Accounting entries for investments in non-current assets (Account 08)
The receipt of goods or intangible assets on the balance sheet of the organization is carried out taking into account all the costs of their acquisition.
This may include installation, delivery and other related costs. The total resulting value of non-current assets is not subject to change, with the exception of possible cases of revaluation, completion, reconstruction and others.
Acceptance of fixed assets or intangible assets for accounting is accompanied by the determination of their useful life. Depending on the decision made, depreciation is calculated monthly, which reduces the initial cost of the object.
When registering intangible assets, there are options for determining and not determining the useful life. The useful life must be determined annually. The same applies to depreciation charges for intangible assets.
If fixed assets are considered in the future as an additional source of income reflected in account 03, then depreciation on them is accounted for separately in the general account for fixed assets - 02.
Tangible and intangible exploration costs involved in the development of deposits of natural minerals and other activities related to the development of natural resources are assessed based on the amount of actual costs incurred, which include:
- amounts paid to suppliers and intermediaries under the terms of contracts;
- consulting fees;
- customs payments;
- non-refundable taxes;
- remuneration of employees involved in development;
- depreciation of operating systems used to create search assets;
- other costs associated with activities of this kind.
The listed types of expenses do not include amounts of refundable taxes, as well as general business expenses, with the exception of situations where they are directly involved in the development of deposits and for performing other operations with minerals.
If the feasibility of development is subsequently confirmed, non-current exploration assets are transferred to the category of fixed assets or intangible assets on a general basis. Otherwise, further costs are stopped and the resulting assets are written off or disposed of.
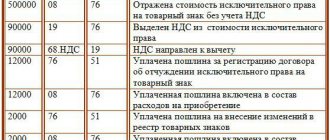
Dt 08 - Kt 60, 76 - the organization acquired fixed assets (intangible assets, other non-current assets)
Dt 19 - Kt 68 - allocated VAT on the purchase of property.
Dt 01 (03, 04) - Kt 08 - the object was accepted for registration (put into operation).
Example. The company purchased equipment for production needs for a total cost of 637,200 rubles, including 18% VAT. The equipment has been registered. What will the wiring look like?
Dt 08 - Kt 60 (RUB 540,000) purchase of fixed assets.
Dt 19 - Kt 60 (97,200 rub.) VAT is reflected upon purchase.
Dt 01 - Kt 08 (RUB 540,000) equipment put into operation.
Kt 68 ― Dt 19 (RUB 97,200) VAT payable.
The main documents that an accountant needs to follow when working with the 08th account:
- Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated October 31, 2000 No. 94n “On approval of the Chart of Accounts for accounting of financial and economic activities of organizations and instructions for its application” (hereinafter referred to as Order No. 94n);
- “Instructions for the application of the Chart of Accounts for accounting financial and economic activities of organizations”, approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated October 31, 2000 No. 94n (hereinafter referred to as Instruction 94n);
- PBU 6/01;
- PBU 17/02.
Accounting account 08 is designed to accumulate data on enterprise investments in tangible and intangible non-current assets, which in the future can be recorded in accounts 01, 03, 04 as fixed assets, intangible assets or profitable investments, respectively. Today, order No. 94n established eight subaccounts to account 08.
IMPORTANT! In the working chart of accounts, an enterprise can clarify the contents of the list of second-order accounts (sub-accounts), excluding or merging them. If necessary, additional subaccounts can be introduced if this is required by the specifics of the activity or such introduction is dictated by the need to deepen its control and analysis.
According to Order No. 94n, subaccounts 1, 2, 4, 5 and 7 to account 08 are intended to account for investments in finished non-current assets. Account 08-1 is intended for synthesizing data on capital investments of an enterprise for the acquisition of land plots. Investments in environmental management facilities are accounted for in subaccount 08-2.
Subaccount 3 is intended to accumulate information on the construction of environmental facilities, and subaccount 6 takes into account the costs of raising young animals before transferring them to the main herd. The 8th subaccount takes into account expenses associated with research, design work, and the development of new technological and management processes.
Analytical accounting for accounts 08-1, 08-2, 08-3, 08-4, 08-5 is maintained for each fixed asset (purchased or constructed). According to accounts 08-6 and 08-7 - for each species (group) of animals. According to account 08-8 - for each type of work (service) or R&D.
You can clarify the procedure for reflecting the balance of account 08 in the balance sheet in the material “On which line should the balance of account 08 be reflected in the balance sheet?”
In accordance with the order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation “On approval of the Chart of Accounts” dated October 31, 2000 No. 94n (hereinafter referred to as the chart of accounts) account. 60 “Settlements with suppliers and contractors” is used to record transactions for the following business relationships with suppliers:
- acquisition of inventory items;
- acceptance of completed work;
- consumption of services provided;
- uninvoiced deliveries.
- other operations that are reflected in account 60 and provided for by the chart of accounts.
At the same time, for detail and correct reflection of information on transactions, sub-accounts to account 60 are used. An important point when opening sub-accounts is the need to secure them in the company’s working chart of accounts, which is approved by the accounting policy.
For recommendations on drawing up a working chart of accounts, see the material “Working Chart of Accounts - Sample 2017”.
Let's look at examples of possible subaccounts to account 60:
- 60.01 - settlements with suppliers and contractors;
- 60.02 - settlements for advances issued;
- 60.03 - settlements on bills issued;
- 60.04 - settlements for uninvoiced deliveries.
It is also possible to open other sub-accounts regulated by the company’s working chart of accounts.
In the form of non-current assets, fixed assets with intangible assets and investments of a financial nature act. Account 08 is intended to systematize information about non-current assets upon receipt in the absence of a final price for them or conditions for immediate commissioning.
After the process of calculating the final price for the asset is completed, the 08 accounting account is closed by transferring amounts from it to the appropriate accounts. If the price is known immediately after the transaction for the purchase of an object and its change is not expected, then the account. 08 will play a transit role.
