Home Accounting and HR Documents
The classification of individual legal forms of organizations is assigned to a system under the abbreviation OKOPF, which has two categories of positions: name and collection of forms. This allows you to refer to the explanation and decoding of codes with an alphabetical index for the convenience of a practical approach to these sources.
The objects inspected by OKOPF are the forms of economic, individuals and legal entities that are engaged in business. The OKFS (All-Russian Classification of Forms of Ownership) states that all business organizations are divided into state, private, municipal, national and foreign types of ownership. State property is divided into: official and owned by the Russian Federation; and private property is divided into: property of private figures and legal representatives.
In order to correctly and correctly fill out tax reporting statistics, you need to enter the code of the organization or enterprise that is indicated in the classifier. Next, you need to find in the official source the decoding and name of the code in the provided column corresponding to the property you are looking for.
What is the OKOPF code?
The all-Russian classification of organizational and legal formations is necessary for:
- Formation of information sources about economic entities;
- Analysis and resolution of issues in taxation, property economics, statistical data.
- Forecast of social and economic processes.
- Improved regulation of economic activity.
The objects under consideration in the classification are organizations that are commercial or non-profit. Such organizations mean the securing of property by an enterprise and all the formative legal forms in this regard.
A legal entity, which is guided by the main motive of the activity of its enterprise as making a profit, proceeds from the method of securing property under a code. Communities organized on a commercial basis are called “commercial” - they create enterprises such as: economic entities, economic partnerships and communities, industrial activities, various unitary organizations.
Farms are commercial organizations. Non-profit communities create such associations as: consumer, religious, public, charitable, non-profit, autonomous.
Organizations that can create their work without legal representatives include such associations as: separate points, branches, mutual funds, various partnerships, district and city courts.
International organizations that can operate on the borders of the Russian Federation include such enterprises as: intergovernmental, on the basis of an international agreement, private international purposes, financial assistance.
The classifier provides explanations that are formed by the federal organizational and legal form, which is entered in form “A”.
What is the OKPO code and how to find it out through the Rosstat website using the TIN
What is the OKPO code and how to find it out through the Rosstat website using the TIN OKPO is considered the main and most important code of the all-Russian classifier of aggregate legal entities. The current classifier was introduced on July 1, 1994 within the framework of Decree of the State Standard of the Russian Federation dated December 30, 1993 No. 297. Summary of the article
All-Russian classifier of organizational and legal forms OK 028-2012 (OKOPF) 2015
All-Russian classifier of organizational and legal OK 028-2012 (OKOPF) 2020 (adopted and put into effect by order of the Federal Agency for Technical Regulation and Metrology dated October 16, 2012 N 505-st) Date of introduction January 1, 2013. Introduced to replace the All-Russian Classifier of Organizational and Legal Forms OK 028-99 The basis for the development of a new version of the All-Russian Classifier of Organizational and Legal Forms is the Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated October 2, 2006.
The objects of classification are the organizational and legal forms of legal entities that are commercial or non-profit organizations; organizations created in accordance with the law without the rights of a legal entity, and international organizations, as well as citizens engaged in commercial activities or activities not classified as entrepreneurship by law.
The organizational and legal form is understood as the method of securing (forming) and using property by an organization and the ensuing legal status and goals of entrepreneurial activity.
Code generation
The code itself can consist of five digits. The codes are divided into:
- 50102 — Individual enterprises;
- 12300 – Organizations with limited functions;
- 12247 – Public organizations;
- 12267 – Non-public organizations.
The code numbers are deciphered as follows:
- The first number is the classification section;
- The second and third numbers are the type of organizational forms;
- The fourth and fifth numbers are the type of organizational forms.
Main groups of sections of organizational and legal forms by numbering:
- 10000 – legal commercial forms;
- 20000 – legal non-commercial forms;
- 30000 – organizations without a legal founder and leader;
- 40000 – international communities;
- 50000 – civil organizations.
The table is formed from two blocks: code and name. Each block respectively contains a five-digit number and the name of the organizational form. A more detailed breakdown of all organizations will be presented below.
OKOPF as a body of self-organization of the population
Since the organizational and legal form of economic entities (and not only) is officially recognized by law, there must be a way to regulate economic entities, which is the method of registration of OKOPF. Based on the fact that OKOPF can include any legal representation that can conduct its business without resorting to establishing a legal entity, in the classifier the code means only an individual code that is not used anywhere else.
