What are tax deduction codes for?
The tax deduction code is a digital code. A deduction is an amount that, if there are documented grounds, can be reasonably deducted from the tax base, thereby reducing not only it, but also the amount of tax accrued from this base.
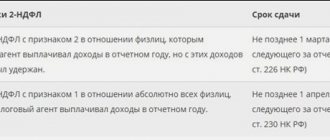
The deduction code is required when filling out the tabular part of the 2-NDFL certificate, which serves:
- a tax agent reporting form on the payment of income and the amount of tax withheld from it;
- tax agent reporting form on unwithheld tax on income paid;
- a document confirming the amount and types of income received by the taxpayer at the place of work, and the amount of personal income tax paid by him when applying to various authorities (for example, for a new job, to the Federal Tax Service, bank).
https://youtu.be/TZcRg-SBRIU
Codes of professional tax deductions for personal income tax
They are provided for in Art. 221 Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
| Deduction code | Decoding |
| 403 | The amount of actually incurred and confirmed expenses that are directly related to the performance of work or provision of services under GPC contracts (civil law). |
| 404 | The amount of actually incurred and confirmed expenses that are directly related to the receipt of royalties or remunerations for the creation/performance or other use of works of literature, science, art, as well as remuneration to the authors of inventions/discoveries, utility models and industrial designs. |
| 405 | The amount within the limits of cost standards that are associated with receiving royalties for the creation/execution and other use of works of literature, science, art, as well as remunerations to the authors of inventions/discoveries, utility models and industrial designs (as a percentage of the amount of accrued income). |
Under the personal income tax deduction code 405, they reflect amounts the amount of which is set as a percentage of the amount of remuneration received.
Which deduction table is used in 2019-2020?
The last time changes were made to the deduction table was from 01/01/2018. A new deduction code 619 was added to it, which is intended to display a positive financial result for transactions that are recorded on an individual investment account (Order of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated October 24, 2017 No. ММВ-7-11 / [email protected] ). But the main changes in the table of deduction codes occurred from December 26, 2016 (order of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated November 22, 2016 No. ММВ-7-11 / [email protected] ). The most noticeable thing for most tax agents then was the change in deduction codes for children.
What has been changed in the list of deduction codes?
The adjusted table of deduction codes has retained the main set of codes used in the old table, but at the same time a number of codes have been excluded from it, new ones have been added, old codes have been replaced with new ones, and deduction description texts have been adjusted.
Broken down by type of deduction, the changes look like this:
- Standard codes - excludes codes 114-125. Codes 126–149 have been introduced instead. Now they differ depending on who the deduction is provided to: natural parents (adoptive parents) or persons who replace them.
- Reducing the base according to Art. 214.1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (transactions with securities and financial instruments of forward transactions) - in codes 205–207, instead of expenses on operations with financial instruments of forward transactions, expenses on operations with derivative financial instruments are now indicated, and codes 209–210 reflect no loss on operations with financial instruments of futures transactions, and losses on transactions with derivative financial instruments. Additionally, code 208 was introduced, which reflects losses on transactions with derivative financial instruments.
- Reducing the tax base for securities lending transactions in accordance with Art. 214.4 - instead of code 221, which was used to reflect the amount of expenses on transactions with securities accounted for in an individual investment account, codes 225–252 were introduced. Codes 250–252 have been added, reducing the tax base for transactions accounted for on an individual investment account in accordance with Art. 214.9 Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
- From investment tax deductions provided for in Art. 219.1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, code 617 is excluded.
Structure of the new table of deduction codes
Thus, the new table of deduction codes consists of 14 sections named by types of deductions, and 1 additional code 620, which includes other types of deductions not listed in the table.
The sequence of sections and numbering of codes in them is as follows:
- standard deductions under Art. 218 Tax Code of the Russian Federation - codes 104, 105,126–149;
- reducing the base according to Art. 214.1 Tax Code of the Russian Federation - codes 201–203, 205–210;
- reducing the base according to Art. 214.3 Tax Code of the Russian Federation - codes 211, 213;
- reducing the base according to Art. 214.4 Tax Code of the Russian Federation - codes 215–220; 222–241;
- reducing the base according to Art. 214.9 Tax Code of the Russian Federation - codes 250–252;
- property deductions under Art. 220 Tax Code of the Russian Federation - codes 311, 312;
- social according to clause 2 p. 1 art. 219 Tax Code of the Russian Federation - codes 320, 321;
- social according to clause 3 p. 1 art. 219 Tax Code of the Russian Federation - codes 324–326;
- social according to clause 4 paragraphs 1 art. 219 Tax Code of the Russian Federation - code 327;
- social according to clause 5 p. 1 art. 219 Tax Code of the Russian Federation - codes 328;
- professional deductions under Art. 221 Tax Code of the Russian Federation - codes 403–405;
- deductions for non-taxable income under Art. 217 Tax Code of the Russian Federation - codes 501–510;
- reducing the base according to Art. 214 Tax Code of the Russian Federation - code 601;
- investment deductions under Art. 219.1 Tax Code of the Russian Federation - code 618;
- other deductions - code 620.
The table ends with 5 notes referring to the document details on the basis of which social deductions and deductions with codes 509 and 510 should be applied for non-taxable income.
Code table for 2020
| CODE | CONDITIONS OF DEDUCTION |
| Standard (Article 218 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation) | |
| Deduction code 104 in certificate 2-NDFL | Allows you to apply a deduction of 500 rubles. to the payer, if he falls under the categories specified in subparagraph. 2 p. 1 art. 218 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (heroes of the USSR, the Russian Federation, participants in the Second World War, parents and spouses of deceased servicemen, disabled people since childhood, etc.) |
| Code 105 | Allows you to apply a deduction of RUB 3,000. payers named in sub. 1 clause 1 art. 218 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (disabled people of the Second World War who suffered from the accident at the Chernobyl nuclear power plant, as well as from the accident at the Mayak production association, participants in nuclear weapons tests, etc.) |
| Codes 114–125 | Code 114 with personal income tax deduction and further up to code 125 have been excluded from the table since the end of 2020 |
| Deductions for parents in relation to the children they provide for: | |
| Deduction code 126 in certificate 2-NDFL | For the first minor child, as well as for each child under 24 years of age who is studying full-time at a university, including graduate school and residency (hereinafter referred to as students) |
| Deduction code 127 in certificate 2-NDFL | For the second minor child, as well as for each student child |
| Deduction code 128 in certificate 2-NDFL | For the third and subsequent minor children, as well as for each student child |
| Deduction code 129 in 2-NDFL | Deduction code 129 for personal income tax applies to a disabled minor child, as well as a disabled student child of groups I and II |
| Deductions for adoptive parents in relation to the children they provide for: | |
| Deduction code 130 in certificate 2-NDFL | In relation to the same categories of children who are listed on the line with code 126 |
| Code 131 | In relation to the same categories of children who are listed on the line with code 127 |
| Code 132 | In relation to the same categories of children who are listed on the line with code 128 |
| Code 133 | In relation to the same categories of children who are listed on the line with code 129 |
| The single parent is entitled to a double deduction according to the codes indicated below: | |
| Deduction code 134 in 2-NDFL | Code 134 in 2-NDFL gives the right to a deduction in relation to the same categories of children who are listed on the line with code 126 |
| Code 136 | In relation to the same categories of children who are listed on the line with code 127 |
| Deduction code 138 in certificate 2-NDFL | In relation to the same categories of children who are listed on the line with code 128 |
| Code 140 | In relation to the same categories of children who are listed on the line with code 129 |
| The only adoptive parent is entitled to a double deduction according to the codes indicated below: | |
| Deduction code 135 in certificate 2-NDFL | In relation to the same categories of children who are listed on the line with code 126 |
