the reporting period, increases, then the corresponding part of the reserve is included in the reduction in the value of material expenses recognized in the period following the reporting period.
The accrued reserve is written off to increase financial results (account “Other income and expenses”) as the inventories related to it are used or sold.
Thus, the balance on account 14 “Reserves for impairment of the value of material assets” represents the difference between the actual cost and the current market value, relating exclusively to materials at the end of the reporting period. When closing this account, it is assumed that all carry-over balances of material assets will be completely used up during the next reporting period.
5.14. Inventory of inventories
The safety and correct registration of operations on the movement of inventories are confirmed by the results of periodically conducted inventory.
The main purpose of inventory is to identify the actual availability of inventory in physical and monetary terms.
During the inventory process, the safety of inventory items is checked; correctness of their storage, release, condition of weighing and measuring instruments; the procedure for keeping records of the movement of inventory items.
The head of the organization or his deputy, or the chief accountant organizes and manages the inventory. The inventory work is carried out by a commission consisting of competent persons, which is appointed by order of the head of the organization.
At the time of the inventory, the accountant draws up an inventory list of inventory items in warehouses (form No. inv-3). Warehouse operations are not carried out during this period; In this inventory, the warehouse manager gives a receipt that all warehouse documents are recorded in materials accounting cards and submitted to the organization’s accounting department.
To identify inventory results, a book of material balances can be used, which provides special columns for recording material balances in kind according to inventory records.
In all cases, discrepancies identified as a result of inventory (surpluses or shortages) are documented through the preparation of matching statements and assessed at actual cost. Valuables found to be in surplus are subject to capitalization with a reduction in general business expenses ( Debit 10 Credit 26 ). The shortage of valuables is written off to account 94 “Shortages and losses from damage to valuables” with a decrease in their value and quantity in the accounts of material assets (account credit 10).
By decision of the head of the organization, the amount of the shortage within the limits of natural loss norms is attributed to production costs: debit 25.26 credit 94 “Shortages and losses from damage to valuables.” Shortages in excess of natural loss norms (at retail prices) are attributed to financially responsible persons:
Didn't find what you were looking for? Use the search: