Accountants often have doubts about how to properly prepare an invoice and when it should be recorded in the accounting journals. Let's figure out what this document is and how it should be used.
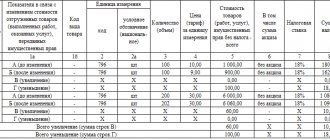
An invoice is a common document according to which both payment for goods and tax deductions are calculated. In international accounting, this document looks like this:
What the Tax Code says
According to the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the period for issuing an invoice is limited to 5 working days - in fact, one week. This period is calculated as follows:
- on the day of receipt of advance payment (one hundred percent or fractional) for further deliveries or transfer of ownership rights;
- on the day of actual shipment of goods (provision of services or performance of work), transfer of ownership rights.
The five-day period is counted from the day following the date of first shipment. If the invoice was issued for work or services, the period for issuing the invoice starts from the moment the work or services are fully provided. Please note: here we are not talking about the start of work, but rather the full provision of the agreed services or works. The exception is cases when the work will be performed on an advance payment and this circumstance is expressly stated in the business contract. In this case, advance invoices are issued to the counterparty. The deadline for issuing these documents is five days from the date of receipt of money into the account.
Examples of such situations are:
- uninterrupted provision of services or sales of goods related to the transportation of energy resources (light, gas, oil, etc.);
- provision of telecommunication services;
- sale of food products, which takes place every day in multiple quantities.
In such cases, the date for issuing the invoice by the seller is set no later than the fifth day of the month following the previous one. The preparation and registration of these documents in the “Sales Book” is carried out according to the quarter in which the products were sold or services were provided.
In order to avoid questions about the timing of presentation of invoices, contracts for supplies or services are concluded between two counterparties, indicating the procedure and timing for issuing this documentation.
Working and non-working days
It happens that the deadline for issuing falls on a non-working day. In this case, Art. 6.1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation allows the seller to postpone the deadline for issuing an invoice to the first working day after the expiration of the five-day period. But this rule should be used extremely carefully, since even a one-day delay will result in the invoice not being counted during the next tax audit. Therefore, auditors and experienced chief accountants recommend in this case to issue invoices in advance, without waiting for the end of the five-day period. An invoice can be issued on the same day on which the corresponding business transaction was carried out. If necessary, the invoice can always be adjusted.
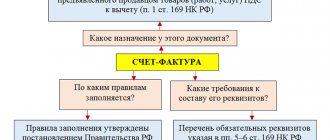
What is an invoice?
The specified business paper is used only for VAT accounting. The format of this fiscal paper is strictly specified.
An invoice is the same paper that serves as the basis for the customer of work or service to accept the amount of VAT designated by the contractor for deduction.
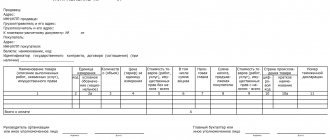
Example of an invoice
In general, there is reason to assert that the designated form is issued to the customer in order to:
- document the fact of provision of services or performance of work;
- justify the amount of value added tax paid, which will allow it to be counted later.
An invoice is a serious document that is regulated by the obligations prescribed by current legislation. In any situation, when purchasing or receiving a product or service, the client receives an invoice, a document confirming the transaction.
Dear reader! Our articles talk about typical ways to resolve legal issues, but each case is unique.
If you want to find out how to solve your particular problem, please use the online consultant form on the right or call.
It's fast and free!
Unified invoices
According to the Tax Code, some commercial enterprises are allowed to issue single (consolidated) invoices for sales at the end of the reporting month. The right to work under a single account must be enshrined in the contract. Contractors who carry out:
- continuous release of goods;
- continuously provide transportation or logistics services;
- supply of electricity, fuel resources;
- provide communication services;
- sell goods daily and continuously.
If the counterparties have worked for less than 30 calendar days, the invoice should be issued by the time of the last delivery deadline. But in this case, inspectors may insist that the principle of regularity and continuity of supplies is violated. Therefore, new counterparties with a single invoice standard should be approached with caution.
As for Tax Code, the deadline for issuing invoices for the reporting month is within five days of the month following the reporting month. But such accounts need to be registered in the month in which the first sales of received goods were made.
Requirements for issuing an invoice and issuing procedure
- upon receipt of an advance payment for future deliveries or provision of goods or services , when transferring rights to property, it is necessary to issue an invoice to the buyer within five calendar days from the date of receipt of payment for the supply of goods or services, transfer of property rights;
- during the provision of goods or services , as well as property rights, the person who pays taxes is obliged to issue an invoice to the purchasing person within five days from the time of shipment of products, provision of services or transfer of rights to property.
