What are the requirements?
The tax inspector may require the following from the taxpayer:
- Pay arrears of penalties, fines and taxes. To make such a requirement, the taxpayer must have arrears under the relevant budget classification codes. This requirement specifies the deadline by which the existing debt must be repaid. If this is not done, the tax office itself will make a decision to write off funds from the taxpayer’s account.
Example.
The organization has arrears of penalties in the amount of 2 rubles on insurance premiums for compulsory pension insurance. The Federal Tax Service cannot simply write off this debt from the organization’s account. First, the inspector issues a demand, which is sent to the payer. The request specifies a deadline. If the organization does not pay the penalty within this period, then even such a small amount as 2 rubles will be written off from the organization’s account by the Federal Tax Service.
- Provide explanations for discrepancies in the information available to the tax inspectorate and provided by the business entity, or submit a corrective return.
Example.
The tax inspectorate has information that the organization applies a general taxation system. But when calculating insurance premiums, the organization indicates 08 in the payer code, which corresponds to organizations using the simplified tax system. In this case, the inspector will request an explanation from the organization for what reason it submits reports indicating a reduced rate of insurance premiums.
- Requirement to provide certain documents confirming the facts of economic life.
Example.
The inspector of the Federal Tax Service may request to provide documents confirming the delivery of raw materials from one city to another. For example, waybills and a car rental agreement or invoices.
Article 69 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. Request for payment of tax, fee, insurance premiums (current version)
As a general rule, in accordance with paragraph 2 of Art. 69 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the requirement to pay tax is sent to the taxpayer. However, since 2012, in accordance with paragraph 1 of Art. 1 of the Federal Law of November 16, 2011 N 321-FZ “On amendments to parts one and two of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation in connection with the creation of a consolidated group of taxpayers”, payers of corporate income tax can, on the basis of an agreement, voluntarily unite to create a consolidated group of taxpayers . In such a group, the rights and obligations of the corporate income tax payer are assigned to the responsible participant of the consolidated group. Therefore, if there is an arrears of corporate income tax from a consolidated group of taxpayers, the requirement to pay the tax is sent to the responsible participant in the consolidated group of taxpayers (paragraph 2, clause 2, article 69 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
The content, form of the demand, the procedure for its transmission and the deadline for fulfilling the demand are regulated by paragraphs 4 - 6 of Art. 69 Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Despite the fact that the legislator does not directly classify the information that must be contained in the tax payment request, it can be divided into two parts: mandatory information and optional information.
Based on the meaning of paragraph 4 of Art. 69 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation in the requirement to pay tax, mandatory information includes:
— the amount of tax debt;
— the amount of penalties accrued at the time the claim was sent;
— deadline for fulfilling the requirement;
— measures to collect tax and ensure the fulfillment of the obligation to pay tax, which are applied in the event of failure to comply with the requirement by the taxpayer;
— the basis for levying the tax;
- contains a reference to the provisions of the legislation on taxes and fees, which establish the taxpayer’s obligation to pay tax.
Optional information should include information whose content in the tax payment requirement depends on certain conditions. Such conditions include the category of the taxpayer and the assumption that a violation of the legislation on taxes and fees has been committed, containing elements of a crime.
Thus, in the case of sending a request to pay a tax to an individual, the request to pay the tax must contain information about the deadline for paying the tax established by the legislation on taxes and fees.
If the amount of arrears revealed as a result of a tax audit allows us to assume that a violation of the legislation on taxes and fees has been committed, containing elements of a crime, then the request for tax payment must contain a warning about the obligation of the tax authority in the event of non-payment of arrears, penalties and fines in full within the prescribed period, send the materials to the investigative authorities to resolve the issue of initiating a criminal case.
Despite the direct indication in the Tax Code of the Russian Federation of the information that must be contained in the request for payment of tax, in accordance with judicial practice, this information is considered from the position that it should be known to the taxpayer and its absence in the request for payment of tax is not a reason for recognizing the demand for payment tax is invalid if the request contains a reference to documents that contain this information (clause 52 of the Resolution of the Plenum of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation dated July 30, 2013 N 57 “On some issues arising when arbitration courts apply part one of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation "). In other words, “a demand can be declared invalid only if it does not correspond to the taxpayer’s actual obligation to pay tax or is drawn up with significant violations of the requirements of the law.” In judicial practice, significant violations are understood, for example, as the absence of the amount of penalties, the lack of calculation of penalties taking into account the dynamics of the refinancing rate of the Bank of Russia in relation to the deadlines for fulfilling the tax obligation, or the lack of information on the basis of which it is possible to determine the amount of arrears and the period for which penalties were accrued.
