What is the income tax in Russia and who should pay it?
Personal income tax is a direct tax, which is calculated from the difference between all income received by individuals and expenses that are confirmed by documents drawn up in accordance with current legislation, or tax deductions.
Read about the objects falling under this tax in the articles in the personal income tax section:
- "Object of taxation";
- “Income not subject to personal income tax (2019-2020).”
Personal income tax payers are individuals who, for tax calculation purposes, are divided into two groups:
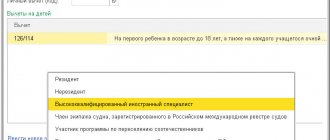
- Residents of the Russian Federation are those who receive income and are in Russia for at least 183 calendar days during the year without interruption. They pay a tax of 13% of their salary (the amount of personal income tax on other income will be discussed below).
- Non-residents of the Russian Federation are those who stay in the Russian Federation for less than 183 days and receive income on its territory. The income tax on their income is generally 30%. However, for some types of non-residents the personal income tax rate is 13%. Non-residents whose income from their main work activities are taxed at a rate of 13% include (clause 3, article 224 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation):
- workers from EAEU countries (see important nuance here);
- working under a patent;
- highly qualified specialists;
- foreigners who are refugees or have received asylum in Russia;
- participants in the State Program to Assist Voluntary Resettlement in the Russian Federation;
- crew members of ships flying the State Flag of the Russian Federation.
K+ experts have prepared background information on personal income tax rates depending on residence, and also collected letters from the Ministry of Finance and the Federal Tax Service explaining the application of personal income tax rates in different situations. Get free trial access to the system.
https://youtu.be/i5tc_yiMBIE
How can a tax agent return overpaid personal income tax?
If an employee contacts the employer with a request for a refund of overpaid personal income tax, or the tax agent himself notices an error, it is necessary to refund the tax to the taxpayer in one of the following ways:
- transfer the unlawfully withheld part of the income to the employee’s account;
- offset the overpayment of personal income tax against future tax payment periods.
To do this, you need to write a letter to your Federal Tax Service and attach documents that would prove the fact of an overpayment of personal income tax.
Tax officials will conduct an audit and report their decision to the tax agent within 10 days.
What percentage of salary and other income is income tax?
How much income tax will be in the end depends on the rate at which an individual’s income is taxed. Art. 224 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation provides for 5 interest rates for personal income tax:
- 9% on the amount of income in the form of interest on mortgage-backed bonds issued before 01/01/2007. The same rate is established on the amounts of income of the founders of trust management of mortgage coverage received on the basis of the acquisition of mortgage participation certificates issued before 01/01/2007.
- 13% personal income tax on the amount of income of individuals (salaries, remunerations under civil contracts, income from the sale of property, etc.). From 2020, the same rate applies to dividends. The tax base for dividends must be calculated by separating it from other income, which is taxed at a rate of 13%.
- 15% of the amount of dividends received by non-resident individuals from equity participation in Russian organizations.
- 30% on the amounts of all other income received by non-resident individuals.
- 35% from the amounts of winnings, prizes and participation in any competitions, amounts of interest on deposits in banks (in terms of exceeding the established rates of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation), amounts of savings on interest from loans received, etc.
Since 2020, special rules have been in force regarding the payment of advance tax payments from foreigners who operate on the basis of a patent tax system. When receiving or renewing a patent, they must make an advance payment based on the amount of 1,200 rubles, multiplied by the deflator coefficient established for the corresponding year, and by a coefficient taking into account the characteristics of the regional labor market. When subsequently calculating personal income tax for such an employee, the advance payments paid by him must be taken into account.
NOTE! The deflator coefficient for 2020 is 1.813. Basis: Order of the Ministry of Economic Development dated October 21, 2019 No. 684.
Residents and non-residents
The tax agent must withhold tax from both residents of the Russian Federation and non-residents. In the first case, income received from sources in the Russian Federation and abroad is subject to taxation. In the second case, tax is withheld only from income received in the Russian Federation (Articles 208, 209 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Let us add that if a company has an employee - a foreign citizen who has a patent for working in the Russian Federation, then when paying him income, personal income tax should be withheld, taking into account the tax paid when purchasing the patent (Clause 2 of Article 226, Article 227.1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation ).