| Code 137 | In relation to the same categories of children who are listed on the line with code 127 |
| Code 139 | In relation to the same categories of children who are listed on the line with code 128 |
| Code 141 | In relation to the same categories of children who are listed on the line with code 129 |
| If one of the parents refused the deduction by writing a corresponding statement, then the other parent can receive a double deduction using such a document using the codes: | |
| Deduction code 142 in certificate 2-NDFL | In relation to the same categories of children who are listed on the line with code 126 |
| Code 144 | In relation to the same categories of children who are listed on the line with code 127 |
| Code 146 | In relation to the same categories of children who are listed on the line with code 128 |
| Code 148 | In relation to the same categories of children who are listed on the line with code 129 |
| If one of the adoptive parents, upon application, refuses the deduction due to him, then the second one will be able to receive a double deduction using the codes: | |
| Deduction code 143 in certificate 2-NDFL | In relation to the same categories of children who are listed on the line with code 126 |
| Code 145 | In relation to the same categories of children who are listed on the line with code 127 |
| Code 147 | In relation to the same categories of children who are listed on the line with code 128 |
| Code 149 | In relation to the same categories of children who are listed on the line with code 129 |
| Deductions under Art. 214.1 Tax Code of the Russian Federation | |
| Deductions for transactions with securities (hereinafter referred to as securities) are provided using the following codes: | |
| Code 201 | For expenses on transactions with securities that are traded on the organized securities market (hereinafter referred to as securities on the ORTS) |
| Code 202 | For expenses on transactions with securities that are not listed on the ORSM (hereinafter referred to as the Central Bank not on the ORSM) |
| Code 203 | For expenses on transactions with securities not on the Ordinary Securities Market, if on the date of acquisition they fell under the category of securities on the Ordinary Securities Market |
| Code 205 | By the amount of loss from transactions with securities on the ORTS, which reduce the tax base for transactions with derivatives traded on the organized market (hereinafter referred to as derivatives on the OR) |
| The following codes are provided for expenses incurred in connection with transactions with derivatives: | |
| Code 206 | For expenses on transactions with derivative funds on open market, if their underlying asset is the Central Bank, stock indices |
| Code 207 | For the amount of expenses for transactions with derivative funds on OR, if their underlying asset is not the Central Bank, stock indices |
| Code 208 | By the amount of loss received from transactions with derivatives on the OR, which reduces the basis for transactions with the securities on the ORTS |
| Code 209 | By the amount of loss received from transactions with derivatives on the open market, if the underlying asset is not the Central Bank, stock indices, which reduces the basis for transactions with derivatives |
| Code 210 | By the amount of loss received from transactions with derivatives on the open market, if the underlying asset is the Central Bank, stock indices, which reduces the basis for transactions with derivatives |
| Deductions under Art. 214.3 Tax Code of the Russian Federation | |
| Code 211 | On loan interest under repo transactions |
| Code 213 | For expenses associated with closing a short position, as well as for the amount of costs for transactions for the acquisition and sale of securities objects of repo transactions |
| Deductions under Art. 214.4 Tax Code of the Russian Federation | |
| Code 215 | The amount of interest paid on loans |
| Code 216 | By the amount of excess of interest paid on loans over received interest, which reduces the basis for transactions with the Central Bank on the Ordinary Securities Market |
| Code 217 | By the amount of excess of interest paid on loans over received interest, which reduces the basis for transactions with the Central Bank not on the Ordinary Securities Market |
| Code 218 | By the amount of coupon expense, when opening a short position on the securities on the Ordinary Securities Market |
| Code 219 | By the amount of coupon expense when opening a short position on securities not on the Ordinary Securities Market |
| Code 220 | For expenses on transactions with derivative funds not on OR |
| Code 222 | By the amount of loss on repo transactions, which reduces the tax base from transactions with the Central Bank on the Ordinary Securities Market |
| Code 223 | By the amount of loss on repo transactions, which reduces the tax base from transactions with the Central Bank not on the Ordinary Securities Market |
| Code 224 | For losses from transactions with the Central Bank on the ORSB, which reduces the financial the result of transactions with securities not on the Ordinary Securities Market, if at the date of acquisition they fell under the category of securities on the Ordinary Securities Market |
| In relation to those expenses that the payer takes into account on an individual investment account, the following are provided: | |
| Code 225 | For expenses similar to those indicated in the table for code 201 |
| Code 226 | For expenses similar to those indicated in the table for code 202 |
| Code 227 | For expenses similar to those indicated in the table for code 203 |
| Code 228 | For expenses similar to those indicated in the table for code 206 |
| Code 229 | For expenses similar to those indicated in the table for code 207 |
| Code 230 | For expenses similar to those listed in the table for code 211 |
| Code 231 | For expenses similar to those indicated in the table for code 213 |
| Code 232 | For expenses similar to those indicated in the table for code 215 |
| Code 233 | For expenses similar to those indicated in the table for code 218 |
| Code 234 | For expenses similar to those indicated in the table for code 219 |
| Code 235 | For expenses similar to those indicated in the table for code 220 |
| Code 236 | For a loss similar to that provided for under code 224 |
| Code 237 | For a loss similar to that provided for under code 216 |
| Code 238 | For a loss similar to that provided for under code 217 |
| Code 239 | For a loss similar to that provided for under code 222 |
| Code 240 | For a loss similar to that provided for under code 223 |
| Code 241 | By the amount of loss received from transactions with derivative funds that are traded on the ORS (if the underlying asset is the Central Bank, stock indices), which reduces the tax base for transactions with derivative funds on the ORTS |
| Deductions under Art. 214.4 Tax Code of the Russian Federation | |
| Code 250 | For a loss similar to that provided for under code 205 |
| Code 251 | For a loss similar to that provided for under code 208 |
| Code 252 | For a loss similar to that provided for under code 209 |
| Property (Article 220 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation) | |
| Deduction code 311 in 2-NDFL | The amount of the payer’s costs for the construction or acquisition of housing for himself, as well as land plots for individual housing construction |
| Code 312 | The amount of the payer's expenses for repaying interest on loans and credits received to finance such construction or acquisition of real estate |
| Social | |
| A deduction is provided for the payer’s expenses for training in the following cases (subclause 2, clause 1, article 219 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation): | |
| Code 320 | To study for yourself or your brother (sister) under 24 years of age in full-time programs |
| Code 321 |
|
| Deductions are provided for medical expenses incurred by the payer (subclause 3, clause 1, article 219 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation): | |
| Deduction code 324 in 2-NDFL | For treatment costs for yourself, your spouse, parents and minor children |
| Code 325 | According to the costs of paying contributions under DLS agreements for the payer, his spouse, parents and minor children |
| Code 326 | According to the cost of expensive treatment |
| Regarding the costs of paying pension insurance contributions, the Tax Code of the Russian Federation provides deductions: | |
| Deduction code 327 in certificate 2-NDFL | Deduction code 327 in 2-NDFL is applied to the costs of paying contributions under agreements with non-state funds in relation to oneself and close relatives |
| Deduction code 328 in 2-NDFL | Deduction 328 in the 2-NDFL certificate applies to additional costs. contributions to funded pension |
| Professional (Article 221 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation) | |
| Deduction code 403 in certificate 2-NDFL | For costs incurred under GPC agreements |
| Code 404 | Based on actual costs incurred to obtain royalties by the payer |
| Code 405 | For expenses within the framework of standards incurred in order to receive royalties by the payer |
| Deductions under Art. 217 Tax Code of the Russian Federation | |
| Deduction code 501 for personal income tax | Applies to the amount of gifts that the payer received from a company or individual entrepreneur |
| Code 502 | From the cost of incentive prizes that the payer received during state competitions and competitions |
