The costs of holding a corporate event are reflected in the company’s accounting records as part of other expenses and do not affect the amount of income tax (there is an alternative option). Amounts of “input” VAT on purchases for the event are not refundable. In some cases, it will additionally be necessary to accrue and pay personal income tax on the benefits received by the company’s employees.
The personnel policy of many organizations involves celebrating employees together. This is an opportunity to strengthen team spirit, unite the team, and take a break from work issues. Large holdings annually prepare corporate programs for the New Year, company birthdays, and other holidays. The most common expenses of funds:
- rental of premises for an event;
- organization and service (host, musical accompaniment, waiters, etc.);
- cost of the menu at the banquet;
- room decoration, etc.
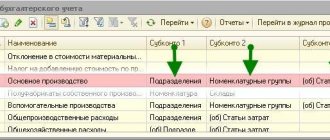
Accounting for corporate party expenses is carried out as part of other expenses (account 91.02) in correspondence with the accounts of counterparties (or).
Is it possible to reduce income tax
In most cases, the costs of holding corporate events amount to a very large amount, so companies are beginning to look for ways to take into account the costs incurred when calculating income taxes. However, Art. 252 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation determines that when calculating the tax base for income tax, only economically justified expenses supported by documents can be taken into account. Cash expenses must be inextricably linked with the ongoing business activity (aimed at generating income in the future).
In addition: accounting entries for income tax accounting.
There are two ways to conduct a corporate accounting meeting:
- Event for company employees. In this case, the costs of a corporate event do not fall under the legally approved definition of justified expenses; they cannot be deducted from the tax base; the event is paid for from net profit. In the company's accounting records, such expenses are reflected in full, so the company has a permanent tax liability (20% of the amount of displayed expenses).
- There is an alternative way to conduct a corporate event, when part of the expenses can be taken into account as entertainment expenses. To do this, you should invite business partners to the celebration.
Requirements for a representative event:
- an order, certified by the company’s management, to hold a celebration with representatives of partner companies to discuss cooperation;
- a program for the future event has been drawn up;
- a cost estimate has been drawn up. All incurred expenses of funds have documentary evidence (agreements, acts, UPD, TORG-12 and invoice, etc.);
- Business partners are invited to the event;
- expenses are reimbursed directly for the official part of the gala evening (banquet menu, room rental). Entertainment expenses are not included;
- payment documents confirming expenses;
- upon completion of the corporate event, a report on its results is compiled;
- Attached is a calculation of the standard for entertainment expenses.
Limitation! The law sets a limit on entertainment expenses - no more than 4% of personnel costs. Everything above is covered by the company’s net profit.
Corporate for employees - accounting for an accountant
From the article you will learn:
1. Is it necessary to charge personal income tax and insurance premiums on the cost of participation in a corporate event?
2. Is it possible to accept expenses for corporate events for tax accounting?
3. How to reflect the holding of a festive event for employees in accounting.
Holding corporate entertainment events is a great way to combine business with pleasure. On the one hand, this is an opportunity to relax and escape from everyday work, and on the other hand, such events help strengthen team spirit and improve relationships within the team. Therefore, almost all employers organize New Year’s banquets, organization “birthdays”, sports competitions, etc. for their employees. – There are a great many options to suit every taste and budget. Moreover, many employers spend quite significant sums on corporate events for employees. In this regard, the issues of accounting and taxation of such costs arise especially acutely, because inspectors are unlikely to ignore the “big party” holiday. Is participation in a corporate event considered employee income? Is it possible to reduce taxes due to “holiday” expenses? – we will consider these and other questions in this article.
