General information
The concept of a living wage
The subsistence level is usually understood as the amount of money per person that he needs to finance his basic needs.
That is, this is the minimum cost of the subsistence basket, which includes food and non-food products, as well as the cost of services (utilities, transport costs, etc.).
The composition of the consumer basket is periodically reviewed (every five years). This indicator is set by the federation and local authorities, taking into account the living conditions in each region. This value is calculated quarterly for each category of citizens (able-bodied, pensioners, children).
Attention! Its value is used in determining the minimum wage, minimum amounts of benefits and pensions. The cost of living indicates the well-being of citizens and how effectively the state implements social policy in the country.
The cost of living in Russia
The cost of living is calculated based on existing prices for goods and services, taking into account established inflation rates. The formula for determining this value includes the norms of consumption of goods and basic services established
Rosstat price index, as well as the existing demand for this product among citizens. Initially, a federal calculation is made, and then local authorities form a local minimum based on it.
The cost of living is determined after a quarter. Therefore, the value currently in effect is that which was calculated based on data from the 3rd quarter of 2021.
The following federal values of this indicator can be distinguished:
- for the working population - 11,310 rubles;
- for a pensioner - 8846 rubles;
- for minors - 10,302 rubles.
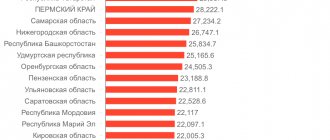
Attention! These values are all-Russian. Each subject sets its own values.
Living wage in bankruptcy
The adoption by the Arbitration Court of a decision to declare a debtor citizen bankrupt will be the basis for the formation of a bankruptcy estate. At the expense of this mass, all possible settlements with creditors will be made. One of the ways to replenish the bankruptcy estate is precisely the debtor’s income.
A component of these incomes is wages. In different situations, the level of the debtor varies differently. For some, this income is equal to the minimum wage, and for some it reaches 100,000 rubles.
In any case, as a general rule, the subsistence minimum must be excluded from the bankruptcy estate. By the way, in our region, according to the latest act adopted, it was equal to 10,933 rubles per month. It follows that every month, as part of the current bankruptcy procedure, you will be returned the established amount of the subsistence minimum.
Can wages be below the subsistence level?
The Labor Code of the Russian Federation establishes that wages should not be less than the subsistence minimum. But this is a theory. Since this indicator is revised quarterly, the comparison is made with the minimum wage, which is determined for the current year on the basis of the subsistence minimum in force in the second quarter of the previous year. Therefore, when comparing, it is assumed that the salary will be less than the subsistence minimum for the selected period.
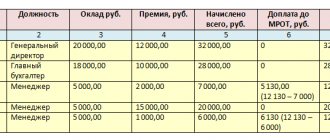
In addition, it must be taken into account that the salary for comparison should be summed up, and not for any part of it. Thus, in the presence of bonuses and additional payments, the answer to the question - can the salary be less than the subsistence minimum - becomes clear - yes.
You might be interested in:
Dismissal of an employee due to death: what date is the order issued, how to issue it
It is also taken into account whether the salary was paid for the entire standard duration of the month, or whether it is due to the employee at a certain rate, for example, 50%. That is, when working part-time, it is allowed that the accruals made to the employee may be less than the subsistence level.
Attention! It is necessary to understand the difference between accrued and paid wages. Therefore, when determining whether an employer can legally pay its employee less than the cost of living, the answer is yes.
Responsibility for wages below the minimum wage
If an organization has assigned a salary to an employee, taking into account all permitted allowances, less than the established minimum wage, it must make an additional payment up to the minimum wage. If you do not do this, you can receive a large fine under Art. 5.27 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation for violating the requirements of labor legislation. The fine will be:
• for a legal entity - from 30,000 to 50,000 rubles;
• for officials - from 10,000 to 20,000 rubles;
• for individual entrepreneurs - from 1000 to 5000 rubles.
