Types of taxation in the Russian Federation
Tax legislation provides an opportunity for organizations and individual entrepreneurs to choose the types and procedure of taxation. From the moment of registration, all organizations and individual entrepreneurs apply a common taxation system. The taxpayer must notify the Federal Tax Service of his decision to apply other types of tax regimes.
Taxation systems in Russia: table 2020
| Types of tax systems | Abbreviation | Heads of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation | Who can apply | Reporting provided in connection with the application | ||
| Organizations | Individual entrepreneurs | Name | Periodicity | |||
| Conventional system | OSN | 21, 23, 25, 30 | V | V | VAT declaration | Quarterly |
| Income tax return | ||||||
| Declaration and quarterly calculations for property tax | ||||||
| Financial statements | Annually | |||||
| Information on the average number of employees | ||||||
| Simplified system | simplified tax system | 26.2 | V | V | Declaration according to the simplified tax system | Annually |
| Financial statements | ||||||
| Information on the average number of employees | ||||||
| A single tax on imputed income | UTII | 26.3 | V | V | Declaration on UTII | Quarterly |
| Unified agricultural tax | Unified agricultural tax | 26.1 | V | V | Declaration on UTII | Annually |
| Patent system | PSN | 26.5 | — | V | — | |
Next, we will try to indicate in more detail the tax regimes in force in the Russian Federation and describe the limitations of the forms of taxation in Russia.
Features of preferential types of taxation
Russian tax legislation is a complex system, but its main goal is flexibility, i.e., providing each taxpayer with the opportunity to determine for himself the optimal types and procedure of taxation. Each mode has both its pros and cons, and before choosing one of them (or several), you need to pay attention to a number of criteria:
- the type of activity you plan to engage in;
- organizational and legal form – legal entity or individual entrepreneur;
- full-time number of employees;
- amount of income;
- the cost of fixed assets on the balance sheet of the enterprise;
- regional features of doing business and taxation;
- regularity of profit;
- procedure for paying insurance premiums;
- direction of activity (export or import);
- the possibility of applying a preferential tax rate;
- who will be the main consumer (client);
- the ability to correctly confirm the expenses incurred in documentary form.
Types of activities of LLC or individual entrepreneur
If the business is firmly on its feet, makes a profit, and the enterprise employs a large number of people, you can safely work according to OSNO. For start-ups and small businesses or individual entrepreneurs, it is better to start with some kind of preferential treatment. Types of taxation for LLCs and individual entrepreneurs have restrictions:
- USN. They cannot use the mode (the exact list contains Article 346.12 (3) of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation):
- banking and microfinance organizations;
- investment and non-state pension funds;
- organizations engaged in insurance activities;
- pawnshops;
- appraisal organizations;
- in the production of excisable goods;
- during the extraction and sale of minerals (with the exception of common ones - sand, crushed stone, etc.);
- foreign organizations;
- state and budgetary institutions;
- gaming business organizations;
- using unified agricultural tax;
- with a workforce of 100 or more people.
- Unified Agricultural Sciences. Only certain categories of taxpayers have the right to apply preferential tax treatment:
- individual entrepreneurs and organizations engaged in the production of agricultural products, but on the condition that the share of the sale of agricultural products produced by them in the total revenue is at least 70%;
- marketing, processing, gardening, horticultural, livestock agricultural cooperatives, where the amount of income from the sale of agricultural products of their own production or from the performance of work or services for members of such cooperatives is at least 70% of the total income;
- some fishery organizations and individual entrepreneurs.
- UTII. Clause 2 346.26 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation contains a complete list of types of activities for the use of UTII, but local authorities have the right to reduce this list. The main ones here are:
- retail;
- parking services;
- veterinary medicine;
- road transport;
- domestic services;
- public catering;
- repair and maintenance of vehicles, etc.
- PSN. This includes several dozen types of activities, including: hairdressing and beauty services, clothing repair and tailoring, photography services, home renovation, etc. Local authorities can supplement the list with other types that are in OKUN.
