View from above
According to estimates by the Ministry of Labor of the Russian Federation, companies use about 40 types of personnel documents in various variations. 100% of the company’s employees interact with them, so converting these papers into electronic form and subsequent automation of processes immediately saves a lot of resources.
But the devil is in the details. The first thing to be faced with is the need to ensure the significance of personnel documents. They may be required both by the employee himself and by a dozen external organizations (the Russian Ministry of Labor, pension and compulsory health insurance funds, courts and other authorities).
Everything is clear with paper: you must have a copy with a stamp and signature on hand. As for working with electronic documents, there is not much practice yet.
Why another experiment is needed?
The Ministry of Labor decided not to wait for the next changes in legislation regarding electronic digital signatures to appear. In addition, officials are confident that practical experience of switching to electronic documents is much more useful for drafters of the bill than any other options for collecting information. Therefore, over the next three years, it is planned to conduct another experiment on the transition to ECD. The corresponding bill has already been prepared and should soon be submitted to the State Duma.
The goal of the second pilot project is to identify and, if possible, find a solution to problems associated with the use of electronic signatures, archival storage of e-documents, and other issues when working with electronic digital signatures. Moreover, a business that agrees to participate in the experiment will have to work at a time when other regulations are also changing. According to the Ministry of Labor, amendments to the following Federal laws must be approved by 2020:
- “On archiving in the Russian Federation”;
- “On the mandatory copy of documents”;
- “On information, information technologies and information protection”;
- other regulatory legal acts that contain references to electronic documents, procedures for storing and using an electronic duplicate (electronic image) of a document or the document itself.
As for the project participants, they are still unknown, but it is planned that there will be about 10 organizations ready for changes in their work. All expenses that employers will have to bear are entirely their responsibility. At the same time, they will be able to choose which types of electronic signatures to use and which personnel documents to maintain exclusively in electronic form. The only rule is to be sure to use an enhanced qualified electronic signature if:
- employment contract;
- agreement on liability;
- student agreement.
Or if changes are made to them.
It is also clarified that as part of the experiment, companies will have to develop and ensure the functionality of their own information system, which will allow storing electronic documents and providing access to them to different categories of users for various actions (making changes, monitoring, receiving an extract (copy), etc.).
Officials have not forgotten about the rights of workers. Companies that will participate in the pilot project will be required to stipulate in collective agreements or individual agreements with employees that they are not against transferring documents to an online format.
According to the plans of the Ministry of Labor, the experiment should take place from 01/01/2019 to 12/31/2022. But if State Duma deputies do not have time to approve the bill, the deadlines may change. Follow our news.
Frame digitization, where to start?
All personnel documents can be divided into 2 parts:
1. Personal - this is an employment contract and orders that affect only one employee (on changing the provisions of the employment contract, dismissal, acceptance, transfer, etc.).
2. Massive - all kinds of instructions, orders, regulations, which all employees of the organization or relevant departments must be familiar with.
It is not so difficult to create an electronic form of a document as to ensure its legal significance in the future. On the one hand, there is Federal Law No. 63 of 04/06/2011 “On Electronic Signatures”. It allows the use of an electronic signature (ES) and obliges documents signed by it and with one’s own hand to be recognized as equivalent. On the other hand, there is the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, which allows the use of electronic documents only by remote employees and only with the use of an enhanced qualified electronic signature - UKEP.
Results of the first pilot project to introduce electronic document management in the personnel sector
From March 23 to October 1, 2018, the Ministry of Labor and Social Protection conducted an experiment on converting documents and information about employees on labor relations issues into electronic form.
The rules for its implementation are regulated by Order No. 194 dated March 26, 2018. It states, in particular, that new work rules will be tested at such important stages as concluding employment contracts and arranging business trips, issuing work permits, familiarizing the employee with the vacation schedule and some employer's personal identification documents. 11 large companies participated in the pilot project: Gazprombank JSC, AvtoVAZ PJSC, Rosbank PJSC, Mechel PJSC, Severstal Management JSC, Rostelecom PJSC, SIBUR LLC, Alfa-Bank JSC, PJSC Tatneft, LLC Agrotorg. Among their tasks were:
- test the mechanism for maintaining personnel documents electronically;
- evaluate the costs and effects obtained from the new rules for maintaining personnel records;
- identify problems and risks from maintaining personnel document flow in email. form;
- prepare proposals for optimizing documents mandatory for employers;
- provide initiatives to amend legislation in order to allow electronic personnel document management (EDF).
