Tax calculation example
Consider an example of how to calculate the tax rate in various cases.
Example 1:
Locksmith Ivanov earned his salary this month in the amount of 14,500 rubles. Plus, he was given a fixed bonus of 3,500 rubles. His total income for this month was 18,000 rubles.
It is necessary to calculate how much income he will pay from his salary to the state, and how much he will receive in his hands.
(18000 – 400) * 13% = 2288 rubles
400 rubles is the standard deduction that mechanic Ivanov is entitled to.
The received amount of 2288 rubles is the amount of personal income tax, which will be deducted from the money earned.
18000 – 2288 = 15712 rubles.
Ivanov will receive 15712 for the entire month worked.
Larger deductions may be made from the amount of calculated income if the person is included in special categories or is entitled to additional deductions. Like, for example, when buying an apartment.
If you use an online calculator to make personal income tax calculations, all the described actions are performed in one click.
How to deduct income tax from salary calculator
Wanting to control their income, many workers do not know how to correctly calculate their salaries on their own. Let's take a comprehensive look at this topic. To calculate your salary based on your salary, you can use the online calculator below.
To make payroll calculations, you will need individual data.
For the calculation, two categories of figures are needed: For the calculation, the following data will be required: The amount of the monthly salary or the rate. Salaries are calculated using two methods: time-based and piece-rate.
Time-based earnings depend on the amount of time spent at work and are not related to the volume of work performed.
In this case, it does not matter how much a person did in a day, the main thing is that he is at work.
His presence or absence is noted on the work sheet, according to which payment is made.
Personal income tax rate options
The calculator provides the option to select the desired personal income tax rate - 9, 13, 15, 30 or 35%.
The specifics of applying this or that rate will be discussed below. As for direct calculations, you only need to select the rate you need and enter in the calculator field the amount from which you want to calculate the income tax.
The convenience of the calculator is that the amount does not need to be rounded to the nearest whole number. You can enter the amount in rubles and kopecks in the field, separating them with a comma.
Depending on what kind of calculation you need, you can click on the “Select personal income tax” or “Calculate personal income tax” button options. Accordingly, the calculator will give you the result in the form of personal income tax from the amount or the amount with personal income tax added to it.
Standard rate
The standard rate is 13%. It is used to calculate income tax in relation to citizens - residents of the Russian Federation, for whom, in accordance with Art. 224 of the Tax Code does not provide for a different rate.
Taxation at a rate of 13% applies to:
- wages;
- gbonus and vacation payments;
- dividends received.
For non-residents of the Russian Federation, a 13 percent rate applies in the following cases:
- receipt of income by a non-resident in the Russian Federation;
- official employment of a non-resident in the Russian Federation by invitation for highly qualified personnel;
- employment of a non-resident on the territory of the Russian Federation within the framework of the program for the resettlement of compatriots, for the entire duration of their stay as non-residents;
- employment in the Russian Federation of persons who have refugee status or under conditions of temporary stay in the Russian Federation;
- employment of non-residents on ships whose port of registration is the ports of the Russian Federation.
Rate of 30%
A 30 percent rate is applied to tax income received from securities, with the exception of dividends on Russian-issued shares, which are taxed at a 13 percent rate.
A rate of 30 percent applies to:
- accrual of taxes on income from securities for non-residents of the Russian Federation;
- accrual of taxes to any of the taxpayers who have not provided the Federal Tax Service with data allowing taxation at a different rate in accordance with the requirements of Art. 214 NK.
There are no deductions at this tax rate.
Rate of 35%
Calculation of personal income tax based on a rate of 35% is applied in accordance with Art. 224 Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Payers are individuals, both residents and foreigners, who receive income in the Russian Federation. At the same time, tax residents are taxed at a rate of 30% in cases of receiving income from sources located both in Russia and abroad. Foreign citizens become taxpayers at a 30 percent rate only on income received from Russian sources.
A 30 percent tax applies on income originating from:
- winnings and prize money from promotions worth more than 4 thousand rubles;
- income from bank investments that exceed the key rate of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation by 5 points for domestic currency and over 9% for deposits in the currencies of other countries;
- income received as a result of savings on loan funds.
Deductions for such types of income are not applied.
