Who can I give a gift to?
Most commercial organizations in their activities are faced with the need for gifts for their employees, business partners, and third parties. But according to the law, a company cannot make a gift to any person; there are certain restrictions in this matter.
You cannot give anything:
- state and municipal employees;
- commercial enterprises;
- employees of medical and educational institutions, enterprises providing social services;
- other categories of recipients in accordance with Article 575 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation.
https://youtu.be/1Y2n-oWlHII
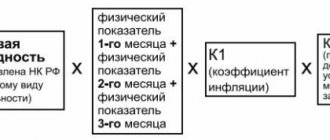
Graphic scheme for accounting for gifts to customers depending on the conditions
Graphic scheme for accounting for gifts to customers depending on the conditions
- 1Letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated September 18, 2017 N 03-03-06/1/59819.
- 2 Clause 16 art. 270 Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
- 3 Subclause 4 clause 1 art. 575 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation.
- 4 Subclause 22, clause 1, art. 264 Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
- 5 Letters of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated March 25, 2010 N 03-03-06/1/176, dated August 16, 2006 N 03-03-04/4/136.
- 6 Clause 16 art. 2, paragraph 2 art. 18 of the Law of November 22, 1995 N 171-FZ; Part 3 Art. 14.17 Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation.
- 7 Clause 2 art. 264 Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
- 8 Letters of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated 04/10/2014 N 03-03-РЗ/16288, dated 11/01/2010 N 03-03-06/1/675.
- 9 Subclause 28, clause 1, clause 4, art. 264 Tax Code of the Russian Federation; Letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated 06/04/2013 N 03-03-06/2/20320; Resolution of the AS MO dated October 11, 2016 N F05-14103/2015.
- 10 Letter of the Federal Tax Service of Russia for Moscow dated October 18, 2010 N 16-15/ [email protected]
- 11 Letter of the Federal Tax Service of Russia for Moscow dated April 30, 2008 N 20-12/041966.2.
- 12 Letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated August 16, 2006 N 03-03-04/4/136.
- 13 Subclause 1 clause 1 art. 146 Tax Code of the Russian Federation; Letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated 06/04/2013 N 03-03-06/2/20320.
- 14 Clause 2 of Art. 154 Tax Code of the Russian Federation; Letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated October 4, 2012 N 03-07-11/402.
- 15 Clause 3 of Art. 168 Tax Code of the Russian Federation; clause 3 of the Rules for maintaining the sales book, approved. Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated December 26, 2011 N 1137.
- 16 Subclause 1, clause 2, art. 171, paragraph 1, art. 172 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
- 17 Clause 7 art. 171 Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
- 18 Subclause 25, clause 3, art. 149 Tax Code of the Russian Federation; Clause 12 of the Resolution of the Plenum of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation dated May 30, 2014 N 33.
- 19 Clause 1 of Art. 420 Tax Code of the Russian Federation; clause 1 art. 20.1 of the Law of July 24, 1998 N 125-FZ.
- 20 Clause 28 Art. 217 Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
- 21 Clause 5 of Art. 226 Tax Code of the Russian Federation; Order of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated October 30, 2015 N ММВ-7-11/ [email protected]
How to properly formalize a donation
Before purchasing anything to give as a gift, you should make a list of people for whom the gift is planned. Gifts for employees of an organization will differ from gifts intended for business partners or clients of the company. Therefore, the next step will be to draw up a cost estimate for gifts, which will reflect the types and costs of all gifts.
After the preliminary expenses for this item have been calculated, the head of the organization must issue an order with the obligatory indication in it:
- persons responsible for organizing gifts;
- delivery deadlines;
- cost of gifts.
The purchase of gifts is formalized by a sales contract with the seller. The purchase must be confirmed by primary documents such as invoice, check, acceptance certificate.
Situation 2. Souvenirs - for entertainment or advertising expenses
When distributing gifts bearing the symbols of the organization (for example, pens, notepads, calendars, flash drives, T-shirts, etc.), it is important for tax accounting whether the circle of recipients is known in advance.