When an initiative appears from a group of people about the desire to organize a community body independently in rural or urban areas, the council must submit an appeal from the residents of this area at their place of residence. The appeal will be valid only if more than 50% of the population of the area wants to organize a community. As a rule, the leader of such self-organization is an initiative group that will represent the interests of all residents. The appeal is submitted in the form of an application for the creation of a self-organization and a protocol of residents at their place of residence. The application must indicate: the main direction of the organization and a list of willing participants with passport details.
The issue of creating a body will be raised at the council of the local conference. If the creation of a self-organization is approved, permission is granted by the local council. But the council may refuse to create an organization with clearly substantiated violations of filing a petition.
After approval by the council about self-organization, the community is legalized by registering it with OKOPF. To register, you will need the following data: a copy of the council’s permission, minutes of all residents, approval of residents, composition of the organization’s members. The village or city council then organizes legal assistance and regulates the established organization.
www.finanbi.ru
OKOPF positions
The following positions have been introduced into the classification:
- Position 19000 – “Other legal representations leading a commercial organization”, where all actions established by law and introduced into the Code of the Russian Federation are introduced.
- Position 29000 – “Other non-profit enterprises that are not included in other groups.” This includes non-profit enterprises that have successfully passed state registration control, as provided for by Federal legislation.
For more convenient use of the classifier, all OKOPF positions are given in a separate Appendix “B” and listed alphabetically.
How to find out OKOPF by TIN?
How to find out OKOPF by TIN? How and where can I find out the OKOPF code of my organization using the TIN?
There is a website kodyrosstat.rf, where you can view/print all the statistics codes of an organization or individual entrepreneur, including the OKOPF code. An example of searching for an OKOPF code by TIN: Find your region in the list on the left, click on it - you will go to its page.
Click on “legal=”” persons”=”” or=”” “individual=”” entrepreneurs.”=”” enter=”” one=”” of=”” three=”” values:=”” inn, ="" ogrn/ogrnip="" or="" okpo.="" alt="How to find out the code by okopf">
Decoding of units
- Divisions of legal commercial forms 10000:
- 11000 – “Business partnerships” – enterprises that include investments of participating share capital.
- 11051– “General partnerships” - a business partnership that has turned into a full or “team partnership.” The parties to the agreement carry out work on behalf of the established company and are responsible for all the resources available to this company.
- 11064 – “Partnerships on faith” is a business partnership created on trust. The participants of the partnership include several individuals who are responsible for all losses of the community. Several participants or one legal entity are established, which are called “contributors”, bearing the risk up to the amount contributed by all members of the community.
- 12000 – “Business societies” are a type of auction company, but with less permissible opportunities and responsibilities.
- 12100, 12165, 12166 – “Societies with limited or additional responsible powers” - commercial enterprises with property divided between several entrepreneurs. The capital established for contribution to the organization's fund is divided into parts or shares for which the risk of loss is borne within the amount of the share. In organizations with additional liability, community members are liable in a subsidiary mode on a joint and several basis.
- 12200 – “Joint-stock organizations” are enterprises whose capital is distributed over the number of shares that secure the rights of their participants.
- 12247 — “Open joint-stock enterprises” are joint-stock enterprises where participants have the right to limit their shares.
- 12267 – “Closed joint-stock enterprises” - distribution of shares among participants.
- 13000 – “Business partnerships” - the participants of which are both the owners and persons invited and approved by the partnership.
- 14000 – “Artels or production cooperative” - associations of persons on a voluntary basis for any joint activity in production.
- 14100, 14153 – “Agricultural cooperatives and collective farms” are the same as artels, only cooperatives were created for the sale and processing of produced raw materials.
- 14154 – “Fish collective farms” are artels created for the processing and marketing of fish raw materials.
- 14155 – “Cooperative farms or collective farms” are cooperatives created by main farmers who run subsidiary businesses on a voluntary basis. This includes livestock raising and land cultivation.
- 14200 – “Production cooperative” - participation on a voluntary basis with a contribution from personal resources.
- 15000 – “Unitary enterprise” - organization and management of a business without vested rights.
- 15100 – “State-owned enterprises” are unitary enterprises organized under the right of operational management.
- 15141 – “Federal government organizations” are unitary enterprises where property belongs to operational management rights.
- 15142 – “State-owned organizations of the Russian Federation” - organizations where the rights belong to the bodies of the Russian Federation.
- 15243 – “Municipal unitary organizations” are unitary organizations where the property belongs to them on the basis that the operational management is the municipal board itself.