Rate 15%
It is applied as a tax rate for non-residents of the Russian Federation who receive income as a result of owning shares in the capital of companies and organizations of the Russian Federation.
The tax base includes all types of income, namely:
- cash receipts;
- natural product;
- material benefit.
If there are different types of income, personal income tax is calculated separately for each of the above types.
Rate 9%
Article 224 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation determines a 9 percent rate for calculating tax on:
- income received as interest on bonds with an issue date no later than January 1, 2007;
- income of the founders under trust management agreements by virtue of certificates issued no later than January 1, 2007.
Deduction of personal income tax from wages, types of tariffs
The online payment system has the following tariffs for calculations:
- The Labor Code assumes 13% of the salary received by a citizen at his official place of work. This percentage also goes towards remuneration and bonuses at the place of work.
- 13% also applies to dividends from citizens of the country; for foreigners, a 15% calculation threshold is provided.
- Foreign citizens, to calculate personal income tax, take into account the 30% rate. This percentage is provided for by federal legislation and is the same for all foreign citizens who receive income of any kind throughout Russia.
- Winnings and interest on deposits are subject to a 35% rate.
A penalty for non-payment is assessed by tax agents after receiving payments, a fine for unpaid tax is imposed in case of violation of compliance with legal and regulatory acts.
To know how to deduct personal income tax from your salary, use an online calculator; for citizens of the country there is a single tax rate of 13%.
Calculating tax on labor or dividends received is simple with an available Internet resource in the form of a calculating machine. The state withholds interest on the income received, while the type of material income is fixed by a number that is important to know when making deductions.
Interest rates in 2020 table
| Purpose of payment | What percentage of accrued wages |
| Pension benefits within the maximum salary amount established by law | 22% |
| Pension benefits over the maximum amount | 10% |
| VNIM (disability and maternity) for accruals within the maximum limit | 2,9% |
| FSS in relation to foreigners and stateless persons within the limits established by law | 1, 8% |
| VNIM above the maximum limit | 0% |
| Medical from the entire accrued salary amount | 5,1% |
Its size depends on the professional risk class assigned to the organization: from 0.2% to 8.5%.
How much does an accountant deduct from his salary? In Russia in 2018, there are interest rates at which taxes paid are calculated. The employee himself is spared the calculations.
In 2020, the employer is obliged to transfer the amount of taxes from the salary of each employee as a percentage of the accrued salary:
- Personal income tax – 13% for residents, 30% for non-residents;
- Pension Fund – 22%;
- FFOMS – 5.1%
- Social Insurance Fund – 2.9%;
- injury insurance - how much interest will be charged depends on the type of main activity. The minimum rate is 0.2%.
Taxes paid are taken into account in organizations using special accounting entries. Usually, when hiring a new employee, he is told about the amount of salary that he will receive after all mandatory deductions.
Online Salary Calculator 2020 Including Child Deduction
- participated in competitions and games held for advertising purposes and won prizes in an amount exceeding 4,000 rubles;
- received interest (coupon) on ruble bonds of Russian organizations issued after 01/01/2017, which exceeded payments over interest calculated based on the nominal value of the bond and the refinancing rate of the Bank of Russia, increased by 5% (starting from 01/01/2018);
- saved on interest on ruble loans (credits), but exceeded the amount of interest calculated based on 2/3 of the refinancing rate of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation on the date of actual receipt of income.
- received interest on ruble deposits placed in banks in the Russian Federation if they exceeded the amount of interest calculated based on the Bank of Russia refinancing rate increased by 5%;
- received interest on deposits in banks in Russia in foreign currency, if the amount of interest exceeds 9% per annum;
Apartment sales tax
Calculates the amount of tax that must be paid when selling an apartment
The owner who sells the apartment pays tax on the income from its sale. The following calculator will help you determine the exact amount of income tax when selling your apartment:
Taxes when selling an apartment
The amount (in rubles) for which you are selling the apartment (documented)
How long has the apartment been owned?
The year in which the property was purchased.
Documented expenses for the purchase or renovation of the apartment being sold
What part of the apartment is your property (in percentage).
Cadastral value as of January 1 of the year in which the apartment is sold.
A method of obtaining ownership of a real estate property.