- those who are exempt from VAT;
- for transactions that are not taxed;
- for transactions that are subject to tax;
- according to the amount of advance payment received;
- buyers of property that is municipal or state, but not registered by institutions representing the municipal or state treasury;
- enterprises and individual entrepreneurs that are registered with the tax service, purchasing certain goods, services or work in Russia from foreigners who are not registered with the tax authorities.
Responsibility for failure to meet deadlines
The Tax Code of the Russian Federation does not indicate penalties for violating the deadlines for issuing invoices. But, as a rule, inspectors are guided by Art. 120 of the Tax Code and are called for late issuance of an invoice as for failure to issue an invoice at all. This is especially true for documents that need to be created at the junction of two reporting periods. For example, if an invoice should have been issued last month, but was created only this month, inspectors may regard this as a lack of an invoice and fine the company.
Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated November 10, 2020
2. Recognize as invalid the order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated April 25, 2011 No. 50n “On approval of the Procedure for issuing and receiving invoices in electronic form via telecommunication channels using an electronic digital signature” (registered by the Ministry of Justice of the Russian Federation on May 25, 2011 g., registration No. 20860, Rossiyskaya Gazeta dated June 3, 2011, No. 119).
Interesting: How to find out who has been fined by the order number
1.8. Qualified certificates of keys for verifying electronic signatures are issued in the manner established by the Federal Law of April 6, 2011 No. 63-FZ “On Electronic Signatures” (Collected Legislation of the Russian Federation, 2011, No. 15, Art. 2036; No. 27, Art. 3880; 2012, No. 29, Art. 3988; 2013, No. 14, Art. 1668; No. 27, Art. 3463, 3477; 2020, No. 11, Art. 1098; No. 26, Art. 3390).
Advance payments
So far we have been talking about invoices issued for the first event, such as the delivery of goods or the actual performance of services. How to correctly write out and calculate the deadline for issuing an advance invoice? Within what time frame must it be submitted to the counterparty?
The timing of advance invoices is directly related to the company's tax obligations. Money received by a company in connection with commercial activities automatically becomes the basis for taxation, and an invoice is a document certifying the correct receipt of money.
If the first event is the receipt of funds into the current account, then the period for issuing an advance invoice begins in the same period and under the same conditions as the invoice for the supply of goods. Thus, for funds transferred in advance, a tax liability arises within five days after receipt of money, which should be reflected in the appropriate document. These deadlines for issuing advance invoices are fixed in Article 164, paragraph 4 of the current Tax Code.
Online magazine for accountants
To provide the counterparty with an electronic invoice, the written consent of the buyer is required. With electronic document management, when is an invoice issued - before or after payment? After payment, if an advance payment has been made, before payment in the case of shipment of goods.
More to read: What fillings are included in the compulsory medical insurance program Krasnodar Territory Seversky District 2020
For ease of accounting, it is recommended to issue an invoice on the same date as the act or invoice. This is especially true for operations on border dates - at the junction of quarters. The rules for issuing a single invoice allow you to combine in one document operations for the shipment of several consignments of goods on different days. The main condition is compliance with the 5-day period. The period for issuing a document is counted according to the date of the invoice for the first delivery of materials or the first of the signed acts (Letter of the Ministry of Finance, dated January 12, 2020, No. 03-07-09/140).
Electronic documents
09/02/2010 The Tax Service of the Russian Federation recognized the right of taxpayers to work with electronic samples of tax and accounting documents. For the first time, an electronic document is recognized as equivalent and is accepted along with paper documents. This norm is enshrined in paragraph 1 of Art. 169 NK. The timing for issuing electronic invoices is similar to the period for issuing paper documents, since in this case both paper and virtual documents are identical.
To implement this provision, a separate order of the tax service approved the formats of electronic invoices, logs of these documents and other accounting books. The procedure for working with such documents is similar to paper document flow. One day is given for each exchange of accounts, but in fact, thanks to the Internet, the operation takes a few seconds. The exchange of accounts is fixed by Order 174 n and consists of the following:
- The date of appearance of the invoice in the accounting records of the counterparty is the date of receipt of such a file by the operator. Please note: not the date of invoice, but the date of receipt by the operator.