The cost of the property is taken into account in the amount of additional costs for installation, delivery and modification of the asset. An important nuance - the VAT amounts for each object should be attributed to account 19. The answer to the question “08 account - active or passive” is unambiguous - the account is active. That is, all incoming amounts are recorded as a debit, and disposals are recorded as a credit.
Accounting account 08 includes assets that:
- used in the form of a contribution to the authorized capital;
- acquired;
- received free of charge;
- created economically or by intermediaries.
The balance sheet for account 08 will help ensure the correctness of accounting records regarding investments in non-current assets. If the turnover in it is equal, the balance is zero, then the accountant did everything without errors. When a balance appears, it is necessary to pay attention to the presence or absence of unfinished construction at the enterprise.
Non-current assets are subsequently accepted for accounting and tax accounting as a fixed asset, land plot, environmental management facility or intangible asset.
The main aspect of using subaccount 08.03 “Construction of fixed assets” is that the subaccount reflects:
- All costs for the construction of buildings and structures;
- Equipment installation costs;
- Other expenses indicated in the financial estimates for capital construction by contract or business method:
The contract method of construction is construction work and installation work performed in accordance with the concluded construction contract (Articles 740, 743, 746 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
The economic method of construction is construction work and installation work performed by the organization’s employees.
Account 01 in accounting
Account 01 in accounting is used to solve problems of accounting for fixed assets of an enterprise in the context of their cost and location of operation. Each movement of an asset is recorded and reflected in accounting documents. Amounts for fixed assets must be shown in the balance sheet.
Characteristics of account 01
An object can be recognized as a fixed asset provided:
- it is intended to be used in production;
- period of use – more than a year;
- the object will bring economic benefits;
- they are not going to resell it.
Account 01 is intended for accounting for assets with a value of 40 thousand rubles; items with a lower price are classified as inventories and are immediately written off as expenses. Account 01 in accounting is active, and in the Chart of Accounts it is located in the section of non-current assets. The debit turnovers show:
- receipt of fixed assets;
- increase in asset value.
Credit turnover indicates the disposal of objects or their depreciation. Account 01 involves reflecting the value of assets at their original cost excluding VAT. The initial cost may reflect not only the purchase price, but also the amounts paid for delivery, assembly, installation, and customs duties.
Subaccounts to account 01 “Fixed assets”
Each type of object has its own subaccount. What subaccounts does account 01 have:
- 01.1 – assets related to production fixed assets are shown;
- account 01.2 is intended for other production facilities;
- 01.3 for non-production objects;
- 01.4, taking into account livestock;
- 01.5 applies to perennial plantings;
- 01.6 relates to land plots and environmental management facilities;
- 01.7, taking into account assets with non-inventory properties;
- 01.8 for inventory accounting with household supplies;
- 01.9 for leased fixed assets;
- 01.10 to reflect the value of other assets;
- 01.11 when registering the disposal of fixed assets.
It is important to distinguish the purpose of the asset, since account 01.01 “Fixed assets” reflects only those objects that are used in the production process in the main activity of the enterprise.
Analytical accounting for account 01
Account 01.01 in accounting and other sub-accounts require maintaining inventory cards. The document reflects assets by location and depreciation groups.
Account card 01, a sample of which is presented in the unified form OS-06, is created and maintained for each asset separately, including leased objects. Basic information is entered from acceptance certificates and technical documentation.
If there are precious metals in the accounting object, the mass of these metals must be indicated.
https://youtu.be/fzQ-5M_YRLM
For analytical accounting purposes, standard account card 01 can be used, a sample of which can be filled out in any accounting program. It reflects the balance at the beginning of the period, debit and credit turnover, and the resulting balance at the end of the selected time interval.
The balance sheet for account 01 is needed to correctly calculate the amount of income tax and determine the base for property tax. In the first option, the emphasis is on the amount of depreciation and the proceeds from the sale of the asset. In the second case, the specifics of the formation of the residual value of each object are taken into account.
The balance sheet for account 01, the sample of which assumes the presence of only debit balances at the beginning and end of the reporting period, can be generated separately for each object or in the context of groups of assets. To bring tax and accounting data closer together, it is recommended to use a classification of fixed assets depending on their service life.
Typical transactions for account 01
To reflect the receipt of a new fixed asset, correspondence D01 - K08 is used. Costs associated with the acquisition of an asset, bringing it to working condition and the allocation of VAT amounts will be reflected in the debit of account 08, after which account 01 can correspond with K08.
The depreciation of fixed assets is reflected by posting D91.02 - K01, the revaluation involves the creation of correspondence between D01 and K83.
In the case of the sale of a fixed asset, it is necessary to form its residual value. If the residual value is higher than the sales price, the transaction is considered unprofitable; if the residual value is lower than the sales income, the transaction will be profitable. Postings to account 01 “Fixed Assets” will look like this:
- D62 – K91 for the amount of the transaction for the sale of property.
- D91 – K68 in the amount of VAT on the object being sold.
- D02 - K01 when forming the residual value by writing off depreciation.
- D91 - K01 to reflect the fact of write-off of the residual value of the sold property.
Account 01: postings as an example
Within a month, the company modernized its existing production equipment in the amount of 7,000 rubles. and purchased new fixed assets to increase production volumes in the amount of 90,000 rubles, excluding VAT. The cost of delivery of new assets was 2,500 rubles. Postings for account 01:
- D01 – K08 in the amount of modernization performed for 7000 rubles.
- D08 - K60 in the amount of the cost of the new asset received by 90,000 rubles.
- D08 - K60 to reflect the costs of delivery of purchased equipment in the amount of 2,500 rubles.
- D01 – K08 when accepting a new object for accounting at a cost of 92,500 rubles. (90,000+2500).
Source: https://spmag.ru/articles/schet-01-v-buhgalterskom-uchete
What is account 08 intended for?