| Deduction code 503 for personal income tax | From the amount of financial assistance from the employer |
| Code 504 | From the cost of medications prescribed by a doctor, which the employer company reimbursed its employee |
| Code 505 | From the cost of incentive prizes that the payer received during advertising competitions |
| Code 506 | From the amount of financial assistance to a disabled person, which was provided by a public organization of disabled people |
| Code 507 | From the amount of material and financial assistance and gifts received by WWII veterans, widows of those killed in WWII and other categories named in clause 33 of Art. 217 Tax Code of the Russian Federation |
| Deduction code 508 in certificate 2-NDFL | Deduction code 508 for personal income tax applies to the amount of one-time financial assistance to an employee from the employer company upon the birth of a child. |
| Code 509 | From the amount of remuneration in kind for employees of agricultural enterprises |
| Code 510 | From the amount of insurance pension contributions that the employing company pays for its employees |
| Deductions under Art. 214 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation and Art. 219.1 Tax Code of the Russian Federation | |
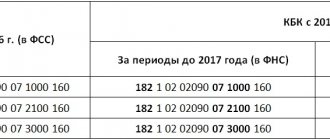
| Code 601 | By an amount that reduces the tax base for dividends |
| Code 618 | On the value of the payer’s profit from the redemption of securities traded on the Ordinary Securities Market, if such securities were in his ownership for more than three years |
| Code 619 | The amount of profit from transactions on an individual investment account |
| Deduction code 620 in certificate 2-NDFL | By the amount of other amounts that also reduce the payer’s income tax base in accordance with Chapter. 23 Tax Code of the Russian Federation |
Standard deduction codes 104, 105, 126–149 in the 2-NDFL certificate
These deduction codes, which give the employee the right to a personal deduction either due to special merits or because he has children, are most often included in the 2-NDFL certificate. In the new table, those that have been used since 2012 are kept unchanged. They are divided into the following groups:
- codes 104 and 105 - personal deductions in the amount of 500 rubles. and 3,000 rubles, provided to a person who has special services to the country (combatants, liquidators of accidents at nuclear facilities, holders of state awards);
- deduction codes 126, 127, 128 - presented to parents, spouse of a parent, adoptive parent for the 1st, 2nd, 3rd (and subsequent) children under the age of 18 years or up to 24 years old if the child is studying;
- code 129 - for a deduction provided to the parent, spouse of the parent, adoptive parent, who is supporting a child under the age of 18 years or up to 24 years old, if the child is a disabled person of group I or II;
- codes 130, 131, 132 - deductions for a child under 18 years of age or up to 24 years of age if the child is studying; deductions are submitted to the guardian, trustee, adoptive parent, spouse of the adoptive parent;
- code 133 - for a deduction for a guardian, trustee, foster parent, spouse of a foster parent who is supporting a child under the age of 18 or under 24 years if the child is a disabled person of group I or II;
- codes 134, 136, 138 - double deduction presented to the only parent, adoptive parent for the 1st, 2nd, 3rd (and each subsequent) child under the age of 18 years or up to 24 years old if the child is studying;
- codes 135, 137, 139 - double deduction presented to the sole guardian, trustee, foster parent, adoptive parent for the 1st, 2nd, 3rd child under the age of 18 years or up to 24 years old if the child is studying;
- code 140 - for a double deduction provided to the only parent, the adoptive parent, who is supporting a child under the age of 18 or up to 24 years, if the child is a disabled person of group I or II;
- code 141 - double deduction provided to the sole guardian, trustee, foster parent who is supporting a child under the age of 18 or up to 24 years if the child is a disabled person of group I or II;
- codes 142, 144, 146 - double deductions for the 1st, 2nd, 3rd (and subsequent) children under the age of 18 years or 24 years old if the child is studying; such deductions are presented to one of the parents of their choice on the basis of an application for the refusal of the second parent to receive a tax deduction;
- codes 143, 145, 147 - double deductions for the 1st, 2nd, 3rd (and subsequent) children under the age of 18 years or 24 years old if the child is studying; deductions are presented to one of the adoptive parents of their choice on the basis of a statement of refusal of the second adoptive parent to receive a tax deduction;
- code 148 - double deduction for a disabled child under the age of 18 or a student under the age of 24 who is a group I or II disabled person, which is presented to one of the parents of their choice on the basis of an application for the second parent’s refusal to receive a tax deduction;
- code 149 - double deduction for a disabled child under the age of 18 or a student under the age of 24 who is a group I or II disabled person, who is presented to one of the adoptive parents of their choice on the basis of an application for the refusal of the second adoptive parent to receive a tax deduction .
New income and deduction codes for personal income tax in 2020: table with explanation
When filling out a 2-NDFL certificate, special codes are used to indicate the basis for an individual’s receipt of income, which are the same for all taxpayers and are established and periodically revised by the tax service. Let's look at what income codes are used in 2020.
The article contains a table with a breakdown of each code. And we analyzed the most complex codes that raise questions among accountants separately.
What do the 2020 personal income tax codes mean?
For a more compact presentation of information in income tax reporting forms, four and three-digit codes are used to indicate the reason for accrual of income, as well as to reflect information about tax deductions for personal income tax.
The decoding of these codes and the codes themselves were approved by order of the Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation dated September 10, 2015 No. ММВ-7-11/ [email protected] The use of these codes is mandatory.
Tax authorities regularly review codes.
You can calculate personal income tax and deductions for free online in our Bukhsoft program. It allows you to maintain tax and accounting records and prepares primary documents and reporting in one click. Get access to the program for 365 days. Consultation on all accounting issues is available to users 24 hours a day, 7 days a week.
Go to the program
Have new income and deduction codes appeared for the 2-NDFL certificate in 2019?
Since 2020, an updated list of codes has been in effect. The changes were approved by order of the Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation No. ММВ-7-11/ [email protected] Most of the changes affected deductions, but officials also slightly added to the list of codes for income.
Basically, the addition will affect the completion of 2-NDFL certificates on income from transactions with securities and other financial instruments. But two new codes have been introduced that employers can use:
- 2002 – awards;
- 2003 – bonuses based on profits, targeted revenues or special sources of financing.
In addition, by order of the Federal Tax Service dated October 24, 2017 No. ММВ-7-11/ [email protected] new income codes were introduced:
- 2013 — Amount of compensation for unused vacation
- 2014 — The amount of payment in the form of severance pay, average monthly earnings for the period of employment, compensation to the manager, deputy managers and chief accountant of the organization in the part exceeding in general three times the average monthly salary or six times the average monthly salary for workers dismissed from organizations located in regions of the Far North and equivalent areas
- 2301 — Amounts of fines and penalties paid by an organization on the basis of a court decision for failure to voluntarily satisfy consumer requirements in accordance with the Law of the Russian Federation of 02/07/1992 No. 2300-1;
- 2611 — The amount of bad debt written off in accordance with the established procedure from the organization’s balance sheet
- 3021 — The amount of income in the form of interest (coupon) on circulating bonds of Russian organizations denominated in rubles
The same order approved a new deduction code:
- 619 — The amount of positive financial results obtained from transactions recorded on an individual investment account
Types of income for personal income tax in 2020
Income subject to personal income tax is determined by Chapter 23 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. In Art. 208 of this chapter shows the main taxable income, and Art. 217 lists non-taxable income.
Almost every possible income of an individual has its own code, which is indicated when filling out income tax reporting forms.
It should be noted that the order of the Federal Tax Service does not list all income, but for unmentioned income to an individual, a single code 4800 “Other income” is provided.
Where can I get the personal income tax code in 2020?
A complete list of salary codes is given in the already mentioned order of the Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation dated September 10, 2015 No. ММВ-7-11 / [email protected] On our website you can download a table with codes in the next section.
