Receipt and expense orders are the main primary documents in the cash desk of any organization. How should you keep track of and control these important papers, and how to fill out the cash register without errors? Read in this article.
Absolutely all organizations that have a cash register and operations on it are required to fill out cash register documents regarding the receipt and expenditure of cash. These are the overwhelming majority, because despite the spread of electronic means for non-cash payments, cash is usually needed for small household needs. This means that most organizations also need a journal for recording incoming and outgoing cash orders . Therefore, let's get to know him in more detail.
Magazine form
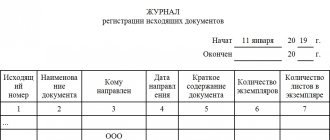
The journal for registering incoming and outgoing cash documents is an accounting book in which it is necessary to enter information and details of all documents issued by the cashier. Its unified form was approved by Resolution No. 88 of the State Statistics Committee of the Russian Federation dated August 18, 1998. It is called No. KO-3, but if desired, organizations may not use it and develop their own version. Indeed, since 2013, the use of such unified forms of primary accounting documents has been recommended. Although the remaining cash papers, in particular the same cash registers, in accordance with information from the Ministry of Finance No. PZ-10/2012, are mandatory in the approved form.
The log book is a regular consolidated accounting register, so you can develop it yourself. By virtue of Article 10 of the Federal Law of December 6, 2011 No. 402-FZ “On Accounting,” approval of accounting registers is the prerogative of the head of the organization upon the recommendation of the chief accountant. The main thing is to indicate the option used in the accounting policy. But if desired, you can use a unified form (this should also be mentioned in the accounting policy). However, this is always a book that must be numbered end-to-end and stitched. Typically, the inside of the journal form for registering incoming and outgoing orders consists of two halves of equal volume:
- For receipt orders.
- For expense orders.
They are carried out simultaneously. Information about income is usually placed on the right side of the sheet, and information about expenses is on the left. The legislation allows keeping a register not only on paper, but also in electronic form. In this case, it should be possible to print the completed form and generate it within a certain period of time. In addition, you don’t have to use paper copies if the responsible person (accountant or cashier) has a qualified electronic signature with which he can certify the records.
Concept
Any funds that are deposited into the cash register or spent for certain purposes must be recorded in cash orders:
PKO – cash receipt order;
RKO – expense cash order.
The following can be used as an expense order:
- payment statement;
- invoices for payment;
- application for the issuance of funds.
It should be understood that each payment document has its own digital code, in accordance with the All-Russian Documentation Classifier.
Any documentation related to cash reporting contains the required information:
- name and legal address of the legal entity;
- type of operation performed;
- sides;
- serial numbers, as well as the time and date of the financial transaction.
- data of persons signing documents;
- requisites.
Cash documents must be registered in the accounting department of the enterprise and filled out by the responsible employee by order of the head of the organization. After that, they are transferred to the cashier for transactions.
Before carrying out any cash transaction, the cashier is obliged to check the accuracy and correctness of filling out the provided documentation. When transferring cash to the cashier, the completed and signed tear-off PQO must be handed over to the person who deposited the funds as payment for the financial transaction, and the order remains with the cashier. The cash settlement must be signed by the person who accepted the funds with a stamp confirming the fact of payment, otherwise problems may arise with proving the transaction.
At the end of the work shift, the cashier is required to reconcile the remaining cash with the documentation, taking into account all transactions performed for the day.
No corrections or blots can be made in cash documents, otherwise problems may arise with regulatory authorities, for which responsibility is provided.
Filling out the cash register: sample
On the title cover, regardless of whether a self-developed or recommended journal form for registering receipts and expenditures is used, there must be the name of the organization, its structural unit where the cash desk is located, and the name of the form itself. In addition, you need to write the date when maintaining the form began, and the details of the person responsible for it (position and full name). It will look like this:
Inside the form, it is necessary to provide columns to indicate the following information for each cash order:
- order number and date of its preparation;
- amount of expense or income;
- a note indicating a brief purpose of the amount of money issued or received.
Numbers for incoming and outgoing orders must be assigned separately for each of these types of cash papers. Continuous numbering of income and expenses is not allowed.
An example of filling out a journal of cash documents, form KO-3
Incoming and outgoing cash documents, on the basis of which cash is received and issued from the cash register, must be recorded in a specially created journal, which is called the log of registration of incoming and outgoing cash documents. You can download this form below. The unified form of the journal is KO-3. Despite the fact that filling out the KO-3 journal should not cause any difficulties, in this article we will dwell in more detail on the design features.
This standard form must be present in every enterprise that carries out cash transactions. All cash documents entering and leaving the enterprise must be recorded in a journal. This may include cash receipt orders (sample order KO-1 can be downloaded here), expenditure orders (sample order KO-2 can be downloaded here), pay slips.
Documents are registered at the time of their preparation, and they are assigned a serial number according to the registration log.
Online cash registers
When asked whether a cash register is needed for online cash registers, the answer is clear - no. Transactions are recorded and receipt numbers are assigned automatically by the device’s fiscal storage device. Therefore, no additional accounting registers are provided in this situation. Before the introduction of cash register equipment with the function of online data transfer, cashiers-operators kept journals for registering receipt and expenditure orders, in which they recorded data on revenue; now this obligation has been canceled for them. The relevant explanations on this matter were given by the Russian Ministry of Finance in letter dated June 16, 2017 No. 03-01-15/37692.
Who fills out the log book?
As a rule, the journal is filled out by the cashier or an appointed accounting employee who knows the filling rules assigned by the head of the organization. This person is financially responsible, for which an agreement is drawn up with him in advance. Illiterate maintenance, errors in the registration log of PKO and RKO, which are identified by the auditor, entail administrative liability (Article 15, paragraph 1 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation).