According to the Chart of Accounts, introduced by order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated October 31, 2000 No. 94n, account 08 “Investments in non-current assets” accumulates the costs incurred by the organization in objects that are planned to be used as:
- depreciable and non-depreciable fixed assets (hereinafter referred to as fixed assets);
- intangible assets (hereinafter referred to as intangible assets);
- adult animals belonging to the category of productive (working) livestock.
For key aspects of accounting for investments in non-current assets, see the article “Rules for accounting for investments in non-current assets”.
For information on how to reflect data on account 08 in reporting, see the article “On which line should the balance of account 08 be reflected in the balance sheet?”
Account 01 in accounting: Fixed assets
Accounting account 01 is the active account “Fixed Assets” and reflects information about the organization’s fixed assets (Fixed Assets), their value and movement. The account belongs to the non-current assets section of the approved Chart of Accounts.
Definition of fixed assets
Fixed assets of an enterprise are the material assets of an enterprise used in economic activities and transferring their value to the cost of production.
Fixed assets
The OS includes:
- production equipment and machinery;
- buildings and constructions;
- roads;
- transmission networks (heating networks, electrical networks, etc.);
- means of transport;
- power machines and equipment;
- various equipment and tools;
- working and breeding livestock;
- other OS.
In addition, fixed assets include capital investments in leased fixed assets, in land improvement, and the land plots themselves. Fixed assets, as non-current assets, participate in the production process as a means, not an object.
Conditions for recognizing an object as a fixed asset
To recognize an OS object, the following conditions must be present simultaneously:
- purpose - use in the production activities of the organization;
- expected SPI over 12 months;
- promising economic benefits;
- not intended for resale.
OS costing less than 40,000 rubles. can be taken into account as part of inventories and immediately written off as costs.
Account 01 in accounting
The fixed assets accounting account is active, its structure is displayed in the form of a table:
In the standard version, synthetic account 01 includes subaccounts for breakdown by type of fixed assets.
https://youtu.be/aH6gWoiRYF0
To reflect disposals, a sub-account for the disposal of fixed assets is also often opened, into which the initial and written-off costs are collected, and the write-off is carried out from this account. If the disposal account is not used, then transactions Dt 02 - Kt 01 arise.
For the correctness of analytical accounting, a breakdown is carried out by objects. Items in the account are stated at their original cost, which may include shipping costs, fees, etc.
Get 267 video lessons on 1C for free:
If an asset is owned by several organizations, then in the accounting of each of them its value is reflected in proportion to the share of ownership.
Main correspondence of account 01
Typical correspondence of the fixed assets accounting account is presented in the table:
Depreciation of fixed assets
Depreciation of fixed assets in accounting refers to the gradual transfer of their value to the cost of manufactured products.
There are categories of property that are not subject to depreciation:
- land;
- environmental management facilities;
- livestock;
- non-production housing facilities;
- forestry, road management;
- external landscaping.
If repairs last more than one year, and conservation of objects lasts more than three months, then depreciation is suspended.
In the balance sheet, fixed assets are reflected at their residual value: original cost minus accumulated depreciation. Non-depreciable property is reflected in the balance sheet at historical cost.
Depreciation starts from the month following the commissioning date. The accrual will stop in the next month after the cost has been completely written off.
After the book value of the asset becomes zero, the asset is not reflected in the balance sheet.
Example 1. Acceptance of fixed assets for accounting
Karuna LLC in April 2020 purchased from the OS supplier the contract price of 110,000 rubles, excluding VAT. Delivery services - 10,000 rubles. The term of the fixed assets is 36 months, the method of calculating depreciation is linear. The OS will be used in the main production activities.
To reflect the acquisition and acceptance of fixed assets for accounting, the Karuna accountant makes the following entries in April:
| Dt | CT | Operation description | Amount, rub | Document |
| 08 | 60 | Reflection of OS receipt | 110 000 | Invoice |
| 08 | 60 | Reflection of delivery costs | 10 000 | Invoice |
| 01 | 08 | Acceptance of fixed assets for accounting (110,000 + 10,000) | 120 000 | Accounting information |
The monthly depreciation amount will be: 120,000 / 36 = 3,333 rubles)
Depreciation calculation in May:
| Dt | CT | Operation description | Sum | Document |
| 20 | 02 | Monthly amortization | 3 333 | Accounting information |
In what cases is the posting Dt 08 Kt 60 drawn up?
In this video lesson, Natalya Vasilievna Gandeva, an expert on the “Accounting for Dummies” site, explains accounting for account 08 “Investment in non-current assets”, standard postings and 7 accounting examples are discussed. To watch, click on the video below.
When purchasing fixed assets, the following entries should be made:
- according to Dt 08 and Kt 60 to reflect the price of the asset;
- Dt 19 and Kt 60 for the allocation of VAT;
- Dt 68 and Kt 19 for VAT refund.
Accounting account 08 debits the amount of expenses of auxiliary workshops when creating an object on their own in correspondence with account 23. Expenses for materials and wages related to the asset being created are recorded using correspondence Dt 08 and Kt 10 (70 and 69).
Posting account 08 when receiving assets free of charge is created with crediting to accounts 76 in case of donation and 98.02 when accepted for accounting based on inventory results. The price is determined based on the average market value.
Postings to account 08 when contributing assets to the authorized capital - Dt 08 Kt 75. If the received equipment requires installation or configuration work, then these costs are included in Dt 08 and Kt 07.
In the case of animals, account 08 in accounting records is generated as follows:
- at the time of accepting the cost of animals that have reached the required age for transfer to the main herd, subaccount 08.06 is debited and account 11 is credited;
- when reflecting an increase in the value of the main herd, the amount is written off from 08.06 on credit by debiting 07.
The 08 account scheme assumes the absence of an opening and closing balance, with the exception of objects that require lengthy construction or installation work. Ideally, during the reporting period, all amounts under debit 08 should be closed.
The correspondence of account 08 when putting property objects into operation is reflected by postings Dt 01, 04, 03 and Kt 08. If this is not done when the object is ready for its intended use, the tax authorities will issue claims due to an understatement of the property tax base.