- Receiving electronic VAT invoices, the period for issuing these documents is counted not from the date on the document, but from the sending of the invoice to the buyer by the operator. The deadline for issuing an invoice by the seller thus depends not only on the first event, but also on the transmission of the electronic document to the operator.
A notice may serve as proof of receipt of the document. Previously, it was a mandatory requirement for an electronic invoice. Now this document is an addition to the invoice and is issued only in the event of an additional agreement between the counterparties.
Invoices
Tax accounting for VAT consists of three levels
Tax accounting
Tax accounting for VAT is a system for recording transactions subject to and not subject to VAT for the purpose of calculating VAT. The legal basis for tax accounting for VAT is:
Tax Code of the Russian Federation;
Resolution No. 914;
Letter of the Ministry of Taxes of the Russian Federation dated May 21, 2001 No. VG-6-03/404 “On the use of invoices when calculating value added tax.”
1. Primary documents:
An invoice is a document that serves as the basis for accepting the presented tax amounts for deduction or reimbursement in the manner prescribed by the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Invoices are issued by sellers to buyers within 5 days from the date of shipment of goods (performance of work, provision of services).
2. Tax registers:
Double accounting of primary tax accounting documents for VAT (invoices) is assumed. Initially, invoices are posted in the received and invoiced journals, respectively. The role of these documents is to register primary tax accounting documents (invoices). Recording received and issued invoices in journals does not affect the calculation of VAT amounts. Next, the invoices recorded in the journals fall into the purchase books and sales books, respectively. In the purchase book or sales book, not only the invoice is registered as a tax accounting document, but also the amount of VAT contained in the invoice. The total amounts for the purchase book and sales book are the basis for calculating VAT amounts in each specific tax period.
3. Tax return:
At this level of tax accounting, a VAT tax return is prepared based on data from the purchase book and sales book. It summarizes information from tax registers and calculates the VAT tax base, as well as the amount of VAT payable or refundable for a specific tax period.
In accordance with clause 1 of Article 169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, an invoice is a document that serves as the basis for accepting for deduction or reimbursement from the budget the amounts of VAT presented by the seller of goods (works, services), property rights (including the commission agent, agent who carries out the sale goods (works, services), property rights in one’s own name). The requirements for this document are established by the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, and their failure to comply will result in a refusal to deduct or refund VAT paid to the counterparty (clause 2 of Article 169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Invoices are issued to the buyer for each transaction for the sale of goods (work, services), including for sales transactions not subject to VAT, within 5 days counting from the date of shipment of the goods (performance of work, provision of services) - clause. 3 Article 168 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
An invoice is issued in the following cases:
- when selling goods (works, services) subject to VAT. In this case, VAT is highlighted on the invoice as a separate line;
- when selling goods (work, services), operations for the sale of which, in accordance with Article 149 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, are not subject to taxation (exempt from taxation);
- when selling goods (work, services) by a person exempt from the duties of a taxpayer in accordance with Article 145 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
In the second and third cases, invoices are issued without allocating the corresponding tax amounts (clause 5 of Article 168 and clause 3 of Article 169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). In this case, the corresponding inscription or stamp “Without tax (VAT)” is made on these documents. If these persons issue an invoice to the buyer with an allocated amount of VAT, they will be obliged to transfer this amount to the budget, and they will not have the right to a deduction (clause 5 of Article 173 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). The person who received such an invoice will also be denied the right to deduction by the tax authorities.
It should be noted that invoices are also issued in the absence of sales (clause 1, clause 3, article 169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation) in cases of receipt of funds in the form of:
1. financial assistance;
2. to replenish special-purpose funds;
3. interest on bills;
4. interest on a trade loan in the amount exceeding the amount of interest calculated in accordance with the refinancing rate of the Bank of Russia;
5. insurance payments under insurance contracts for the risk of non-fulfillment of contractual obligations by the counterparty of the insured-creditor, if the insured contractual obligations provide for the supply by the insured of goods (work, services), the sale of which is recognized as an object of taxation in accordance with Article 146 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation;
6. to increase income or otherwise related to payment for goods (work, services) sold.
In addition, invoices are issued in the following cases:
- when performing construction and installation work for own consumption;
- when transferring goods (performing work, providing services) for one’s own needs;
- in case of gratuitous transfer of goods (performance of work, provision of services);
- when performing the duties of a tax agent.