Income amount
An important feature when choosing the type that will be used for taxation is the limitation on income received as a result of business activity. For each mode the following standards are established:
| View | Sum |
| simplified tax system |
|
| Unified agricultural tax | No restrictions, but not less than 70% of total income |
| UTII | No restrictions |
| PSN | No more than 60 million rubles |
OSN: what types of taxation exist
As mentioned above, OCH is applied by default. To apply it, there is no need to notify the Federal Tax Service. Notification will only be required if the company previously applied the special regime and then decided to return to the normal system.
The following types of taxes are paid on OSN:
- Organizations - VAT, income tax, property tax;
- Individual entrepreneur - VAT, personal income tax.
Also, such taxpayers pay all other taxes for which they have obligations under the law.
https://youtu.be/g3xrWbSlN3c
General taxation system (OS, OSN, OSNO)
OSN is a type of taxation in which a legal entity (organization) or an individual (individual entrepreneur or individual entrepreneur) must pay all general taxes.
Such taxes include:
- VAT;
- property tax;
- for individual entrepreneurs – personal income tax;
- for organizations – income tax.
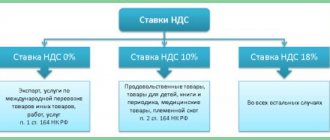
VAT (value added tax). This is an indirect tax that is formed immediately when the product is created. Tax rate 0%, 10% and 20%.
Property tax. Paid to the regional budget for certain types of property. For individual entrepreneurs, this tax is calculated by the tax authorities (FTS); organizations calculate the payment independently, based on the average annual or cadastral value. The tax rate is no more than 2.2%.
Personal income tax (personal income tax). Direct tax levied on individual entrepreneurs on income minus expenses. Rates 13% (basic), 9%, 30%, 35% (depending on the type of income).
Income tax. Profit is the money received, consisting of the difference between income and expenses. Base rate 20%. Of these, 17% are paid to the regional budget, and 3% to the federal budget. For some categories, the legislation provides for reduced tax rates (federal legislation up to 0%, regional legislation up to 13.5%).
Advantages:
- possibility of application to any type of activity;
- assigned automatically, no need to submit any documents;
- there are no restrictions on the number of employees, income, or the cost of fixed assets;
- ability to charge VAT;
- possibility of reducing VAT paid;
- the tax base is calculated minus expenses;
- there are benefits for some types of activities;
- opportunity to receive an investment deduction.
OSNO is suitable for any type of activity and is applied by default if an individual entrepreneur or legal entity has not declared a transition to another type of taxation.
It is beneficial for VAT payers to work under this system, since only with OSN it is possible to reduce the amount of tax on a given payment.
If a company is engaged in activities that fall under the exemption, it pays less income tax. These types are:
- agricultural enterprises;
- educational activities;
- medical field;
- provision of social services to the population, etc.
It is also possible to receive an investment deduction for the purchase and modernization of certain types of fixed assets.
Weak sides:
- serious accounting activities;
- high taxes;
- complex reporting;
- Entrepreneurs and legal entities also pay additional taxes for certain types of activities.
Accounting reporting is characterized by issuing invoices and invoices with VAT, maintaining a tax register for VAT.
Since three types of taxes are paid under OSN, reporting is submitted for each type of tax separately. This is an income tax return (submitted every quarter), a VAT return (every month or quarter depending on turnover), calculations for advance payments and property tax (for legal entities every quarter, individual entrepreneurs do not provide this reporting), a tax return -Personal income tax once a year (for individual entrepreneurs).
Additional taxes are levied on those organizations that engage in the following specific activities:
- mining;
- activities related to the use of earth's subsoil and water resources;
- gambling business, etc.
If the property has land or transport, additional land/transport taxes are paid.
