Inventory of material assets
Ideally, all material assets and liabilities of the enterprise should, in fact, correspond to accounting data.
In order to get as close as possible to the reliability of accounting data, there is such an accounting method as inventory. It represents a periodic comparison of actual and accounting data on the company's assets and liabilities. In addition to checking the availability of objects and ensuring the reliability of accounting, inventory has the following purposes:
– analysis of the condition of the property in terms of its market value and the need for revaluation or write-off;
– checking compliance with the operating conditions of fixed assets and storage of other types of inventory;
– identification of overdue debts and analysis of the reasons for their occurrence.
– inventory is carried out not only for one’s own property and obligations, but also for leased objects, as well as for valuables accepted for processing.
The legislation defines mandatory cases of conducting an inventory, which are enshrined in clause 27 of the Regulations on Accounting and Reporting. Among the cases of mandatory reconciliation are:
– the need to prepare annual financial statements;
– dismissal and hiring of new financially responsible persons, which primarily include storekeepers and cashiers;
– rental of property or equipment;
– cases of detection of theft or damage to property and inventory;
– damage to the organization’s property as a result of natural disasters or emergencies;
– liquidation of a company or enterprise.
The main purpose for which it is necessary to carry out inventory reconciliation is measures to preserve the property of a company or enterprise, as well as the organization of a timely procedure for payment of taxes and business contracts.
Accounting entries for disposal of inventory items
D 20 (23, 29) K 10 – transfer to production. D 08 K 10 – leave for self-construction. D 91 K 10 – write-off upon sale or gratuitous transfer.
Analytical accounting of inventory items is organized in storage areas, i.e. in storerooms, and represents the mandatory maintenance of accounting cards for each item of materials. The responsible persons are storekeepers, and the controllers are accounting workers. At the end of the month, the storekeeper displays the balances of inventory items on cards, which indicate the movement, beginning and ending balances, the accountant checks them with the documents and certifies the accuracy of the storekeeper's calculations with a signature in a special column of the card.
In accounting, based on documented transactions, the accountant displays the balance of inventories in value terms, which is recorded in the second section of the balance sheet as the cost of inventory items. A breakdown of the balances for each item is given in the materials accounting statement.
The Ministry of Finance explained: There is no official definition of the term “inventory”. And the term “inventory” itself corresponds in economic content to the term “inventories”. Accordingly, fixed assets are not included in inventory.
Our comment: Indeed, there is no definition, but there is a term. This term is used (except for the Inventory Instructions 1 mentioned in the letter) also in the Instructions on the application of the Chart of Accounts 2 in the explanation for the off-balance sheet subaccount 023 “Tangible assets in safekeeping”, where records are kept of inventory items accepted for safekeeping, inventory items that are received from suppliers, but not paid and which are not allowed to be spent before payment, inventory items received in excess, etc. It can be unambiguously stated that both inventories and fixed assets belong to the property of the enterprise (Article 139 of the Criminal Code).
And depending on the economic form that property acquires in the process of carrying out business activities, as well as the definition of the terms “inventories” and “fixed assets” specified in P(S)BU 9 and P(S)BU 7, respectively, property values will be relate either to fixed assets, or to working capital, or to funds, or to goods. We agree with the statement of the Ministry of Finance that in terms of economic content, inventory items are more likely to be classified as inventories than as fixed assets. True, for some enterprises that sell, for example, agricultural machinery, or cars, or some other large and valuable items, which inherently relate to fixed assets for those who purchase them, and for sellers they will be only goods, inventories or Inventory purchased for resale.
2 Approved by order of the Ministry of Finance dated November 30, 1999 No. 291.
Galina BEDNARCHUK, Debit-Credit
On the form and procedure for financial reporting on economic activities List of the State Administration of Ukraine dated March 16, 2007 No. 1897 Accounting The list of information about legal entities included in the Unified State Register is supplemented with information about the financial statements of a legal entity (except for budgetary institutions) as part of the balance sheet and the report on annual financial results. State Committee of Ukraine on Regulatory Affairs. DK's comment.
On the provision of information (extract) Sheet Other dated 12.2.2015 No. 339/4/99-99-19-01-01-13 No. 22 (1.6.2015) :: Accounting Income in the form of alimony paid to a taxpayer by a resident is not considered subject to military levy. .
On the list of countries covered by the Convention on Mutual Administrative Assistance in Tax Matters Sheet Other dated 30.3.2015 No. 10909/7/99-99-12-01-03-17 No. 22 (1.6.2015) :: Accounting SFSU provided an updated list of countries and jurisdictions covered by the Convention on Mutual Administrative Assistance in Tax Matters. .