After all, if souvenirs with a company logo are intended for an indefinite number of people, then their cost can be recognized as part of advertising expenses in an amount not exceeding 1% of sales revenue.
If souvenirs are given to representatives of counterparty companies during negotiations, then in this case the cost of the gifts, due to the certainty of the persons receiving them, cannot be taken into account as advertising expenses. At the same time, the tax authorities allowed it to be recognized as entertainment expenses. However, the Ministry of Finance has a different opinion. It is impossible to include such expenses in entertainment expenses, since they are not mentioned in paragraph 2 of Art. 264 Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Tax accounting of expenses for gifts
Let's look at the procedure for tax accounting for expenses on gifts using a conditional example. The company purchased 200 notebooks depicting its symbols for a total amount of 23,600 rubles (including VAT 3,600 rubles) to hand them over to its clients. How to reflect these transactions in tax accounting?
From a legal point of view, the provision of gifts by a commercial enterprise to its customers is regarded as a gratuitous transfer . Therefore, VAT in the amount of 3,600 rubles is charged on the cost of the gift, which is subsequently subject to offset. It should be noted that the cost of gifts (20,000 rubles) cannot be recognized as an expense to determine the amount of income tax. It does not matter to whom the gifts were given.
When calculating income tax, it is necessary to take into account the need to tax income in the form of a gift, the value of which exceeds 4,000 rubles. Exceeding the value of the gift entails the obligation of the donor company to submit a declaration f. to the tax service. 2-NDFL.
Calculation of personal income tax on gifts to employees
A gift can have any form - material, monetary, but in any case it is regarded as the employee’s income, therefore, it is necessary to charge personal income tax on it. All such transactions must be reflected in tax and accounting records. Gifts are taxed (clause 28 of Article 217 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation) only if their value is above 4,000 rubles. (tax is charged on the amount of the gift minus 4,000 rubles).
The employer acts as a tax agent whose responsibility is to calculate and withhold personal income tax. Accounting for gifts in accounting is carried out at the total cost of items that are transferred to the employee during the reporting period.
Let's look at a specific example. During 2020, management encouraged the employee several times. On March 8, she was presented with a set of home textiles worth 2,900 rubles. The price of this gift is less than 4,000 rubles, therefore, personal income tax is not charged on it. The second gift was a birthday set worth 3,300 rubles. In accounting, gifts will be reflected in the total amount (2900 + 3300 = 6200 rubles). Since the total amount of gifts is more than 4,000 rubles, personal income tax will be withheld from the excess. That is, tax is charged on 6200 – 4000 = 2200 rubles.
During the same reporting period, management presented the employee with several more gifts. Since each subsequent incentive increases their total amount, which has already exceeded 4,000 rubles, they are all subject to taxation. The personal income tax rate for residents is 13%, and for non-residents 30%.
Letter of the Federal Tax Service dated August 22, 2014 No. SA-4-7/16692 introduces some clarifications into the mechanism for accounting for gifts. Thus, the form of the gift affects the procedure for withholding and transferring personal income tax:
- If the incentive is given to an employee in cash from the company’s cash desk or by transfer to a personal current account, then personal income tax is reflected in accounting records and transferred on the same day.
- If any item is presented, then personal income tax is calculated and withheld on the day of the next salary or advance payment. If the donation is made at the end of the calendar year and no cash payments are expected before December 31, then the company must notify the tax office and its employee in writing that it has no ability to withhold tax. This action must be completed by the end of January. During this period, the accounting department prepares and sends to the Federal Tax Service a certificate in form 2-NDFL with information about the cost of the gift and the data of the donee; the value “2” is entered in the “Attribute” column.
Information regarding the receipt of gifts by employees is reflected in the 2-NDFL accounting certificate in the following order:
- Code 2720 is assigned to income equal to the amount of each gift (including those not exceeding 4,000 rubles).
- Code 501 is assigned to a deduction from the amount of the souvenir that is not subject to personal income tax (i.e., up to 4,000 rubles).
How to account for gifts to employees in the form of alcoholic beverages and food packages
Many domestic employers practice giving alcoholic beverages (champagne or stronger versions) to their employees on holidays, such as the New Year. The costs of their acquisition can be documented as expenses for organizing an official reception, i.e. entertainment expenses. The presentation of such gifts requires the execution of an order and an estimate for the reception.