According to information from the Ministry of Labor dated October 19, 2018, certain difficulties have been identified that the government will have to solve before specific regulations on ECD appear. Here are the problems the business pointed out:
- High cost of acquiring and using a digital signature. It is assumed that electronic document management will require the acquisition of at least 1 digital signature annually. Now its cost per person ranges from 1000 to 5000 rubles. If this price does not decrease, then the economic effect of introducing ECD will be negligible.
- Lack of unified requirements for a universal digital signature. Currently, several types of digital signatures are approved by law, which are used for various situations. The most popular is an enhanced qualified signature, since it can be used in a wider range of legal relations. However, for personnel records management, the law has not yet established the type of digital signature that should be used and its features.
- Technical problems. The companies participating in the experiment came to the conclusion that maintaining documents exclusively online is unprofitable for the employer due to the high risk of being punished due to technical problems. Thus, the employer will have to answer for the loss of data, unauthorized use by third parties, and software errors during the transmission or processing of information. If the lost documents are needed by the court or regulatory authorities, then not only the company will suffer, but also the employee whose information was lost. This means that both the employee and the control and supervisory authorities will be able to hold them accountable.
- If the employer loses documents, there are also risks for employees. Without documents, they will not be able to protect their rights.
Since the problems are significant, the Ministry of Labor, the Russian Union of Industrialists and Entrepreneurs and the Federation of Independent Trade Unions proposed to first find solutions to them, and then gradually implement all initiatives. In addition, officials believe that first we need to wait for changes in the IT field so that rules regarding a universal electronic digital signature, archival data storage, data transfer protection, and the legal significance of e-documents, including in court, will appear. According to the government's plans, the relevant bills should be prepared within the following time frames:
- by December 2020 - initiatives relating to the formation, acquisition and use of an electronic signature, the establishment of unified requirements for it, its visualization in an electronic document;
- by July 2020 - projects where the concepts of an electronic document, procedures for storing and processing electronic documents and their duplicates (electronic images) will be clarified.
The Ministry of Labor is confident that only after all these legal frameworks have been adopted can active development of a bill allowing employers to maintain personnel records only in electronic form begin. According to officials, the document will appear no earlier than 2021.
All rise, the court is in session
Let's look at recent case law. Interesting facts about the use of electronic means in the field of labor law can be noted:
- the court considered it legitimate for employees to familiarize themselves with local regulations (hereinafter referred to as LNA) by e-mail: Ruling of the Primorsky Regional Court of March 6, 2014 in case No. 33-1126;
- It is permissible to use a simple electronic signature when reading electronic documents: Decision of the Novo-Savinovsky District Court of Kazan dated January 16, 2014 in case No. 2-1091/14.
Thus, attention should be switched from digitalizing the entire personnel flow to mass documents. At least until changes are made to the Labor Code.
AUTOMATED WORK WITH PAPER DOCUMENTS
First, let's look at how you can use electronic document management systems when working with paper documents.
HR Dictionary Document flow - the movement of documents in an organization from the moment of their creation or receipt until completion of execution or dispatch
The HR department processes the following documents:
- incoming (coming from other organizations);
- outgoing (sent to other organizations);
- internal (created in the organization for use in management processes).
The peculiarity of personnel documentation is that they are mainly internal documents.
The process of working with documents of all types comes down to their transfer from one official to another, i.e., in fact, to their movement within the company along a certain route:
- incoming - from receipt to execution;
- outgoing - from creation to sending;
- internal - from creation to execution. When moving documents, certain procedures are followed,
- the set of which depends on the type of document. Some of them can be automated.
What document processing procedures can be automated?
First of all, approval of draft documents, registration, control of execution and search in the electronic document management system.
Let us note the main features of the implementation of these procedures in relation to personnel documentation.
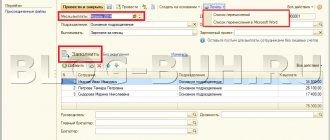
1. Electronic approval of documents.
The need for approval of documents arises when preparing orders for personnel, submissions and proposals for transfer to another job, rewarding employees and in many other cases.
Preparation of personnel documents in an automated mode allows you to avoid the labor-intensive and time-consuming procedure of traditional approval using duplicate copies of the draft document.
Having the responsible executors have an electronic signature allows you to abandon the “paper” approval of documents and speed up the process of their preparation and acceptance.