Accounting for inventory must be carried out in accordance with relevant accounting regulations
In this article we will consider the main aspects of inventory accounting and pay attention to its organization in the enterprise
The concept of goods and materials
From the previous paragraph we already know the decoding of goods and materials. But it would be a mistake to believe that inventory assets are only materials that are necessary during production. This group also includes:
- Accessories.
- Containers for packaging, storage and transportation.
- Household equipment.
- Waste that is planned to be reused.
- Goods that the company purchased from other organizations, as well as finished products.
- Depending on the specifics of the company’s activities - building materials, fuel, semi-finished food products available in the warehouse
In terms of their importance, inventory items are in second place after the financial assets of a particular enterprise. Inventory and materials are used most effectively during the calendar year.
Inventory assets at an enterprise require accounting
Preparation of accounting correspondence for inventory items
To record in accounting the moment when materials were received from the supplier, the posting is generated by posting a debit turnover on the 10th account.
To reflect transactions with finished products, synthetic account 43 is used. It is active, income is recorded as a debit movement, and expenses are indicated in credit turnover.
The cost of goods and the size of the markup on them are accumulated in the debit of account 41.
| Operation | Dt | CT | Explanation |
| materials received from the supplier (posting) | Dt 10 | Kt 60 | according to incoming materials |
| Dt 19 | Kt 60 | according to the VAT amount on the invoice | |
| Dt 68 | Kt 19 | according to the amount of VAT to be reimbursed | |
| finished products arrived (accounting at actual cost) | Dt 43 | Kt 20 (23, 29) | when accounting for actual cost based on the amount of finished products received |
| finished goods received (accounting cost method) | Dt 43 | Kt 40 | when accounting at book value based on the amount of finished products received |
| Dt 40 | Kt 20 | for the amount of actual cost | |
| Dt 90-2 | Kt 40 | for the amount of discrepancies between the cost and the accounting value (direct or reversing at the end of the month) | |
| goods have arrived from the supplier | Dt 41 | Kt 60 | at the cost of purchasing goods |
| Dt 19 | Kt 60 | according to the VAT amount on the invoice | |
| Dt 68 | Kt 19 | according to the amount of VAT to be reimbursed | |
| Dt 41 | Kt 42 | by markup amounts for trade organizations |
If they reflect the internal movement of valuables, for example, when materials are released into production, the posting is made using analytical subaccounts.
Disposal of working capital in storage may occur as a result of:
- transfer to another division of the company;
- sales to final consumers;
- transportation to the branch structure;
- gratuitous donation to third parties;
- culling.
| Operation | Dt | CT | Explanation |
| materials released into production (posting) | Dt 20 (23.29) | Kt 10 | based on the average cost of this type of materials |
| Dt 20 (23.29) | Kt 10 | when used and FIFO by cost in order from old to new batches in warehouse | |
| Inventory and materials were allocated for administrative and general business expenses | Dt 25 | Kt 10 | by the amount of inventory supplied |
| Dt 26 | Kt 10 | by the amount of issued IBP | |
| Dt 44 | Kt 10 | by the amount of containers and packaging issued for goods sold | |
| goods released to customers | Dt 90 | Kt 41 | when recognizing used revenue based on the amount of goods sold |
| Dt 45 | Kt 41 | until the moment of recognition of sales revenue based on the amount of goods sold | |
| finished products released to customers | Dt 90 | Kt 43 | when recognizing used revenue based on the amount of finished products sold |
| Dt 45 | Kt 43 | until the moment of recognition of revenue from the sale based on the amount of finished product | |
| transferred inventory items to the branch | Dt 79 | Kt 10 (43, 41) | by the amount of shipped separately. division of goods and materials |
In all cases of write-off of materials, postings are generated through crediting account 10 in conjunction with cost accounts. This approach to compiling accounting correspondence is also implemented in relation to goods with finished products, but with the participation of accounts 41 or 43.
The reason for excluding working resources from the balance sheet may be:
- loss of original qualities of products or raw materials;
- damage to material;
- depreciation of the asset;
- recording shortages based on inventory results.
Also see “Inventory of goods and materials”.
Disposal must be confirmed by a set of supporting documentation to establish the need to remove valuables from circulation.
When registering the write-off of goods that have become unusable, transactions are made for the amount indicated in the write-off act. The debit account will always appear as 94.
| Operation | Dt | CT | Explanation |
| write-off of materials (postings) | Dt 94 | Kt 10 | according to the amount from the act |
| write-off of goods that have become unusable (postings) | Dt 94 | Kt 41 | according to the amount from the act |
| write-off of finished products (postings) | Dt 94 | Kt 43 | according to the amount from the act |
Also see “How materials are written off.”
Sales of materials: wiring
Accounting for materials in a manufacturing enterprise is a significant part of the overall accounting process and consists of many components.
Companies strictly limit their inventories, making sure that their value does not exceed established calculated limits, and that materials are used effectively and efficiently in production, without lying in warehouses and thereby diverting funds from circulation.