A tax resident is a person who has resided in the Russian Federation for 183 days or more.
The tax is calculated from the so-called tax base. According to the tax code, the tax base is the amount of income reduced by the amount of tax deductions due to the taxpayer. When selling an apartment, a taxpayer is entitled to a tax deduction in the amount of 1 million rubles if the apartment is owned for less than the minimum permissible period of ownership. The minimum tenure is 5 years, or 3 years if the apartment was purchased before 2020. In addition, a period of 3 years is established for apartments donated or inherited from close relatives, apartments acquired as a result of privatization or an apartment acquired by the rent payer as a result of the transfer of property under a lifelong maintenance agreement with dependents. If the apartment has been owned for more than 5 years (or more than 3 if it was purchased before 2016), then you do not have to pay taxes upon sale. Otherwise, you will have to pay 13 percent of the tax base, that is, 13 percent of the sale amount minus 1 million rubles. For non-residents the interest rate is higher - 30%. If the sale price is lower than 70% of the cadastral value of the apartment, then the tax will have to be paid on 70% of the cadastral value. Instead of using the right to receive a property tax deduction, the taxpayer has the right to reduce the amount of his taxable income by the amount of expenses actually incurred and documented by him in connection with the receipt of this income. Accordingly, if you can document the costs of purchasing or renovating an apartment for sale in an amount exceeding 1 million rubles, then it is more profitable to use this method of calculating the tax base. The old tax calculator can be found here Taxes on the sale of an apartment until 2020.
Advice on obtaining tax deductions and filling out a personal income tax return can be obtained here.
Types of taxable income
An able-bodied citizen of the Russian Federation has official earnings, income, and monthly payments are subject to a single tax.
Individual indicators can influence the amount of money received; any income of citizens is taken into account:
- monthly salary, bonuses;
- income after the sale of a house or apartment that has been used for less than 3 years;
- money from renting out the property;
- monetary rewards, income brought by business from abroad;
- gift and winning certificates.
Money that is transferred by inheritance, real estate, by will or deeds of gift is not subject to taxation. Nuances and aspects of taxation are prescribed in federal legislation.
The income of citizens must be recorded in a single tax report and declarations. After receiving property, money, bonuses or winnings, the citizen undertakes to enter information into the taxation document to avoid fines.
Each case of calculation is individual, the system is applied with clarifications and additions for a specific case.
How and who calculates personal income tax
In most cases, it is up to the employing organizations to calculate the amount of personal income tax that must be withheld from payments in favor of the taxpayer and transferred to the local budget. After all, they are the ones who act as tax agents for personal income tax in relation to all persons to whom payments are made. But taxpayers themselves must sometimes also be able to calculate how much they owe the state if they received income on their own: they sold an apartment or a car, or received money for services from other individuals. Someone plans to receive a tax deduction for the past year. Then citizen payers will have to fill out and submit a 3-NDFL declaration with the correctly indicated amounts of income received and calculated tax. Organizations, in turn, must submit 2-NDFL certificates for employees. An online personal income tax calculator can help them with this; However, this program will not cope with deductions for children; you will have to calculate them yourself.
Algorithm for working with the application
Initial indicators are the basis for future calculations; an online calculator will help you calculate personal income tax from the amount of income received.
To deduct, you will need wages and income received during the tax period; after entering the data, the application will calculate the figure to the penny. The salary amount is a mandatory column that calculates for a specific employee, taxpayer.
The legislation establishes two options for calculating the amount of total tax for an employer or employee:
- Enter the salary amount before tax is deducted, the amount is calculated automatically. The final amount of wages after the tax is removed is also calculated.
- The amount after the tax has been withdrawn is entered, then the calculation is done in reverse, the application issues the amount to be calculated, it is important not to forget to indicate deductions, if any, to correct the automatically issued amount.
The program allows you to select any calculation option that the user needs.
For deduction and reliable results, personal information will be required:
- the amount of earnings received;
- interest rate, if there are individual characteristics;
- the amount of income is entered into a special window in the calculator;
- the taxpayer selects an interest rate and indicates it;
- The calculation button will allow you to see the result.
The calculation window differs in appearance, but has the same characteristics. To get the correct result, enter data in the required required fields. Legislation controls the final sum process.