However, if, on the basis of documents referenced in the tax payment request, the taxpayer is able to identify the amounts being collected and verify the legality of their collection, then the absence of even this information in the tax payment request will not be considered a significant violation.
Based on the meaning of clauses 5 and 6 of Art. 69 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the requirement to pay tax can be in paper or electronic form. The demand form was approved by Order of the Federal Tax Service of October 3, 2012 N ММВ-7-8/ [email protected] “On approval of document forms on identification of arrears, demands for payment of taxes, fees, penalties, fines, interest, as well as documents used tax authorities when applying interim measures and measures to collect debt on mandatory payments to the budget system of the Russian Federation,” while the form of the requirement to pay tax for organizations and individual entrepreneurs differs from the form of the requirement to pay tax for individuals who are not individual entrepreneurs.
The format of the electronic form of the request for tax payment is established by Order of the Federal Tax Service of December 28, 2010 N ММВ-7-6 / [email protected] “On approval of the Format of documents used by tax authorities in the exercise of their powers in relations regulated by the legislation on taxes and fees "
The authority to send a demand for tax payment belongs to the tax authority with which the taxpayer is registered, or the tax authority that made a decision to bring to justice for committing a tax offense or a decision to refuse to bring to justice for committing a tax offense (Clause 5 of Art. 69 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
In accordance with paragraph 6 of Art. 69 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the requirement to pay tax can be transferred to the taxpayer in three ways:
- personally against signature;
- by registered mail;
— in electronic form via telecommunication channels.
Since the entry into force of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (Part One) dated July 31, 1998 N 146-FZ until now, three significant changes have occurred in the methods of transmitting a tax payment requirement to a taxpayer.
Firstly, the list of methods for transferring the requirement to pay tax, enshrined in Art. 69 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, became exhaustive, in accordance with the Federal Law of July 27, 2010 N 229-FZ “On amendments to part one and part two of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation and some other legislative acts of the Russian Federation, as well as on the recognition of certain legislative acts (provisions of legislative acts) of the Russian Federation in connection with the settlement of debts on taxes, fees, penalties and fines and some other issues of tax administration.” Until 2010, the list of methods for submitting a tax claim was open.
Secondly, the legislation on taxes and fees enshrined the provision that the tax authority, in accordance with existing circumstances and capabilities, has the right to choose any acceptable method of transmitting the demand for tax payment. For example, immediately send a request for tax payment by registered mail. The power of the tax authority to choose the method of transmitting the tax payment requirement to the taxpayer appeared in the legislation on taxes and fees in 2010 after amendments were made to the Tax Code of the Russian Federation by Federal Law of July 27, 2010 N 229-FZ. Before the changes were made, the priority method for transmitting a tax payment request was to hand it over in person against a signature, and only if the tax payment request could not be served in person, it was sent by registered mail. However, in accordance with judicial practice, sending a demand immediately by registered mail was not considered a violation of the procedure. Currently, judicial practice and the provisions of paragraph 6 of Art. 69 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation coincide.
Thirdly, in the current version of paragraph 6 of Art. 69 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation there is no requirement for mandatory confirmation of the fact and date of receipt of the request for tax payment by the taxpayer. However, it is worth noting that all three methods of transferring a tax payment requirement allow you to fix the date of transfer of this requirement.
For each method of transmitting a tax payment request, there is a different way to confirm receipt of a tax payment request.
When transferred personally to the head of an organization or an individual, confirmation of receipt of the request for payment of tax will be the receipt of the recipient in the request for payment of tax indicating the date of receipt.
When sent by registered mail in accordance with clause 6 of Art. 69 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the request will be considered received after six days from the date of sending the registered letter. In this case, the procedure will be followed regardless of the actual receipt by the taxpayer (his representative) of the request for payment of tax sent by registered mail (clause 53 of the Resolution of the Plenum of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation dated July 30, 2013 N 57 “On some issues arising when applying by arbitration courts part one of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation"). However, despite the provisions of paragraph 6 of Art. 69 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the fact of receiving a request for tax payment by registered mail on the sixth day after sending can be refuted when considering the relevant dispute in court (clause 2 of the Determination of the Constitutional Court of the Russian Federation of April 8, 2010 N 468-О-О “On refusal to accept for consideration complaints from citizens Viktor Vasilievich Drozdov and Elena Alekseevna Drozdova about violation of their constitutional rights by Article 52 and paragraph 6 of Article 69 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation”).