Personal income tax on employee income from participation in a corporate event
In order to understand whether participation in a corporate event is the income of an employee from whom personal income tax must be withheld, let us turn to the Tax Code of the Russian Federation:
- when determining the tax base for personal income tax, all income of the taxpayer received by him both in cash and in kind is taken into account (clause 1 of article 210 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
- An employee’s income in kind includes payment (in whole or in part) by the employer for goods (work, services) or property rights, including food and rest. The tax base is defined as the cost of such goods (work, services) (clauses 1, 2 of Article 211 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
When organizing a corporate party for employees, the employer pays for the rental of the hall, banquet services and meals, entertainment services, travel arrangements to the event venue and other expenses. Thus, employees taking part in a corporate event receive a material benefit equal to the cost of the specified services (goods) per person. From this amount the employer, as a tax agent, must calculate and withhold personal income tax.
This position is adhered to by the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation; moreover, representatives of the department explain that the employer must take all possible measures to assess and take into account the economic benefits (income) received by employees from participating in corporate events (Letters of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated August 14, 2013 No. 03-04- 06/33039, dated 04/03/2013 No. 03-04-05/6-333, dated 03/06/2013 No. 03-04-06/6715). Such measures include compiling last name lists of employees actually present at the corporate event, using rented transport to travel to the event venue, etc. In this case, the taxable income of each employee is calculated by dividing the total amount of expenses for holding a corporate event by the number of participants.
However, in real life, determining the income of each employee from participation in a corporate event is often quite problematic. The most common case is the lack of reliable information about the number and composition of participants. In such situations, when it is impossible to personify and evaluate the economic benefit received by each specific employee, income subject to personal income tax does not arise. This opinion is shared by the Ministry of Finance (Letters of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated 08/14/2013 No. 03-04-06/33039, dated 04/03/2013 No. 03-04-05/6-333, dated 03/06/2013 No. 03-04-06/6715) and judicial authorities (Resolutions of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the Northern Territory of February 21, 2008 No. A56-30516/2006, Federal Antimonopoly Service of the Moscow Region of September 23, 2009 No. KA-A40/8528-09).
! Please note: To ensure that tax inspectors do not have grounds to charge additional personal income tax on employee income from participation in a corporate event, it is better to avoid directly indicating the quantity in documents related to its holding (contracts, invoices for payment, certificates of services rendered, etc.) participants of the event, cost per person, and even more detailed lists of those present.
Insurance premiums from the cost of participation in a corporate event
Insurance contributions to the Pension Fund of the Russian Federation, the Federal Compulsory Medical Insurance Fund and the Social Insurance Fund are levied on payments and other remuneration made within the framework of labor relations (clause 1, article 7 of the Federal Law of July 24, 2009 No. 212-FZ “On insurance contributions to the Pension Fund of the Russian Federation, the Social Insurance Fund of the Russian Federation”). Federation, Federal Compulsory Medical Insurance Fund"). Such payments include wages and other accruals included in the remuneration system, such as bonuses and gifts given as incentives for work. At the same time, the base for calculating contributions includes payments and rewards not only in cash, but also in kind.
However, there is no need to charge insurance premiums for the cost of employee participation in a corporate event. This clarification was given by the Ministry of Labor in Letter No. 14-1-1061 dated May 24, 2013. According to paragraph 4 of this letter, the organization’s expenses for holding corporate events on the occasion of holidays are not targeted payments in favor of specific employees. Therefore, contributions to extra-budgetary funds are not subject to taxation.
Accounting for corporate expenses when calculating income tax, simplified tax system
The costs of organizing and holding a festive corporate party can be very significant. Therefore, the question of including these amounts in tax expenses worries many accountants. Let's figure it out.
In accordance with the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, expenses for tax accounting purposes are recognized as justified, that is, economically justified, and documented expenses (clause 1 of Article 252 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). In addition, the expenses must relate to activities aimed at generating income. It is obvious that the costs of corporate entertainment events are not justified from an economic point of view and are not associated with generating income. Therefore, when calculating income tax, expenses for holding a corporate event do not reduce the tax base.
When calculating tax according to the simplified tax system (with the object of taxation “income-expenses”), expenses for holding a corporate event also cannot be taken into account, since they are not included in the closed list of accepted expenses established in Art. 346.16 Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Thus, the costs associated with holding entertainment corporate events are not taken into account either when calculating income tax or the simplified tax system. This position was expressed many years ago by representatives of the Ministry of Finance (Letters of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated December 20, 2005 No. 03-03-04/1/430, dated September 11, 2006 No. 03-03-04/2/206).