Invoices are not issued:
1. organizations and individual entrepreneurs who are not taxpayers;
2. organizations and individual entrepreneurs of retail trade and public catering when selling goods for cash, as well as other organizations and individual entrepreneurs performing work and providing paid services directly to the population, when issuing a cash receipt or other document of the established form to the buyer - in accordance with clause 7 Article 168 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation;
3. taxpayer organizations for transactions involving the sale of securities (with the exception of brokerage and intermediary services) - in accordance with clause 4 of Article 169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation;
4. banks (for transactions not subject to VAT in accordance with Article 149 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation) - in accordance with clause 4 of Article 169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation;
5. insurance organizations (for transactions not subject to VAT in accordance with Article 149 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation) - in accordance with clause 4 of Article 169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation;
6. non-state pension funds (for transactions not subject to VAT in accordance with Article 149 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation) - in accordance with clause 4 of Article 169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Invoice deadline
According to the general rule, stated in clause 3 of Article 168 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, an invoice is issued no later than 5 days, counting from the day of shipment of the goods (performance of work, provision of services).
It must be borne in mind that the preparation of invoices and their registration in the sales book must be carried out in the tax period in which the sale took place in accordance with the accounting policy adopted by the organization for tax purposes.
Registration of invoices
Accounting for invoices, which are the basis for tax transactions, is kept in accounting journals. Since January 2020, only tax payers are required to keep such journals. But there are exceptions to this rule. Thus, according to existing rules and regulations, the invoice journal must be available:
- from taxpayers;
- for persons exempt from the obligation to be a taxpayer;
- from persons not registered as taxpayers, if they periodically issue or receive invoices when conducting commercial activities, while representing the interests of other persons on the basis of bilateral agreements.
A complete list of principles for processing and storing these documents is contained in the Rules for maintaining an invoice journal, approved in 2011.
In what cases is it necessary to issue an invoice to the buyer?
However, it is not prohibited for individuals to draw up invoices when selling goods. On its own initiative, the organization has the right to draw up such documents and register them in the sales book. Moreover, it is possible to draw up not single, but summary invoices, which record not one, but several transactions for the sale (free transfer) of goods to individuals for a certain period (for example, a quarter). Such invoices should be drawn up in one copy, and dashes should be placed in lines 6 “Buyer”, 6a “Address” and 6b “TIN/KPP of the buyer”.
Operations involving the transfer of goods on the territory of Russia (performance of work, provision of services) for one’s own needs are not subject to VAT if the costs of such operations are taken into account when calculating income tax. This follows from the provisions of subparagraph 2 of paragraph 1 of Article 146 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Procedure for filling out invoices
According to the Filling Rules, taxpayers have the opportunity to indicate additional information in this document. These include:
- details of the primary document (invoice, bank statement);
- name of the person issuing the invoice with current statutory and settlement details.
The mention of primary documents allows the seller to indicate additional information not only for sellers, but also for buyers, so it is possible to clarify the date of acceptance of goods or the completion date of work, and other information of interest to the opposite party. In order to regulate the flow of necessary information, such an addition was allowed.
Requirements for the document
Main information:
- List of services provided and products issued.
- Details and names of participants in the transaction.
- Designation of prices for all items.
- Full cost, rate and tax amount.
By mutual agreement of the parties, a decision is made on what form to submit the documentation (paper or electronic).
The following documents are required to be drawn up:
- all those who pay VAT in transactions that are subject to taxation;
- tax agent - for the service provider;
- those who use their VAT exemption under Article 145 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Also in these categories there may also be intermediaries who pay taxes in accordance with the general regime, with the simplified tax system or other special payment regime.
These documents should not be completed:
- entrepreneurs and firms engaged in retail trade, catering or providing services to the public for cash (with supporting documents);
- those who carry out tax-free transactions;
- those who pay taxes under special regimes (with certain exceptions);
- if an advance has been received for future supplies of industrial materials, and the production cycle is long;
- persons who entered into a transaction in the sale of goods and services and do not pay or are exempt from VAT (taxable - 0% rate, non-taxable - in accordance with Article 149 of the Tax Code).
Due to errors when filling out the form, the tax office may withdraw the deduction and the tax amount will be increased. We are talking about the following errors:
- Errors that make it impossible to determine the name of the purchased product or service.
- Those errors or distortions that make it impossible to determine information about the seller and buyer.
- If it is impossible to see the VAT rate for the product.
- If it is impossible to determine the amount of tax fees.