- 15300 – “Farms” - a farm created as a legal entity where citizens take voluntary participation in the process of manufacturing and marketing raw materials.
- 19000 – “Other legal entities” - farms organized by a legal entity under the law.
- Divisions of organizational and legal forms of non-profit organizations:
- 20100 – “Consumer cooperatives” - an association on a voluntary basis of citizens, with proof of membership, to achieve the material or other needs of the organization’s members by the method of share contributions of each participant.
- 20101 – “Garage cooperation” is a voluntary association with the goal of meeting the garage needs of participants.
- 20102 – “Residential and housing-construction cooperation” - associations on a voluntary basis in order to meet the housing needs of participants.
- 20103 – “Housing and savings cooperatives” - associations on a voluntary basis for the purpose of joint savings.
- From 20104 to 20106 inclusive - “Credit cooperation” - associations of legal representatives that, on the basis of participation (membership) and on a local basis, are united in order to satisfy the credit needs of participants.
- 20107 – “Consumer societies” - associations on a voluntary basis on a territorial basis using the method of share contributions to satisfy the trading activities of participants.
- From 20109 to 20115 inclusive - “Agricultural processing cooperation” - service, supply, gardening, livestock cooperation. Participation is based on a common need to satisfy the processes of production and marketing of agricultural raw materials.
- From 20200 to 20300 inclusive - various public cooperations, which include the following movements: political, trade union, public, amateur bodies, religious organizations. These are self-governing organizations initiated by citizens based on some common interests.
- From 20401 to 20404 – Funds, which include: charitable, non-state, pension, public and environmental. The interests of the organization are to satisfy social, cultural or charitable needs.
- 20500 – “Non-profit partnerships” - created to satisfy the social, cultural, charitable, sports and other interests of citizens on a private basis.
- From 20600 to 20608 – Associations, which include: economic interaction of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation, municipalities of the constituent entities, credit cooperatives, cooperatives, public associations, indigenous peoples, consumer societies. This is the satisfaction of the goals of citizens of a non-commercial nature.
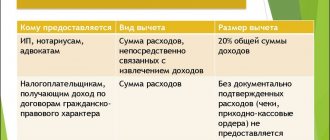
- From 20800 to 20803 inclusive - Chambers, including: lawyers, notaries, commercial and industrial. This is an association of participants based on professional interests.
- From 20900 to 20908 - Institutions, which include: autonomous, charitable, budgetary, government, public, private, academies of sciences, religious.
- From 21000 to 21003 inclusive - Gardening, horticulture and all dacha associations of citizens. This is the sale of participants for the sale of gardening and land plots.
- From 28000 to 28017 – Non-profit organizations, which include: autonomous, lawyers, state academies of sciences, state companies, state. cooperatives, Cossack societies, bar associations, mutual insurance, communities of small peoples, employers' associations, farms (unions), non-governmental organizations, homeowners, territorial self-government, non-membership organizations. All members are not obligated to respond to commitments, and the community is not obligated to respond to commitments from participants.
- 29000 - “Other organizations.” Territorial organizations record its registration according to the principle of location at the place of residence of the legal entity or municipal address. There are also partnership owners - an association of all owners of dwellings, premises, apartments or an apartment building for the management of joint real estate or a complex. Foreign organizations undergo a registration procedure under the article of the Federal Law.
- 30000 – Representative offices of organizational and legal forms of organizations that were created without the right of legal representative.
This includes various legal entities. persons: representative offices, branches, separate divisions, structural divisions, mutual funds, partnerships, district and city courts. These are organizations that operate without a legal entity.
- 40,000 – Representative offices of organizational and legal forms of international enterprises conducting their industry in the Russian Federation.
This includes intergovernmental and non-governmental organizations. Enterprises created on the basis of international agreement to solve international problems. Agreement is made by creating a charter or statute. It is also the coordination of all expenditures and efforts of the government in order to solve an international problem. Non-governmental international organizations are created with the aim of promoting international communication and cooperation through improvement in the political, economic, cultural, scientific, and technical fields.
- 50000 – Representative offices of organizational and legal forms for the activities of individuals. All commercial activities of individuals or citizens that do not involve the creation of an enterprise. At the same time, the entrepreneur has the right to hire employees and operate autonomously.
- 50101 – “Farm Organizers” - activities of an enterprise without a legal entity. persons with state registration persons not related to entrepreneurship.
- 50102 – “Private entrepreneurs” are individual entrepreneurs who have passed state registration. Also for the activities of individual citizens not related to business, but registered.