However, situations when a segment of illiquid assets is formed in the structure of inventories often occur. Then the company's management is faced with the question of selling unused materials, since unnecessary in one organization, they may be needed in another. Let's consider what accounting records are used to record the sale of materials in manufacturing companies.
Features of external sales of goods and materials
The sale of inventory items in the company is carried out at selling prices agreed upon by both parties to the transaction and specified in the concluded agreement.
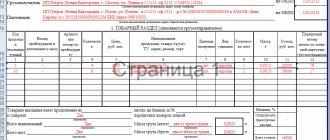
Based on the agreements, an invoice is drawn up (if the seller is a VAT payer) and an invoice form M-15 for the supply of goods and materials to the party. It contains information about the seller and buyer, the materials being sold, their quantity, price, and cost.
If delivery of goods and materials is carried out by the seller, then another document is drawn up - a consignment note.
Income from the sale of inventory items is considered income from non-operating activities, since materials and raw materials are intermediate assets for the company that do not themselves represent objects of sale.
Therefore, to summarize data on sales of raw materials and supplies, other income and expenses account 91 is used.
Inventories are written off from the materials account at cost prices in accordance with the accepted policy for their determination in the company (at the cost of each unit, average cost or FIFO method).
Postings for the sale of materials
As a rule, ownership of goods and materials sold is transferred to the buyer at the time of shipment. Upon shipment, the accountant makes the following entries:
| Operation | D/t | K/t |
| Sales without prepayment | ||
| Write-off of inventory items for sale (at cost of materials) | 91/2 | 10 |
| VAT is charged on the sales price | 91/2 | 68/2 |
| Sales proceeds at selling price | 62/1 | 91/1 |
| Payment by the buyer for materials sold | 51 | 62/1 |
| Sales on prepayment | ||
| Advance payment received from buyer | 51 | 62/2 |
| VAT on prepayment | 76/advances | 68/2 |
| Write-off of inventory items | 91/2 | 10 |
| Sales of materials are reflected by wiring | 62/1 | 91/1 |
| VAT charged | 91/2 | 68/2 |
| Prepayment credited | 62/1 | 62/2 |
| VAT credited on prepayment | 68/2 | 76/advances |
If the agreement provides for a special procedure for the transfer of ownership rights (later shipment of materials to the third party), then the sale of inventory and materials is reflected using account 45 “Goods shipped”. In this case, the wiring will be like this:
| Operation | D/t | K/t |
| Transfer of goods and materials to the buyer | 45 | 10 |
| Costs associated with the sale (delivery, loading) are written off | 45 | 20,23,60 |
| VAT on the cost of shipped goods and materials | 76 | 68/2 |
| The cost of inventory and materials was written off on the date of transfer of ownership rights | 91/2 | 45 |
| Proceeds from sales (as of the date of transfer of ownership) | 62,76 | 91/1 |
| VAT charged on revenue | 91/2 | 76 |
At the end of the month, the accountant calculates the result from the sale - the data from account 91/1 is transferred to the subaccount. 91/9. If the credit turnover on the account exceeds, the sales result will be a profit, and the debit turnover will be a loss. Next count. 91 is closed and the profit is reflected by posting Dt 91/9 Kt 99, and the loss - Dt 99 Kt 91/9.
Here are examples of how to register the implementation of inventory items with postings in relation to different situations:
Example 1. Sale of goods and materials without prepayment on a pick-up basis by the buyer:
OJSC Stroitel sells materials in the amount of 236,000 rubles. in view of VAT. The cost of materials according to accounting documents is 140,000 rubles. Accounting entries for the sale of materials:
| Operation | D/t | K/t | Sum |
| Revenue (at selling price) | 62/1 | 91/1 | 236 000 |
| VAT on sold inventory items | 91/2 | 68/2 | 36 000 |
| Write-off of inventory items (at cost) | 91/2 | 10 | 140 000 |
| Receipt of payment from Efrat LLC | 51 | 62/1 | 236 000 |
| VAT listed | 68/2 | 51 | 36 000 |
| Profit from sale reflected (236,000 – 36,000 – 140,000) | 91/999 | 91/291/9 | 60 00060 000 |
Example 2. Sales of materials (wiring) on an advance payment basis:
sells materials to the enterprise Liana LLC on the terms of 100% prepayment in the amount of 354,000 rubles. (including VAT). The cost of goods and materials is 180,000 rubles.