How to organize electronic approval of documents?
The electronic document management system must include a list of documents subject to approval, indicating the following mandatory information:
If the organization has a representative body of workers, for example, a trade union committee, the above list should indicate all cases provided for by the Labor Code of the Russian Federation for issuing documents on issues of working with personnel that require taking into account the opinion of the trade union committee (another representative body of workers).
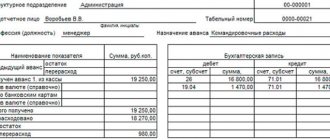
2. Registration of documents.
Registration of personnel documents is traditionally carried out using books, registration journals, and record cards listed in Art. 695 List of standard administrative archival documents generated in the process of activities of state bodies, local governments and organizations, indicating storage periods, approved. by order of the Ministry of Culture of Russia dated August 25, 2010 No. 558 (hereinafter referred to as the List of documents with storage periods).
What registration forms can be maintained electronically?
Most of the personnel documents can be taken into account in an automated mode. The only exceptions to this rule are those registration forms that provide for the personal signature of a personnel service employee after entering information about the document and (or) the signature of an organization employee upon receipt of the document - for example, a book for recording the movement of work books and inserts in them.
Forms of registration books, magazines, cards are developed and approved by the employer independently. However, in some cases, registration forms established by regulatory legal acts must be used:
- a book for recording the movement of work books and inserts in them, as well as a receipt and expenditure book for accounting for forms of a work book and inserts in it, the forms of which are attached to the Instructions for filling out work books, approved. Resolution of the Ministry of Labor of Russia dated October 10, 2003 No. 69;
- NA No. 12'2009 is a logbook for employees leaving on business trips from the sending organization, and a logbook for employees who arrived at the organization to which they are sent, the forms of which are approved by order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of Russia dated September 11, 2009 No. 739n.
How to automate the document registration process?
The corresponding registration forms with instructions for completing them must be included in the electronic document management system. Let us give examples of such forms.
Electronic registration of documents allows you to subsequently search for information about working with personnel and compile analytical reports and statistical reports in an automated mode.
Since the establishment of our company, personnel records have been kept in paper journals and registration books. Starting next year, we want to switch to automated registration and have transferred the existing registration forms to spreadsheets. This work also made it possible to verify that we have some problems with the numbering of personnel documents. I would like to build a logical and competent system for registering them. Are there any rules according to which documents must be assigned registration numbers?
When building a system for registering personnel documents, you really need to pay attention to their indexing (numbering). This issue is not regulated by regulations and is decided by the employer, but it is advisable to take into account the following recommendations.
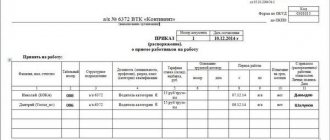
1. Employment contracts are registered within a calendar year.
For indexing, simple serial numbers are used, to which, in order to speed up the search for documents, you can add: the year when the employment contract was concluded, the index of the structural unit to which the employee was hired, etc.
2. Orders for personnel are registered and indexed separately depending on the period of their storage.
Most personnel orders have a long shelf life of 75 years. The exception is orders with a retention period of 5 years: on the provision of annual paid and educational leave, on the secondment of employees within the country, on the imposition of disciplinary sanctions, on duty (clause “b” of Article 19 of the List of documents with retention periods).
In established practice, the method of alphanumeric indexing has been used for many years, when a letter designation is added to the serial number of the order, for example 1-k, 1 l / s, etc. In the case of a large number of orders for personnel, when registering, they are divided not only by storage periods, but also by variety (subject-specific basis): about hiring, about transfer to another job, about dismissal, etc. Each array is assigned its own alphanumeric index.
3. When registering employee personal cards and personal files, different methods can be used - for example, documents and files are assigned simple serial numbers, and newly hired employees “inherit” the numbers of personal cards and personal files of those who quit (similar to assigning personnel numbers to employees). Often, the employee’s personnel number is simply used to number personal cards and personal files.
4. Statements, acts, protocols, internal correspondence (reports and explanatory notes) are numbered within a calendar year using simple sequential numbering.
5. Official letters, as a rule, are registered centrally with the assignment of indexes built according to the following scheme: the serial number of the document from the beginning of the calendar year and the number of the file in which the executed received document will be filed in the future, or the number of the file in which a copy of the sent document will be placed .