What to do in this case? There are at least two options: do not accept corporate expenses for tax accounting and sleep peacefully, or try to “disguise” these expenses as accepted ones.
The most common option for disguising expenses for a corporate event is to register them and record them as entertainment expenses. Let me make a reservation right away that this option is not suitable for organizations using the simplified tax system, since entertainment expenses, like expenses for a corporate event, do not reduce the tax base for the single tax. But organizations that pay income tax have the right to take entertainment expenses into tax accounting (clause 1, paragraph 22, article 264 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation), but their amount should not exceed 4% of labor costs.
! Please note: When choosing this option for accounting for expenses for a corporate event, you need to make sure that the documents “clearly” show the fact of holding a representative event, that is
- Representatives of other organizations (business partners, clients, potential clients, etc.) are invited.
- The event is official and not entertainment in nature. Entertainment expenses include expenses for an official reception (breakfast, lunch or other similar event) of representatives of other organizations and representatives of the taxpayer, transportation support for the delivery of these persons to the venue of the event, and buffet service. But expenses for organizing entertainment and recreation do not apply to entertainment expenses (clause 2 of Article 264 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
- there are all the necessary primary accounting documents (contracts, certificates of services rendered, etc.), as well as supporting documents (an order for a hospitality event, an estimate of entertainment expenses, a report on the event, indicating the purpose and results achieved, etc.). d.) (Letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated November 1, 2010 No. 03-03-06/1/675).
For example, a New Year's banquet, if in addition to employees, representatives of business partners are also invited to it, it is quite possible to register and record it as a representative event, the purpose of which is to sum up the results of the outgoing year and discuss plans for cooperation for the next year. In this case, of course, the conditions listed above must be met, otherwise inspectors will have every reason to reclassify such expenses and charge additional income tax.
VAT on the cost of the corporate event
Organizations and individual entrepreneurs that are VAT payers have the right to reduce the calculated tax by the amount of input VAT. In this case, only those amounts of tax that were presented to the taxpayer in connection with the purchase of goods and services intended for carrying out transactions recognized as objects of taxation under VAT are subject to deduction (clause 2 of Article 171 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Therefore, it is impossible to deduct VAT on the cost of goods and services purchased for a corporate event. When carrying out corporate events, the object of VAT taxation, and, accordingly, the right to deduction, does not arise (Letters of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated December 13, 2012 No. 03-07-07/133 and dated March 28, 2011 No. 03-07-07/11) .
Accounting
In accounting, unlike tax accounting, expenses for holding a corporate event must be reflected in full, as part of other expenses. In this regard, organizations that are taxpayers for income tax and apply PBU 18/02 “Accounting for calculations for income tax of organizations” have a permanent tax difference in the amount of costs for carrying out the event and, accordingly, a permanent tax liability. Let me remind you that small businesses are not required to apply the specified PBU.
I propose to consider the accounting procedure for corporate events using an example.
Example. The head of Snezhinka LLC decided to organize a New Year's corporate party for employees. For this purpose, cafe services for banquet services and hall rental were purchased in the amount of 118,000 (including VAT 18,000), as well as the services of a toastmaster - an individual not registered as an individual entrepreneur, in the amount of 25,000. The LLC entered into an agreement with the toastmaster civil contract. LLC applies the general taxation system. According to the accounting policy for tax accounting purposes, the LLC applies PBU 18/02.