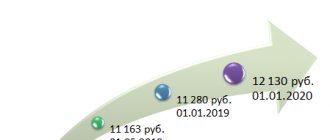
Let us remind you that today in Russia as a whole the minimum wage is 9,489 rubles (Article 3 of the Federal Law of December 28, 2017 N 421-FZ). From May 1, 2021, it will increase to 11,163 rubles per month. Regions of the Russian Federation can set their own minimum wage, the value of which cannot be lower than the federal one. The regional minimum wage is mandatory for all employers, except for the public sector.
Source: https://ppt.ru
No ConsultantPlus?
Fill out a request for delivery of the full version of the document or select a kit , taking into account the characteristics of your organization
Where and how to complain about low wages?
If the wage is set below the minimum subsistence level (minimum wage), then the employee can file a complaint against the employer with the trade union, labor inspectorate, prosecutor's office or court.
Labour Inspectorate
The first regulatory body to which an employee should file a complaint about a small salary is the labor inspectorate. This body is precisely intended to monitor compliance with current labor legislation.
You can write the application directly to the inspectorate, submit it with your authorized representative, or use the mail. Upon application, the inspector must conduct an inspection of the company’s activities and, if necessary, issue an order to eliminate shortcomings. It is also within his competence to impose an administrative fine.
If the results of the inspection are unsatisfactory, you can complain to a higher inspection, or submit applications to the prosecutor's office or court.
Attention! It should be noted that the labor inspectorate cannot oblige the payment of funds - this can only be done as a result of legal proceedings.
Prosecutor's office
A body that has the right to receive complaints from employees regarding violations of labor laws and conduct inspections.
In order to fill out an application, you must contact the prosecutor's office in person and write it to the employee on duty, and also hand it over with your authorized representative who has a power of attorney, or send it by postal service.
Checks on complaints are carried out suddenly, without prior notification to the company. Based on the results, the employer may be given an order to eliminate violations, and in some cases, the inspection materials may be transferred to the judicial authorities.
For what reasons might wages be less than the minimum wage?
In accordance with Part 1 of Art. 59 of the Labor Code of the Republic of Belarus, Art. 1 of the Law of the Republic of Belarus “On the establishment and procedure for increasing the minimum wage”, the minimum wage (monthly and hourly) is the state minimum social standard in the field of remuneration, which the employer is obliged to apply as the lower limit of wages for workers for work under normal conditions during normal working hours when performing the employee’s duties arising from legislation, local legal acts and an employment contract.
Monthly minimum wage
– the minimum amount of remuneration for employees for a calendar month established by law is applied to employees whose remuneration is made on the basis of monthly tariff rates (salaries, official salaries).
Resolution of the Council of Ministers of the Republic of Belarus dated August 29, 2019 No. 582 established the monthly minimum wage from January 1, 2020 in the amount of 375 rubles.
Hourly minimum wage - calculated from the monthly minimum wage established by law, the lowest amount of remuneration for workers for one hour of working time, is applied to employees whose wages are paid on the basis of hourly tariff rates (salaries, official salaries).
Hourly minimum wage
determined by the employer by dividing the amount of the monthly minimum wage by the ratio of the estimated standard working time for the calendar year, established for the relevant categories of workers by the employer in accordance with labor legislation, and the number of months of the calendar year.
Thus, with the estimated working time according to the production calendar for 2021 for a 40-hour five-day work week with days off on Saturday and Sunday - 2032 hours, the hourly minimum wage will be 2.21 rubles. (375 / (2032 / 12).
The results of the analysis of the reasons for accruing wages to employees of organizations in the Vitebsk region below the monthly minimum wage indicate that in the vast majority of cases these reasons are related to the duration of working hours (working by the employee on a part-time basis, being on leave without pay in connection with training, for family, domestic and other valid reasons, or on leave without pay or with partial pay at the initiative of the employer, downtime not through the fault of the employee, etc.).
The estimated standard working time for a five-day work week with days off on Saturday and Sunday in February 2021 is 160 hours, in March 2021 – 176 hours.