When transmitting a demand in electronic form via telecommunication channels, the date of receipt of a demand for payment of tax will be the date indicated in the receipt of receipt, signed with a qualified electronic signature of the taxpayer (clauses 12 - 13 of the Procedure for sending a request to a taxpayer to pay a tax, fee, penalty, fine in electronic form via telecommunication channels, approved by Order of the Federal Tax Service of December 9, 2010 N ММВ-7-8 / [email protected] ). In this case, the demand will not be considered accepted if (clause 14 of the Procedure for sending a request to a taxpayer to pay a tax, fee, penalty, fine in electronic form via telecommunication channels):
— erroneously sent to the taxpayer;
— does not correspond to the approved format;
— it does not contain (does not correspond to) a qualified electronic signature that allows identifying the relevant tax authority (the owner of the qualified certificate).
Thus, in only one of the transmission methods is there a presumption of receipt by the taxpayer of the demand for payment of tax - by registered mail. In other cases, the tax authorities must confirm that the taxpayer has received the request.
As a general rule, in accordance with paragraph. 4 p. 4 art. 69 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the requirement to pay tax must be fulfilled within eight days from the date of receipt of the requirement to pay tax. However, the demand for payment of tax may specify a longer period of time for its execution. At the same time, before the expiration of the period established by law or in the requirement, the tax authorities do not have the right to take any action to collect taxes (Resolution of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the North Caucasus District dated July 31, 2008 N F08-4387/2008 in case N A53-2180/2008- C5-22).
In this case, it is necessary to take into account the provisions of paragraph 4 of Art. 69 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, which establishes that the deadline for fulfilling a requirement begins from the date of receipt of the request for tax payment. This provision appeared in 2006 and for several years tax authorities often violated this provision. Currently, failure to comply with deadlines for payment of taxes is a rare procedural violation.
Despite the fact that in the text of Art. 69 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation only mentions the requirement to pay tax, in accordance with paragraph 8 of Art. 69 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the rules provided for in Art. 69 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, apply to requirements for payment of other payments. In the original version of the provisions of Art. 69 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation were also applied in relation to the requirement to pay fees and taxes payable in connection with the movement of goods across the customs border of the Russian Federation. Currently, the process of submitting a demand for tax payment is universal for any debt arising in accordance with the legislation on taxes and fees for payment (clause 8 of Article 69 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation):
— taxes;
— fees;
- fines;
— fines;
— percent provided for by Chapter 9 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
The recipients of claims for these payments are also specified:
— payers of fees;
- tax agents.
How to respond to tax demands
It is not necessary to respond to a request in which the inspector indicates the amount of debt indicating its payment if you have paid this debt. But you can also write a response in which you indicate that the arrears have been paid and attach a copy of the payment order from the bank. If you do not agree with the amount of debt, then you need to understand the current situation, and the sooner the better. Because after the expiration of the period specified in the request, the tax office will write off the money from the taxpayer’s account. In order to understand where the arrears came from, you need to order a statement of reconciliation of settlements with the Federal Tax Service and a statement of transactions on the tax account where the arrears arose.
Deadline for filing a penalty claim
The Ministry of Finance of Russia, in a letter dated August 3, 2016 No. 03-02-07/1/45510, told what deadlines must be observed by tax authorities when making demands for payment of penalties. The financiers prepared explanations with the participation of their colleagues from the Federal Tax Service of Russia.
General rules
The same rules established by Art. 70 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation for issuing demands for payment of tax (clause 3 of Article 70 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Therefore, we present the procedure in force for tax requirements.
The deadline for submitting a tax payment requirement depends on how the arrears were discovered.
If it is identified during a tax audit, the requirement must be raised within 20 days from the date of entry into force of the corresponding decision based on the results of the audit (clause 2 of Article 70 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
In a situation where the debt is discovered by tax authorities outside the scope of the audit, the deadline for sending the claim depends on the amount of the arrears. If its amount is less than 500 rubles, the claim must be made within one year from the date of discovery of the arrears. Otherwise (if there is a tax debt of 500 rubles or more), no more than three months are allotted for filing a claim from the date the arrears were identified (clause 1 of Article 70 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Having discovered arrears, tax authorities immediately charge penalties on them. After all, penalties are transferred to the budget simultaneously with the payment of taxes and fees or after payment of such amounts in full. This is stated in paragraph 5 of Art. 75 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Thus, in the case of accrual of penalties on the amount of the identified arrears, they are billed to the taxpayer along with the tax debt in one request within the time limits specified in clauses 1 and 2 of Art. 70 Tax Code of the Russian Federation. The claim form was approved by order of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated October 3, 2012 No. ММВ-7-8/ [email protected] and provides for the reflection in it of both the amount of arrears and the amounts of penalties, fines and interest.