| Debit | Credit | Sum | Contents of operation |
| Cafe services | |||
| 91/2 | 60 | 100,000 rub. | Cafe services for banquet services and hall rental were accepted for accounting on the basis of an act of services rendered |
| 19 | 60 | 18,000 rub. | The amount of VAT on the cost of cafe services has been taken into account |
| 91/2 | 19 | 18,000 rub. | The VAT amount is written off for other expenses |
| 60 | 51 | 118,000 rub. | Funds were transferred to pay for cafe services |
| 99 | 68/Income tax | RUB 23,600 | A permanent tax liability is reflected (118,000 x 20%) |
| Toastmaster services | |||
| 91/2 | 76 | 25,000 rub. | Toastmaster's services are accepted for accounting on the basis of the act of services rendered and the contract. |
| 76 | 68/NDFL | RUB 3,250 | Personal income tax withheld from the amount of remuneration to an individual (25,000 x 13%) |
| 76 | 51 | RUB 21,750 | Remuneration transferred to an individual for the services of a toastmaster |
| 91/2 | 69 | RUB 6,775 | Insurance premiums are calculated from the amount of remuneration under a civil contract * (25,000 x (22% + 5.1%)) |
| 99 | 68/Income tax | 5,000 rub. | A permanent tax liability is reflected (25,000 x 20%) |
* Please note: Despite the fact that expenses for holding an entertainment corporate event are not taken into account for tax purposes, expenses in the form of insurance premiums from the amounts of remuneration under civil contracts related to the holding of such an event can be taken into account for tax purposes (clause 1 clause 1 article 264 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, Letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated March 20, 2013 No. 03-04-06/8592).
So, in this article we found out how the costs of holding a corporate event are reflected in accounting and tax accounting. If, in addition to organizing a festive event, employees are paid bonuses or given gifts, then I recommend reading the articles Bonuses for employees in accordance with labor and tax laws and Gifts for employees: registration, taxation, accounting.
Now, dear colleagues, the main question for you, I hope, will be what outfit to choose for the holiday.
If you find the article useful and interesting, share it with your colleagues on social networks!
If you have any comments or questions, write to us and we’ll discuss them!
Normative base
- Tax Code of the Russian Federation
- Federal Law of July 24, 2009 No. 212-FZ “On insurance contributions to the Pension Fund of the Russian Federation, the Social Insurance Fund of the Russian Federation, the Federal Compulsory Medical Insurance Fund”
- Resolutions of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the Northern Territory of February 21, 2008 No. A56-30516/2006, of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the Moscow Region of September 23, 2009 No. KA-A40/8528-09
- Letter of the Ministry of Labor of the Russian Federation dated May 24, 2013 No. 14-1-1061
- Letters from the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation:
- dated 08/14/2013 No. 03-04-06/33039,
- dated 04/03/2013 No. 03-04-05/6-333,
- dated 03/06/2013 No. 03-04-06/6715,
- dated December 20, 2005 No. 03-03-04/1/430,
- dated 11.09.2006 No. 03-03-04/2/206,
- dated 01.11.2010 No. 03-03-06/1/675,
- dated December 13, 2012 No. 03-07-07/133,
- dated March 28, 2011 No. 03-07-07/11,
- dated March 20, 2013 No. 03-04-06/8592
Find out how to read the official texts of these documents in the Useful sites section
Personal income tax
Rent a hall for a corporate event, banquet menu, fireworks, etc. – all this creates benefits for the company’s employees and is subject to personal income tax. This rule applies only if the exact number of guests is known or personalized expenses have been paid (for example, purchasing tickets for specific employees). If you have information about the number of guests, it is necessary to divide all the costs of the holiday and calculate the benefit for each guest separately, and calculate personal income tax.
If the corporate party is an open event, and it is unknown how many guests there will be, then it is not possible to determine the personal benefit for each employee - the obligation to accrue and pay personal income tax does not arise.
Note! To be exempt from personal income tax, the company’s documents (for example, the manager’s order to hold a corporate event) should avoid specifying the exact number of guests at the event.
Are corporate expenses subject to personal income tax?
In order for an organization to have an obligation to pay personal income tax, all participants in the New Year’s event must be identified, and the income of each of them must have a certain established amount.
