Inventory control
This concept is used to define constant quantitative and grading accounting carried out in a warehouse. Without taking into account the goods placed in the warehouse, it is difficult to ensure their safety. For this process, a materials warehouse card is used, which is a form approved by law for recording the movement of materials of a particular type, size and grade in the warehouse. They are filled in for each item number of the material. They are managed by a financially responsible person, for example a warehouse manager or a storekeeper.
Before entrusting the warehouseman with the material reserves of the enterprise, as a rule, an agreement is concluded with him. It describes the types of work the employee performs and the extent of responsibility in the event of loss or damage to products stored in the warehouse.
Without reporting - nowhere
Accounting for warehouse operations involves daily monitoring of the remaining inventory at the disposal of the enterprise. Every month, the person responsible for the warehouse, analyzing the primary documentation, prepares a report for the head of the enterprise. The report is sent to the accounting department, supported by documentation reflecting the receipt and departure of valuables.
The report must reflect such materials, products, quantities, composition of which changed during the reporting period. At the beginning of each month, a separate report is prepared, indicating in it how large the balances for various positions are at the disposal of the enterprise. The company's primary documentation serves as the basis for recording the arrival and departure of valuables. Based on these data, a summary and balance are prepared, reflecting the state of the company at the end of the month. The information specified in the reporting must be similar to that present in the warehouse accounting system and in the position cards.
Organization of warehouse accounting
A well-organized process of accounting for materials located in the warehouse is a very important and necessary segment of the organization’s activities. For efficient warehouse operation, two common accounting systems are used: batch and sort. But regardless of the fact which choice is made, financially responsible employees will keep records of the company's products in kind. This procedure is carried out through the use of incoming and outgoing commodity orders.
If we take into account the information contained in the manuals for accounting of a company's inventories, we can conclude that analytical accounting of inventory items is carried out through the use of the balance method or revolving invoices. With these approaches, accounting is carried out in the context of each storage location, as well as within them, recording item numbers, various product groups, synthetic and subaccounts.
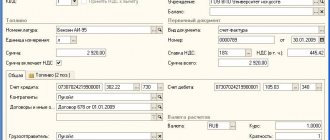
1C programs for trade and warehouse
Accounting for goods at storage locations is implemented in the following configurations:
- "TiS 7.7" (outdated).
- “Trade Management 8” (there is a basic and PRO version) has the most complete functionality.
- "1C: Retail 8" is suitable for organizations and individual entrepreneurs engaged in retail trade, including retail chains.
- "Enterprise Accounting 8". It contains the basic mechanisms for accounting for items at storage locations.
- KA 8 and ERP 8 are solutions suitable for manufacturing enterprises.
In addition, there are solutions in industry and specialized configurations (for example, for logistics accounting).
Subscribe to our channel in Yandex Zen - Online Cashier! Be the first to receive the hottest news and life hacks!
Accounting in 1 C Trade and warehouse 7.7
Until recently, the TiS configuration was the most common program designed for trade and warehouse accounting. However, starting in 2003, it stopped updating and developing the 7.7 technology platform itself. And at the moment, “1C: Trade and Warehouse” is a seriously outdated configuration that has fallen behind the requirements of the time.
Experts strongly recommend transferring accounting from systems running TiS 7.7 to Trade Management 8, which replaced it. And although the words “1C warehouse” are no longer in the name, the warehouse part has become even more functional and versatile compared to the outdated version.
The transition to “Trade Management” will greatly increase the efficiency of the organization, since “UT 8” uses the new capabilities of the 8.3 platform. A special transition assistant is designed to download data from 7.7 and transfer it to the UT 11.3 configuration, which can be very useful for companies with a large number of items.
1C: Trade Management 11
"UT 11" is designed mainly for wholesale trade. It contains:
- multi-stage reservation of goods;
- purchasing and sales planning;
- control of mutual settlements with clients (you can track overdue debts, set a ban on the shipment of goods if there is a debt), etc.
The program has a very wide functionality that allows you to manage goods at storage locations, namely:
- order warehouses;
- shelf life of items and batches;
- storage by address and much more.