In the commented letter, officials noted that the Tax Code does not provide for the submission of a demand for payment of penalties after a demand for payment of arrears has been issued.
The arrears have been repaid, but penalties remain
But the need to accrue penalties may arise even when the tax arrears have already been paid. For example, the taxpayer transferred the tax in violation of the established deadline for its payment, but did not pay the penalty for the days of delay.
If this fact is discovered, the tax authorities will demand that he pay penalties. But what deadlines for filing a claim apply in this case?
The Plenum of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation in paragraph 51 of Resolution No. 57 of July 30, 2013 “On some issues arising when arbitration courts apply part one of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation” explained that the demand for payment of penalties must be sent no later than three months from the date of payment by the taxpayer of the entire the amount of the arrears, and in the case of repayment of the arrears in parts - from the moment of payment of the last part.
Please note that this clarification was given by the Plenum of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation during the period of validity of the old version of clause 1 of Art. 70 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, which established only one deadline for submitting a claim - three months from the date of discovery of the arrears. In this regard, in the commented letter, the financiers indicated that the position of the Plenum of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation must be applied taking into account the explanations given by specialists of the Federal Tax Service of Russia in letter No. SA-4-7/16692 dated August 22, 2014. According to them, it is necessary to take into account the changes made to paragraph 1 of Art. 70 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation regarding the deadlines for sending claims for debt, the amount of which is less than 500 rubles.
Thus, if the amount of tax arrears paid by the taxpayer is less than 500 rubles. a demand for payment of penalties may be sent within one year from the date of payment of the arrears.
If the deadline is missed
The Tax Code does not say anything about what consequences are entailed by tax officials missing the deadline established for submitting a demand for payment of taxes, penalties, or fines. Therefore, taxpayers are interested in the question: will a demand sent in violation of the deadline be considered valid?
The legal position on this issue is contained in the Resolution of the Presidium of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation dated November 1, 2011 No. 8330/11. This document states that the deadline for sending a demand for payment of a tax, fee, penalty or fine is not preemptive. Its omission cannot be considered a basis for invalidating a claim if, at the time of issuing the claim, the tax authority has not lost the opportunity to collect tax debt, taking into account the deadlines specified in paragraph. 1 clause 3 art. 46 Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Let us remind you that according to this norm, the decision on collection must be made no later than two months after the expiration of the period specified in the request for tax payment.
If the decision on collection is made after the expiration of the above two months, it is considered invalid and cannot be executed. In this case, the tax authority may apply to the court to collect the amount of tax due from the taxpayer. The application may be filed with the court within six months after the expiration of the deadline for fulfilling the requirement to pay the tax. District courts also believe that the tax inspectorate missing the deadline for sending a demand for payment of a tax, fee, penalty or fine cannot be grounds for declaring it invalid (Resolution of the Administrative Court of the North Caucasus District dated November 20, 2015 No. F08-8587/2015 (Determination of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation dated 05/06/2016 No. 308-KG16-399 refused to transfer the case for review), FAS of the West Siberian District dated 04/28/2014 in case No. A03-13103/2013, Volga District dated 04/15/2014 in case No. A12-16429/2013 , West Siberian District dated January 24, 2013 in case No. A27-10166/2012, Far Eastern District dated December 25, 2012 No. F03-5697/2012).
How to respond to requests for clarification
You must respond to the regulatory authority in free form. The main thing is that the answer contains the explanations required by the tax authorities.
In general, we can highlight the following main points when compiling: (click to expand)
- It is necessary to indicate to whom the explanation is sent and from whom it is - the name, address, TIN and checkpoint of the taxpayer;
- The letter should be titled something like this: “Response to the request for a tax number...”, “Providing clarifications as requested by the Federal Tax Service,” etc.
- The body of the letter contains a detailed description of the subject’s position with an indication of documents confirming the facts;
- It is necessary to attach copies of documents proving the taxpayer’s position;
- At the end of the document, the signature of the director and the seal of the organization are indicated.