- See also: New form of 2-personal income tax from 2020
New personal income tax codes in 2020 with explanation in the table
This table shows the main codes for the types of income that a tax agent may encounter.
Code
Decoding the code
| 1010 | Dividends |
| 1211 | Amounts of insurance premiums paid for individuals at the expense of employers or other enterprises and individual entrepreneurs that make similar payments |
| 1300 | Payments for copyright and similar rights (use) |
| 1301 | Payments for copyright and similar rights (alienation) |
| 1540 | Payments for the sale of shares in the authorized capital of enterprises |
| 1542 | The actual value of the share in the authorized capital of the enterprise that a participant receives upon exit |
| 2000 | Payment for individuals for performing labor or similar duties; taxable payments (except for those specified in clause 29 of Article 217 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation) for military personnel and for similar individuals (except for receipts under GPC agreements) |
| 2001 |
|
| 2002 | Bonuses within the framework of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, provided for by an employment, collective agreement or regulation on remuneration, with the exception of bonuses under code 2003 |
| 2003 | Amounts of any payments made at the expense of enterprise profits, special purpose funds or targeted revenues |
| 2010 | Payments under GPC agreements (except for royalties) |
| 2012 | Vacation pay |
| 2300 | Sick leave benefits |
| 2510 | Payment for an individual by enterprises or individual entrepreneurs for goods (work, services) or property rights, including utilities, food, recreation, training for an individual |
| 2520 | Income in kind, excluding wages |
| 2530 | Salary in kind |
| 2610 |
|
| 2720 | Present |
| 2760 | Financial assistance from employers |
| 2762 | Mat help from employers for children |
| 2770 | Reimbursement (payment) by employers to their employees, their spouses, parents and children, their former employees (age pensioners), as well as disabled people for the cost of medications purchased by them (for them), prescribed to them by their attending physician |
| 2013 | Amount of compensation for unused vacation |
| 2014 | The amount of payment in the form of severance pay, average monthly earnings for the period of employment, compensation to the manager, deputy managers and chief accountant of the organization in the part exceeding in general three times the average monthly earnings or six times the average monthly earnings for workers dismissed from organizations located in the regions Far North and equivalent areas |
| 2611 | The amount of bad debt written off in accordance with the established procedure from the organization’s balance sheet |
| 3021 | The amount of income in the form of interest (coupon) on circulating bonds of Russian organizations denominated in rubles |
You can download the full list from the link The table is valid in 2020
Deduction codes for the 2-NDFL certificate (2019, subject to changes)
Who gets the deduction and for which child?
First child (RUB 1,400)
Second child (RUB 1,400)
Third and subsequent (3000 rub.)
Disabled person (12,000 or 6,000 rubles)
| Parent, spouse, adoptive parent | ||||
| Single size (regular deduction) | 126 | 127 | 128 | 129 |
| In double size: | ||||
| - only parents | 134 | 136 | 138 | 140 |
| - if the second parent refused the deduction | 142 | 144 | 146 | 148 |
| To the adoptive parent, guardian and trustee | ||||
| Single size (regular deduction) | 130 | 131 | 132 | 133 |
| In double size: | ||||
| - sole adoptive parent, guardian, trustee | 135 | 137 | 139 | 141 |
| - if the second adoptive parent refused the deduction | 143 | 145 | 147 | 149 |
Salary code in certificate 2-NDFL in 2020
All labor income in the 2-NDFL certificate is collected under code 2000. For payments under civil contracts, code 2010 is allocated.
Within the framework of labor relations, the following income may also occur:
- 2012 – payment of vacation pay;
- 2300 – sick leave benefits.
Bonus income type code in 2020
For income in the form of bonuses received from the employer, 2 new codes have appeared: 2002 and 2003. The latter code applies only to bonuses paid from profits, earmarked proceeds or special-purpose funds. And all other bonuses are coded in the 2-NDFL certificate as 2002.
Personal income tax on dividends: rate and income code - is there any dependence?
Dividends are taxed at a general rate of 13%.
An increased rate is established for dividends received by non-residents - 15%. But the code for this type of income does not depend on the rate. For detailed information on the payment of dividends, see the article “How can an accountant use the simplified tax system to calculate and pay dividends.”
Dividend code in certificate 2-NDFL 2020
Dividends are the very first item in the list of income codes. Regardless of the rate with which they are taxed (remember that for non-residents this rate is 15%), the income code is indicated the same -1010.
Financial assistance - income code and deduction code
The code for indicating financial assistance depends on its intended purpose. Typically, financial assistance income codes are paired with deductions, since some targeted payments are not taxed at all, and non-targeted payments are not taxed in amounts up to 4,000 rubles. inclusive.
https://youtu.be/_bz_WG44z88
The pair for non-targeted payments of financial assistance is 2760 for income and 503 for deductions.
The same codes are used for financial assistance issued by the employer in connection with the death of a family member. In this case, the amount of the deduction will be equal to the amount of income, regardless of its size.
For financial assistance in connection with the birth or adoption of a child, the following pair of codes is used - 2762 for income and 508 for deductions. In this case, the deduction cannot exceed RUB 50,000.
Revenue code 4800 - what is it?
The list of income given in the order of the Federal Tax Service is not closed. If taxable income is not classified by the tax authorities, then code 4800 “Other Income” is provided for it in the reporting forms. It is used if the individual’s income does not fall into any other category.
You can generate 2-personal income tax with new deductions online for free in our Bukhsoft . The program will allocate the correct deductions automatically.
Fill out 2-NDFL online
Property deduction codes
There are 2 main types of property deductions related to the purchase of housing, which, with permission obtained from the Federal Tax Service, can be fully used at work:
- code 311 - deduction for direct expenses on the purchase or construction of housing;
- code 312 - deduction for interest paid for a mortgage related to the acquisition of housing, which also takes into account interest paid when refinancing mortgage loans.
To learn how to get a deduction for an apartment purchased with a mortgage, read the material “Tax deduction when purchasing an apartment with a mortgage (nuances)” .
Codes of property tax deductions for personal income tax
Property deductions are issued when buying or selling property. Certain codes have been approved for them:
- 311 - the amount spent by the taxpayer on new construction or purchase of an object on the territory of the Russian Federation (apartments; houses; rooms; shares/shares in them; land plots or shares/shares in them provided for individual housing construction; land plots or shares/shares in them , on which the residential buildings being purchased or a share/shares in them are located).
- 312 - the amount aimed at repaying interest on targeted loans/credits, which was actually spent on the purchase of an object or new construction, as well as to repay interest on loans that were issued for the purpose of refinancing/on-lending for new construction or the purchase of an object on the territory of the Russian Federation.
To receive such deductions, you must provide documents confirming your right to receive a deduction.
Social deduction codes
Since 2020, in a manner similar to the provision of property deductions (with a permit issued by the Federal Tax Service after checking documents confirming the right to deduction), it is possible to receive social deductions at the place of work. Their codes have not changed:
- code 320 - deduction for expenses for own education or full-time education of a sister (brother) under the age of 24;
- code 321 - deduction for expenses for full-time education of children (including foster children or wards) under the age of 24 years;
- code 324 - deduction for medical expenses for yourself, your spouse, parents or children (including adopted or warded children) under the age of 18;
- code 325 - deduction for contributions paid for voluntary health insurance for oneself, spouse, parents or children (including adopted or warded) under the age of 18;
- code 326 - deduction for expenses for expensive treatment;
- code 327 - deduction for expenses on paying contributions to non-state pension funds or under long-term voluntary life insurance contracts for yourself, your family members, close relatives;
- code 328 - deduction for additionally paid by the taxpayer savings contributions to the Pension Fund.
Codes of social tax deductions for personal income tax
They are provided for the costs of training, treatment and other costs provided for in the legislation of the Russian Federation.