- 50201 – “Lawyers” - registered law offices for lawyers who have decided to carry out the work process on a private basis under the article of legal practice.
- 50202 – “Notaries” are persons engaged in private notarial practice who have passed state registration. A notary can hire and fire subordinates, control income and expenses, participate in litigation and carry out other actions taken into account in the legislation.
https://youtu.be/Z4M45dE81uU
All-Russian classifier of organizational and legal forms OK 028-99 (OKOPF)
Based on the goals of entrepreneurial activity, business entities that are legal entities are divided into organizations that pursue profit as the main goal of their activities (commercial organizations) or do not have profit as such a goal and do not distribute the profits between participants (non-profit organizations) .
We recommend reading: One on Electricity in the Kemerovo Region
Legal entities that are non-profit organizations can be created in the form of consumer cooperatives, public or religious organizations (associations), owner-financed institutions, charitable and other funds, as well as in other forms provided by law (non-profit partnerships, autonomous non-profit organizations, etc. .).
Classification of codes and their designations
The classifier of forms of ownership used in Russia consists of 2 digits, the first of which indicates that the company belongs to the state (there are 4 of them in total, in order). The second carries information about the class of property.
In order to find out the classifier, you need to contact sources that publish new information (see above), as it is constantly updated and supplemented.
The first order group includes property located on the territory of Russia:
- 11 – state-owned companies;
- 12 – federal enterprises;
- 13 – companies of constituent entities of the Russian Federation;
- 14 – property of municipalities;
- 15 – property of religious and public organizations;
- 16 – private property;
- 17 – mixed property located on the territory of Russia;
- 18 – property of persons who have Russian citizenship but live outside their homeland;
- 19 – property of consumer cooperatives.
The second ordinal group includes those organizations that carry out their business activities in Russia:
- 21 – international companies;
- 22 – property of foreign countries;
- 23 – foreign legal entities;
- 24 – enterprises of persons who do not have Russian citizenship (or do not have it at all);
- 27 – mixed foreign property.
The third ordinal group includes property owned by Russian and foreign entrepreneurs:
- 31 – firms of joint foreign and federal ownership;
- 32 – joint property of a foreign country and a constituent entity of the Russian Federation;
- 33 – joint municipal and foreign property;
- 34 – organizations of private and foreign ownership;
- 35 – property of religious and public organizations owned by Russian and foreign owners.
The fourth order group includes property owned by the state and private individuals (but not related to the previous three groups):
- 41 – share of federal and state property;
- 42 – joint share participation of the state and its subjects;
- 43 – mixed state ownership, with subject and federal shares;
- 49 – mixed property of various types.
OKOPF 12165 – Limited liability companies
So the number 5 indicates that he is an individual. In turn, for commercial organizations the number 1 is used, and for non-profit organizations - 2. When it becomes necessary to fill out various documents with submission to regulatory authorities, entrepreneurs try to figure out what OKOPF is and why this concept is needed. International organizations whose activities are carried out, including on the territory of the Russian Federation, include permanent associations of an intergovernmental and non-governmental nature, created on the basis of international agreements, charter, statute or other constituent document and which are international in their goals, membership, structure and financial support .
OKOPF code: 1 23 00
This is the rule that applies in most cases. There are many theories and assumptions that a man will face a lot of unpleasant consequences after interrupted sexual intercourse. Only after this you can register on the bank’s website and manage your funds via the Internet.
Non-governmental international organizations are created with the aim of promoting international communication and cooperation through improvement in the political, economic, cultural, scientific, and technical fields.
What is OKOPF for LLC and its changes in 2020
There are deductions from wages that reduce the amount due to the employee and charges to the general wage fund, which are carried out at the expense of the enterprise. The amount of taxes and contributions Salary is reduced by the amount of personal income tax, its amount is 13% for citizens of the Russian Federation and 30% for non-residents.
President of the Russian Federation “On additional measures to improve the efficiency of the investment policy of the Russian Federation” dated July 25, 1995.
Amendment 2/2014 OKOPF came into force with the right of early application in legal relations arising from September 1, 2014.
Business partnerships can be created in the form of a general partnership and limited partnership.
Forms of ownership
According to the classifier of forms of ownership, organizations can be divided into private, municipal, state and others . The division also concerns whether the company belongs to: the Russian Federation, a foreign state or a mixed type. In turn, the division affects state property, into federal property and that belonging to its subjects.
Important! Private property is divided into property of legal entities and individuals.
Read more about the various forms of ownership according to the OKFS here.