For example, if an employee whose wages are paid on the basis of a monthly tariff rate, with a five-day working week with days off on Saturday and Sunday, is assigned part-time work of 20 hours a week (from Monday to Friday, 4 hours a day), when performing responsibilities arising from legislation, local legal acts and an employment contract, in February 2021, the working hours under normal conditions amounted to 80 hours (20 days of 4 hours each), and the amount of accrued wages was lower than the monthly minimum wage, the employer is obliged to make an additional payment up to the monthly minimum wage, that is, up to 187.5 rubles. (375 rubles / 160 hours x 80 hours), unless the collective agreement (agreement) establishes a larger monthly minimum wage. In a similar situation, an employee whose wages are paid on the basis of an hourly tariff rate will receive an additional payment of up to 176.8 rubles. (80 hours x 2.21 rubles).
If an employee, whose wages are paid on the basis of a monthly tariff rate, with a five-day working week with days off on Saturday and Sunday, worked from February 3 to February 7, 2020 (5 days for 8 hours, 40 hours in total), and from 10 to 28 February 2020 was temporarily disabled, the amount of accrued wages must be at least 93.75 rubles. (375 rubles / 160 hours x 40 hours). In a similar situation, an employee whose wages are paid on the basis of an hourly tariff rate will receive an additional payment of up to 88.4 rubles. (RUB 2.21 x 40 hours). Temporary disability benefits are calculated in accordance with the established procedure.
According to Part 1 of Art. 71 of the Labor Code of the Republic of Belarus, in case of non-compliance with production standards, defects and idle time not due to the fault of the employee, the wage cannot be lower than two-thirds of the tariff rate (tariff salary) established for him.
An employee whose wages are paid on the basis of a monthly tariff rate, with a five-day working week with days off on Saturday and Sunday, who worked only from March 2 to March 6, 2021 due to downtime not due to the employee’s fault from March 9 to March 31, 2021, the amount accrued wages must be at least 85.23 rubles. (375 rubles / 176 hours x 40 hours). In a similar situation, for an employee whose wages are paid on the basis of an hourly wage rate, the amount of accrued wages must be at least 88.4 rubles. (RUB 2.21 x 40 hours). In addition, wages during downtime through no fault of the employee must be no lower than two-thirds of the tariff rate established for him.
An employee whose wages are paid on the basis of a monthly tariff rate, with a five-day working week with days off on Saturday and Sunday, who worked only from March 16 to March 31, 2020 (12 days for 8 hours, a total of 96 hours) due to being on vacation without pay from March 2 to March 13, 2021, the amount of accrued wages must be at least 204.55 rubles. (375 rubles / 176 hours x 96 hours). In a similar situation, for an employee whose wages are paid on the basis of an hourly tariff rate, the amount of accrued wages must be at least 212.16 rubles. (RUB 2.21 x 96 hours).
Employees who, without good reason, have not fulfilled the obligations arising from legislation, local legal acts and an employment contract, for example, including those who have committed absenteeism or been absent from work without good reason for a short time, should not receive additional payment up to the minimum wage.
Methodological aspects: “On the minimum wage”
Deputy Head of the Department for Supervision of Compliance with Labor Legislation of the Vitebsk Regional Administration of the Department of State Labor Inspection G.A. Galai, “Vitebsk News”, March 26, 2021
Judicial practice on this issue
The court is the only body capable of making a decision on the recovery of funds from the employer. In this case, you can request not only the funds themselves, but also compensation for their underpayment.
To file a claim, you must write an application and attach supporting documents to it. Ideally, these should be pay slips that directly indicate the amounts of accruals and deductions.
Judicial practice on issues of additional calculation of wages up to the minimum wage is extensive, and almost always the trial ends in favor of the employee. It is impossible to attribute a low minimum wage to a lack of funds.
Disputes often arise over the procedure for calculating wages using northern allowances. Thus, employers often set the salary level so that after all calculations it is no less than the minimum wage.