Journaling rules require making accurate entries in fields that are required to be filled in.
Regulations of the Federal Law “On the Central Bank of the Russian Federation” No. 86, art. 34 of July 10, 2002 instructs the Bank of Russia to streamline cash transactions carried out by legal entities and entrepreneurs. Thus, this Federal Law establishes unified rules that are binding on the listed persons.
There is a concept of a cash limit for any enterprise. Its size is determined by the Central Bank - it is also agreed on an individual basis with the management of the organization. The amount of money exceeding the established limit must be kept in the bank.
It is worth considering in a little more detail what receipt and expense orders are that are subject to registration.
Related documents
- Journal of transactions on accounts “c” (instruction of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation dated July 26, 1996 No. 45)
- Journal order No. 1 for credit of account No. 50
- Journal order No. 14 for the credit of account No. 14
- Journal order No. 2 for credit of account No. 51
- Journal order No. 2.1 for the credit of account No. 52
- Journal order No. 6 for the credit of account No. 60
- Journal order No. 7 for the credit of account No. 71
- Borrower's application
- Analytical accounting card for account No. 52 “currency account”
- Cash report. Form No. 5-g
- Worker and employee personal account
- Personal account for saving material resources. Form No. m-20
- Invoice for internal movement of materials. Form No. m-12
- Invoice for internal movement of materials. Form No. m-13
- Invoice for the release of materials to the third party. Form No. m-14
- Invoice for the release of materials to the third party. Form No. m-15
- Working balance (turnover sheet) for synthetic accounts
- Sample. The act of disposal of low-value and high-wear items. Form No. MB-4
- Sample. Act of inventory of precious stones, natural diamonds and products made from them. Form No. inv-9 (Decree of the State Statistics Committee of the USSR dated December 28, 1989 No. 241)
- Sample. Act of inventory of precious metals and products made from them. Form No. inv-8 (Resolution of the USSR State Statistics Committee dated December 28, 1989 No. 241)
Found documents on the topic “magazine warrant No. 1 Kazakhstan”
- Sample. Registration journal of memorial orders Accounting statements, accounting → Sample.
Registration journal of memorial orders registration journal for 20 - serial numbers date of compilation amount for memorial memorial orders orders -+-+- ... - Magazine—order No. 14 on credit account No. 14
Accounting statements, accounting → Journal order No. 14 for the credit of account No. 14journal - order no. 14 on account credit no. 14 “revaluation of values” for 20 +-+ no. accounts to debit accounts from credit account...
- Magazine—order No. 2 on account credit No. 51
Accounting statements, accounting → Journal order No. 2 for the credit of account No. 51journal - order no. 2 on account credit no. 51 “current account” to debit accounts +-+ str- date 06 26 50 58 60 67 68 69 76 81 93…
- Sample. Magazine—order № 11
Accounting statements, accounting → Sample. Journal-order No. 11journal - order no. 11 on credit accounts no. 40 “finished products”, no. 41 "products", no. 42 “trade margin”, no. 43 "commercial...
- Magazine—order No. 1 on account credit No. 50
Accounting statements, accounting → Journal-order No. 1 for the credit of account No. 50journal - order no. 1 on account credit no. 50 “cash” in the debit of accounts +-+ cash date line 51 70 71 76, etc. total no. ...
- Magazine—order No. 2.1 on account credit No. 52
Accounting statements, accounting → Journal order No. 2.1 for the credit of account No. 52journal - order no. 2/1 on account credit no. 52 “currency account” in debit accounts +-+ statement date line no. no. no. 50 60 etc...
- Sample. Magazine—order № 16
Accounting statements, accounting → Sample. Journal-order No. 16journal - order no. 16 on credit accounts no. 07 “equipment for installation”, no. 08 “capital investments”, no. 11 "animals of...
- Sample. Magazine—order № 8
Accounting statements, accounting → Sample. Journal-order No. 8journal - order no. 8 on credit accounts no. 06 “long-term financial investments”, no. 09 “rental obligations due”, ...
- Sample. Magazine—order № 10.1
Accounting statements, accounting → Sample. Journal-order No. 10.1journal - order no. 10/1 on credit of accounts no. 02 “depreciation of fixed assets”, no. 05 “depreciation of intangible assets”, no. 10 "mother...
- Sample. Magazine—order № 15
Accounting statements, accounting → Sample. Journal-order No. 15journal - order no. 15 on credit accounts no. 80 "profits and losses", no. 81 “use of profits”, no. 83 “future income...
- Sample. Magazine—order № 15
Accounting statements, accounting → Sample. Journal-order No. 15journal - order no. 15 on credit accounts no. 80 "profits and losses", no. 81 “use of profits”, no. 83 “future income...
- Magazine—order No. 7 on credit account No. 71
Accounting statements, accounting → Journal order No. 7 for the credit of account No. 71journal - order no. 7 on account credit no. 71 “settlements with accountable persons” and analytical data for this account for 20...
- Sample. Magazine—order № 13
Accounting statements, accounting → Sample. Journal-order No. 13journal - order no. 13 on account credit no. 01 “fixed assets”, no. 03 “long-term leased fixed assets”, no. 04 "n...
- Sample. Magazine—order № 3
Accounting statements, accounting → Sample. Journal-order No. 3journal - order no. 3 on credit accounts no. 55 “special bank accounts”, no. 56 “monetary documents”, no. 57 “translations on the way”...
- Sample. Magazine—order № 9
Accounting statements, accounting → Sample. Magazine order No. 9journal - order no. 9 on credit accounts no. 78 “settlements with subsidiaries”, no. 79 “intra-economic calculations” and analytics...