Payroll calculation procedure
First of all, it is necessary to calculate the salary due to each employee, based on the chosen remuneration system. For the calculation, data from the working time sheet form T-12 or T-13 is used, from which data on the number of days (hours) worked in the billing month is taken.
Standard tax deductions for personal income tax are amounts determined by the Tax Code of the Russian Federation by which an employee’s salary can be reduced in order to withhold personal income tax. At their core, tax deductions are benefits that are provided to an employee under certain conditions. Their values are established by Articles 218-221 of the Tax Code.
Having calculated the salary for each employee based on the remuneration system established for his position, it is necessary to determine what deductions are due to each employee. After that, the amount of deductions due must be subtracted from the calculated salary, after which personal income tax must be withheld from the resulting amount.
It turns out that standard tax deductions are used only for the correct deduction of personal income tax; thanks to their use, taxable earnings are reduced, thereby reducing personal income tax.
When calculating wages, the following standard personal income tax deductions are used in 2020:
- 3000 rub. (Article 218 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation) - the deduction is due to certain groups of disabled people and veterans, mainly this includes workers who in the past were in one way or another connected with nuclear power plants, radiation, nuclear weapons, as well as WWII veterans, a detailed list of persons who are entitled you will find this deduction in Article 218 of the Tax Code;
- 500 rub. (Article 218 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation) - the deduction is due to various groups of military personnel and war veterans, a detailed list can be found in the specified article of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation;
- 1400 rub. – a deduction for the first and second child is applied until the salary, calculated on an accrual basis from the beginning of the year, reaches the maximum value of 280,000 rubles. (from January 1, 2016 – 350,000 rubles). Once this value is reached, this deduction does not apply.
- 3000 rub. – a deduction for the third and subsequent children, similar to the previous one, is applied until reaching 2,800,000 rubles. (from January 1, 2016 – 350,000 rubles).
- 12000 rub. – applies to parents raising a disabled child of group 1 or 2 (from January 1, 2020);
- 6000 rub. – applies to guardians and adoptive parents of a disabled child of group 1 or 2 (from January 1, 2020).
Personal income tax is a personal income tax; for the purpose of calculating wages, the Tax Code of the Russian Federation has established a personal income tax rate of 13%. The tax base for determining the amount of personal income tax will be the amount of accrued wages minus deductions due to the employee. The obligation to pay personal income tax on wages rests with the employer. For more information on how personal income tax is calculated and what tax deductions are, see here.
Thus, having calculated the salary, we determine the standard deductions due to the employee, subtract the amount of deductions from the accrued salary, and from the resulting value we calculate 13%, this will be the personal income tax (NDFL). The employer deducts the tax amount from the employee's salary and pays it to the budget.
The employee will receive his salary minus personal income tax. That is, despite the fact that the employer must pay personal income tax for its employees, the funds for payment are taken from the employees’ salaries. The employer does not bear any expenses here.
Insurance premiums are payments that an employer is obliged to pay for its employees for compulsory pension, social and health insurance, as well as against injuries. These contributions are paid to the Pension Fund, Social Insurance Fund and Compulsory Medical Insurance Fund. Insurance premiums are already expenses of the employer; he pays them not at the expense of the employee, but from his own funds.
In 2020, the following insurance premium rates are established:
In this case, you need to pay attention to the total wages that the employee has earned since the beginning of the year. There is a limit for calculating insurance premiums
Each type of insurance premium has its own limit. Only contributions to the FFOMS are always paid at the same rate, regardless of income.
Insurance contributions are calculated from the amount accrued in the first point of the salary and are paid to the budget by the employer. They are not taken away from employees' salaries.
The employer pays the calculated salary minus personal income tax to the employees. Salaries are paid on the basis of form T-53 “Payroll”, it can also be form T-49 “Payroll”.
What entries reflect the accrual and payment of wages in accounting? Read about it in the next article.
Examples of calculations for 2019
Below are several examples of calculating income tax from various employee payments:
- wages with and without deductions;
- salaries to be paid.
How is it calculated from salary without taking into account deductions?
Initial data:
Let's calculate the income tax of E. A. Akseeva. She earns 40 thousand a month, and in May 2020 she received a bonus of 10 thousand for good work.