“UT 11” implements financial accounting of an enterprise in the context of several types of activities, reports on financial results and a management balance sheet are printed. The program includes several options for calculating the cost of goods. That is, UT in edition 11 is a powerful software package for management accounting, although processes for retail are also fully implemented:
- there is printing of cash register receipts;
- RMK;
- the requirements of Law No. 54-FZ of May 22, 2003 are supported;
- You can pay with bonus points, etc.
Why is it sometimes written “1C: Trade Management 8”, and in other cases “UT 11”? Both spellings are correct. Number 8 is the version of the current 1C:Enterprise 8.3 platform, and 11 is the edition of the UT program itself. Currently the latest is 11.4.
If you want to download 1C Warehouse for free and check whether it is suitable for accounting in your enterprise, you can use the demo version from the 1C website. Below in the article we will tell you in more detail how to do this.
1. Ask our specialist a question at the end of the article. 2. Get detailed advice and a full description of the nuances! 3. Or find a ready-made answer in the comments of our readers.
1C: Retail 2 and its difference from UT
“1C: Retail 2” is a program that is more likely intended for retail chains and small stores. We can say that “Retail 2” is a “stripped down” version of “UT 11” with minor additions.
The developers have expanded the settings of the RMK (cashier workstation), and it itself has become more functional. The program provides the most complete support for various retail equipment compared to UT; there are more tools for managing the range of goods and prices.
“Retail 2” is designed for the simultaneous work of fewer employees than “UT 11”, and it is assumed that one employee can be assigned several functions. In “Trade” it’s the other way around: each operation is assigned a separate employee or even a department.
Added to the program:
- personnel management (with tracking of hours worked);
- motivation systems;
- visitor counters.
The configuration implements accounting for orders from buyers and suppliers, as well as reserving goods (albeit a little simplified). There are also bank documents (without client-bank). All this makes it possible to maintain full accounting of goods in 1C: Retail 2 without unnecessary complications. And one more significant point: “Retail 2” costs much less than “UT 11”.
- 1C:Enterprise 8 PROF. Client license for 10 workstations
41 400 ₽
41400
https://online-kassa.ru/kupit/1s-predpriyatie-8-prof-klientskaya-litsenziya-na-10-rabochih-mest/
OrderMore detailsIn stock
- 1C: Retail 8
11 reviews
3 300 ₽
3300
https://online-kassa.ru/kupit/1s-roznitsa-8/
OrderMore detailsIn stock
- 1C: Trade Management 11
2 reviews
7 200 ₽
7200
https://online-kassa.ru/kupit/1s-upravlenie-torgovlej-11/
OrderMore detailsIn stock
Using cards
Warehouse accounting of materials, the basis for which are turnover sheets, in most cases involves the use of the two above-mentioned methods. This allows you to optimize warehouse operations and achieve higher levels of productivity.
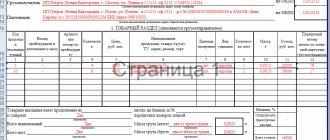
In the first option, a warehouse accounting card is used, which opens for each type of inventory item stored in the warehouse. It displays quantitative and summary data, which, in essence, is the movement of materials. The basis for filling out such cards are primary accounting documents.
Keeping inventory records using cards also involves displaying balances on the first day and calculating turnover for the month. With the help of such documentation, turnover sheets are compiled for each warehouse separately. In addition, the data of those cards that are in the accounting department are verified with the documentation located in the warehouse.
It is also possible that the accounting cards are not kept in the accounting department. In this case, expenditure and receipt documentation is grouped by item numbers. Afterwards, with the help of these documents, the totals for the month are calculated, and data on expenses and income are recorded separately. This information is then displayed on the turnover sheet. Those balances that were displayed in these statements are compared with the balances recorded in the warehouse accounting cards.
And how do we work?
The characteristics of warehouse loading and unloading operations depend on what kind of cargo needs to be handled and what kind of transport to serve. The level of mechanization of the simplest processes has a strong influence on work. Acceptance of goods for quality is one of the most important moments of the entire complex associated with the receipt of items at the warehouse.
How exactly to control the flow of material assets is decided by analyzing information about the quantity and quality of items in the warehouse. Practice shows that often the data in accounting systems is incorrect and incomplete, which leads to management errors and losses for the company. Technological operations that take place during the logistics of goods are associated with unplanned changes in quantity and quality. Cargo can be stolen, damaged, lost; there is the concept of “excessive loss.” Personnel may make mistakes, form batches incorrectly, or ship goods incorrectly. All this leads to shortages, mis-grading, and excess volume.