Note! Not all registration books (magazines) can exist only in electronic form
As already mentioned, registration forms for personnel documents are included in the List of Documents with Retention Periods.
Books of registration of employment contracts, personnel orders (with a long shelf life), personal files, personal cards of employees, etc. are stored for 75 years.
Therefore, they cannot exist only in electronic form. When working with such registration forms, you should adhere to the following rules.
Rule 1. At the end of the calendar year, electronic registration books (magazines) must be printed page by page and bound in hard or soft covers, depending on the storage period, which is equal to the storage period of the documents registered in the book (magazine).
Rule 2. All registration forms, regardless of shelf life, must be stitched and not glued or fastened with metal staples. The pages of books (magazines) are numbered before using the form.
Rule 3. Books (magazines) in which documents of long-term (over 10 years) and permanent storage periods are recorded are not only stitched and numbered, but also laced and then certified. The certification inscription indicates in numbers and in words the number of stitched and numbered sheets of the book (magazine). The certification is made by the head or specialist of the personnel service and is certified by the seal of the personnel department. In its absence, the certification signature is made by the head of the organization or a person authorized by him and certified by the seal of the organization.
What features of registration forms are established by regulations?
Special requirements are imposed on the book for recording the movement of work books and inserts in them and the receipt and expenditure book for recording forms of the work book and inserts in it. According to clause 41 of the Rules for maintaining and storing work books, producing work book forms and providing them to employers, approved. By Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of April 16, 2003 No. 225 “On work books”, these books must be numbered, laced, certified by the signature of the head of the organization, and also sealed with a wax seal or sealed.
3. Control of execution of documents.
Of great importance for the personnel service is monitoring the execution of documents, as well as monitoring compliance with the requirements of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation when working with personnel.
When an employee is actually admitted to work, the employer is obliged to draw up an employment contract with him in writing no later than three working days from the date of the employee’s actual admission to work (Part 2 of Article 67 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). The employer's order for employment is announced to the employee against signature within three days from the date of actual start of work (Part 2 of Article 68 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
When an employee is actually admitted to work, the employer is obliged to draw up an employment contract with him in writing no later than three working days from the date of the employee’s actual admission to work (Part 2 of Article 67 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). The employer's order for employment is announced to the employee against signature within three days from the date of actual start of work (Part 2 of Article 68 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
New acquaintance
What will ultimately be required to “legalize” familiarization with LNA without paper? You can organize the process with local acts by email.
To do this you need:
- approve the relevant regulations on the procedure for working with email;
- inform the employee in writing against his signature;
- assign email addresses to an employment contract or other document signed by the employee.
The provision should include:
- regulations on the use of email by employees;
- deadlines for responding to letters and storing received and sent messages;
- the employee’s obligation to notify the sender of receipt of the letter and regularly check the receipt of e-mail for a specified period;
- a clause stating that correspondence between an employer and an employee is equivalent to the exchange of paper documents.
It will be more reliable to record information using an electronic signature.
Will HR EDI become mandatory in 2020?
The introduction of electronic work books can be considered the first stage of the process of automation of regulated personnel records, which is gaining momentum every year. The high degree of government involvement in increasing the pace of automation will force business to take part in this process, no matter - in 2020 or 2021, but it will still have to be done.
The important thing is that today there are IT solutions that comply with current legislation and can quickly adapt to any changes in the outside world. They enable a business not only to join the process of transition to EDI without losses, but also to benefit from it - to reduce costs and speed up processes many times over, which will ultimately have a beneficial effect on the rate of growth and development of the entire business as a whole.
Signature. Electronic. Its
An electronic signature is additional information that is needed to identify the signer, the immutability of the document and its details. The main advantage of an electronic signature over access through corporate systems is the inability of anyone other than the key owner to generate the same set of information.
More economical options are enhanced unqualified (UNEP) and simple electronic (PEP) signatures.
Federal Law No. 63 allows the use of an unqualified electronic signature on the same basis as a qualified one, but with some differences.
In the case of UNEP, the certification center may not be accredited. At the same time, the employer can independently deploy services to maintain the electronic infrastructure. They will allow you to generate key pairs and issue them to employees so that employees can sign documents in the information system.
Thus, . But it alone is not enough to use UNEP. The employer must also prepare and implement a set of documents for the correct use of an electronic signature:
- areas of responsibility and operating procedures of the CA;
- rules for using keys;
- conditions and means of formation and verification;
- the procedure for recording applications, issuing, confiscating and destroying media and keys.