Let's consider special (preferential) types of taxation of business activities.
simplified tax system
The transition to a simplified system eliminates the need for organizations to pay VAT, income and property taxes, and individual entrepreneurs - VAT and personal income tax. You can switch to the simplified tax system on a voluntary basis either from the start of business or from the beginning of a new calendar year. To do this, you must submit a notification to the Federal Tax Service and also meet certain criteria:
- annual income does not exceed 150 million rubles;
- average number of employees - no more than 100 people;
- residual value of fixed assets - no more than 150 million;
- the share of other organizations in the authorized capital is a maximum of 25%;
- the organization has no branches or representative offices.
What types of taxation systems there are on the simplified tax system are indicated in Article 346.14 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. The payer has the right to choose the object of taxation on which the rate will depend:
- “Income” - rate 6%;
- “Income minus expenses” - the rate is 15%.
Who counts the amount charged?
According to the method of taxation, the items in this article are divided into cadastral (aka non-cash) and declaration (cash). Cadastral taxes are calculated by the tax authorities themselves based on available information about the value of the taxable object. For example, for individuals, all taxes related to property are cadastral. Including:
- Transport tax (tax inspectors receive information about whether individuals own vehicles from the State Traffic Safety Inspectorate).
- Property tax, as well as land tax (the tax service receives the cadastral value of real estate from the database of the Federal Service for State Registration, Cadastre and Geography - Rosreestr).
The Tax Service annually calculates the amount of tax and sends out notifications to taxpayers about the need to pay cadastral taxes. In contrast, return taxes are calculated based on data provided by the taxpayer himself. For example, if a citizen resells a recently purchased apartment, then he is obliged to independently draw up an income statement, send it to the tax authorities and pay the appropriate amount of tax.
UTII
The use of UTII is possible only for certain types of activities. Their complete list is given in paragraph 2 of Art. 346.26 Tax Code of the Russian Federation. The decision to introduce UTII is made by local authorities. Therefore, in some regions this special regime does not apply (for example, in Moscow).
UTII, like the simplified tax, replaces the payment of VAT, income and property taxes, as well as personal income tax (for entrepreneurs). In addition to the type of activity, there are also other restrictions for the use of the special regime:
- the share of other organizations in the authorized capital is a maximum of 25%;
- average number of employees - no more than 100 people.
The amount of payment to be transferred to the budget does not depend on the actual income of the payer. It is calculated based on imputed income at a rate of 15%. Local authorities may set a different rate depending on the category of taxpayer or type of activity in the range from 7.5 to 15%.
Imputed income is determined based on the basic profitability for the type of activity and the physical indicator characterizing the activity (Article 346.29 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Progressive, regressive and proportional tax systems
One of the most important components of the tax is the fiscal payment tariff. This is the amount of contributions to the budget, depending on the tax base. Tariffs can be fixed (a certain amount) or expressed as a percentage. The size of the tariff is different for different types of fiscal payments; it is established by law. In Russia, the document regulating the rules for calculating and paying tax contributions, as well as the size of the rate, is the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
https://youtu.be/UhUvUL3e_xE
The size of the fixed tax rate is an absolute value that does not depend on the tax base. Basically, fixed rates are established for types of fiscal fees for which it is difficult to determine the tax base. In Russia, such tariffs are established for state duties. So, for example, to register a legal entity, you need to pay a fee. In 2020, its size is 4,000 rubles. regardless of the amount of authorized capital, the type of organizational and legal form, or the projected profit that the enterprise will receive.
There are three types of percentage tax calculation systems:
- Proportional.
- Progressive.
- Regressive.
The proportional type involves taxpayers paying a certain percentage of the tax base. This percentage is fixed and does not depend on the amount of income and other financial or physical indicators. Most types of fiscal fees in Russia belong to this calculation system. For example, value added tax, profit tax, and personal income tax.
If a progressive type of tax system is used, then the amount of tax depends on the tax base - the larger it is, the larger the fiscal fee. This system is used to calculate income tax in many countries - the USA, Australia, Norway, and most countries that are members of the European Union.
The principle of a regressive type of tax system is the opposite - if the tax base grows, the fiscal tax decreases. Although such pricing is very rare, it is still used.