| Operation | D/t | K/t | Sum |
| Advance payment received from Liana LLC | 51 | 62/2 | 354 000 |
| VAT on prepayment | 76/advances | 68/2 | 54 000 |
| Write-off of cost of goods and materials | 91/2 | 10 | 180 000 |
| Revenues from sales | 62/1 | 91/1 | 354 000 |
| VAT charged | 91/2 | 68/2 | 54 000 |
| Advance offset | 62/1 | 62/2 | 354 000 |
| VAT credited on prepayment | 68/2 | 76/advances | 54 000 |
| VAT is transferred to the budget | 68/2 | 51 | 54 000 |
| Sales result (354,000 – 54,000 – 180,000) = profit 120,000 rubles. | 91/999 | 91/291/9 | 120 000120 000 |
Source: https://spmag.ru/articles/realizaciya-materialov-provodki
Valuation of inventory items during release
When releasing inventories into production, as well as during other disposals, inventory items are assessed using one of the methods, which is necessarily stipulated by the company's accounting policy. They are applied for each group of materials, and one method is valid for one financial year.
Inventory materials are assessed by:
• cost of one unit;
• average cost;
The first of these methods is used for inventories used by companies in an unusual manner, for example, when producing products from precious metals, or with a small range of groups of materials.
The most common method is to calculate the price using the average cost. The algorithm is as follows: the total cost of a type or group of materials is divided by the quantity. The calculation takes into account inventory balances (quantity/amount) at the beginning of the month and their receipt, i.e. such calculations are updated monthly.
In the FIFO method, the cost of materials upon disposal is equal to the value of the acquisition price at an earlier date. This method is most effective if prices rise and loses relevance if the emerging situation provokes a fall in prices.
Calculation of the average price in the 1C program
Let's look at how the average price for the “Apple jam” position is calculated. For example, before it was written off, there were only two receipts of apple jam in your store.
100 kilograms of apples x 1000 rubles = 100,000 rubles;
80 kilograms of apples x 1200 rubles = 96,000 rubles;
The average write-off amount will be equal to (100,000 + 96,000)/(100+80) = 108.89 rubles.
We multiply the resulting amount by 120 kilograms of apples and get 130,666.67.
At the moment, during the write-off, we used the moving average.
After the write-off, another receipt occurred. We received 50 kilograms of apples for 1,100 rubles.
Based on this, the average weighted amount for the month will be equal to:
(100,000+55,000 + 96,000)/(100+50+80) = 1091.30 rubles. If we multiply this by 120, we get a sum equal to 130,956.52.
The difference that we get by subtracting one value from another will be written off in 1C when closing the month and after performing the “Adjustment of item cost” operation. It is important to remember that 1C rounds the amount, so there may be a difference of 1 kopeck.
Postings for accounting of inventory items in accounting
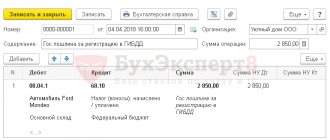
Example 1. Purchase of goods and materials from a counterparty by bank transfer
The acquisition of inventories (MPI) by bank transfer is regulated by clauses 5-11 of PBU 5/01, clause 1 of Article 254 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Purchase of materials for non-cash transactions:
Get 267 video lessons on 1C for free:
| Debit Account | Credit Account | Transaction amount, rub. | Wiring Description | A document base |
| 10.01 | 60.01 | 50 000 | Receipt of supplies | Consignment note (TORG-12) |
| 19.03 | 60.01 | 9 000 | VAT on purchased inventories included | Invoice received |
| 60 | 51 | 59 000 | Payment to the supplier for inventories | Bank statement |
| 68.02 | 19.03 | 9 000 | VAT is accepted for deduction | Book of purchases |
Example 2. Purchase of goods and materials for cash with VAT
Purchasing materials through an accountable person posting:
| Debit account | Credit account | Transaction amount, rub. | Wiring Description | A document base |
| 71.01 | 50.01 | 15 000,00 | Issuance of funds to an employee on account for the purchase of goods and materials | Manager's order, Expense cash order (KO-2) |
| 10.09 | 71.01 | 12 711,86 | Employee's advance report on purchased inventory items | Advance report, Consignment note (TORG-12) |
| 19.03 | 71.01 | 2 288,14 | VAT on purchased inventory items has been taken into account | Invoice received |
| 68.02 | 19.03 | 2 288,14 | VAT is accepted for deduction | Book of purchases |
Example 3. Purchase of goods and materials for cash without VAT
Purchase of materials without VAT through an accountable person posting:
| Debit account | Credit account | Transaction amount, rub. | Wiring Description | A document base |
| 71.01 | 50.01 | 20 000,00 | Issuance of funds to an employee on account for the purchase of goods and materials | Manager's order, Expense cash order (KO-2) |
| 10.09 | 71.01 | 22 500,00 | Employee's advance report on purchased inventory items | Advance report, Sales receipt |
| 71.01 | 50.01 | 2 500,00 | Issuance of funds to an employee (amount of overexpenditure according to the advance report) | Advance report, Expense cash order (KO-2) |
Example 4. Write-off of materials to main production
According to the “4x4 Boards” nomenclature, the organization had a balance of 150 pieces for a total amount of 40,500.00 rubles:
- Let's calculate the average cost: 40,500.00 / 150 = 270.00 rubles;
- Let's calculate the cost of the material transferred to production: 70 * 270.00 = 18,900.00 rubles.