In turn, the employee must know:
- procedure for obtaining electronic signature keys;
- where to use it;
- what actions in the system will form an electronic signature.
He must also understand that he is personally responsible for the key pair issued to him, and the electronic signature is analogous to a handwritten signature.
What was decided using the electronic work book?
Initially, officials wanted to combine the initiative to switch to an electronic work book with the idea of completely transferring employers to EKD. However, as the sample experiment showed, electronic document management in personnel records management should be developed separately. Unions of trade unions and all-Russian associations of employers insisted on this.
So the Ministry of Labor decided to promote the bill on an electronic work book now, in order to introduce a web document in domestic companies in 2020. According to officials, the initiative is ready, and it assumes that (quote from information from the Ministry of Labor dated October 19, 2018):
employers will send electronic information to the Russian Pension Fund about the work activities of employees, that is, about hiring, transfer to another workplace, dismissal. The project is large-scale as it affects all employers. Workers will have the opportunity to see in the information system at any time the records made by the employer, as well as send their data electronically to the employer, for example, when applying for a job, including for working remotely in another location.
You can read about the pros and cons of an electronic work book in our material “The government is ready to introduce electronic work books from 2020.”
Pros and cons of switching to electronic personnel document management
Electronic HR document management has a huge number of advantages over traditional methods of document management. Thus, the positive aspects of introducing electronic personnel document management in an organization include the following features:
Accelerating interactions.
Traditional document flow requires a significant amount of time to transport physical storage media. In the case of large companies, a letter can travel from one city to another within several days. At the same time, electronic document management allows for the transfer of information instantly.- Reduced costs. This advantage of electronic personnel document management directly stems from the previous one. Due to the absence of the need to transfer physical documentation, the enterprise does not incur costs in this area of activity in principle.
- Simplification of record keeping. Due to the presence of an electronic register of personnel documentation, its accounting is greatly simplified and the possibility of creating documents with duplicate numbers is eliminated. This speeds up the search for necessary documents and ensures their effective use.
- Improving organizational capabilities. Electronic personnel document flow can be carried out, including in relation to administrative documentation in the organization. This approach allows, simultaneously with the publication of such documents, to provide step-by-step control of their implementation and verification of the effectiveness of decisions made, with the possibility of adjustments by management in real time and without the need for personal control of execution on the spot.
However, electronic personnel document management also has a number of significant disadvantages, both related to the regulatory settlement of this issue, and global ones inherent in such an interaction mechanism in principle. The disadvantages of electronic personnel document flow in an organization include the following features of this method of organizing interactions:
- Significant initial costs. The need to organize an electronic personnel document management system requires the acquisition of special software solutions, provision of material and technical base, training of employees to work with the system, as well as the acquisition of electronic signatures, with the exception of a number of situations.
- Additional security risks. Any electronic personnel document management system also requires additional costs to ensure the required level of security, because within its framework the processing of personal data of employees will be mandatory. In this case, violation of the processing procedure can lead to negative consequences for the enterprise.
- Lack of legislative regulation. Currently in the Russian Federation, legislation allows the use of electronic personnel document management only in a limited form in relation to certain nuances and aspects of personnel records management.
Thus, electronic personnel document management in the Russian Federation is not yet completely possible in principle. At the same time, the experience of a number of other world countries indicates that such systems can be implemented and can significantly improve the efficiency of the entire company as a whole and at least its HR department in particular.
Participation of employees and job seekers
Employees and candidates for vacant positions have the right to join the experiment or refuse it. In the latter case, the organization or individual entrepreneur cannot fire the employee or use the refusal as a reason not to hire the applicant.
An employee who agreed to participate in the experiment may change his mind at any time by notifying the employer in writing no later than two weeks in advance.
If an employee needs any personnel document compiled electronically, it can be requested from the employer. To do this, you must submit an application and indicate the method of transferring the document: in electronic form (signed by the employer’s EPC), in the form of a certified paper copy, or through the employee’s personal account on the “Work in Russia” portal. The company or entrepreneur is required to provide the requested documents free of charge within three working days. Similarly, upon dismissal, a copy of the order to terminate the employment contract is submitted.