When accepting goods, it is very important to carefully evaluate the incoming goods, regularly comparing the values with the stated list. Therefore, accompanying documents, usually invoices, must be drawn up for any positions. Documenting each step is the most effective method of obtaining accurate data on the warehouse situation.
Balance accounting
This form of warehouse accounting differs from the previous one. The key difference comes down to the fact that qualitative and total accounting in the context of inventory items is not maintained in the accounting department. Turnover statements, accordingly, are also not compiled.
With this type of organization of warehouse work, inventory accounting is carried out in the context of subaccounts, product groups and balance sheet accounts, which are used to record inventory items exclusively in monetary terms. Accounting is carried out by financially responsible persons. For this process, a warehouse ledger or appropriate journal is used.
As for accounting, it is responsible for receiving primary accounting documentation from financially responsible persons and subsequently checking the received data. When the reconciliation process is completed, those balances of materials that were recorded on the first day are transferred to the balance sheet.
Batch accounting
Trade and warehouse in this case are organized in such a way that a specific batch of goods is stored separately. Moreover, for each of them the storekeeper writes out a batch card in two copies. A special book is used to register such cards. In this case, it is the number of the accepted batch that is the registration number in this book. After entering the necessary information, one copy is transferred to the accounting department, and the other remains in the warehouse and serves as a warehouse accounting register.
It is worth noting the fact that the inventory of one item is determined as a batch. This product must be supplied by one supplier. As for the number of deliveries, there may be several.
When filling out a batch card, the warehouse employee must indicate the date of preparation, its number, the time of filling out the receipt of goods, the type of transport, the supplier’s details, the number and date of the invoice, the name of the product, the place of departure, as well as the weight and grade.
Warehouse accounting of materials, which uses the batch method, implies the reflection during the release of goods of the date of this action, the number of the consumable commodity document, the type of transport, the name of the recipient, the quantity and grade of products released. At the same time, the number of the batch card is indicated in the expenditure document.
When all the stocks of a particular batch are used up, the warehouse manager and merchandiser put their signatures on the card and transfer it to the accounting department, where it will subsequently be checked.
It is possible that during the inspection a shortage will be identified. In this case, warehouse accounting implies the following actions: the accountant, before the next inventory, writes off the shortage as distribution costs, but only on the condition that it was within the limits of natural loss. If the norms were exceeded, then the shortage must be recovered from those persons who are financially responsible for the products stored in the warehouse.
It is also worth considering the information that the batch warehouse accounting system includes drawing up a report for a completely consumed batch of goods and materials.
Warehouse: we accept positions
One of the most important operations in a warehouse is receiving goods. An automated program for warehouse accounting is usually configured for quantitative accounting, but in addition to it, qualitative accounting must also be carried out.
The operator responsible for receiving items checks the number of received items and controls the quality of each of them. In this case, first you need to clarify the compliance in terms of volume, only then - in terms of quality. In some warehouses, acceptance falls on the storekeeper, the warehouse manager, or the manager; in some, the responsibility is divided between the manager and technical staff.
If the warehouse accepts materials belonging to special categories - the so-called responsible assignment, a commission is appointed for acceptance. The procedure for accepting valuable positions is similar. The warehouse accounting program must contain complete items in the database in accordance with the order approved at the event. By the same order, a selection committee is introduced, appointing members by name. In some companies, the responsibility for issuing the order falls on the chief engineer.
How are warehouse journals used in sort accounting?
If this method of accounting is used, the storekeeper opens one or several pages in the product journal for each variety and name of product. A separate card can also be created. The number of pages depends on the volume of operations carried out for receiving and disbursing.
In the title of the card or magazine page, you must indicate the article, name, grade and other characteristics that distinguish a particular product. The remaining space on the page is used to reflect receipts, expenses and product balances.
A warehouse accounting book (magazine) is necessary to record data when processing each receipt or expenditure document.