Write-off of materials to main production - postings and documents:
| Debit account | Credit account | Transaction amount, rub. | Wiring Description | A document base |
| 20.01 | 10.01 | 18 900,00 | Transfer of materials to production | Requirement-invoice for release of materials according to form No. M-11 |
Example 5. Write-off of materials for general business expenses
The organization had balances in the range of Notebooks in the amount of 400 pieces for a total amount of 10,280.00 rubles, in the range of Pens in the amount of 550 pieces for a total amount of 8,525.00 rubles.
Let's calculate the average cost:
- notebooks 10,280.00 / 400 = 25.70 rubles;
- pens 8,525.00 / 550 = 15.50 rub.
Let's calculate the cost of written-off material for general business expenses:
- notebooks 50 * 25.70 = 1,285.00 rub.;
- pens 100 * 15.50 = 1,550.00 rub.
Thus, materials with a total cost of 2,835.00 rubles were written off as general business expenses, which is reflected by the posting:
| Debit account | Credit account | Transaction amount, rub. | Wiring Description | A document base |
| 26.01 | 10.01 | 1 285,00 | Write-off of office supplies (notebooks) to the Accounting department | Requirement-invoice for release of materials according to form No. M-11 |
| 26.01 | 10.01 | 1 550,00 | Write-off of office supplies (pens) to the Accounting department |
Features of accounting
According to Chapter 34 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, the type of investment under consideration is fixed assets that are leased by an organization for the purpose of making a profit over a certain period of time.
In accordance with the law, they must be reflected in accounting and reporting.
Reflection
It is necessary to review the Instructions for using the chart of accounts to determine which of them indicates the enterprise's profitable investments. Account 03 of the same name is intended for this, where they are accounted for at their original cost, formed in accordance with the requirements used in the process of accounting for all fixed assets (clause 8 of PBU 6/01).
Analytical accounting of the account must be maintained depending on the type of object and the tenant of the property.
Depreciation of the objects in question is calculated in accordance with the general procedure established for fixed assets (section III of PBU 6/01). Depreciation is displayed on account 02 of the same name.
According to the order of the Russian Ministry of Finance, separate accounting rules are established for the type of investment in question, which is the subject of a leasing transaction.
The organization's income-generating investments are reflected in the balance sheet at their book value. They are included in non-current assets in line 1160 of the same name. It is worth noting that information about them must be fully disclosed in the section of explanations of financial results.
Write-off
Investments made by an enterprise for the purpose of making a profit are subject to write-off from the balance sheet in the cases established for all categories of fixed assets.
The need for this procedure arises when property is disposed of from the company's ownership. Also, write-off occurs when material assets lose their ability to bring economic benefits to the company, regardless of the reasons. Income and expenses received from writing off fixed assets from accounting are also subject to crediting. For this purpose, the profit and loss account is used. They are indicated as other income and expenses in accordance with clause 31 of PBU 6/01.
In order to account for the disposal of fixed assets, the company needs to open a sub-account with the corresponding name in account 03.
Its credit indicates the amount of accumulated depreciation, and its debit indicates the value of the written-off property. After the disposal procedure is completed, the residual value must be written off from account 03. Then it is transferred to account 91, which reflects other income and expenses.
Entrepreneurs and accountants should take into account that the specific method of accounting for the disposal of fixed assets must be established in the company's accounting policy in the section of accounting purposes in accordance with clause 7 of PBU 1/2008. By specifying a suitable method, the accounting procedure can be significantly simplified. This procedure should be carried out by an experienced specialist who is able to perform it at a professional level and is familiar with innovations in legislation.
Posting examples
To familiarize yourself with the topic in more detail, it is worth considering a specific example.
An enterprise purchases a car for the purpose of renting it out. Its cost was 1,500,000 rubles, VAT – 270,000. The vehicle was purchased through an intermediary, whose services cost 20,000 rubles, VAT – 9,600. An employee of the organization was sent on a business trip to carry out the purchase/sale transaction and subsequent delivery of the car. Costs amounted to 3,000 rubles, VAT – 540 rubles.