- If there are errors in determining the price of services or goods, or in the prepayment.
Go to What documents confirm land ownership?
There are rules for numbering an invoice:
- The number is recorded in accordance with chronology and in ascending order.
- It is indicated in the first line.
- The numbering is supplemented with the help of digital indexes through “/” if the document was compiled by trustees or separate divisions.
- Renewal of numbers is at the discretion of the company.
The execution and preparation of such a document requires compliance with all regulations and standards; the invoice itself is a document from the supplier indicating details and data.
The account must always be assigned a registration number of both parties, which must match when verified. It is also mandatory to have the date of the transaction.
The document is always executed on behalf of the owner of the service provider, in the name of the recipient. The details of the supplier and buyer must always be indicated.
The invoice is issued in 2 copies, one of which remains with the client, and the other with the supplier. Each enterprise is required to maintain an open register of accounts in which to enter each form received.
All information on issued and received invoices must be displayed in reports generated for VAT.
total cost
The value of the invoice is regulated by VAT; for this, the document must be submitted on time to the tax office.
All such documents on deadlines are provided quarterly and can be sent by email, but only with wet stamps and original signatures.
Invoices are provided to the tax office to eliminate the total cost of taxation. To do this, you must provide a VAT invoice and multiply the price of the product or service by the general regulated rate - 18% or 10%, depending on the type.
Due to the fact that the VAT amount is excluded under a special regime, it must be deducted every quarter and transferred to the budget:
- 18% is the total bet amount.
- 10% – special types of goods and services, for example, medicines and drugs, children's products, some types of products.
- 0% – rare, very individual situations.
Thanks to the specified amount of payment for a product or service, it is possible to clearly calculate the amount of VAT deduction for transactions that will be charged to the supplier. This amount may be specified in the contract, or agreed upon as a monthly payment.
It should be understood that when choosing a certain percentage, the calculated rate will be equal to:
- 18-188.
- 10-110.
Some situations are regulated in which organizations are not burdened with the payment of VAT and invoices on a general basis, such as, for example, UTII, simplified tax system.
This rule is prescribed in tax legislation.
But it is always necessary to understand that when issuing an invoice, the supplier and the client undertake to pay the percentage indicated in the form and indicate the transaction and tax in the tax return.
The requirements of paragraph 5 of Article 169 of the country’s key fiscal document state that the invoice issued by the supplier for the sale of work or services must necessarily contain such details as:
- serial number and date of formation of this paper;
- name, localization and tax identification number of each party (supplier and customer);
- name and location of the recipient and sender of the cargo;
- number of the financial document, if advance and other payments have been made against future income;
- the name of the work performed and services provided along with an indication of their unit of measurement;
- the number of works and services performed;
- indication of the currency in which payment will be made;
- price of services or work per unit according to the signed agreement without tax. If government-regulated prices are used, the tax amount should also be indicated;
- the total cost of goods and services shipped;
- the amount of excise tax if we are talking about excisable goods;
- tax rate;
- the amount of VAT presented to the customer;
- country of origin of works or services;
- Number of customs declaration;
- code of the type of product corresponding to the unified Commodity Nomenclature of Foreign Economic Activity.
New changes
In 2020, changes were made to the document form. Thus, a mandatory detail is the code of the type of goods of the Commodity Classification of Foreign Economic Activity, which is necessary to supervise deductions for the raw materials group of goods. For the raw material group, the deduction is accepted in the old order, and for transactions with non-commodity goods, the deduction is carried out according to the new form. The code of the type of goods under the TN VVED became mandatory for indication in the document. This is due to the fact that this code is necessary for monitoring deductions for goods of the raw materials group, which are accepted in the old order. All other product groups are issued in accordance with the current form.
New invoices must indicate an address that must correspond to the data from the Unified State Register of Legal Entities. Previously, it was enough to indicate the details from the constituent documents, but now the new rules oblige you to enter correspondence both into the invoice and into the Unified State Register of Legal Entities database.
What is the deadline for issuing an invoice by the seller in 2020-2020
Although the indication in the invoice of a date that violates the established deadlines for its issuance is not named in the list of reasons that make the deduction impossible (clause 2 of Article 169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation), and the courts adhere to the same position (Resolution of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the Moscow District dated December 23, 2011 No. A40-142945/10-118-831), we recommend that, in order to avoid disputes, you always indicate the correct date on the invoice.