Social deduction codes:
- 320 - the amount that was paid in the tax period for your own education or the education of a brother/sister under the age of 24 who is studying full-time.
- 321 - the amount paid by a parent for the education of his children under the age of 24, by a guardian for the education of his wards under the age of 18 in full-time education or under the age of 24.
- 324 - the amount paid in the tax period for medical services provided to the taxpayer, his spouse, parents, children (including adopted children, wards) under the age of 18, as well as the cost of medications for medical use prescribed by the attending physician, and acquired at the expense of the taxpayer’s personal funds.
- 325 - the amount of insurance premiums that were paid in the tax period under contracts of voluntary personal insurance, insurance of their spouses, parents, children (including adopted children and wards) under the age of 18, which were concluded with insurance companies (organizations) licensed to conducting such activities.
- 326 - the amount of expenses for expensive treatment.
- 327 - the amount of pension contributions paid by the taxpayer during the tax period under a non-state pension agreement/agreements concluded with a non-state pension fund in his own favor or in favor of family members or close relatives; the amount of paid contributions under voluntary pension insurance contracts, as well as the amount of paid contributions under voluntary life insurance contracts, if they are concluded for a period of at least 5 years in one’s own favor or in favor of a spouse, parents, children (including adopted children, wards) ).
- 328 - the amount of additional insurance contributions paid by the taxpayer during the tax period for a funded pension.
To receive a deduction, you must provide contracts concluded with insurance organizations that have certain licenses in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation.
Deduction codes for non-taxable income
Deductions for non-taxable income have not changed. However, they also appear in the 2-NDFL certificate quite often, so it makes sense to recall their list:
- codes 501 and 502 - deductions for the value of gifts given at work and prizes received at competitions;
- codes 503 and 504 - deductions for payment of financial assistance to employees and reimbursement of the cost of medicines;
- code 505 - deduction for prizes received as a result of participation in promotional events;
- code 506 - deduction for financial assistance paid to a disabled person by a public organization of disabled people;
- code 507 - deduction for financial assistance or gift given to a WWII participant;
- code 508 - deduction for financial assistance at the birth (adoption) of a child.
- code 509 - deduction for income issued by products to an employee of an agricultural producer;
- code 510 - deduction for additional savings contributions to the Pension Fund of the Russian Federation paid by the employer for the taxpayer.
Investment deduction codes
The bulk of these deductions are associated with operations that have a fairly limited distribution. Their codes are used by professional participants in the securities market to compile 2-NDFL certificates. Most regular employers do not require these codes.
Among this group, only deduction code 601 for dividend income may be of interest to an ordinary employer. From January 2020, as noted above, a new investment deduction with code 619 was introduced.
As of January 1, 2018, taxpayer income codes indicated in the 2-NDFL certificate have also been updated. See details here .
Results
Deductions allow you to reduce the tax base for personal income tax. All deductions are encrypted with special codes, which are recorded in the 2-NDFL certificate. At the end of 2020, the list of codes was significantly expanded, and in December 2017, a new code 619 for investment deduction was added.
Many standard tax deduction codes help Russian citizens get back at least a small part of their investments. These discounts are addressed to families with disabled veterans, former Chernobyl NPP workers, minor children, etc. All this is being introduced to improve the social standard of living for citizens. There is also a direction for financial support for people who have various services to the state. These include codes 104 and 105.
Concept and structure of the tax system of the Russian Federation
The tax system is a group of various fees and duties that are levied on citizens of the Russian Federation for the purpose of financial support of the state. The level of taxation determines the sufficiency of the budget level that is available for credit. A citizen’s income is taxed at a rate of 13% and is available only to residents of the Russian Federation who have official earnings. There are three levels of the legislative framework of the National Assembly:
- local (legal acts are adopted by local authorities);
- regional (the adoption of laws by constituent entities of the Russian Federation in a specific region of the country);
- federal (bills and decrees that are adopted in accordance with the Constitution throughout the state).
Tax deductions code 104
In 2020, only 14 taxes can be noted throughout Russia: three local, three regional and eight federal.
Deduction 104 in personal income tax certificate 2
Personal code 104 provides for a payment of 500 rubles monthly for the entire duty period. This deduction is intended for citizens who have committed some important actions for the state. What is the designation 104 deduction code in personal income tax certificate 2? To whom can it be provided? The following are entitled to a deduction:
- WWII participants, heroes of the USSR;
- citizens who have received orders and awards of state significance;
- individuals who participated in eliminating the accident at the Chernobyl nuclear power plant;
- disabled people since childhood, as well as persons with 1st or 2nd group disability.
The purpose of personal income tax certificate 2 is to fully reflect all possible types of income of a working employee. The employer fills out such certificates and all documentation is submitted to the Federal Tax Service. All calculations are made only from the worker’s salary; the employer (tax agent) does not waste his money on paying personal income tax.
Note! If the total earnings of a citizen for the entire reporting period are higher than 280,000 rubles, the procedure for providing a deduction is canceled.
Sample of a completed certificate for personal income tax form 2
Tax deductions for personal income tax in 2019
Tax deduction - what is it?
In simple words, this can be expressed like this: if you overpaid tax, return it. Or document it so that it is not withheld from your income. Based on this, we conclude that tax deductions for individuals are divided into two types:
- when the tax base decreases and as a result the tax amount becomes lower;
- when the tax has already been withheld and transferred to the budget, and then it is returned to the taxpayer.
All personal income tax deductions are of a declarative nature. This means that not a single tax agent (employer), not a single tax inspector will reduce the tax base and return the tax without a personal statement from an individual.
What income can be reduced with tax deductions? Only official ones and only those that are taxed at a rate of 13%.
EXAMPLE 1. Ivanova I.P. two minor children. According to the law, she has the right to a tax deduction in the amount of 2800 rubles monthly, that is, her tax must be reduced every month by 364 rubles (2800 * 0.13). For a year this is a pretty decent amount (364*12=4368).
But if Ivanova does not declare her right to a deduction and does not present documents (copies of children’s birth certificates), then the employer is not only not obligated, but does not even have the right to provide such deductions.
This is due to the fact that in Russia, part-time work is allowed for many specialties. A person may work for several employers. And the law allows you to receive deductions for personal income tax only at one place of work (at the employee’s choice).
It should be emphasized that tax benefits apply only to those citizens whose activities meet the following conditions:
- they are tax residents;
- receive official income on the territory of the Russian Federation;
- their income is taxed at 13 percent.
Types of tax deductions in 2020
Tax benefits for individuals are regulated by the Tax Code of the Russian Federation and are divided into three large groups:
- Standard (Article 218 Tax Code).
- Social (Article 219 of the Tax Code).
- Property (Article 220 Tax Code).
Reasons for receiving a standard tax deduction
Standard deductions, in turn, can be divided into subgroups:
- those that are provided personally to the employee;
- deductions for the employee’s children.
Tax benefits are given to those workers who are liquidators of the consequences of the Chernobyl disaster and other work related to radioactive contamination, as well as disabled military personnel. For this category of citizens, the deduction is 3,000 rubles monthly.
Heroes of the Soviet Union, Heroes of Russia and some other military personnel (this is described in detail in the law) receive a monthly benefit in the amount of 500 rubles.
Deductions for minor children are provided to all parents and adoptive parents in the following amounts.