The accountant must reflect transactions aimed at acquiring an object with the following entries:
| Debit | Credit | Amount, rubles | Note |
| 19 | 60 | 270 000 | VAT on car |
| 08-4 | 60 | 1 230 000 (1 500 000 – 270 000) | expenses for purchasing a car |
| 16 | 60 | 9 600 | VAT for intermediary services |
| 08-4 | 60 | 10 400 (20 000 – 9 600) | expenses associated with purchasing a vehicle |
| 19 | 71 | 540 | VAT on expenses incurred for an employee’s business trip to purchase a car |
| 08-4 | 71 | 2 460 (3 000 – 540) | travel expenses |
| 68 | 19 | 280 140 (270 000 + 9 600 + 540) | accepted for deduction of VAT on the cost of purchasing a car |
| 03 | 08-4 | 1 242 860 (1 230 000 + 10 400 + 2460) | car cost |
This example allows you to understand how the accounting procedure is carried out using the example of a company purchasing a car, which occurs quite often.
Nuances: write-off of materials during construction
While an organization is conducting its activities, it is often necessary to write off materials that have become completely unusable. The process is distinguished by its features in accounting policies. They depend on:
- Proof of the guilt of a specific employee or any other person that everything went wrong.
- Standards for writing off inventories. Are these standards exceeded or fully complied with?
Cleaning equipment
As for the price of damaged materials, it is written off within the limits of norms associated with natural loss. The process uses accounts that list production costs. The standards are exceeded if the presence of guilty persons is proven or there are additional costs.
The following addition is provided for those who work with the write-off of low-value, wear-and-tear goods. Accountants can write off the cost at the same moment when the object is put into operation. It is permissible to carry out so-called uniform accounting. But the application of the scheme is relevant in the case of items with a service life of 1 year or more. In the accounting policy it is necessary to write about which method is used in a particular case.
Inventory and household supplies are a group of items for which calculations are carried out using similar schemes. Legislatively, the composition of the group itself is not detailed. But in practice, this property includes:
- Equipment for cleaning the area, fire extinguishing equipment
- Electronic equipment such as cameras and video recorders
- Kitchen appliances
- Office furniture
The cost of materials largely determines how much the work itself, where these objects are used, will cost. This is especially important for those objects that belong to the elite category. When an organization draws up an estimate, it is important to lay down certain standards associated with costs.
Inventory commission
Standards for estimates are a whole set of data on prices, where items are combined into separate categories. This is necessary in order to understand how much certain actions will cost.
The estimate norm is all the resources in the aggregate established for the adopted meter in various types of work. Estimated standards perform one main function - calculating the amount of resources that are normally required to complete a particular process.
But the documents are drawn up on the basis that normal conditions are observed during the implementation of the project, and that no external factors complicate this process. If any complications are present, then special coefficients are simply added to the documentation to the calculation results. The coefficients themselves are described in legislative norms.
Estimated standards are:
- Regional.
- Departmental.
- Federal.
Users can create their own database. Several generally accepted methods are used to determine costs in construction. Some of them are transferred to other directions.
- Resource method. All costs in this method are simply summed up in physical terms with current prices. Among the indicators used, it is worth noting:
- Consumption of materials with components.
- The period during which machines are used in construction.
- Labor intensity.
- Basis-index calculations. In this method, the cost of construction is determined in its own way. To obtain the result, experts add up the prices of all types of building materials, which can be called consolidated. The resulting amount is multiplied by indices after recalculating the base prices into current ones.
- Resource-index methods. The resource method determines the total using basic prices. Then multiplication by indices is carried out, bringing the cost to the modern level.
- Basic compensation option. The cost of work and expenses is summarized at a basic level. To these are added additional costs associated with the fact that market indicators have changed quite significantly.
- Using data about objects that have already been built.
Account 10.08 “Building materials” takes into account materials used for construction, installation and repair work, if the organization is not engaged in construction. In a construction organization, such materials are accounted for in account 10.01 “Raw materials and materials”.
On the Materials tab, specify the list of materials used in construction.
We suggest you read: How to buy a share in an apartment from a relative
On the Cost Account tab, enter:
- Cost account - 08.03 “Construction of fixed assets”;
- Construction sites - Finished products warehouse: a construction site where all costs for creating an operating system are collected;
- Cost item - a cost item with Expense Type Material costs;
- Construction methods - Economic method, because construction is carried out in-house.
The document generates transactions
- Dt 08.03 Kt 10.08 – the cost of materials is taken into account when determining the initial cost of the fixed assets.
See also Creation of OS economic method (CMP)
Importance in the activities of the enterprise
The stability of the enterprise directly depends on the level of provision with material assets. The production process and positive financial results are the main criteria for assessing the availability of resources.
Here it is important to understand what the structure of material assets consists of and what is the share of each individual type in the total value of assets. There is a calculation formula: Kma = MA: A, where MA is the book value of tangible assets, A is the book value of all assets
There is a calculation formula: Kma = MA: A, where MA is the book value of tangible assets, A is the book value of all assets.
Who is a material desk accountant?