ELECTRONIC DOCUMENTS
NA No. 6'2013 The introduction of new changes to labor legislation allows us to talk about the beginning of the transition to paperless technologies when documenting work with personnel. Federal Law No. 60-FZ dated 04/05/2013 introduced a new chapter 491 into the Labor Code of the Russian Federation “Features of regulation of labor of remote workers” (came into force on April 19, 2013), which for the first time talks about the exchange of electronic documents between the employer and the employee.
The issue of the need for legal regulation of the work of remote workers has been discussed for more than a year or two - in practice, such an organization of work “unofficially” has existed for quite a long time. Now remote workers work legally.
The need for the transition from paper documents to electronic ones is caused primarily by the peculiarity of remote work itself, which is understood as the performance of a labor function defined by an employment contract outside the location of the employer, its branch, representative office, other separate structural unit (including those located in another area), outside the stationary worker a place, territory or facility directly or indirectly under the control of the employer, subject to the use of public information and telecommunication networks, including the Internet, to perform this job function and to carry out interaction between the employer and employee on issues related to its implementation (Part 1 of Article 3121 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
The Labor Code of the Russian Federation directly states that remote workers are considered to be persons who have entered into an employment contract for remote work (Part 2 of Article 3121 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation) and they are subject to labor legislation and other acts containing labor law standards (Part 3 of Article 3121 Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
All this means that, in general, remote workers must be registered for work according to general rules, including compliance with the requirements for documenting labor relations. At the same time, traditional documents drawn up on paper can be replaced by electronic ones in virtually all situations that arise in working with personnel.
How do documents prepared for a remote employee differ from regular personnel documents?
Electronic documents compiled for a remote worker in form and content generally correspond to traditional paper counterparts, containing the same details: name of the organization, type of document, registration date, registration number, place of document preparation, title to the text, text, signature, approval visas (if necessary), familiarization visas. The registration of these details must comply with the requirements of GOST R 6.30-2003 “Unified documentation systems. Unified system of organizational and administrative documentation. Documentation requirements."
However, the information contained in these documents is presented not in paper, but in electronic form and is transmitted using information and telecommunication networks, therefore, one of the most important details of documents, which directly affects their legal force, is drawn up completely differently - the “Signature” detail, as well as the details “Visa for familiarization of the employee with the document.”
Electronic signature
The exchange of electronic documents requires the use of a new type of signature - electronic. The absence of it from a citizen (future remote worker) will not allow the transition to paperless information technologies when documenting work with personnel.
Article 2 of the Federal Law of 04/06/2011 No. 63-FZ “On Electronic Signatures” (hereinafter referred to as the Law on Electronic Signatures) defines such a signature as information in electronic form that is attached to other information in electronic form (signed information) or is otherwise connected with such information and which is used to identify the person signing the information.
Article 5 of the Law on Electronic Signatures provides for two types:
Type 1. Simple electronic signature - through codes, passwords or other means, it confirms the fact of the formation of an electronic signature by a certain person.
Type 2. Strengthened electronic signature, it can be unqualified and qualified.
Unqualified electronic signature:
A qualified electronic signature meets all the characteristics of an unqualified electronic signature and the following additional characteristics:
- the electronic signature verification key is specified in the qualified certificate;
- To create and verify an electronic signature, electronic signature tools are used that have received confirmation of compliance with the requirements established by the Law on Electronic Signatures.
What type of electronic signature is used when exchanging electronic documents between an employer and a remote worker?
This is directly stated in Part 4 of Art. 3121 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation: if interaction between a remote worker or a person applying for remote work and the employer is provided through the exchange of electronic documents, enhanced qualified electronic signatures are used.
Creates certificates of electronic signature verification keys, issues such certificates to persons who apply for them (applicants), sets the validity period of certificates, cancels them, etc. the certification center is a legal entity or individual entrepreneur (Articles 2, 13 of the Law on Electronic Signatures ).
Is there a validity period for a qualified electronic signature?
Note! If the certification center is recognized by the authorized federal body as meeting the requirements of the Law on Electronic Signatures, then it receives accreditation (Article 2, 15 of the Law on Electronic Signatures)
A qualified electronic signature is recognized as valid until a court decision establishes otherwise, subject to the following conditions being simultaneously met (Article 11 of the Law on Electronic Signatures):
- the qualified certificate was created and issued by an accredited certification center;
- the qualified certificate is valid at the time of signing the electronic document or on the day the validity of the specified certificate is checked;
- there is a positive result of checking that the owner of the qualified certificate has a qualified electronic signature;
- a qualified electronic signature is used subject to the restrictions contained in the qualified certificate of the person signing the electronic document (if such restrictions are established).