Table 1. Standard Child Tax Credits
| № | Categories of taxpayers | Deduction for the first child, rubles (up to 18 years old or up to 24 years old if studying full-time) | Deduction for the second child, rubles (up to 18 years old or up to 24 years old if studying full-time) | Deduction for the third and subsequent children, rubles (up to 18 years old or up to 24 years old if studying full-time) | Deduction for a disabled child under 18 years old, rubles | Deduction for a disabled child of groups 1 and 2, full-time student under 24 years old, rubles |
| 1 | Parents, adoptive parents | 1 400 | 1 400 | 3 000 | 12 000 | 12 000 |
| 2 | Guardians, trustees, foster parents | 1 400 | 1 400 | 3 000 | 6 000 | 6 000 |
| 3 | Sole parent (adoptive parent) | 2 800 | 2 800 | 6 000 | 24 000 | 24 000 |
| 4 | Sole guardian, trustee, foster parent | 2 800 | 2 800 | 6 000 | 12 000 | 12 000 |
EXAMPLE 2. There are four children in the family of Marina and Sergei Seleznev:
- Andrey, 23 years old, graduated from university, works.
- Artyom, 21 years old, college student.
- Yuri, 19 years old, works after college.
- Alina, 10 years old, schoolgirl.
According to the provisions of Article 218 of the Tax Code, parents can claim the following tax deductions for personal income tax in 2020:
- for Artem (second child, student, under 24 years old) - 1,400 rubles;
- for Alina (fourth child, under 18 years old) - 3,000 rubles.
Andrei and Yuri are already adults, they have completed their studies, and they are not entitled to deductions.
https://youtu.be/4GKIU54qPRU
To receive standard tax deductions from an employer, you must submit the following documents:
- personal statement requesting a deduction;
- child's birth certificate;
- documents for establishing guardianship or trusteeship;
- decision on adoptive family;
- a certificate from an educational institution if the child is already 18 years old;
- medical documents for a disabled child.
Standard tax deductions are provided until the month in which the total amount of income, starting from January 1 of the current year, does not exceed 350,000 rubles.
In the event of a change of place of work during a calendar year, the employee is obliged upon dismissal to receive a salary certificate of Form 2-NDFL and submit it to the new place of work. When providing standard tax deductions, accounting always considers accrued wages from the beginning of the year, even if the employee changed employers more than once during the year.
EXAMPLE 3. Lidiya Petrovna Lyubimova is a single mother and has a minor child. From January to March she worked in organization No. 1 and earned a total of 57,000 rubles. On April 1, Lidia Petrovna began working in organization No. 2.
I left there in October, having earned 175,000 rubles. Lyubimova began working in organization No. 3 on November 1 and applied for a standard child deduction.
Based on salary certificates from the first two places of work, the accounting department provided her with the following tax benefits, since the income limit was not exceeded: 57,000 + 175,000 = 232,000 rubles.
Social deductions for personal income tax in 2019
This group of deductions can also be divided into subgroups:
- education;
- treatment;
- contributions to a non-state pension fund;
- transfer of additional contributions to the funded part of the pension provision;
- transfer of donations;
- payment for an independent assessment of your qualifications.
Social tax deductions are regulated by Article 219 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation and are also provided upon submission of an application and relevant supporting documents. But there is also a difference from standard deductions: to receive any of the listed social deductions, you must fill out and submit a tax return form 3-NDFL.
As practice shows, social deductions for education and medical services are most in demand among the population.
Table 2. Social tax deductions for individuals in 2020
| Who is entitled to deduction | For education | Simple medical care | Medical care is expensive |
| Personally taxpayer | No more than 120,000 rubles per year | No more than 120,000 rubles per year | In full amount of treatment costs |
| Children of the taxpayer (up to 24 years old) | No more than 50,000 rubles per year for each child | No more than 120,000 rubles per year – up to 18 years of age | In the full amount of treatment costs – up to 18 years |
| Brothers and sisters of the taxpayer under 24 years of age | No more than 50,000 rubles per year for each child | No more than 120,000 rubles per year – up to 18 years of age | In the full amount of treatment costs – up to 18 years |
| Guardians of a taxpayer under 24 years of age | No more than 50,000 rubles per year for each child | No more than 120,000 rubles per year – up to 18 years of age | In the full amount of treatment costs – up to 18 years |
| Taxpayer's spouse | X | No more than 120,000 rubles per year | In full amount of treatment costs |
| Taxpayer's parents | X | No more than 120,000 rubles per year | In full amount of treatment costs |
Guardianship and trusteeship by law ends with the onset of majority, when the child turns 18 years old. But if the guardian continues to pay for the education of his former ward, then the law allows him to take advantage of the deduction until the student reaches 24 years of age.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=aePEQXr-dSc
To receive deductions for treatment and training, the following conditions must be met:
- State license of an educational and medical institution.
- The costs of treatment and training are made from the taxpayer’s personal or credit funds, without the involvement of government programs, employer resources or charitable foundations.
The deduction for a child’s education is limited to 50,000 rubles per year. And the costs of personal training and simple treatment of yourself and your family are deductible in a total amount of no more than 120,000 rubles per year.
The peculiarity of these types of social deductions is that tax deductions for personal income tax reduce the tax base only for the year in which the expenses were incurred. That is, you can return tax for 2020 only for the amount that was paid for treatment or education in 2018. The amounts of these deductions are not carried over to the next year.
Social deductions also take an application form: to receive them, you need to prepare a tax return, attach a personal statement and all supporting documents to it.
Property tax deductions in 2020
Another type of tax benefit that is popular among the population is property deductions. They are provided to both property buyers and sellers.
Tax deductions for the sale of property are provided to owners in the following order.
Table 3. Amount of tax deduction in 2020 when selling property
| Type and period of ownership of property | Amount of tax deduction for the sale of housing and land, rubles | Amount of tax deduction for the sale of other real estate, rubles | Amount of tax deduction for the sale of other property, rubles |
| Purchased or built less than 5 years ago | 1 000 000 | 250 000 | X |
| Inherited less than 3 years ago | 1 000 000 | 250 000 | X |
| Received as a gift from a close relative less than 3 years ago | 1 000 000 | 250 000 | X |
| Privatized less than 3 years ago | 1 000 000 | 250 000 | X |
| Received as an annuity less than 3 years ago | 1 000 000 | 250 000 | X |
| Owned for less than 3 years | X | X | 250 000 |
In the case of the sale of property, the tax base is reduced by a certain amount (1 million or 250 thousand rubles). That is, in this case there will be no tax refund, but a reduction, that is, a tax deduction is a reduction in the tax base.
Typically, such a tax deduction is used in a situation where the seller cannot prove the expenses received or they are less than the deduction of 1 million or 250 thousand rubles.
EXAMPLE 4. Pertsev V.V. I bought a car last year for 560,000 rubles. Due to current circumstances, I was forced to sell it this year for 420,000 rubles. Unfortunately, the financial documents on the purchase of the car were lost and cannot be restored. In this case, the tax base (sale amount) can be reduced by a deduction of 250 thousand rubles.
By April 30, 2020, Pertsev is required to complete and submit a tax return form 3-NDFL and, by July 15 of the same year, to pay tax on income received in the amount of 22,100 rubles:
- 420,000 – 250,000 = 170,000 rubles (base for tax calculation);
- 170,000 * 0.13 = 22,100 rubles (amount of tax payable).
EXAMPLE 5. Simonov S.S. In 2020, I inherited an apartment with a cadastral value of 5,600,000 rubles. In 2018, he sold it for 3,500,000 rubles. Since Simonov did not bear the costs of purchasing the apartment, he cannot reduce the sale amount by these costs. But you can take advantage of at least a deduction of 1 million rubles.
The tax calculation is as follows:
- cadastral value for calculating tax: 5,600,000 * 0.7 = 3,920,000 (tax is calculated from this amount, although the apartment was sold cheaper, by law at least 70% of the cadastral value is taken into account);
- 3 920 000 – 1 000 000 = 2 920 000;
- 2,920,000 * 0.13 = 379,600 rubles - Simonov must contribute this amount of tax to the budget.