Let's calculate how much she needs to send to the budget of the Russian Federation for the period January - May:
Calculation:
- 40000 * 4 + 10000 = 170000 earned by E. A. Akseeva for a given period of time, taking into account the bonus.
- 170000*0.13 = 22100 rubles – income tax that must be paid.
- 170000 – 22100 = 147900 – will be received in hand.
From the salaries of employees with children
Article 218 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation provides a complete list of deductions that an employee can receive. Once you know the amount of the benefit, you can easily calculate how much personal income tax is withheld from your salary. You should subtract the non-taxable amount from your salary, then multiply the resulting number by 0.13 (the rate for residents of the Russian Federation).
From 2020, if the threshold of 350 thousand rubles per year is exceeded, the employee is deprived of the opportunity to use standard deductions for children.
Example:
Initial data:
- 40 thousand accrued for March 2020;
- three children 5 years old (deduction 3000, since he is the third in the family), 15 years old (1400, since he is the second) and 25 years old (no benefits).
Calculation:
- Personal income tax = (40000 – 1400 – 3000) * 0.13 = 4628.
- Salary on hand = 40000 – 4628 = 35372.
From income issued in hand after withholding
For the convenience of employees, the employer often names the amount of wages after personal income tax has been withheld. The amount of deduction can be determined using two formulas:
- After deducting tax, it turns out that the employee receives 87%. Thus, total salary = Amount issued in hand / 87%.
- You can determine the amount of tax by multiplying the amount received in hand by 0.13.
Example:
Initial data:
A. A. Dmitriev learned at an interview that the employer plans to give him “clean” 60 thousand rubles.
Calculation:
Let's calculate the amount of the full salary before tax, as well as the withheld tax:
- Full salary = 60,000 / 0.87 = 68,965.51 rubles.
- Tax withheld from salary = 60,000 * 0.13 / 0.87 = 8965.51 rubles.
That is, the withheld personal income tax is 8966 (rounded according to the rules of mathematics) rubles.
Video lesson The procedure for paying wages to employees of an organization
When paying the insurance premium for an incomplete year (when starting a business activity not from the beginning of the year or when terminating the activity), the amount of the contribution is correspondingly reduced in proportion to calendar days. In this case, the day of registration or the day of termination of activity MUST be included.
Individual entrepreneurs have the opportunity to make quarterly contributions. Once every three months, they fill out an interim declaration, which cumulatively calculates the income received and the tax deducted from it. And at the end of the year, general reporting is provided, on the basis of which the final recalculation is made.
Salaried employees pay monthly income. This deduction allows the deductions to be distributed evenly rather than being withdrawn as a total amount at the end of the year. However, according to the general rules, the accountant calculates income contributions on an accrual basis.
Video lesson from the teaching teacher, chief accountant Gandeva N.V. To watch the video click below ⇓
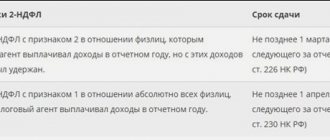
Help on form 2-NDFL: tax rates
For each tax rate, its own 2-NDFL certificate must be completed. If an employee receives a salary subject to 13% tax, and also wins the lottery (the winnings are taxed at a 35% rate), Form 2-NDFL is filled out twice for him, each certificate reflects its own type of income and its taxation.
Important point! If the form indicates that an individual has Russian citizenship, it is not necessary that the payer receives the tax rate required for a resident of the country. When summing up the results of the year, it may well turn out that a citizen of a country is not its resident.
Let us remind you that a resident of the Russian Federation is considered a person who lives on its territory for at least 183 days over the next twelve months in a row. An exception is made for:
- representatives of local government bodies;
- military personnel in service;
- employees of law enforcement or government agencies;
Resident status is not lost by people making short-term trips (no more than six months in a row) related to receiving medical care or education, or work trips for the purpose of extracting hydrocarbon resources from fields in the seas.
Tax calculation rules
The rules by which personal income tax is calculated are the same for everyone. In the Russian Federation, this value does not have a floating coefficient, but is calculated based on the established percentage for all population groups.
Personal income tax can be calculated using the following formula:
(D – V) * 13%
13% is the established tax rate for individuals.