We plan to enter into employment contracts with remote employees. We thought about the need to use enhanced electronic signatures in electronic document management. Do the employee and employer have additional responsibilities in connection with obtaining and using an enhanced electronic signature?
The obligations of participants in electronic interaction when using enhanced electronic signatures are established in Art. 10 of the Law on Electronic Signatures.
Responsibility 1. Ensure the confidentiality of electronic signature keys.
Obligation 2. Notify the certification center that issued the electronic signature verification key certificate and other participants in electronic interaction about a violation of the confidentiality of the electronic signature key within no more than one business day from the date of receipt of information about such a violation.
Responsibility 3. Do not use the electronic signature key if there is reason to believe that the confidentiality of this key has been violated.
Responsibility 4. Use electronic signature tools that have received confirmation of compliance with the requirements established in accordance with the Law on Electronic Signatures to create and verify qualified electronic signatures, create keys for qualified electronic signatures and keys for their verification.
Please note the very important provisions of Art. 6 of the Law on Electronic Signatures. It defines the conditions for recognizing electronic documents signed with an electronic signature as equivalent to paper documents signed with a handwritten signature. Information in electronic form signed with a qualified electronic signature is recognized as an electronic document equivalent to a document on paper signed with a handwritten signature, except if federal laws or regulations adopted in accordance with them establish a requirement for the need to draw up a document exclusively on paper.
Exchange of electronic documents
Next, we will consider situations when the exchange of electronic documents occurs when registering labor relations.
Situation 1. Documents required for employment in accordance with Art. 65 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, can be presented to the employer by a person applying for remote work in the form of an electronic document (Part 3 of Article 3122 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation), i.e. can be sent by e-mail.
The introduction into practice of organizing the exchange of electronic documents, of course, requires the introduction of appropriate additions to the internal labor regulations, and the procedure for implementing electronic document management and the requirements for its organization should, in our opinion, be set out in the Instructions for personnel records management.
When a future remote employee sends scanned personal documents to the employer, the question inevitably arises of confirming their authenticity. Some personnel officers, not without reason, believe that in order to avoid forgery, for example, documents on education and qualifications, it is necessary to scan not only the originals of these documents, but also their notarized copies.
Organization of internal electronic document management of personnel services
So, to organize the internal electronic document flow of personnel services, an automated workplace and “ACS-personnel” are needed. An automated workstation is mainly aimed at a user who does not have special training in using computer technology. The main purpose of workstations can be considered decentralized processing of information at workplaces, the use of appropriate “own” databases with the simultaneous possibility of entering local networks of workstations and PCs, and sometimes into global computer networks that include powerful computers. An automated workplace is a specialized system, which is a complex of hardware and software aimed at a specific specialist (from the head of the HR department to the timekeeper and the pass office on duty). An automated workplace is the main means of automating professional activities, a system whose structure (that is, the totality of all subsystems and elements) is determined by its functional purpose. It includes a set of subsystems: technical, informational, software and organizational. The technical subsystem includes the hardware necessary to perform a specific job function. An equipped workstation usually includes a PC, a printer, a scanner, means of communication with other workstations operating in the general network of the institution, as well as other means of communication (telephone, telex, telefax). One of the most important factors determining the efficiency of working on an automated workplace is the presence of “friendly” interface tools in relation to the HR department employee, ensuring the comfort of working on the machine. Hardware requires application programs such as word processors, spreadsheets, business graphics, that is, office applications. The information subsystem includes arrays of information stored in local databases, usually on disk drives. This also includes database management systems. The software includes operating systems, service programs, standard user programs and application program packages, designed on a modular basis and aimed at solving a certain class of problems determined by the purpose of the workstation. If necessary, the software also includes software packages for working with graphic information. Organizational support for automated workplaces is aimed at organizing their functioning, development, personnel training, as well as administration. The latter includes work planning, accounting, control, analysis, regulation, documentation of the rights and obligations of automated workplace users. “ASU-frames” is a program that actively uses the network connection of individual computers into a local area network (LAN). Only in this way does it become possible to transfer information from any user workstation to the server and back. The speed of data transfer over the network naturally affects the overall speed of the entire workstation. In turn, the speed of information passage from the server to the user’s local computer is determined by a set of software and hardware that make up the local computer network. Currently, there are various ways to connect disparate computers into a single whole, that is, into a network. The range of hardware and software for managing them is wide. How to choose the type of network and its software? An incorrect choice may subsequently lead to the inability of programs to function if the number of workstations increases or the requirements for the speed and volume of transmitted information increase. It is clear that it is necessary to sufficiently understand the principles of organizing a LAN in order to correctly select hardware and software for its construction. Let us clarify what the typical workstations of the head of the personnel service and the performer of personnel work should be. At the same time, the choice of specific technical means (which differ in functional, volume and cost indicators) is influenced by such factors as the volume of document flow, the method of operating the technical means, the volume of copied documents, the technological and operational characteristics of the equipment, the brand (manufacturer), and the cost of operation. Thus, the workstation of the head of the HR department and the HR manager consists of: - a PC, which includes a system unit, display (monitor), keyboard, mouse; — telephone and multifunctional device, which includes a scanner, printer and copier (per department); — a fax modem, which is used to transmit electronic documents stored in the computer’s memory; - shredder - paper shredder. Such an automated workplace will ensure the exchange of information between the human resources department and the accounting department, as well as the supply of open personnel information to other departments. In addition, it will allow you to create a data bank about the organization’s personnel, promptly replenish this bank and promptly provide the necessary information to authorized users.