- The entire set of documents for a specific shipment will be very convenient to use. For individual documents, it will contain the same dates and total amounts; if the numbering order is organized correctly, it will also contain document numbers.
- There will be no problems with accounting for VAT at the junction of periods when the shipment was made in one quarter, and the invoice for it is dated the next. Moreover, this problem will primarily affect the supplier himself, since he will reflect the sales in accounting in one quarter, and the VAT document will relate to another. At the same time, in the accounting program, the invoice will automatically, based on the date of creation of the VAT, go into the sales book of another quarter, and if you manually adjust the date of entry in the book, the program may refuse to record there a document dated later than the quarter of shipment.
- Advance invoices, the date of which will coincide with the date of receipt of money, will be convenient to use.
- The date of the adjustment invoice will coincide with the date of signing the agreement to change the quantity or price of the goods, which will also make it easier to work with these documents.
Budget and adjustment billing periods
Before learning about the deadlines for issuing adjustment invoices, it would be a good idea to familiarize yourself with the agreement under which the business activity of this enterprise is conducted with the counterparty. If the contract specifies the possibility of changes, they should be made within a five-day period after agreement. Confirmation of such consent can be a Certificate of Established Discrepancy, certified by both parties.
All tax actions with invoices and adjusting invoices relate to the period in which these documents were issued. Based on an adjustment invoice issued in the direction of reducing the total cost of delivery, the supplier has the right to reduce its own tax liabilities. To receive a VAT deduction, the seller generates a negative invoice. Thus, the VAT amount is reduced by the amount of the full invoice minus the amount of the correcting invoice. The buyer, on the contrary, has an additional obligation to increase his VAT based on the issued invoice. Similar requirements apply to electronic invoices. The deadline for issuing a correction invoice in electronic format is similar to actions with paper documents - within five days after signing the Statement of the identified discrepancy.
When an invoice is issued - practical nuances
The law does not prescribe in any way the form of agreement for the use of electronic documentation, therefore, business behavior tactics can be used as conditional consent, this could be, for example, oral consent, or a condition specified in the contract. This advice is listed as one of the most important on the official resource of the Ministry of Finance, in order to subsequently avoid misunderstandings.
- Those who do not pay value added tax.
- Individual entrepreneurs who trade or provide goods and services at retail.
- Organizations whose activities are related to public catering.
- Enterprises that provide goods and services for non-cash payments.
- Some individual special transactions of banks or organizations that are legally exempt from taxes.
- Some insurance companies.
- Pension funds.
Also read: Certificate of completion of work performed by an individual sample
Correcting errors in invoices
This is possible if the invoice contains:
- error in the details of the buyer or seller;
- incorrect tax rate;
- simple typo.
If an invoice needs to be corrected, a new, corrected document must be drawn up to accompany it. Regardless of when the correction was issued, the corrected invoice is assigned to the same tax period in which the transaction was carried out and the original invoice was generated. If an invoice that was issued with an error does not lead to a refusal to refund VAT, then it does not need to be corrected.
The numbering of main and correcting invoices within one period is continuous. Corrections for adjustment invoices are prepared in the same way as for the original ones. But the numbering of corrected invoices within one invoice always starts with one. An entry is made in the accounting journals: invoice number such and such, correction No. 1, and it is this invoice that should be taken into account when calculating VAT.
In what cases is it necessary to issue an invoice to the buyer?
If the buyer (customer) is not a VAT payer or is exempt from paying this tax, then the seller (executor) may not issue him invoices, provided that an agreement on non-issuance of invoices has been signed between them. This conclusion was reached by the Ministry of Finance (clause 3 of Article 169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated March 16, 2020 No. 03-07-09/13808).
In addition to these organizations, invoices must also be issued by companies that sell goods (work, services) on their behalf under an intermediary agreement. Of course, provided that the principal (principal) applies the OSNO (clause 1 of Article 169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, clause 20 of Section II of Appendix 5 to Resolution of the Government of the Russian Federation of December 26, 2011 No. 1137).
17 Jul 2020 stopurist 249
Share this post
- Related Posts
- Loan for starting a small business from scratch
- Studying at the institute is included in the work experience
- International passport through government services production time 2020 reviews
- How to find out the tax rate for land tax by cadastral number
Procedure for drawing up an invoice for services
To begin with, it is worth noting that from January 1, 2020, the VAT rate increased, and therefore column 7 in the invoice has changed. Now this column indicates a new rate - 20%. There were no other changes in the form of the document.