An accountant of any department is, first of all, a specialist involved in accounting. No matter the size of the enterprise, such an employee must be present. If the organization is small, then one employee is responsible for maintaining all areas of accounting: payroll, inventory accounting, working with suppliers and contractors, generating and submitting reports, and much, much more.
If the enterprise is large, then an entire accounting service is created, headed by a chief accountant. Each specialist is assigned a specific area of work. In very large corporations, accounting specialists will be divided into departments, for example, a material department, where each specialist will be responsible for accounting for a certain type of inventory.
The position of a material accountant is one of the most difficult, as it requires the greatest scrupulousness, perseverance and even pedantry. Usually such places are occupied by women, since such a task is too painstaking for men.
With the advent of computer technology and special programs, the work of an accountant has become easier. A material desk accountant has to work with a huge amount of paper documents every day. This is a high-level specialist, since at any moment he must provide accurate information about the availability of material assets.
In order to understand the essence of the work of a material accountant, you must first understand the subject of accounting. Inventory and materials are the current assets of an enterprise; without them, its normal existence is not possible and they are in constant motion. Briefly, inventory items can be called industrial inventories and include the following groups of materials:
- raw materials and materials;
- spare parts;
- semi-finished products, both our own production and purchased from suppliers;
- finished products of own production;
- purchased goods;
- fuels and lubricants (fuels and lubricants - gasoline, diesel fuel, oil, antifreeze and similar materials);
- returnable waste and useful residues;
- household equipment;
- container
That is, a material accountant is engaged in accounting for the current assets of the enterprise, objects of labor, and other material assets used in the production process, which have a direct impact on changes in the cost of the final product.
This position is mainly in demand at enterprises involved in the production of various products.
Accounting for material assets occurs at enterprises in various industries, but the accounting officer has a slightly different area of activity and name. So in the field of trade - this is a storekeeper or warehouse manager, in enterprises involved in transportation - a specialist in accounting and write-off of fuels and lubricants.
The essence of the activity is, of course, very similar, but a material table accountant is a specialist of a higher level and qualification.
Results
Accounting for inventory at an enterprise requires the development of a methodology specially selected for a specific case. This methodology is reflected both in the accounting policy and in the internal regulations for working with inventory items. In our article, we examined the main issues that should be disclosed in these documents.
Sources:
- PBU 5/01, approved. by order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated 06/09/2001 N 44n
- FSBU 5/2019, approved. by order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated November 15, 2019 N 180n
You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Full and free access to the system for 2 days.
Warehouse for third parties
After receipt, the goods are sent to storerooms or warehouses. There they are stored until further use. Sometimes entities provide their own premises for storing foreign goods and materials. Thus, stocks are subject to storage not only as a result of their own acquisition. Of course, such an operation is not related to the production of the entity, therefore it is reflected in the off-balance sheet account 002, where inventories in secondary storage are recorded.
The essence of inventory items is that they are current assets, that is, they constantly move in production cycles, arriving and departing from various accounting sectors. Options for disposal of material assets:
- release for processing;
- transfer for own use;
- transfer for sale;
- departure due to an unforeseen situation.
As with the receipt, in each case of expense, various documents are drawn up. For example, the release of materials according to standards requires an M-8 limit card. If stocks are not limited, then a regular invoice M-11 is generated. If inventory items are sold for resale, they are accompanied by an M-15 invoice.
Write-off of materials: detailed instructions
https://youtu.be/WGVlSbkFCc4
Materials are inventories that are purchased by an organization. These are the means to obtain products and service the production process. To display such reserves, account 10 is almost always used. Subaccounts are opened for it. To display the movement of fixed assets, you can also use accounts 15 or 16.
Write-off in the program
- Quantitative and price characteristics, amounts.
- The reason why valuables need to be written off.
- The name of the materials themselves.
- Personal information of each member of the commission.
In addition, all participants sign the document. You cannot do without indicating the date by which the procedure was carried out.
Separate entries are made when the materials are already considered written off.
- K94 – if everything happens within the limits of natural decline.
- D20 – information on main production.
- K10 – to reflect the value of materials on the balance sheet.
- D94 – Shortage, loss of specific properties of an item.
Place in accounting
Accounting records and reports all transactions, assets and liabilities. Even the most insignificant inventory items in accounting are reflected in the section of current assets in the form of their balances at the beginning and end of the year. The dynamics of these values throughout the year are shown in accounting registers and primary documents. In general, accounting is based on a double reflection of arrivals and departures in various accounts.
The arrival of material assets is indicated by the following operations:
- delivery under a purchase and sale agreement with payment for the acquired assets;
- conclusion of an exchange agreement and barter receipt of valuables;
- transfer on a free basis from certain suppliers - own founders, managers or third-party organizations and individuals;
- obtaining useful waste and residues during repairs and disassembly of old equipment and machinery;
- production in-house.