D - income received over a separate period of time.
B – tax deduction required by law.
The indicated 13 percent tax is unchanged for all amounts received from work, so you should not check the legislation every time to clarify this value. But the amount of deductions varies depending on the social category to which the taxable person belongs and other preferential parameters. Earned income also varies and not all of it is taxable.
How to calculate tax using this tool:
Our free tax calculator has a user-friendly interface; You just have to stick to the following to get the personal income tax calculator: • First of all, you have to add the income value in the Income field. • For the immediate future, you should select your filing status from the Single Filer, Married Filing Jointly, Married Filing Separately, or Head of Household drop-down list. • You must then enter your age in years • Immediately after entering your 401(k) contribution, this is not required as these limits are set by the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) and are subject to adjustment each year. • Next, you must enter the amount you contribute to the traditional, Roth, or other types of IRAs in the appropriate IRA Contribution field. • Next time you have to enter the amount towards taxes paid or withheld • Then you have to select the tax method: “Standard Deduction” or “Itemized Deduction” – If you have selected “Itemized Deduction” then you have to enter the amount of itemized deductions. • Finally, click the Calculate button on the 2020 tax calculator to get your taxable income, effective tax rate, estimated federal taxes, and federal taxes withheld. Well, this federal personal income tax calculator will estimate the amount you'll get back.
How to calculate personal income tax in an online calculator from income, from the amount in hand
Calculate income tax on income in the first calculator. Indicate the amount received and the type of income, then the online form will perform the calculation itself and display the tax amount and the amount remaining after taxation.
Calculate the income tax on the amount in hand in the second calculator. Enter in the only field the monetary value that you received in your hands. Also indicate why the amount was received - select the appropriate option from the list provided in the drop-down menu. Next, an online calculation is carried out, the result of which is a known amount of personal income tax and the initial income value.
Calculators are extremely simple. The task is to correctly determine the type of income. The personal income tax rate at which the calculation must be made depends on this.
In general, all rates are fixed in the tax code. The smallest is 9%, the largest is 35%. The value is influenced not only by the type of income, but also by the person who received it (whether he is a resident of the Russian Federation). Non-residents pay more.
Tax rates in 2020 - 2020
There are only 5 personal income tax rates, expressed as a percentage:
- items 9 - apply only to bonds before 01/01/2007;
- the next 13 is the most common; wages, dividends for Russian residents, and all other income amounts not listed below are taxed;
- 15 - applies only to dividends purchased by non-residents;
- 30 - relevant for income from securities, also applies to income of non-residents, unless otherwise established for them;
- the largest 35 is a fairly large list of income, in particular this is prize money, gifts, if their amount is over 4 thousand rubles. The list also includes the following income:
Features of working with the calculator
From 2020, tax is deducted after actual receipt of income. The process is regulated by the Tax Code; the date of receipt of income is entered into a single tax base to confirm payments. The online assistant will allow you to calculate tax interest individually. A reliable result will be obtained after entering personal data.
The date recorded in the documents upon receipt of payments shows the following information:
- The specified date is the day the salary is received and the funds are transferred to the bank account of the trustees.
- Receiving the amount in kind.
- Do they receive income by carrying out monetary manipulations, completing legal procedures, or purchasing securities? Income is recorded upon receipt of the right to use a valuable object.
- Repayment of a previously received loan, if debt obligations were issued, indicate the date of receipt of the debt by the taxpayer.
- At an official place of work, the dates of receipt of advance payments, sick leave, vacations, and bonuses required by law are recorded.
The actual payment is the basis for the calculation of the tax authorities; based on the data, the agent calculates the personal income tax. Calculated interest is withheld from the actual income received by the taxpayer. Personal income tax on unforeseen payments is submitted to the tax service before the end of the current month.
Withholding tax on income received raises controversial situations that are resolved in court after the taxpayer files a claim for unlawful actions against him. The date of receipt of money or income acts as evidence in complex legal situations. Legal standards for resolving such disputes are prescribed in the Tax Code and federal legislation of the Russian Federation.
Tax withholding obligation
For example, from 20,000 rubles. 2600 rubles are withheld. – from a resident and 5200 rubles. from a non-resident. The withholding procedure is approved by the Government and regulated by the Tax Code.