Posting Dt 08 Kt 10 is used by organizations when creating (installing, modernizing) non-current assets on their own and reflects the write-off of materials used to increase the initial cost of non-current assets.
Example
Stroy Market LLC, which provides services for the renovation of premises and the construction of houses and applies a general taxation system, decided to expand its scope of activity and begin selling building materials through a stationary store-warehouse and an online store.
A warehouse store intended for trading was built by our own master builders. Construction materials worth RUB 265,460 were used during construction. (VAT included).
Drinking water worth 5,670 rubles was spent on the needs of the employees involved in the construction of the store-warehouse. (VAT included).
In-house programmers created an online store website, the exclusive right to which was transferred to Stroy Market LLC. Materials worth 1,640 rubles were spent on maintaining the equipment used to create the site. (VAT included).
| Operations | Dt | CT | Sum | Rationale | |
| BOO | WELL | ||||
| Construction materials have been capitalized | 10 | 60 | RUB 224,966.10 = 265,460 – 265,460 × 18 / 118 | clause 5, clause 6 PBU 5/01 | clause 2 art. 254 Tax Code of the Russian Federation |
| VAT allocated | 19 | 60 | RUB 40,493.90 = 265,460 × 18 / 118 | ||
| Consumables for servicing IT equipment were capitalized | 10 | 60 | RUB 1,389.84 = 1,640 – 1,640 × 18 / 118 | ||
| VAT allocated | 19 | 60 | RUB 250.16 = 1,640 × 18 / 118 | ||
| Drinking water has been registered | 10 | 60 | RUB 4,805.08 = 5,670 – 5,670 × 18 / 118 | ||
| VAT allocated | 19 | 60 | RUR 864.92 = 5,670 × 18 / 118 | ||
| The initial cost of the warehouse store reflects the costs of building materials | 08 | 10 | RUB 224,966.10 | clause 8 PBU 6/01 | clause 1 art. 257 Tax Code of the Russian Federation |
| The initial cost of an online store website reflects material costs | 08 | 10 | RUB 1,389.83 | clause 9, clause 10 PBU 14/2007 | clause 3 art. 257 Tax Code of the Russian Federation |
| The cost of drinking water is reflected in general business expenses | 26 | 10 | RUB 4,805.08 | clause 8 of PBU 6/01, clause 10 PBU 14/2007 | subp. 7 clause 1 art. 264 Tax Code of the Russian Federation |
According to paragraph 2 of Art. 170 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, clause 8 of PBU 6/01, clause 10 of PBU 14/2007, VAT presented by sellers is reflected in the initial cost of fixed assets and intangible assets by organizations:
- not related to VAT payers;
- exempt from VAT;
- who have acquired (created) fixed assets and intangible assets used in activities not subject to VAT and carried out outside the Russian Federation.
For the rules for preparing VAT entries, see the article “Typical accounting entries for VAT: tax accounting.”
Posting Dt 08 Kt 60 is used when creating (installing, modernizing) non-current assets by third-party organizations and reflects the attribution of the cost of objects (work, services) received from contractors to increase the initial cost of non-current assets.
To decorate the store-warehouse, Stroy Market LLC turned to the contractor for services for the manufacture and installation of display cases, the cost of which was:
- production of display cases - RUB 125,680. (VAT included);
- installation of display cases - RUB 5,740. (VAT included).
In the same period, Stroy Market LLC ordered the development from a third-party IT company:
- accounting program for maintaining trade and warehouse accounting in the amount of 126,430 rubles. (including VAT) - without transfer of exclusive rights to the customer;
- applications to the online store website in the amount of 4,340 rubles. (including VAT) - with the transfer of exclusive rights to the customer.
| Operations | Dt | CT | Sum | Rationale | |
| BOO | WELL | ||||
| The initial cost of display cases reflects the costs of their production. | 08 | 60 | RUB 106,508.47 = 125,680 – 125,680 × 18 / 118 | clause 8 PBU 6/01 | clause 1 art. 257 Tax Code of the Russian Federation |
| VAT allocated | 19 | 60 | RUB 18,171.53 = 125,680 × 18 / 118 | ||
| The initial cost of display cases reflects the costs of their installation. | 08 | 60 | RUB 4,864.40 = 5,740 – 5,740 × 18 / 118 | ||
| VAT allocated | 19 | 60 | RUR 875.60 = 5,740 × 18 / 118 | ||
| The costs of developing an accounting program were written off as deferred expenses. | 97 | 60 | RUB 107,144.06 = 126,430 – 126,430 × 18 / 118 | clause 3 PBU 14/2007, clause 5, clause 7, clause 18, clause 19 PBU 10/99 | subp. 26 clause 1 art. 264 Tax Code of the Russian Federation |
| VAT allocated | 19 | 60 | RUB 19,285.93 = 126,430 × 18 / 118 | ||
| The initial cost of an online store website includes the costs of developing an application. | 08 | 60 | RUB 3,677.97 = 4,340 – 4,340 × 18 / 118 | clause 9, clause 10 PBU 14/2007 | clause 3 art. 257 Tax Code of the Russian Federation |
| VAT allocated | 19 | 60 | RUB 662.03 = 4,340 × 181 / 118 | ||
In accordance with the chart of accounts. 60 is active-passive, so both its debits and its credits can be used for accounting entries. The debit of this account is often used in correspondence with accounts: 50 “Cash”, 51 “Settlement accounts”, 52 “Currency accounts”, 55 “Special accounts in banks”, 62 “Settlements with buyers and customers”, 76 “Settlements with various debtors and creditors" and so on. (according to the instructions for the chart of accounts).
Credit account 60 is often paired with the following accounts: 08 “Investment in non-current assets”, 10 “Materials”, 15 “Procurement and acquisition of materials”, 20 “Main production”, 25 “General production expenses”, 26 “General expenses”, 41 “ Products" and so on.
In addition, for account 60 it is also possible to post Dt 60 Kt 60, the use of which is due to the reflection of transactions using different sub-accounts opened for account 60.