Since personalized records of corporate party guests are not usually kept, the organization does not have any obligations to accrue and withhold personal income tax. According to letters of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated 04/03/2013 No. 03-04-05/6-333, dated 03/06/2013 No. 03-04-06/6715, in order to include the economic benefit of employees in the taxable income received, it is necessary to be able to evaluate it . However, in the case of New Year’s corporate events, especially if the holiday format is a buffet, it is virtually impossible to estimate and calculate the number of participants, therefore there is no need to charge personal income tax (Article 41 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated August 14, 2013 No. 03-04 -06/33039).
Personal income tax will have to be paid if:
- The corporate event is offsite.
- Competitions or drawings held during the holiday provide for the subsequent presentation of gifts. If the price of purchased prizes/gifts is over 4,000 rubles. (clauses 1, 3, article 224, clauses 1, 2, article 226, clause 28, art.
Documentary support for corporate events
- Justification for spending - an order to hold a corporate event, signed by the management of the organization (authorized responsible persons). The order is drawn up in free form.
- The incurred cash costs are reflected in the company's accounting records on the basis of primary documentation from service providers (for example, TORG-12 for the purchase of souvenirs, decorations, etc., an act for renting a banquet hall).
- Additionally, an estimate of the company's expenses can be filled out. It is not mandatory and is drawn up if this rule is enshrined in the company’s internal regulations.
Costs for corporate events in accounting
Unlike tax accounting, in accounting, holiday expenses should be taken into account in fact as part of other expenses. But when choosing the right transactions, you should take into account the form of the corporate event: it was held for an indefinite number of people or as a representative event. In the first case, the chart of accounts dictates how to conduct a corporate event in accounting: use the debit of account 91 (debit 91.2 “Other expenses”, credit 60 “Settlements with suppliers and contractors”) in correspondence with other necessary accounts. Most organizations, after making all the necessary transactions, will have a permanent tax difference in the amount of costs for holding a corporate event. Which, in turn, will result in a permanent tax liability.
If the holiday is intended as a representative event, to register a corporate event in accounting, use the following entries:
| Debit | Credit |
| 20 (26, 44) | 70 |
| 99 | 68.2 |
| 19 (VAT) | 68 (VAT calculations) |
Gifts for company friends and partners
Whether a company will be able to take into account the costs of gifts to counterparties or not will depend on the circle of people to whom they were made: specific or indefinite. In the second case, the company can quite reasonably write off such costs as advertising expenses under Art. 264 Tax Code. It should be remembered that advertising expenses are standardized in tax accounting and when calculating income tax should not exceed 1% of the company’s revenue.
If the circle of persons is determined, then the company does not have the right to include the costs of gratuitously transferred property (work, services) into the income tax base in accordance with clause 16 of Art. 270 Tax Code. Therefore, it is more logical to write off such expenses at the expense of the company’s net profit. The Russian Ministry of Finance confirms this position in its recent Letter dated October 19, 2010 N 03-03-06/1/653. The point of view that it is impossible to include expenses for gifts in company expenses for tax purposes is also confirmed by the Department of the Federal Tax Service for Moscow in Letter dated February 16, 2009 No. 16-15/013724. However, it is worth paying attention to the decision of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the Moscow Region dated October 5, 2010 N KA-A41/11224-10. The court supported the company in classifying the costs of gifts to contractors for the New Year as entertainment expenses. Positive judicial practice in favor of the company can be of great help in justifying its position in the future.
As for value added tax, the company, according to the general rule provided for in paragraph 1 of Art. 146 of the Tax Code, is obliged to charge VAT when transferring ownership rights free of charge, which is recognized as a sale. However, in this case the company is not deprived of the right to VAT deductions.
If the cost of a gift unit does not exceed 100 rubles, then you should be guided by paragraphs. 25 clause 3 art. 149 of the Tax Code, since these transactions are exempt from VAT. In this case, the company will have to document that the goods are transferred to contractors for advertising purposes.
Are corporate expenses subject to personal income tax?