Under the personal income tax benefit, you can return it in the form of deductions. You can receive a mandatory deduction for each child upon your application to the accounting department. Attach to your request copies of birth certificates, marriage certificates (if available), and a certificate of family composition. If you live in a civil marriage, then only the legal parent will receive deductions for the child. Guardians and trustees also have the right to such benefits. Payments for each child are summed up.
The employer can pay insurance premiums for you or deduct them from your accrued salary, but personal income tax is necessarily deducted from the individual’s income. faces. In this regard, your employer acts as a tax agent - this simplifies the procedure. You don’t need to fill out declarations yourself every year and go to the tax office with a report, you don’t need to fill out forms yourself and transfer your 13% personal income tax - all this is done by the employer for each employee.
When you or your children study at a university (necessarily in an accredited one), you need to provide certificates and transcripts from the place of study to work, then you will be reimbursed for your education costs. This system has been in operation for a very long time, but it is used extremely rarely. It is possible to receive such payments against future income tax payments if an unemployed full-time student applies to the tax office. Deductions will be repaid from his future personal income taxes.
Why and how to pay income tax?
Income tax is very important - it is with its help that the lion's share of the local and federal budgets is replenished. Therefore, the state vigilantly ensures that taxes are paid accurately. To make life easier for citizens, the burden of PFDL payments has been shifted to the companies where they are employed.
The employee is freed from filling out certificates and receipts, independently visiting credit institutions, standing in long queues and annually submitting declaration forms to the tax service.
However, there is a nuance. The accounting department “covers” employees only in cases when it comes to labor income. If you managed to sell real estate or win the lottery, you need to declare the funds received yourself. To do this, you need to report to the tax office at your place of residence about the income received, pick up the appropriate receipt from the employee to fill out, and transfer the personal income tax yourself, using the services of the bank.
If the payer decides to submit documents about the unexpected money to the tax office late or not at all, he will receive a fine. By the way, if you pay the fine but still do not submit a declaration, then soon the penalties will return in a larger volume.
Didn't manage to submit your declaration on time? Do you want to know what the consequences are of failure to submit reports on time? Read more about the statute of limitations for tax offenses and how to reduce the amount of the fine in our article.
What deductions are legal?
When determining the amount of income tax, it is important to understand that the Tax Code of the Russian Federation regulates standard deductions that can be “discarded” when calculating personal income tax. According to Article No. 218, the basis for such a deduction may be the presence of minor children. Then the deduction for one or two heirs will be 1,400 rubles, for three or more - three thousand rubles. In the event of a divorce, one of the parents receives the right to double deductions for children, which will last until they reach adulthood or a limit of 350 thousand rubles.
Article 218. Standard tax deductions
Child tax deduction: how to prepare documents
In the material presented, we discuss how to go through this bureaucratic procedure and use the right to receive a cash deduction for children.
The state also implies that parents of disabled children or full-time students can count on a deduction of 12 thousand rubles. If a guardian, trustee or foster parent finds himself in a similar situation, the deduction will be 6 thousand rubles.
Another deduction is included among the standard ones. The tax amount will be reduced by three thousand rubles monthly for the following payers:
- Disabled people of the Great Patriotic War.
- Disabled people of the first, second and third groups who were injured while defending (military service) the Motherland.
- Those injured during the liquidation of the disaster at the Chernobyl nuclear power plant.
- Persons involved in work on the Shelter object (1988-1990).
- Victims at the Mayak production association (1957-1961).
- Persons who, before January 31, 1963, took part in the assembly and testing of nuclear weapons.
A tax deduction of 500 rubles is due to:
- Disabled people since childhood, as well as disabled people of groups II and III.
- Heroes of the USSR and the Russian Federation.
- Awarded the Order of Glory of three degrees.
- Residents of besieged Leningrad.
- Prisoners of concentration camps.
- Persons suffering from radiation sickness or other ailments associated with radiation exposure.
- Bone marrow donors.
- To the parents and spouses of military personnel who died defending the Motherland.
- Evacuees from the Chernobyl exclusion zone.
More detailed information about the categories of citizens who are entitled to tax deductions can be obtained from Article No. 218 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.