Important! However, the court’s position in this case is that earnings must be no less than this level until all increasing factors are applied. As a result, firms have to recalculate wages and pay the difference to employees.
Legal minimum
The subsistence minimum is the minimum amount that consists of the consumer’s conditional consumer basket, consisting of food, taxes and fees, utilities, medical services, and other goods and services. The living wage and the minimum wage (minimum wage) are interconnected. The salary paid to the employee should not be less than the established subsistence level, but in practice it happens differently. Citizens whose income does not reach the subsistence level are considered low-income.
Employer's liability
If an employer pays a salary less than the subsistence minimum, no explanation will help - he may be brought to administrative (most often) or criminal (in some cases) liability.
You might be interested in:
Dismissal for repeated failure by an employee to fulfill his job duties: step-by-step instructions
Administrative
If the employer does not pay wages, or he has set it less than the legally established amount, then he is held accountable on the basis of clause 6 of Art. 5.27 Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation.
It provides a minimum of the following responsibilities:
- For an official, a fine of 10-20 thousand rubles;
- For an entrepreneur, a fine of 1-5 thousand rubles;
- The fine for the organization is 30-50 thousand rubles.
If this offense is registered with this employer again, the consequences will include sanctions:
- For an official, a fine of 20-30 thousand rubles or disqualification for a period of 1-3 years;
- For an entrepreneur, a fine of 10-30 thousand rubles;
- The fine for the organization is 50-100 thousand rubles.
Criminal
Criminal liability occurs when a manager pays a salary below the established minimum wage (subsistence level) for 2 or more months, and does this for personal gain. The punishment is established by Art. 145.1 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation.
It provides the following responsibilities:
- A fine of 100-500 thousand rubles or income for a period of up to 3 years;
- Forced labor for a period of up to 3 years, with deprivation of the right to hold a position for the same period;
- Imprisonment for a period of up to 3 years, with deprivation of the right to hold office for the same period.
If the crime entailed serious consequences for the employee (for example, driving to suicide, begging and vagrancy, etc.), then the punishment increases:
- A fine of 200-500 thousand rubles or income for a period of 1-3 years;
- Imprisonment for a period of 2-5 years, with deprivation of the right to hold office for a period of up to 5 years.
What threatens the employer if the salary is below the minimum wage?
Compliance by employers with the minimum wage is guaranteed by the following regulations:
- Constitution of the Russian Federation (Article 7).
- Labor Code of the Russian Federation (Article 133 and 133.1).
- Law No. 82 (Article 2 and 3).
Ignoring the requirements for compliance with the minimum wage on the territory of the Russian Federation entails liability:
Administrative liability - fine
The violation consists in the determination by the culprit of wages in an amount less than that provided for by labor legislation.
Responsibility under Part 6 and Part 7 (repetition) of Article 5.27 of the Code of Administrative Offenses:
- the violator is an individual entrepreneur - a fine of 1 to 5 thousand rubles will be imposed (if repeated - 10-30 thousand rubles);
- the culprit is an official - they will issue a warning or be fined 10-20 thousand rubles (if repeated - 20-30 thousand rubles);
- if the offender is an organization, then the fine is from 30 to 50 thousand rubles (if repeated - 50-100 thousand rubles).
In parallel, the manager also bears responsibility (part 3 of article 2.1 of the Administrative Code).
Criminal penalty
They may be held liable if an employer pays employees less than the established minimum wage for more than two months A prerequisite is personal or selfish interest.
Liability under Part 2 and Part 3 (grave consequences) of Article 145.1 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation:
- A fine of 100-500 thousand rubles (for serious consequences - 200-500 thousand rubles).
- Forced labor for up to 3 years (part 2 only).
- Imprisonment for a period of up to 3 years (with grave consequences from 2 to 5 years).
Additionally, they may be prohibited from holding a position or conducting a specific activity for a period of 3 (part 2) to 5 years (part 3).