An example response to a requirement can be downloaded here:
Explanation from the Federal Tax Service.
Consequences of failure to pay tax on demand
If for some reason the payment is not reflected in the budget settlement card, the tax authority may send the taxpayer a request to pay the tax (clause 1 of Article 45 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
The request is sent to the taxpayer and is considered received after 6 days from the date of sending the registered letter (clause 6 of Article 69 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). As a rule, the request indicates the deadlines for paying the tax; if there is no data on the deadlines, then the tax must be paid upon request within 8 days from the date of receipt of such a request (clause 4 of Article 69 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
If the tax is not paid upon request, the tax office may forcefully collect the tax by issuing a collection decision. Note!
The decision on collection will be made no earlier than the deadline established in the request, and no later than two months after the end of this period. If the decision on collection is made after a two-month period, then such a decision should not be enforceable. In this case, the tax authority may apply to the court to collect the tax amount.
The taxpayer must be notified of the decision on collection made by the tax inspectorate no later than 6 days from the date of the decision. The tax authority's order to collect funds is sent to the bank where the taxpayer is serviced, and the bank must unconditionally execute the tax authority's order to write off funds from the ruble account no later than one business day following the day the request was received (clause 6 of Article 46 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation) .
The tax authority may also send a decision to the bank to suspend transactions on bank accounts,
or suspension of electronic money transfers (clause 2 of Article 76 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). In this case, the bank will stop debit transactions on the account within the amount specified in the decision to suspend transactions. This can be done to ensure the execution of the decision to collect the tax and cannot be taken before the decision to collect the tax has been made.
Grounds for requesting documents
The basis for the requirement that is presented to a business entity is a tax audit of this entity. This is stated in Article 93 of the Tax Code. There are two types of such checking:
- On-site NP - when an inspector checks the taxpayer at his location during the period of his actual stay;
- Desk NP - when a submitted declaration is checked within 3 months after its submission;
- Counter IR - when during an audit of one taxpayer, his counterparty is also audited.
Important! A requirement may be made to a taxpayer by a regulatory authority during one of the types of inspections - counter, desk or on-site.
How to draw up a payment order
The rules for filling out a payment order are established by Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated November 12, 2013 N 107N and Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated September 23, 2015 No. 148H.
For each line of the request, it is necessary to generate a separate payment order. This can be done manually - transfer the data from the received request to fields 24 and 104-109 of the payment order.
When filling out a payment slip, you can use this table, which will tell you what value you need to indicate in each field. Be careful when entering data - an error in even one figure will lead to the fact that the organization’s money will not go to its intended destination, and the debt will not be repaid.
| Field number | Field name | Meaning |
| 104 | KBK | Budget classification code |
| 105 | OKTMO | OKATO (OKTMO) |
| 106 | Basis of payment | TR |
| 107 | Taxable period | The date specified in the request as the deadline for payment of penalties in the format DD.MM.YYYY |
| 108 | Document Number | Tax authority request number |
| 109 | Document date | DD.MM.YYYY - date of request (next to the number on the stamp) |
| 110 | Payment type | 0 |
| 24 | Purpose of payment | Name of tax (fee) |
You can read complete instructions on how to generate a payment order on the Accounting Online website.
The second option to prepare a payment order is to generate it automatically. This function has recently been available to Kontur.Extern users.
Having received an electronic request for payment in Externa, notify the Federal Tax Service about this by clicking on the button “Send an acceptance receipt to the Federal Tax Service.” Then proceed to create a payment order: follow the “Create payment order” link and enter the name of your bank and current account. The system itself will insert all other data from the request into the appropriate fields of the payment order. You can also choose what type of debt to make a payment for and, if necessary, change the payment amount.
You can create a ready-made payment slip either in Word format and then print it, or download a special text file to then upload to the Internet bank.
Requirement for documents to be submitted
The inspector's request for any documents may include:
- Providing paper documents. In this case, the taxpayer must make copies of the originals and certify them with his signature and seal of the organization;
- Providing electronic documents. In this case, the documents must be submitted in the form of scanned copies and sent to the inspection via telecommunication channels with the signing of their enhanced digital signature.
The deadline for submitting documents is indicated in the table.
| Taxpayer | Term |
| General procedure | 10 days |
| Consolidated group of taxpayers | 20 days |
| A foreign organization registered in the Russian Federation | 30 days |
Important! Tax officials do not have the right to repeatedly make demands for the same documents.