217 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation), then the organization charges personal income tax in the amount of 13% on the total cost of New Year's souvenirs (clause 1 of Article 224 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
If the costs of holding an event are not targeted, then, according to paragraph 4 of the letter of the Ministry of Labor of Russia dated May 24, 2013 No. 14-1-1061, they also cannot be subject to insurance premiums.
Since the costs of holding New Year's corporate parties are not considered payments or other remuneration accrued in favor of individuals, then, accordingly, insurance premiums are not charged to either the Federal Tax Service Inspectorate or the Social Insurance Fund.
"Holiday" VAT
If the company decides to hold a corporate evening at the expense of retained earnings, then in this case the written consent of the company’s founders is required. To do this, shareholders or members of the company hold a meeting, following which a decision is made on the use of the company's retained earnings. It is advisable to issue an order indicating the following information: date and place of the event; name of the holiday; list of invited guests; program and budget for the evening. All documents based on the results of a corporate event, confirming expenses, are stored in accordance with the general procedure.
In accordance with paragraphs. 1 clause 1 art. 146 of the Tax Code, the object of VAT taxation is sales. All company expenses on a corporate evening, as well as the purchase of related products (food, decorations) are not actually used by the company in activities that are subject to VAT. Consequently, the condition established by Chap. 21 of the Tax Code for the deduction of VAT amounts (Articles 171, 172 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). This means that the company does not have the right to take into account “input” VAT on invoices issued by suppliers for goods (works, services) for the purpose of holding an evening.
On the other hand, New Year's Eve can be classified as an event that the company holds for its own interests. And this is already recognized as subject to VAT in accordance with paragraphs. 2 p. 1 art. 146 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, regardless of whether expenses are recognized for tax purposes of the company’s profit or not. With this approach, the company has the right to accept amounts of “input” VAT. However, regulatory authorities often link a company's expenses to the right to deduction. And if the costs are not documented, they do not automatically deduct the amount of “input” VAT that relates to these costs.
The company should pay attention to the recent Resolution of the Presidium of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation dated July 6, 2010 N 2604/10, in which the arbitrators assessed what expenses VAT is deductible in full. Thus, the amounts of “input” VAT are standardized only for representation and travel expenses; for all other expenses, the company has the right to deduct the entire VAT. Consequently, if a company decides to write off expenses for a corporate evening as entertainment expenses, then “input” VAT should be taken into account based on the standards.
A corporate event, of course, includes meals for company employees. Should personal income tax be withheld in this case? After all, in accordance with paragraphs. 1 item 2 art. 211 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the cost of free food is considered the employee’s income, therefore, it must be included in the tax base for personal income tax. However, personal income tax accounting is personalized, which means that it is calculated based on the income of each employee. But at the event it is difficult to say how much income each employee generated. This means that there is no taxable income under personal income tax. This position is also supported by the Russian Ministry of Finance (Letter dated April 15, 2008 N 03-04-06-01/86). A similar conclusion can be drawn regarding the taxable base for insurance premiums, since it is impossible to determine the specific evening expenses for each employee of the company. Therefore, there will be no object of taxation.
The procedure for accounting for expenses for the New Year's holiday. Examples
264 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation), and the corporate event is formalized by order as an official reception, after which it is necessary to summarize the documentary results of the goals achieved. For example, it could be a gala dinner at which the results of the outgoing year were summed up. According to paragraph 2 of Art. 264 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, costs are included in the profit tax base within 4% of the costs incurred in the reporting period for remuneration of employees of the organization.
Concept of corporate event expenses
Cost accounting for corporate events
The concept of “corporate party” is used to refer to entertainment events organized by the company’s management for employees in order to motivate them. As a rule, corporate events take place in the form of parties in a cafe or restaurant and may include the following expenses:
- rental of premises for an event;
- expenses for organization and service (celebrity host, musicians, waiters, catering);
- payment for the banquet;
- expenses associated with decorating the premises for the holiday (decorating the hall in a corporate style, etc.);
A corporate event may include other expenses that, in the opinion of company management, are necessary for the event.