Get a comprehensive accounting reporting solution: automatically generate and send reports via the Internet
Try for free
How to reduce 13%: personal income tax deduction
Individuals who are residents of the Russian Federation have the opportunity to use tax deductions to reduce income subject to personal income tax. The most widely used of them are deductions provided to citizens for children until they reach a certain age from income up to a certain amount.
There are also tax deductions with which you can return previously paid 13% personal income tax when purchasing property, paying for education, treatment, etc. (Articles 218–221 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). From 01/01/2014 it became possible to obtain a repeated property deduction, but with one limitation: the total amount of such deductions cannot exceed 2 million rubles.
To return previously paid 13 percent of personal income tax from the budget, you must provide the Federal Tax Service with a declaration in form 3-NDFL and documents justifying the receipt of a tax deduction. Some types of deductions can be obtained from your employer.
Read about the existing types of deductions in our section “Deductions (NDFL)”.
Responsibilities of a tax agent
An exhaustive list of the responsibilities of a tax agent for personal income tax is contained in Article 230 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation:
- calculate tax on payments to individuals;
- withhold tax;
- transfer tax amounts to the budget;
- within the prescribed period, report on calculated, withheld and transferred personal income tax to the budget using forms 2-NDFL and 6-NDFL.
Payment of tax amounts must be made exclusively on payments to individuals. A tax agent has no right to pay taxes from his own funds.
Has the amount of personal income tax changed in 2020?
The personal income tax percentage in 2020 and, accordingly, the amount of this tax have not changed. Certain tax changes occurred in prior periods.
Thus, the changes in 2020 affected the fee for an independent assessment of an employee’s qualifications:
- it does not fall under the personal income tax withheld from the employee if it is paid by the employer (clause 21.1 of article 217 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
- a social deduction can be claimed for its amount if it was paid by the employee himself (subclause 6, clause 1, article 219 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
In 2020, changes were adopted to paragraph 60 of Art. 217 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, which allows not to tax, subject to certain conditions, income received by an individual during the liquidation of a foreign company (Law No. 34-FZ dated February 19, 2018). These changes apply to legal relations arising from 01/01/2016.
What responsibility does a tax agent bear for personal income tax (fines, penalties)
Difficulties arise for tax agents in cases where workers received income not in the usual form of money, but in the form of material benefits or in kind. If personal income tax is calculated and paid incorrectly, the tax agent will face fines and penalties.
To prevent errors from happening, you should follow 2 rules:
- It is required to withhold personal income tax from payments that will be made to the individual himself or to a third party (on behalf of the individual to whom the income belongs).
- The amount of tax payable must consist of the newly accrued personal income tax and the amount of personal income tax debt.
It also happens that it is simply not possible to withhold and pay personal income tax for an employee for one of the following reasons:
- the employee’s income is simply not enough to withhold the required amount of tax to be paid on account of previously unpaid personal income tax;
- an individual who owes personal income tax to the budget will no longer be paid by this tax agent.
In both cases, the obligation to pay personal income tax will be removed from the tax agent and transferred to the taxpayer himself. But in order for the Federal Tax Service to make such a decision without consequences for the employer, the employer must inform the tax authorities that it is impossible to withhold personal income tax. The notification is sent in form 2-NDFL with sign 2 no later than March 1 after the end of the tax period
.
If this is not done, the arrears will be detected by Federal Tax Service employees, after which an on-site tax audit will be organized, as a result of which the employer will be assigned a fine and penalty in the amount of the arrears for personal income tax. To avoid a fine, a tax agent can take the following actions:
- pay personal income tax and penalties yourself - before the arrears are discovered by the tax authorities;
- submit form 6-NDFL without delay;
- indicate the correct tax amount in the report (not less).
Important!
Even if the person acting as a tax agent is late in submitting a notification about the impossibility of withholding personal income tax for an employee, the notification should still be sent.
Results
Tax rates for personal income tax did not change in 2020. The last change in personal income tax rates was in 2015, when the rate for income in the form of dividends was increased from 9 to 13%.
Despite the relative constancy of personal income tax rates, changes are regularly made to the legislation regarding the procedure for calculating tax, or new tax reporting forms are introduced and the rules for filling them out are changed.
Sources:
- Tax Code of the Russian Federation
- Order of the Ministry of Economic Development dated October 21, 2019 No. 684
You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Full and free access to the system for 2 days.