Penalty
Penalties are accrued for each calendar day of tax delay until the day of its payment (Article 75 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Consequently, since the taxpayer is notified that he has not paid the amount of tax, then at that moment the amount of the penalty has already been calculated for him.
The demand is issued to the taxpayer no later than three months from the date of discovery of the arrears. If the amount of arrears and debt on penalties and fines related to this arrears is less than 500 rubles, the requirement to pay the tax must be sent to the taxpayer no later than one year from the date of discovery of the arrears (clause 1 of Article 70 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
The only exception is the requirement to pay tax, non-payment of which was established during a tax audit. Then the request is sent within 20 days from the date of entry into force of the tax audit decision. For example, a person submitted an income tax return in form 3-NDFL, and during the audit it was determined that the person had underpaid the amount of tax.
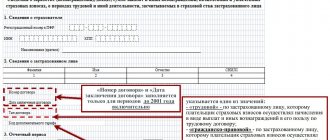
In accordance with paragraph 4 of Art. 69 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the requirement to pay tax must contain:
• information about the amount of tax debt;
• the amount of penalties accrued at the time the claim was sent;
• deadline for fulfilling the requirement;
• measures to collect tax and ensure the fulfillment of the obligation to pay tax, which are applied in the event of failure to comply with the requirement by the taxpayer.
A tax payment request sent to an individual must also contain information about the tax payment deadline established by the legislation on taxes and fees.
Responsibility for failure to provide a response to the inspector’s demands
This responsibility is described in Article 126 of the Tax Code.
The fine amounts for failure to provide documents requested by the regulatory authority are indicated in the table. (click to expand)
| Documents requested from the subject | Fine amount |
| All documents | 200 rubles for each document |
| Information about the taxpayer (payer of insurance contributions) | 10,000 rubles |
How to prevent account blocking and repeated withdrawals of funds
If you receive a request, the first thing you need to do is order a statement of transactions for settlements with the budget. It is better to do this via electronic communication channels. The extract will show when the discrepancy occurred. At the moment, statements of transactions for settlements with the budget are provided for specific years, and in the statement for 2019, you can see everything that happened only in 2020.
If all the details in the payment order are correctly indicated, you must send a letter to the tax office with a request for the correct posting of payments, and also attach copies of payment orders for tax payment. It is very difficult to get through to the tax office, so you need to act as quickly as possible to prevent the suspension of transactions and the debiting of funds from accounts.
Note!
For individual entrepreneurs, statements of account transactions from the Personal Account can only be obtained for 2020, and due to the setup of new software, the information is incorrect.
As a result of the introduction of new software, all payment inconsistencies fell on taxpayers, and now our task is to independently monitor payments and accruals and take timely measures to eliminate these problems.
Have you received a tax request? Delegate this problem to us. Many years of experience in interacting with the tax authorities allows us to solve such problems with the least possible consequences. Find out the cost of accounting services by phone: (495) 661-35-70, or leave a request on the website.
Author: Shiryaeva Natalya
How to write a response to a tax request?
Free consultation by phone Contents The tax system is the main source of government income.
In the Russian Federation it is three-level, there are federal, regional and local levels.
Regional and local laws operate within their region. The tax system of the Russian Federation performs the following functions:
- fiscal – the actual collection of payments;
- control – the Federal Tax Service monitors the activities of tax subjects and issues requirements when violations are detected;
- regulation – the system has a significant impact on economic indicators and makes adjustments to achieve the goals of the state’s tax policy.
- distribution - the Federal Tax Service must transfer received tax payments to the appropriate funds;
There are several tax systems. Tax system The main tax system, all enterprises are in this mode by default.
Each of them has its own taxation system. At the same time, laws at the federal level are binding on all legal entities and individuals.
Therefore, most enterprises are trying to switch to special regimes. Special taxation systems include four regimes:
- A single tax on imputed income, in this case the amount of payment is fixed and must be billed by the state. Not everyone can use UTII, but only enterprises with certain types of activities.
- A simplified system; most individual entrepreneurs and LLCs with a small number of employees and a small turnover operate in this mode. On the simplified tax system, an enterprise can be charged a tax of 6 percent of total income or 15 percent of the difference in income minus expenses.
- Patent system - only individual entrepreneurs can use it. They buy a patent for a certain type of activity at a fixed price.
- The Unified Agricultural Tax is a system for agricultural enterprises.
We recommend reading: Help in a conflict regarding the payment of alimony
Important!
OSN has the highest taxes and accounting is the most complex.
One enterprise