An invoice can be issued for the purchase (sale) of goods or services. In both cases, the document is drawn up in a generally accepted form established by law.
However, there are some differences. Let's look at them in the table.
| Filling out an invoice for the sale (purchase) of products | Filling out an invoice for the sale (purchase) of services |
| The document number and date of the transaction must be indicated | Fill in the same way |
| We indicate the name of the seller, buyer, their addresses and TIN | Fill in the same way |
| Be sure to indicate who the consignee, consignor and their addresses are | No goods are shipped, these lines are not filled in. We put a dash. |
| The payment order number is entered if the buyer made an advance payment | Fill in the same way |
| We indicate the name of the object of sale and quantity | Fill in the same way |
| It is necessary to indicate in what currency the document is drawn up. Basically, of course, these are rubles. | Fill in the same way |
| If a government procurement is carried out, then from July 1, 2020, the government contract identifier is noted | Fill in the same way |
| We indicate the units of measurement of the quantity sold (code and designation) | If it is difficult to determine the unit of measurement, then it is not entered, but a dash is added. If the unit of measurement is still indicated, then you need to select it in accordance with the classifier. |
| Price without VAT | Fill in the same way |
| Total price excluding VAT | Fill in the same way |
| Fill in the Excise Tax column | Excise taxes do not apply to services, so we put a dash in this column |
| VAT rate | Fill in the same way |
| VAT amount | Fill in the same way |
| Amount including VAT | Fill in the same way |
| If the goods are manufactured abroad, indicate the code and name of the country of origin, the customs declaration number | The column is not filled in, a dash is placed |
| From October 1, 2020, the column with the code of the type of goods according to the invoices for foreign economic activity of the EAEU is filled in | Not filled in, put a dash |
There are few differences in the preparation of invoices for products and services. All basic details of the document must be filled out without fail and correctly.
It is recommended to indicate the name of the service in the same way as stated in the contract.
Submission deadlines
As required by the provisions of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the selling party has 5 calendar days to issue the designated document:
- if advance funds were received from the customer for future performance of work or provision of a service, but this service or product was not shipped or delivered. In this case, the date of payment of the advance is considered to be the date of crediting the funds to the seller’s current account;
- if the products have already been shipped, then the countdown of 5 calendar days starts from the moment of their shipment, indicated in the delivery note. When providing services, the designated period is counted from the period specified in the work completion certificate.
How to correct errors in an invoice
If a document is submitted with errors, and they were identified immediately, the incorrect document is usually replaced with the correct one.
If errors are discovered later, then if the amount is indicated incorrectly, for example, an adjustment document will have to be drawn up.
Corrections are made by both the seller and the buyer. They must be approved by the head of the organization. The date of the new document is also indicated and it is indicated which original document the changes are being made to.
Established deadlines for issuing invoices
As a general rule, all invoices are issued within 5 calendar days from the date of shipment of goods or provision of services . There is also an opinion of the Ministry of Finance that the period of 5 days includes the day of shipment. However, it is customary to focus on the deadlines established by the tax code.
In October 2020, the Ministry of Finance issued Letter No. 03-07-14/74899, which states that if there is no interruption in supplies during the month, then one general document can be issued by the 5th of the next month. For some organizations, exhibiting documents in this way is very convenient. For example, security companies and companies that organize the daily delivery of bread can do this.
Unacceptable errors when preparing invoices
Whether the company can accept input VAT for deduction depends on the correct and timely completion of the invoice.
Let's look at the main errors, in the presence of which the tax office will refuse to deduct VAT.
- When drawing up the document, you need to take into account that you need to fill out the details of the seller and buyer very carefully. If the wrong name of one of them, incorrect addresses or TIN are indicated, then the deduction will be denied.
- It is imperative to accurately and clearly indicate which product or service is being sold. The tax office will not pass a document if it does not understand what exactly the organization is buying.
- We all make mistakes. If the tax office finds inaccuracies in the amount of shipment or advance payment, then VAT on such an invoice will not be accepted for deduction.
- Sometimes it happens that the VAT rate is indicated incorrectly in the document. This is also a significant mistake when filling out an invoice.
- It also happens that the VAT rate is indicated, but the amount is not entered. Or the amount of VAT when multiplying the rate by the cost of the goods does not correspond to that indicated in the document.
All these errors are fatal; it is not possible to deduct VAT on such documents.