What tax agents are not allowed to do
The interaction of tax agents with staff and tax authorities should be carried out precisely according to the scheme “withheld personal income tax from wages → paid wages minus personal income tax → transferred personal income tax to the federal budget → reported to the Federal Tax Service of Russia about the time and amount of withholding”
. Tax agents, whether organizations or individual entrepreneurs, do not have the right to perform the following actions:
- pay personal income tax from your own funds (except for cases where personal income tax was additionally assessed after a tax audit);
- undertake an obligation to fully/partially pay personal income tax at your own expense and include such clauses in employment agreements or civil law agreements (civil law);
- shift the responsibility for calculating and paying tax to the employee (personal income tax payer).
Paying payroll taxes in 2020
The wages of citizens, together with a significant part of other income, are subject to personal income tax.
At the same time, the personal income tax rate 2020 directly depends on the status of the taxpayer, whether he is a resident or non-resident of the Russian Federation. Residents/non-residents. If a taxpayer stays for more than 183 calendar days during the last year in the Russian Federation, he is officially considered a resident of the Russian Federation. The time spent in the country is not interrupted, the person does not travel outside the state for short-term (less than six months) training or treatment. Otherwise, if you spend less than 183 calendar days on the territory of the Russian Federation, the taxpayer receives non-resident status.
Personal income tax rate in 2020 for non-residents/residents. Often, the income of residents is taxed at a rate of 13%, and non-residents - 30%.
However, an employee's tax status may change throughout the year. When a non-resident becomes a resident, tax is required to be levied at a rate of 13 percent. It is important to take into account that the tax status must be clarified at the end of the year and, if necessary, personal income tax must be recalculated at the appropriate rate.
The described status applies both to foreign citizens receiving income on the territory of the Russian Federation and to citizens of the Russian Federation.
Where to transfer personal income tax
List the withheld personal income tax according to the details of the tax office with which the organization is registered (paragraph 1, clause 7, article 226 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). At the same time, for organizations that have separate divisions, a special procedure for paying personal income tax applies.
Entrepreneurs transfer the tax to the inspectorate at their place of residence. Entrepreneurs who operate on UTII or the patent taxation system transfer tax to the inspectorate at the place of registration in connection with the conduct of such activities. This is stated in paragraphs and paragraph 7 of Article 226 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Please fill out payment orders for tax transfers in accordance with the Regulations of the Bank of Russia dated June 19, 2012 No. 383-P and the Rules approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated November 12, 2013 No. 107n. For more information about this, see How to correctly fill out a payment order for the payment of taxes (contributions).
An example of calculations with the budget for personal income tax in an organization
LLC "Torgovaya" accrued wages for February in the amount of 300,000 rubles. There were no other taxable payments in March. The amount of calculated personal income tax was 39,000 rubles.
The salary payment deadline established by the organization is the 5th day of the next month. On March 5, the cashier received 261,000 rubles from the bank. (300,000 rubles - 39,000 rubles) to pay salaries. On March 6, the organization submitted a payment order to the bank to transfer personal income tax to the budget.
The Hermes accountant reflected these transactions in the accounting records as follows.
28th of February:
Debit 44 Credit 70 – 300,000 rub. – salaries of employees are accrued;
Debit 70 Credit 68 subaccount “Personal Income Tax Payments” – 39,000 rubles. – personal income tax is withheld from employee salaries.
5th of March:
Debit 50 Credit 51 – 261,000 rub. – received money from the bank to pay salaries;
Debit 70 Credit 50 – 261,000 rub. – salaries were paid to employees;
March, 6:
Debit 68 subaccount “Personal Income Tax Payments” Credit 51 – 39,000 rub. – transferred to the personal income tax budget for February.
Situation: how can an entrepreneur transfer personal income tax from the income of employees engaged in activities on UTII? Over the course of a month, its hired employees alternately work in different municipalities.
Transfer the tax to the budgets of each municipality.
An entrepreneur who operates on UTII must transfer personal income tax to the inspectorate at the place of registration in connection with the conduct of such activities (paragraph 4, clause 7, article 226 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). In practice, situations are possible when an entrepreneur is registered as a UTII payer in different municipalities and during the course of a month his employees alternately work in each of them. In these cases, the personal income tax withheld from the income of such employees must be transferred by the entrepreneur to the budgets of each municipality. The tax amount should be distributed taking into account the time that each employee actually worked in a particular municipality. Such clarifications are contained in the letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated August 15, 2011 No. 03-11-06/3/92. To distribute personal income tax amounts, an entrepreneur will need to organize separate accounting of income and working time for each employee. For example, this can be done using separate time sheets or separate payroll statements.