Posting Dt 60 Kt 60 means repayment of obligations:
- for payment from a previously paid advance (Dt 60.01 Kt 60.02);
- bills (Dt 60.01 Kt 60.03);
- other obligations arising on account 60.
The use of subaccounts helps to reflect the details of a business transaction in more detail than using the entry Dt 60 Kt 60. Let us explain with examples.
Example 1
LLC "Tsvetok" entered into an agreement to purchase products from LLC "Tulip" in the amount of 153,400 rubles. (including VAT RUB 23,400). The contract provided for 100% prepayment. On April 4, 2020, “Flower” transferred 153,400 rubles. to Tulip, and on April 25, 2018, the products were received and capitalized.
1st option (without using subaccounts)
April, 4:
- Dt 60 Kt 51 - prepayment of 153,400 rubles was transferred.
25th of April:
- Dt 10 Kt 60 - products worth 130,000 rubles are taken into account.
- Dt 19 Kt 60 - VAT allocated in the amount of 23,400 rubles. (recorded on the invoice).
- Dt 60 Kt 60 - the advance payment issued in the amount of 153,400 rubles was counted towards payment of the debt for the products.
- Dt 68 Kt 19 - VAT is accepted for deduction of 23,400 rubles.
As you can see, reflecting transactions without subaccounts causes certain inconveniences during further analysis of accounts.
2nd option (using subaccounts)
April, 4:
- Dt 60.02 Kt 51 - advance payment of 153,400 rubles is transferred.
25th of April:
- Dt 10 Kt 60.01 - products are accepted for accounting in the amount of 130,000 rubles.
- Dt 19 Kt 60.01 - VAT allocated in the amount of 23,400 rubles.
- Dt 60.01 Kt 60.02 - the debt for the products was paid in advance in the amount of 153,400 rubles.
- Dt 68 Kt 19 - VAT is deducted in the amount of 23,400 rubles.
If settlements under the agreement are carried out through the cash register, the entry Dt 60 Kt 51 changes to the entry Debit 60 Credit 50. However, in this case, it is necessary to remember to comply with the cash settlement limit (100 thousand rubles) if the parties to the agreement are a legal entity (or an organization and an individual entrepreneur ).
Posting Debit 60 Credit 62 reflects the repayment of mutual claims to counterparties - the supplier and the buyer.
Example 2
LLC "Mag" signed a contract for the purchase of goods from LLC "Optovik" in the amount of 156,000 rubles. (including VAT RUB 23,796.61). On March 14, 2018, “Mag” paid the cost of the goods (RUB 156,000) and on March 17, 2018, registered the goods for the specified amount. On March 30, 2020, “Mag” returned the product in full due to the lack of demand for it.
Dt 60 Kt 51 - prepayment for goods of 156,000 rubles is reflected.
Dt 41 Kt 60 - the cost of the goods is taken into account 132,203.39 rubles.
Dt 19 Kt 60 - reflected input VAT of RUB 23,796.61.
Dt 68 Kt 19 - VAT is accepted for deduction in the amount of RUB 23,796.61.
Dt 62 Kt 90 - return of goods 156,000 rubles.
Dt 90 Kt 68 - VAT charged RUB 23,796.61.
Dt 90 Kt 41 - the cost of goods is written off 132,203.39 rubles.
Dt 60 Kt 62 - offset of obligations in the amount of 156,000 rubles was carried out.
Dt 51 Kt 62 - advance payment of 156,000 rubles was returned.
| Account debit | Account credit | Operation description |
| Reflection in accounting of contract construction | ||
| 08.03 | 60 (76) | The cost of contract work for the construction of fixed assets is taken into account |
| 19 | 60 (76) | VAT claimed by the contractor has been taken into account |
| Reflection in accounting of construction in an economic way | ||
| 08.03 | 10 (23; 25; 26; 60; 70; 76) | All costs of construction of a fixed asset facility suitable for use are taken into account |
| 19 | 60 (76) | VAT is taken into account on all costs of construction of a fixed asset facility suitable for use |
Main entries for the account “Construction of fixed assets”
| Account debit | Account credit | Operation description |
| Reflection in accounting of contract construction | ||
| 08.03 | 60 (76) | The cost of contract work for the construction of fixed assets is taken into account |
| 19 | 60 (76) | VAT claimed by the contractor has been taken into account |
| Reflection in accounting of construction in an economic way | ||
| 08.03 | 10 (23; 25; 26; 60; 70; 76) | All costs of construction of a fixed asset facility suitable for use are taken into account |
| 19 | 60 (76) | VAT is taken into account on all costs of construction of a fixed asset facility suitable for use |
In what situation is the posting Debit 60 Credit 62 applicable?
Let us consider in more detail, using examples, the reflection of transactions on the subaccount 08.03.
In this case, according to the conditions of the example:
- In March, construction materials were purchased - 472,000 rubles, incl. VAT – 72,000 rubles;
- In March, construction materials were spent - 250,000 rubles;
- In April, construction materials were spent - 150,000 rubles;
- The salary of employees involved in the construction of the facility, taking into account social contributions, amounted to 105,000 rubles in March, and in April - 95,000.00 rubles.