The amount of such expenses is limited and cannot exceed 4% of labor costs in the reporting period.
Gifts for company employees may include food products, such as tea, coffee, and sweets. In this case, the costs of their acquisition can be reflected in different ways. If it is possible to personalize the recipient of the gift, then in this case the employer becomes obligated to withhold personal income tax.
The economic benefit of recipients, if they cannot be identified, cannot be determined, therefore, income tax on gifts in the form of food baskets cannot be withheld. However, such a situation may lead to a dispute with the tax authorities during an audit. Costs incurred when purchasing food products for gifts to employees can be taken into account as expenses for their food.
How to deal with VAT
In the standard version, the presentation of gifts at the expense of net profit is recognized as a sale - it is necessary to charge VAT on their value (the tax base is the market value of the gift without taking into account “input” VAT). VAT from the supplier can be deducted in the general manner.
In the case of entertainment purposes: gifts - food and alcohol were not actually sold, but were included in the banquet menu for treating partners. In this case, there is no obligation to charge value added tax. “Input” tax is deductible within established limits.
Advertising expenses: if the cost of souvenir products is 100 rubles or less, then VAT is not charged, and the “input” tax from the supplier is taken into account in the cost of the gift. If the cost is above 100 rubles, then there is an obligation to charge VAT, while the tax from the supplier is deducted within the standard (1% of revenue).
Note from the author! If the souvenirs cost less than 100 rubles, then the company needs to keep tax records for VAT-taxable and non-VAT-taxable transactions.
Gifts for business partners
Accounting for expenses for gifts to business partners depends on the method of documenting them and the sources from which they were financed. Gifts can be formalized as a gratuitous transfer at the expense of the net profit of the donor legal entity. The cost of purchasing gifts is not included in income tax expenses.
Since a gratuitous transfer is considered a sale under the law, the cost of gifts is subject to VAT. You can formalize the delivery of a gift to partners by deed. You can reflect the costs of gifts to partners as entertainment expenses if the following conditions are met:
- during the period when the gifts were given, the donor actually held some official receptions;
- documents for holding receptions and making entertainment expenses are drawn up in accordance with the requirements of the law.
Reporting
Sometimes confusion arises when reporting non-taxable payments. Some do not include them at all in reports and 2-NDFL certificates, others show them everywhere. How to correctly fill out reports in accordance with the rules and legislation?
First of all, look at the instructions for the forms, they are quite detailed, and you can find answers to most questions there. Secondly, note for yourself the difference between payments that are not taxable under the law and those that are not subject to tax or conditional contributions. For example, dividends are not taxable amounts and are not shown at all in the RSV-1 report. At the same time, financial assistance is generally subject to contributions and is exempt from them only in the form of certain exceptions, which means that it should appear in the report.
Commission
Before drawing up the write-off act, a special commission meets. They must consist of at least three people. The chairman of this commission is elected. Each member of the assembled group must be informed that reporting false information in official papers is punishable by law.
All members of the commission check the compliance of the data specified in the paper with the real state of affairs. Their signatures in the documentation indicate that they have found a complete match. If one of the commission members has a special opinion about the presented figures, then he still signs, but formalizes his position in the form of a postscript or an appendix to the act.
https://www.youtube.com/watch{q}v=channel
Sometimes the creation of a commission is prescribed in the manager’s order on holding festive events in the organization.
Documentation procedure
In order to keep accounting records of gifts to employees, fix the conditions and procedure for issuance, it is not at all necessary to make a separate local act. The necessary points can be included in existing documents, for example, internal labor regulations, provisions on social guarantees, bonuses, or a collective agreement (if any) (part one of Article 8 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
They should include all cases when the salon manager deems it necessary to make gifts, record the procedure for documenting gift giving, determine the categories of employees and the maximum cost of surprises. Thus, it is worth establishing that gifts worth up to 2,000 rubles are purchased for craftsmen, up to 4,000 rubles for cosmetologists, up to 6,000 rubles for managers, and up to 1,000 rubles for employees’ children.