Such operations require real documentary evidence. In the case of the purchase of valuables, these are invoices and invoices from suppliers and the formation of receipt orders on their basis in the form of 4-M forms. Such orders fill out general warehouse records in the form of an M-17 card.
If the delivery of assets is carried out without filling out invoices, delivery notes and orders, then according to the rules of document management, at least a transfer act of form M-7 is generated. Such acts are drawn up when posting the delivery and reconciling it with the delivery documents. If during such control a surplus of goods is identified, it is recorded as an accounting liability. Shortages, as a rule, result in questions about this to suppliers.
A common practice is to accept purchases from forwarders, couriers and other similar persons, for whom a power of attorney for representation of one of the forms - M-2 and M-2A - is required to be drawn up and certified. When self-made goods and materials arrive at the warehouse, an invoice-request M-11 is generated.
In the case of dismantling of machinery and equipment, as a result of which useful spare parts were obtained, their arrival is documented by act M-35, which, in addition to information about the valuables themselves, provides information about the disassembled fixed asset.
Accounting for inventory items in accounting: postings and documents
Inventory assets received during the inventory must be received after the inventory according to the register or commodity report. During the inventory, these values are entered into a separate inventory, which is called “Inventory assets received during the inventory.” The inventory indicates the date of receipt, the name of the supplier, the date and number of the receipt document, the name of the product, quantity, price and amount, and on the receipt document an o is made with reference to the date of the inventory. If, due to production needs, valuables are released during the inventory, the released values are entered in a separate inventory under the title “Inventory items released during the inventory.” An inventory is drawn up by analogy with documents for incoming inventory items during inventory.
For inventory items in transit, a separate inventory report of materials and goods in transit is drawn up in the INV-6 form. This act provides the following data for each individual shipment: name, quantity and value, date of shipment, as well as the list and numbers of documents on the basis of which these values are recorded in the accounting accounts.
For inventory items shipped and not paid for on time, an inventory report of goods shipped in the INV-4 form is generated. The act for each individual shipment contains the name of the buyer, the name of the inventory items, the amount, the date of shipment, the date of issue and the number of the payment document.
For inventory items stored in warehouses of other organizations, an inventory list is formed in the INV-5 form. Entries in the inventory are entered on the basis of documents confirming the delivery of these valuables for safekeeping. The inventory indicates the name of the valuables, quantity, grade, cost (according to accounting data), date of acceptance of the cargo for storage, storage location, numbers and dates of documents.
The inventory of inventory items that are not under the control of financially responsible persons at the time of inventory consists of checking the validity of the amounts listed in the relevant accounting accounts. Amounts must be supported by properly executed primary documents.
Containers are reflected in inventories by type, intended purpose and quality condition. For containers that have become unusable, the inventory commission draws up a write-off report indicating the reasons for the damage.
If, as a result of the inventory, discrepancies are revealed between the actual availability and accounting data, a comparison sheet of the results of the inventory of inventory items is formed according to form No. INV-19. The assessment of unaccounted for values identified by the inventory must be made taking into account market prices. Surpluses and shortages of inventory items identified during inventory are reflected in the organization’s accounting records.
Write-off of materials for production
There are several ways to write off materials for production:
- document Requirement-invoice in the section Production – Production – Requirements-invoice;
- document Production report for a shift in the section Production – Product output – production reports for a shift.
The document Requirement-invoice is used if materials are written off in total quantities into production, without dividing them into a specific output.
The legislation does not have strict and clear rules that would describe in detail the write-off process. It is usually said that it is necessary to rely on the volume of the production program and the standards according to the same document. The main thing is that the total amount of valuables does not become uncontrollable. And so that the norms themselves are officially approved.
Write-off according to standards
For consolidation, you can use estimates, technological maps and similar documents. They are developed in departments that personally control the production process. After this, the papers are sent to the manager for approval.
A situation where existing standards are exceeded is acceptable, but each such case requires a separate indication of the reasons. For example, the explanation could be technological losses or the need to fix a defect.
It becomes the responsibility of managers and authorized persons to formalize decisions to exceed the current norm. To do this, a corresponding mark is placed on the primary accounting document. Otherwise, the write-off itself will not be recognized as legal. The cost price will be distorted, which leads to violations in accounting and tax reporting.
Regulatory regulation
Such operations are regulated through documents at various levels. On a general scale, these are government decrees, regulations, orders. At the local level, we are talking about acts, orders, and other regulatory papers.
Thus, the procedure for writing off inventory items requires a special approach and knowledge of the matter. Failure to comply with legal regulations is fraught with a high level of liability and distortion of materials in accounting information.
A competent approach to the operation guarantees successful paperwork and the absence of problems with regulatory authorities, as well as stable profit generation.
You can learn how to write off damaged goods and materials in this video.