Owners can sell their homes at any price. But if their period of ownership is less than that required by law, then the tax is calculated as follows:
- at the sale price, if it is higher than 70% of the cadastral valuation;
- by the amount of cadastral value multiplied by a factor of 0.7.
When selling property, the period of ownership of which does not exceed the period established by law, the taxpayer is required to submit a declaration, even if the tax amount turns out to be zero upon calculation. Otherwise, he will face penalties.
Tax deductions for personal income tax, the procedure for their provision when purchasing a home
Another very significant type of property deduction is a tax refund to reduce costs when purchasing a home.
What is the tax deduction for? The right to receive it is given once in a lifetime for an amount of no more than 2 million rubles.
Moreover, unlike other types of income tax deduction in 2019, its balances can be transferred to subsequent years and to other residential properties.
If housing is purchased on credit, then the amount of tax deduction in 2019 for interest paid to the bank can also be returned, but not more than 3 million rubles. This deduction can be carried over to other years, but it is given only for one object.
Let's summarize: what are tax deductions for in 2020? A deduction can be obtained for taxpayer expenses aimed at improving the social and housing conditions of people:
- for treatment;
- education;
- when purchasing and constructing housing;
- for minor children.
And when selling property (real estate or transport), the state provides a tax deduction so that the seller pays less tax on the income received.
Source: https://nalogu-net.ru/nalogovye-vychety-po-nalogu-na-doxody-fizicheskix-lic-v-2019-godu/
What other codes are there in Form 2 Personal Income Tax?
On January 1 of this year, the Federal Tax Service came into force with some changes in the deduction codes for the 2nd personal income tax certificate. Previously, the article described in detail what the 104 and 105 tax deductions are. But these are not the only ciphers that can be entered into the provided form. Starting with number 104 and ending with number 210, this is the number of tax deduction codes that can be entered into a document. In short, almost all deductions are aimed at the first, second and third child under 18, students, disabled children, deductions for guardians, and single parents. Also, starting from the 202nd number and up to the 210th, we are talking about expenses for transactions with securities that are in circulation on the securities market, etc. The amounts that are returned under these codes start from 500 and up to 3000 rubles. In some of the listed cases there are even double payments. More information about the designations of all codes in personal income tax certificate 2 can be found in Article 218 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Thus, in accordance with the provisions of this article, we can conclude that the state cares about its citizens, especially those who showed love for their native country through selfless work and deeds.
Articles on the topic
Deduction codes are indicated in the 2-NDFL certificate. Each deduction has its own code. For which deductions of deductions codes 104 and 105 are used, read the article.
What are deduction codes?
The legislation of the Russian Federation considers the circumstances due to which the tax base of a particular person can be changed due to deduction codes. Since circumstances can be very different, there are many codes. All of them are divided into six main categories:
- Standard – circumstances such as whether the taxpayer has children or special services to the state are considered.
- Social – the circumstances of the need for training, treatment, etc. are considered. We can talk about the taxpayer or relatives who are financially dependent on him.
- Property – the presence of a mortgage or housing construction are considered.
- For non-taxable income - this includes prizes, gifts, certain types of financial assistance, etc.
- Professional - these are royalties, expenses for creating a literary work, etc.
- Investment is the rarest category, relating mostly to those who work in the securities market.
The state returns deductions to the population only in cases where the conditions are met and documentary justification for the return of part of the personal income tax is provided.
In order to obtain the right to a deduction, the taxpayer must not only have a reason, but also a documented justification for it.
Deduction code in certificate 2-NDFL
Every year, companies submit a 2-NDFL tax certificate. This is necessary to report on employee income and personal income tax amounts.
There are amounts that reduce the tax base for personal income tax - tax deductions. They are also shown in 2-NDFL, for which special codes are used
When drawing up a certificate in form 2-NDFL, use the Procedure, which was approved by order of the Federal Tax Service dated October 30, 2015 No. ММВ-7-11/485. Fill out the certificate information based on information from the personal income tax registers.
Deduction codes are indicated in the table of section 3 of form 2-NDFL. Each deduction has its own code
You can fill out deduction codes for free in 2-NDFL for free in the Bukhsoft program.
What do you need to get a deduction?
Tax deduction with code 104, like all others, is received on the basis of the documents provided.
So, if an employee has a disability of the first or second group, then he needs to go to the accounting department and bring the following documents:
- a copy of the disability certificate, photographed on both sides;
- personal statement with date of submission and signature.
The certificate also indicates by what date the person was assigned disability, or whether it is permanent. In the first case, the employee must bring a certificate every year after passing the ITU.
Participants in combat operations must also bring a copy of their ID and a personal statement, which indicates the reason for receiving the deduction, the date the documents were provided and affixed a signature. A copy of the certificate should only be updated at the request of the accounting department.
The deduction under code 104 is provided either to participants in combat operations or to disabled people of the first and second groups. Of course, in order to take advantage of the right to receive such a benefit, you must submit all documents. Also, each employee can independently calculate the amount of tax to check the employer. The amount of this deduction is 500 rubles, that is, a citizen receives 65 rubles more every month.
>Deduction 114 and 115
Standard tax deduction code 104 and 105
Standard deductions are fixed. The amount depends on the category of the individual to whom the deduction applies. To reflect deductions in 2-NDFL, codes 104 and 105 are used.
Table. Codes and amounts of standard personal income tax deductions for 2-NDFL certificates
Tax deduction code
Deduction amount
Categories of taxpayers covered by the deduction
Base
Standard tax deductions1
for every month
Heroes of the Soviet Union, Heroes of Russia, persons awarded the Order of Glory of three degrees
para. 2 subp. 2 p. 1 art. 218 Tax Code of the Russian Federation
Persons of the civilian staff of the SA and Navy of the USSR, Internal Affairs Directorate and State Security of the USSR, who held regular positions in the institutions of the active army during the Second World War
para. 3 subp. 2 p. 1 art. 218 Tax Code of the Russian Federation
Persons who were in cities during the Second World War, participation in the defense of which is counted towards their length of service for the purpose of receiving a preferential pension
para. 3 subp. 2 p. 1 art. 218 Tax Code of the Russian Federation
Participants of the Second World War, military operations to defend the USSR, who served in institutions that were part of the army, and former partisans
para. 4 subp. 2 p. 1 art. 218 Tax Code of the Russian Federation
Persons who were in Leningrad during its siege from 09/08/1941 to 01/27/1944, regardless of the length of stay
para. 5 subp. 2 p. 1 art. 218 Tax Code of the Russian Federation
Former prisoners of concentration camps and ghettos created by Nazi Germany and its allies during the Second World War
para. 6 subp. 2 p. 1 art. 218 Tax Code of the Russian Federation
Disabled people since childhood, as well as disabled people of groups I and II
para. 7 subp. 2 p. 1 art. 218 Tax Code of the Russian Federation
Persons who have received diseases associated with radiation exposure caused by the consequences of radiation accidents, exercises, tests
para. 8 subp. 2 p. 1 art. 218 Tax Code of the Russian Federation
Medical personnel who received excess doses of radiation exposure while providing medical care from April 26, 1986 to June 30, 1986
para. 9 subp. 2 p. 1 art. 218 Tax Code of the Russian Federation
Persons who donated bone marrow to save lives
para. 10 subp. 2 p. 1 art. 218 Tax Code of the Russian Federation
Persons who received occupational diseases associated with radiation exposure while working in the Chernobyl exclusion zone
para. 11 subp. 2 p. 1 art. 218 Tax Code of the Russian Federation