| Dt accounts | CT account | Transaction amount, rub. | Wiring Description | A document base |
| 10.08 | 60 | 400 000 | The cost of purchased building materials is reflected | Consignment note (TORG-12) of the supplier |
| 19 | 60 | 72 000 | VAT on purchased building materials is reflected | Invoice received |
| 68 | 19 | 72 000 | Paid VAT accepted for deduction | Book of purchases |
| 08.03 | 10.08 | 250 000 | The cost of building materials transferred for the construction of the warehouse in March is reflected as part of capital investments | Invoices, Payroll and social benefits |
| 08.03 | 70 (69) | 105 000 | Reflected as part of capital investments are the wages (including insurance premiums) of employees involved in the construction of the warehouse in March | |
| 08.03 | 10.08 | 150 000 | Reflected in the composition of the cap. investment cost of building materials transferred for the construction of a warehouse in April | |
| 08.03 | 70 (69) | 95 000 | Reflected as part of capital investments are the salaries (including insurance contributions) of employees involved in the construction of the warehouse in April | |
| 01 | 08.03 | 600 000 | A self-constructed industrial warehouse was registered and put into operation (250,000.00 105,000.00 150,000.00 95,000.00) | Transfer and Acceptance Certificate (OS-1), Inventory Accounting Card (OS-6) |
| 19 | 68 | 108 000 | The accrued VAT on construction work carried out using economic methods is reflected ((250,000.00 105,000.00 150,000.00 95,000.00) * 18%) | Invoice received. Book of purchases |
| 68 | 19 | 108 000 | Accrued VAT on construction work carried out using economic methods has been accepted for deduction. |
Let's say VESNA LLC has entered into an agreement with a contractor for the construction of a facility - an industrial warehouse. According to the contractor’s financial estimates, the costs of constructing an industrial warehouse were:
- The cost of services for drawing up an estimate is 59,000 rubles, incl. VAT – 9,000 rubles;
- The cost of construction is 826,000 rubles, incl. VAT—RUB 126,000.
| Dt accounts | CT account | Transaction amount, rub. | Wiring Description | A document base |
| 08.03 | 60 (76) | 50 000 | The cost of the contractor's services for drawing up estimates is reflected | Contract agreement, Work completion certificates, Construction materials consumption reports |
| 19 | 60 (76) | 9 000 | VAT on services reflected | |
| 08.03 | 60 (76) | 700 000 | The cost of constructing a production warehouse is reflected | |
| 19 | 60 (76) | 126 000 | VAT on construction reflected | |
| 68 | 19 | 135 000 | Paid VAT is claimed for deduction |
Example
Example 2
IMPORTANT! Tax officials consider the return of a quality product as a reverse sale (letter from the Ministry of Finance dated February 18, 2013 No. 03-03-06/1/4213).
Example 3
Let's take the conditions from example 2, but agree that the goods from the supplier were not received in full. Upon acceptance of the goods, LLC "Mag" revealed a shortage in the amount of 23,600 rubles. (including VAT RUB 3,600) and filed a claim with the supplier.
Dt 60 Kt 76 - a claim was made for a shortage of goods of 23,600 rubles.
Dt 41 Kt 60 - the cost of the accepted goods is reflected as 112,203.39 rubles.
Dt 19 Kt 60 - reflected input VAT of RUB 20,196.61.
Dt 51 Kt 76 - a refund was received from the supplier for undelivered goods in the amount of 23,600 rubles.
For information on the procedure for generating a balance sheet for account 60, see the article “Features of the balance sheet for account 60.”
Characteristics of account 01 in accounting
Account 01 in accounting is the “Fixed Assets” account , which provides basic information about the movement of cash equivalents and the real amount that is in leased, operational, reserve management and conservation.
In accounting, account 01 receives fixed resources at the original price . When property objects are located in several enterprises, the primary value is displayed on accounts in established ratios.
Fixed assets are the organization's fund, which takes part in the development of the enterprise's activities.
The use of objects whose operating time exceeds more than 12 months , has a production or management purpose, generates income in real time and in the future, such elements of property become fixed assets. The main tools include :
- Device and technical equipment.
- Premises and buildings.
- Vehicles.
- Working tools and devices.
- Improved plots of land investment.
cost of initial resources includes:
- cash equivalents for the acquisition and construction of the operating system;
- payment fees for customs control;
- expenses for supplying goods;
- government fees;
- repair work to assemble equipment.
To form the initial price of fixed assets, general production costs and management costs should be excluded if there are no direct relationships with the purchase.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=hnmJgcyRkGU
It is necessary to obtain detailed information on the fundamental processes of the operating system using account 01. Property that is under conservation, lease, or use is accounted for in accounting.
Commissioning of facilities is recorded in the OS-1 form . If it is necessary to introduce buildings and premises, use the OS-1a form . Form OS-1b was developed for the introduction of group subjects.
Wiring of production elements
It is necessary to reflect the registration of the use of production items by appropriate posting. Correct display of information allows you to resolve emerging issues in organizations of any type of activity . The posting is in the form of debit 01 with subsequent credits :
- 03 – registration of objects upon return by the lessor;
- 20 – recorded operating systems that arrived from production;
- 3 – putting into use a completed element of a capital structure;
- 76 – used fixed assets purchased from another party.
The excess process after the recorded inventory is noted in the credit posting account:
- 91 – installed surplus equipment;
- 11 – the given object entered into working order after the abduction.
If there is a lack of OS, a review and investigation by the commission is carried out in order to identify the culprit. After the decision of the commission board about the unidentified culprit, the price of the missing objects is written off and recorded in accounting.
Account 94, credit 01 – registration of the remaining balance of the missing amount. Debit 91.2, credit 94 – reflection of a loss from a lack of fixed assets (with an unidentified culprit).
Accounts with descriptions will help to re-evaluate the production elements of fixed assets according to the law :
- the component income criteria take into account the additional valuation of fixed assets;
- when adding an investment, a markdown is made;
- registration of the reflection of the discount factor;
- the decrease in value is recorded in the structure of losses.
Absolutely all actions that occur in production with objects are registered according to accounting reports . Removal from the place of use, liquidation of tools, equipment due to failure, transfer to another organization, are taken into account and carried out according to the database:
- calculating the amount for the increase in depreciation of the element that is being eliminated;
- the initial price of the fixed asset is written off;
- accounting for write-off expenses.
The write-off of production equipment under conditions of donation is registered free of charge by the following acts :
- registration of residual value upon liquidation of an object that passes into other hands free of charge;
- accounting for the amount spent during the transfer.
In production departments, there is a need to remove an object from use for a set period or mothball it. During this period of time, no depreciation is recorded. According to the posting, the production element is registered by transfer from subaccount 01 from operational to conservation. You can carry out a control document if you create an order sheet.