Organizational conditions for the introduction and maintenance of electronic document management for personnel
To organize the exchange of information in a local electronic network, both programmers and digital technology specialists recommend software bases (software) and operating systems (OS) Windows or Linux with an adapted DBMS and a process management subsystem “ASU-cadres”. Note that, despite a fairly large set of non-standard additional functions, the ASU-frames program uses only standard operators and constructions. This makes it possible to easily transfer the program to another SQL server. The most common complexes are, for example, the Oracle v. 7.3, 9i under SCO OpenServer OS and Red Hat Linux for the development and implementation of software for the “Labor Resources” circuit (ACS “Personnel”, “Salary”, “Taxes”, “PFR”, etc.). Such complexes also allow you to prepare data for the organization’s reports to the territorial services of statistics, taxation and pension savings and provide additional support for interfaces with the HR IIS SAP R/3 module, used for payroll calculation. Moreover, with such modules it is possible to prepare personal data of employees, salary accruals and deductions with subsequent loading of information both into the SAP R/3, Galaktika, 1C ISs, and into the salary and personnel information storage. The work of the personnel department of any budgetary institution is associated with the accumulation of a large amount of personal data of personnel and the need for their archival storage. Traditionally, information is stored on paper. At the same time, it is difficult to quickly select the necessary data when hiring, dismissing, leaving an employee on vacation, moving to another position, joining the reserve, etc. The issue of reliability of storage and confidentiality of personal data is also important, given that the personnel department staff is often quite large. Based on the requirements of Ch. 14 “Protection of personal data of an employee” of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation (Articles 85-90), access to the information archive should be reduced to a minimum. As a rule, only the head of the human resources department and a human resources specialist appointed by order of the budgetary institution as the person responsible for storing and using personal data of employees should have access. However, all personnel department employees involved in the implementation of document flow and authorized to manage personnel using “ACS-HR” and automated workplaces must have access to certain items of personal data. To do this, at each or separately designated workplace, you need to equip a HR officer’s workstation, taking into account the recommendations of specialists. Legislation does not currently regulate this type of legal relationship between employee and employer, therefore the rights, obligations and responsibilities of the parties must be regulated in local regulations or individual agreements.
Disadvantages of HR EDI and ways to overcome them
The electronic document management system for personnel documents at the present stage is not without serious shortcomings and increased risks:
- difficulties in ensuring the security of electronic data transmission and storage;
- regulatory gaps regarding the use of electronic signatures;
- risks of improper identification of persons signing documents, etc.
At the initial stage, there may be difficulties in resolving labor disputes when using HR EDI in labor relations due to the lack of relevant practice in the courts. The number of experts who can participate in such trials is also insufficient.
In order to painlessly remove paper originals and “live” signatures from business circulation, it is necessary to solve a set of problems, for which the Ministry of Labor is conducting pilot experiments, developing and improving the regulatory framework.
Read more about the shortcomings of various documents and procedures in our materials:
- “Advantages and disadvantages of credit cards”;
- “Tax control in the form of monitoring - shortcomings”;
- "Pros and cons of bankruptcy of individuals."