Legislation allows the use of various forms of journals. An example is a commodity journal in form N MX-2. It must be maintained by a storekeeper or other responsible person. The basis for its completion are documents on the acceptance and issuance of inventory items previously deposited. Such a log contains the following data:
— the date when the inventory items were accepted for storage;
— the department that transferred the inventory to the warehouse;
— name, price, quantity, units of measurement of inventory items;
- number and date of documents that were used during the issuance and reception of products;
- storage.
In order for the goods to be accepted for storage and subsequently issued, it is necessary to certify the relevant documentation with the signatures of the storekeeper and the warehouse manager.
Various types of commodity journals will help to competently organize warehouse accounting of a quantitative type, in which the movement and balances of products are recorded, with the help of which inventory records are kept in storage areas, as well as their consumption is recorded. Such information can also be displayed in the form of statements.
How is inventory markdown carried out?
Trade and storage are inevitably associated with such phenomena as obsolescence of goods, as well as a decrease in demand for them or loss of quality. These problems cannot be ignored and the markdown process is used to effectively solve them. To complete it, you will need an act of depreciation of material assets.
It must be drawn up and signed in two copies. This is done by responsible persons representing a special commission. One copy remains with the warehouse manager (it must be stored), the second is sent to the accounting department. In some situations, one copy may be attached to the delivery note. This is done for the subsequent transfer of this document to an organization engaged in the sale of discounted goods, or for the purpose of returning it to the manufacturer.
Warehouse management systems
One of the key tasks of any business is automation and optimization of all internal processes of the enterprise. This will save time and improve the quality of service.
The warehouse is no exception. In order to speed up various processes related to the receipt and consumption of goods, a warehouse accounting program is used. It may have a different appearance and structure, but the functions of such software remain unchanged.
We are talking about the following possibilities:
— distribution of products in the warehouse by storage cells, batches and responsible persons;
— the ability to dynamically recalculate warehouse balances;
— tracking of cargo along traffic routes;
— use of various methods of determining the price of a product;
— inventory and subsequent generation of up-to-date reporting according to its results;
— formation of receipt and warehouse orders;
— revaluation of goods due to the influence of various factors that shape its value;
— warehouse management.
A well-designed warehouse accounting program allows you to establish the efficient operation of a transit warehouse, as well as general purpose warehouses. It is also practiced to use an electronic analogue of a warehouse accounting card, which has all the latest filters. We are talking about tracking information in the following areas:
— currency used to pay for the goods (according to the matching sheet, statement of surplus and shortage, statement of actual availability, etc.);
— batch of products, shelf life, expiration date of certificates;
— various types of operations with inventory items;
- special purpose;
- re-grading;
— financially responsible persons;
— operations of staffing and dismantling of material assets in the warehouse.
As a rule, such automated warehouse accounting is modified by the developer taking into account the individual characteristics of a particular client’s business.
Integration with an online store
Accounting for the movement of goods in a warehouse and integration allows you to synchronize the work of several departments or retail outlets, and will also allow you to quickly exchange information. Even if only two systems are synchronized, this will allow you to receive accurate information about the quantity of goods in the warehouse and their detailed characteristics in real time. You can connect online payment and other services. Integration can be carried out with almost any system.
Even in a small enterprise, it is necessary to record not only the receipt and consumption of goods through postings, but also analyze documents, maintain statistics, generate profits and withdraw the balance. The warehouse accounting program will help with this, and system automation will allow you to operate with accurate data, maintain statistics and plan.
Current programs
To effectively organize warehouse operations, various software can be used. But one of the most popular options is “1C Warehouse Accounting”. This software has certain advantages, which attract many companies that integrate this program into the operation of their warehouses.
The key functions are as follows:
— quick and timely accounting of material assets, their arrival and movement;
— accurate maintenance of all warehouse documentation;
— timely and convenient maintenance of a warehouse journal (cards);
— availability of all necessary tools for correct inventory taking;
— presentation and processing of the warehouse system.
Using this software, you can qualitatively cover several areas of an enterprise’s economic activity. We are talking about managing sales rules, inventory, finance, purchasing and delivery of goods. The main advantages of 1C include ease of use of the program, the possibility of its correction taking into account the needs of a particular organization and full compliance with Russian legislation.
If you wish, you can use other programs: “Super Warehouse”, “Product-Money-Product” and others.