Conducting business in large manufacturing facilities is difficult. All activities performed should be recorded. It is impossible to reach the profit level without registering accounting transactions.
You can control indicators at the level of finance and management data thanks to the balance sheet , which allows you to analyze material financial successes for certain accounts.
Reporting information is created according to the register, taking into account the remaining funds and their movement during the initial and final reporting periods. The statement is compiled upon completion of depreciation, write-off of production costs, taxation, and recording of cash statements.
https://youtu.be/PX3D7Xeby4U
The creation of a balance sheet is based on tabular data resources . The principle of the balance sheet is the compilation of subaccounts and accounts during any period of time, without the end of the reporting period. The register is divided into three subtypes :
- Synthetic – identifying the exact distribution of funds among accounts.
- Analytical – tracking cash flows in a section of a specific account.
- Chess – providing information on business procedures during the reporting period.
Sample filling
Such specific documentation is not registered in acts of legislation; it has technical data. Standards for filling out documentation :
- report title;
- details of the branch filling out the document;
- intermediate time stage for formation;
- accounting units of the analyzed objects;
- information data of persons responsible for the correct preparation of the statement.
The main information part records license plates and decrypted account indicators, residual passive and active financial equivalents of the initial, final and reporting periods.
The cash fund of an enterprise is both an asset and a source of formation. Account turnover is equal to loan turnover.
The price of the organization's active debits is equal to the value of the company's liabilities.
The main advantage of drawing up a balance sheet is the registration of the amount of cash on the balance at the end of the reporting period, the amount of expenses and income. When creating a company, such a document is considered zero; there are no accounting data or account turnover.
During the registration of the company, the fixed capital is recorded in the debit of account 75, credit 80. The amount is made up of finance, initial funds, equipment, and materials. The procedure is displayed in the table; if there is a discrepancy in the data, it is worth checking the information for errors .
The statement is included in the list of documents according to the requirements of the tax inspectorate. The entries recorded in the initial documentation are maintained in accounting registers. The inventory system takes into account the grouping of accounting elements and the cost of price conversion. For private enterprises, consideration of the register model is established by government agencies .
An experienced entrepreneur facilitates controlled work with the help of accounting statements and registers that allow you to track any deviations from schedules, monitor changes in operating equipment, calculate the cost of missing household tools, and display data on profit growth in a specific period without waiting for the end of the working month.
Accounting software is involved in all activities. Management of organizational and managerial work is facilitated thanks to innovative modern technologies.
Details about this account are in this video.
We recommend other articles on the topic
Source: https://znaybiz.ru/buh/plan-schetov/scheta/01.html
Consequences of incorrect use of wiring Dt 08 Kt 10, 60
When including the cost of materials and contractor services in the initial cost of assets, the legal validity of this action is checked.
Unlawful reflection (non-reflection) of expenses for materials and services of contractors in the initial cost of assets leads to distortion of data in accounting and tax reporting and becomes the reason for the accrual of penalties for non-payment (incomplete payment) of taxes.
| Operations | Dt | CT | Sum | Rationale | |
| BOO | WELL | ||||
| The initial cost of the warehouse store reflects the cost of drinking water | 08 | 10 | RUB 4,805.08 | contradicts clause 8 of PBU 6/01, clause 10 of PBU 14/2007 | contradicts subpara. 7 clause 1 art. 264 Tax Code of the Russian Federation |
| In the initial cost of the accounting program, the costs of its development | 08 | 10 | RUB 107,144.06 | contradicts clause 3 of PBU 14/2007, clause 5, clause 7, clause 18, clause 19 of PBU 10/99 | contradicts subpara. 26 clause 1 art. 264 Tax Code of the Russian Federation |
| Period | Cost of the store-warehouse, calculated in violation of the requirements of PBU and Tax Code of the Russian Federation, rub. | Cost of the accounting program, calculated according to the rules of PBU and Tax Code of the Russian Federation, rub. | ||||
| Initial | Depreciation | Residual | Initial | Depreciation | Residual | |
| 01.01. | 229 771,18 | 1 838,17 | 227 933,01 | 224 966,10 | 1 799,72 | 223 166,38 |
| 01.02. | 229 771,18 | 3 676,34 | 226 094,84 | 224 966,10 | 3 599,44 | 221 366,66 |
| 01.03. | 229 771,18 | 5 514,51 | 224 256,67 | 224 966,10 | 5 399,16 | 219 566,94 |
| 01.04. | 229 771,18 | 7 352,68 | 222 418,50 | 224 966,10 | 7 198,88 | 217 767,22 |
Calculation based on data with violations = (227,933.01 226,094.84 224,256.67 222,418.50) / 4 × 2.2% = 4,953.87 rubles.
Calculation based on correct data = (223,166.38 221,366.66 219,566.94 217,767.22) / 4 × 2.2% = 4,850.27 rubles.
The overstatement of the quarterly property tax amounted to 103.60 rubles. (on 2%).
The property tax calculated for the quarter is written off in the same reporting period as income tax expenses (subclause 1, clause 1, article 264 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). In the event of an erroneous calculation of the quarterly property tax, the amount of income tax expenses is overestimated by 103.60 rubles. and the amount of income tax is underestimated by 20.72 rubles. (103.60 × 20%).
IMPORTANT! The fine for non-payment (incomplete payment) is collected in the amount of 20% of the unpaid amount of tax (clause 1 of Article 122 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). In our case, it will be 4.14 rubles. (20.72 × 20%).