Previously, it was used in Russia. Until 01/01/2010, one of the mandatory contributions for organizations was the unified social tax (UST), paid from employee salaries. It was subsequently replaced by insurance premiums. The procedure for paying UST was prescribed in Chapter 24 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, but now it is not in effect. The unified social tax was calculated according to a regressive system.
The rates were as follows:
- if the employee’s annual earnings did not exceed 100,000 rubles, they charged 26.1%;
- if the income for the year was in the range of 100,000–300,000 rubles, then employers paid 20%;
- if an employee received from 300,000 to 600,000 rubles per year, then the unified social tax was 10% of the amount of earnings;
- high salaries (annual earnings over 600,000 rubles) were taxed at only 2%.
Unified social tax stopped being collected on January 1, 2010. The insurance premiums that replaced it were calculated completely differently.
PSN
This type of special taxation can only be applied by individual entrepreneurs. To use it, you must purchase a patent for the relevant type of activity. PSN can be combined with any other taxation system. Purchasing a patent replaces the need to pay VAT and personal income tax.
The cost of a patent will be calculated by the Federal Tax Service upon its issuance. But you can first make a calculation on the official service of the Federal Tax Service.
There are restrictions on the use of PSN:
- number of employees - no more than 15 people;
- annual income from activities on PSN - no more than 60 million rubles.
Unified agricultural tax
Unified agricultural tax is a specially developed special regime for agricultural enterprises. Thus, the main limitation for its application is agricultural production. The tax rate is set at 6% of the amount of income reduced by the amount of expenses.
Since 01/01/2019, constituent entities of the Russian Federation have been granted the right to establish a differentiated unified agricultural tax rate in the range from 0 to 6%, depending on the type of product produced, location of activity, income level or headcount.
Federal taxes and fees
In accordance with Art. 12 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, federal taxes and fees are such obligatory payments, the transfer of which must be carried out everywhere on the territory of the Russian Federation. At the same time, the effect of federal tax standards is regulated only by the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, which introduces and repeals both the taxes themselves and individual provisions for a particular federal tax.
The amounts of federal taxes go to the budget of the same name of the Russian Federation.
The materials in this section will tell you about the procedure for applying the BCC for various taxes..
And the procedure for making an error in the KBK is discussed in detail by ConsultantPlus experts. Get free access to the system and go to the Ready-made solution.
Insurance premiums
In addition to these payments, any organizations and individual entrepreneurs pay insurance premiums from payments to employees. The normal premium rate is:
- 22% - for pension insurance;
- 2.9% - for social insurance;
- 5.1% - for health insurance.
Some categories of policyholders in special regimes have the right to apply a reduced rate of insurance premiums. It is set at 20% for pension insurance. Contributions to compulsory medical insurance and social security fund are not paid at all. The following are eligible for a reduced rate:
- organizations and individual entrepreneurs on the simplified tax system with the main activities listed in paragraphs. 5 p. 1 art. 427 Tax Code of the Russian Federation;
- Individual entrepreneurs on UTII with a license for pharmaceutical activities;
- IP on PSN
Individual entrepreneurs also, regardless of the system used, transfer insurance premiums for themselves:
- fixed payment (regardless of income received): set annually. In 2020 it is equal to 36,238 rubles;
- additional contribution to the Pension Fund in the amount of 1% on the amount of excess income of 300,000 rubles. in a year.
What is the tax system
The concept hides the collection of payments from the income of individuals or companies to the budget of a country or region. Some financial transactions are also subject to taxation. The adopted rules are regulated by regulations. For example, the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Taxes are the main source of financing government spending. Contributions to the Federal Tax Service are paid voluntarily or compulsorily. The tax rate is clearly fixed in the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, but changes due to the economic situation in the country or political decisions of the authorities.
Each tax payment has its own payment procedure. You can pay at one time or in part. You can use the usual “paper money”, or you can use “bank transfer”.
Next, we will figure out what types of taxation systems are established by the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Back to contents