Persons evacuated, as well as those who voluntarily left settlements exposed to radioactive contamination as a result of the accident in 1957 at the Mayak Production Association and contamination of the Techa River
para. 13 subp. 2 p. 1 art. 218 Tax Code of the Russian Federation
Persons who took part in the liquidation of the consequences of the accident at the Mayak Production Association (1957–1958) and the pollution of the Techa River in 1949–1956
para. 12 subp. 2 p. 1 art. 218 Tax Code of the Russian Federation
Persons evacuated (voluntarily left) from the Chernobyl exclusion zone
para. 14 sub. 2 p. 1 art. 218 Tax Code of the Russian Federation
Parents and spouses of military personnel who died as a result of injuries received while defending the USSR, Russia, or while performing other military duties
para. 15 subp. 2 p. 1 art. 218 Tax Code of the Russian Federation
Parents and spouses of government employees killed in the line of duty
para. 15 subp. 2 p. 1 art. 218 Tax Code of the Russian Federation
Persons discharged from military service (called up for military training) who performed military duty in countries where hostilities took place
para. 16 subp. 2 p. 1 art. 218 Tax Code of the Russian Federation
Citizens who took part, in accordance with decisions of government bodies of the Russian Federation, in hostilities on the territory of the Russian Federation
para. 16 subp. 2 p. 1 art. 218 Tax Code of the Russian Federation
for every month
Persons who have become disabled and have acquired diseases: – associated with the radiation effects of the Chernobyl disaster; – related to the work to eliminate the Chernobyl accident; – due to the accident at the Mayak PA in 1957 and the discharge of radioactive waste into the Techa River; – related to participation in the work to eliminate the accident at PA Mayak; – related to living in areas contaminated as a result of the Mayak accident
para. 2, 3 and 8 sub. 1 clause 1 art. 218 Tax Code of the Russian Federation
Persons who took part in the liquidation of the Chernobyl accident in 1986–1987
para. 4 and 5 sub. 1 clause 1 art. 218 Tax Code of the Russian Federation
Military personnel who served in the Chernobyl Nuclear Power Plant exclusion zone in 1986–1987
para. 6 subp. 1 clause 1 art. 218 Tax Code of the Russian Federation
Military personnel who took part in the work on the Shelter object in 1988–1990
para. 7 subp. 1 clause 1 art. 218 Tax Code of the Russian Federation
Persons directly involved in the assembly of nuclear weapons (until December 31, 1961), nuclear tests, and work on the disposal of radioactive substances
para. 9–13 subp. 1 clause 1 art. 218 Tax Code of the Russian Federation
para. 14 sub. 1 clause 1 art. 218 Tax Code of the Russian Federation
Disabled persons: a) from among military personnel who became disabled in groups I, II and III due to injury received: – during the defense of the USSR, Russia; – due to an illness associated with being at the front; – when performing other military service duties; b) from among former partisans, as well as other categories of disabled people equal in pension provision to the specified categories of military personnel
Deductions
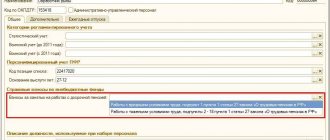
Let's move on to the section "Deductions."At the top there are icons for dividing the section into standard deductions (sheet with a check mark and a pencil), social tax deductions (sheet with a check mark) and property tax deduction (house). Starting with the “Declaration 2011”, the section “Losses of previous tax periods on transactions with the Central Bank” was added. Icon
Let’s look at the “Standard Deductions” section . The screen for entering standard and social deductions corresponds to sheet “K1” of the declaration form for 2008, 2009. In the declaration of 2010, 2011, 2012, 2013 these are sheets “G1”, “G2”, “G3”.
Since earlier, in the section “Income received in the Russian Federation,” we indicated that standard tax deductions are provided by the employer, this section in this case will be filled in by the program automatically.
Otherwise, proceed as follows.
First, let's look at the designation of the codes you see.
Code 103 - means that the employer provided you with a standard tax deduction in the amount of 400 rubles for each month until your cumulative income exceeded 40,000 rubles (applies to all categories of citizens) - for “Declaration 2008”, “Declaration 2009”, “ Declarations 2010”, “Declarations 2011”.
Code 104 - this deduction applies to a certain category of citizens: heroes of the USSR and the Russian Federation, WWII veterans, disabled people since childhood, disabled people of groups 1 and 2, certain persons who took part in the liquidation of accidents at the Chernobyl nuclear power plant and others (for a detailed list, see subparagraph 2 p. .1 Article 218 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation), provided in the amount of 500 rubles for each month.
Code 105 - this deduction also applies to a certain category of citizens, namely: persons affected by the Chernobyl Nuclear Power Plant and the Mayak Production Association, persons associated with nuclear work, disabled veterans, disabled military personnel (for a detailed list, see subparagraph 1, paragraph. 1, Article 218 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation), is provided in the amount of 3,000 rubles.
? – denotes a combination of standard deductions by month. Let’s say in January it’s code 103, and then 104, etc.
In order not to make a mistake when choosing a code, you can refer to the individual’s income certificate (2-NDFL). Look at section 4 of the help and if there is a certain code there (103, 104, 105), put a dot in the program opposite the similar code.
The next subsection concerns the deduction for children.
Select the type of deduction and indicate the number of children. At the same time, registration of children of disabled people of groups I and II is carried out separately, because They provide an excellent deduction amount. If you have two or more children, be sure to indicate this information in the column “ The number of children has not changed and is” , since from 01/01/2011 the amount of deduction for the first and subsequent children is different.
In the declaration for 2011, a column was added for large families: “ The number of children, starting from 3, did not change and amounted to.” If you have three or more children, indicate the number of children in this column. For example, if you have three children, then put the number “1” in this column. And you indicate the previous two children in the column The number of children did not change and amounted to ".
By default, the item “ The number of children did not change and amounted to ” is checked. And if in this case you indicate the number of children in the corresponding column (see the figure below), then the columns by month will be filled in automatically. Otherwise, you need to uncheck the “ Number of children did not change and amounted to ” checkbox and enter the number of children per month.
The item “ The number of children with disabilities of groups I and II has not changed ”
The next subsection is “Monthly income/expenses for entrepreneurs and individuals with private practice.”
In order for standard deductions to be calculated based on income from business activities or private practice, you need to enter the amounts of income and expenses for each month, and check off the months in which you were in the appropriate status (entrepreneur, lawyer, etc.). ).
Go to the section “ Social tax deductions” , to do this, click the “Sheet with a checkmark” button.
The screen for entering social deductions corresponds to sheets “K2”, “K3” and “K4” of the declaration form for 2008, 2009. For the declaration for 2010, 2011, 2012, 2013, these are sheets “G2”, “G3”.
Check the box “Provide social tax deductions” and fill out the fields below. We take data from documents confirming these expenses.
To fill out the “Treatment” in the certificate of payment for medical services for submission to the tax authorities, select service code 1. Clause 2.2 of sheet K2 of the declaration for 2008, 2009 will be filled in accordingly (clause 2.2 of sheet G2 of the declaration for 2010, 2011, 2012, 2013 of the year).
To fill out the column “Expensive treatment” in the certificate of payment for medical services for submission to the tax authorities, select service code 2. Accordingly, clause 1.3 of sheet K2 of the declaration for 2008, 2009 will be filled in (clause 1.3 of sheet G2 of the declaration for 2010, 2011, 2012 ,2013).
Starting with the “Declaration 2009” program, a column was added to the “ Amounts spent on ” subsection - additional insurance pension contributions. It records expenses contributed to the funded part of the labor pension.
To fill out the column “ Amounts paid for children’s education, ” click “Plus.” The “Tuition Amount” window pops up, enter the amount and click “Yes”.
If you are paying for the education of several children, then the tuition amounts must be entered for each child (by clicking “Plus” to add a new line).
To fill out the subsection “ Voluntary pension insurance and non-state pension provision agreements ”, click “Plus”, the “Agreement Data” menu pops up, fill in all the fields, indicate the type of agreement, click “Yes”.