According to the accounting program adopted by Stroy Market LLC as an intangible asset (with an initial cost of 107,144.06 rubles), property tax is not calculated (clause 1 of Article 374 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). The cost of the program is written off by Stroy Market LLC through monthly depreciation deductions (clauses 23–33 PBU 14/2007, Article 253, Article 256, Article 259 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
If the cost of the accounting program is correctly reflected:
- in accounting - reflected in deferred expenses, which during the period of use of the program are written off as basic expenses (clause 3 of PBU 14/2007, clause 5, clause 7, clause 18, clause 19 of PBU 10/99);
- in tax accounting - the full amount is included in other expenses (subclause 26, clause 1, article 264 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
| Accounting and tax reporting data | Erroneous reflection of data, rub. | Correct reflection of data, rub. | Amount of distortions, rub. |
| Initial cost of intangible assets (accounting program) | 107 144,06 | 0,00 | 107 144,06 |
| Monthly depreciation amount | 2 232,17 | 0,00 | 2 232,17 |
| The amount of expenses for the reporting month in accounting | 2 232,17 | 2 232,17 | 0,00 |
| Amount of expenses for the reporting month in tax accounting | 2 232,17 | 107 144,06 | 104 911,89 |
IMPORTANT! If the tax is understated or any line-by-line data in the financial statements is distorted by more than 10%, officials are fined 5,000–10,000 rubles, and for repeated violations – 10,000–20,000 rubles. (clause 1 of article 15.11 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation).
OS upgrade
The main feature of modernization is that its result changes the original characteristics of the OS object. As a result, its cost, period of use, etc. change. When accounting for expenses, it is advisable to open a sub-account on account 08, in which to collect all costs incurred for modernization.
| Debit | Credit | Content |
| 08 | 10 | Material costs written off for modernization |
| 08 | 23 | Auxiliary production costs written off |
| 08 | 60, 76 | A third-party contractor was involved in the modernization |
| 08 | 70 | The salaries of employees involved in the work were written off for modernization |
| 08 | 69 | Social contributions of employees were written off for modernization |
| 01 | 08 | Increased OS cost due to modernization costs |
Sale
When selling, proceeds are recorded in the amount established by the contract. In this case, expenses must include sales costs, as well as accrued depreciation. All transactions are shown in account 91.
| Debit | Credit | Content |
| 62 | 91 | Reflected revenue from the sale of operating systems |
| 91 | 68 | Determined VAT on the sale of fixed assets |
| 01/Disposal | 01 | The original cost of the object is transferred |
| 02 | 01/Disposal | Depreciation calculated over the operating period is transferred |
| 91 | 01/Disposal | The residual value is transferred to other expenses |
| 91 | 60, 76 | Costs for preparation for sale, dismantling, delivery, etc. are indicated. |
| 19 | 60, 76 | The amount of VAT for delivery, dismantling, etc. services has been determined. |
| 68 | 19 | VAT credited |
| 91 | 99 | The financial result of the sale of the OS is reflected |
Modernization
The main feature of the modernization procedure is that in the process of its implementation, the original characteristics of the objects are adjusted. As a result, the period of use and cost change. In order to properly record expenses, it is recommended to open a sub-account on account 08. All expenses that were necessary for the modernization will be collected here. The procedure is carried out in several types.
Sale
Revenue after the sale must be indicated in the reporting documents in the amount specified in the contract. This also includes all losses that went towards depreciation. All transactions must be reflected in account 91.
Liquidation
The procedure for liquidating an object is carried out if its use for the enterprise has become economically unprofitable. The fixed asset is subject to write-off. In the future, they have the right to disassemble it in order to use the resulting materials for other purposes.
Revaluation
The revaluation operation is not mandatory for the organization. But there are cases when this necessity is determined by local acts. In such a situation, the revaluation procedure will need to be carried out on the last day of the year. There are two types of revaluation possible. This can be a markdown or revaluation.
Unaccounted assets based on inventory results
All business entities are required to regularly conduct an inventory of the property on their balance sheet. This is necessary to ensure authenticity. If the inspection reveals objects that are not registered, they must be included in it in the same month. The cost will be indicated based on the current market price for similar properties.
OS shortage based on inventory results
Based on the results of the inventory, a shortage may occur. In such a situation, the company employee is responsible for the damage. If it is not determined, then it is written off as a loss. The amount is determined based on the actual residual value.
Account 01 in accounting plays an important role for the correct accounting of objects on the balance sheet of an organization, enterprise, and related to the main ones. Interaction between accounts helps to correctly track changes in their value during operation.
https://youtu.be/F_DY3C1xNCY
Basic accounting entries
At the end of each reporting period, entries must be made in the accounting department of the enterprise. This simplifies the process of understanding multiple transactions and contributes to the ease of doing business. Typical entries for account 86 look like this:
- Dt 51 Kt 86. This is how cash receipts are reflected. To simplify this process, you can skip the intermediate section. 76 and start from here.
- Dt 08 (4) Kt 51. This entry indicates payment for purchased fixed assets - one of the most common areas of financing.
- Dt 01 Kt 08 (4). This entry reflects the capitalization of this resource.
- Dt 26 Kt 02. This indicates the fact of accrual of depreciation during the operation of certain objects. Only after all these records can you begin to reflect financial receipts for the intended use.
- Dt 86 Kt 91 (1). As part of such an operation, the assistance received is reflected.
- Dt 10 Kt 86. Since financial assistance can be provided not only in the form of money, but also in the form of natural elements, such an entry can be recorded.
- Dt 20 Kt 10. The chart of accounts line in question is not used in this entry. It states that the materials have been written off.
- Dt 86 Kt 91 (1). In this case, the accountant must draw up the main directions for the development of the products that have been received.
As you can see, the funds are reflected in the credit of the item listed above. There is correspondence with a large number of other summary accounts.
The values that contribute to the generalization of this account, in case of violation of the conditions for dissipation of assistance, can be withdrawn, and the investor will no longer be willing to provide any support. Therefore, any deviations and all other operations must be strictly reflected within the reporting document.
Thus, line 86 plays a special role in the accounting activities of any enterprise. It reflects the receipt of financial assistance and the directions of its expenditure. Since it is targeted, the company must monitor costs strictly according to goals.
Additional information regarding account 86 is provided below.
https://youtu.be/J2IfRCpn-JM