How does re-invoicing work?
The law does not provide clear guidelines regarding the sequence of re-invoicing. The nuances of accepting VAT for deduction are also not specified. But it is imperative to focus on the provisions of laws that indirectly relate to the rules of re-listing, and on judicial practice. This will reduce the risk of claims from authorized bodies.
There are general rules regarding re-invoicing. In particular, it is necessary to confirm the expenses incurred by the intermediary at the expense of the customer. Documents are used for this. The corresponding rule is stipulated in paragraphs 1-2 of Article 1008 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation.
The main rules for selling products through an intermediary:
- If an intermediary is involved in the sale of goods, information about him is written down in the invoice for payment. The invoice is issued in several copies.
- A copy of the invoice is issued to the customer.
- The customer must draw up the invoice that the intermediary needs.
When issuing an invoice (IF), the first line of the document contains its number and date of completion. You need to record the date the invoice is submitted to the agent. The principal needs to make a note based on the invoice in the purchase ledger.
Within the framework of the transactions under consideration, agency fees will be considered income. That is, it is from it that VAT will be paid. The relevant provisions are contained in Articles 41, 153 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Accounting for the principal in the program “1C: Accounting 8”
To register the relationship between the agent and the principal in the program, an agreement is drawn up with the counterparty, which indicates the type of agreement: with the commission agent (agent) or with the principal (principal). For contracts of this type, in contrast to ordinary contracts with a supplier or buyer, it is possible to specify the procedure for calculating commissions.
The amount of commission in the program can be calculated as a percentage of the cost of goods or services sold, as a percentage of the difference between the cost at which goods or services were transferred to the agent and the cost of their sale to the buyer, and can also be set manually. The commission calculation parameters may remain blank; in this case, they will need to be specified manually each time when generating the documents Report of the commission agent (agent) on sales or Report to the principal (principal) on sales (see Fig. 1).
Rice. 1
Let's consider the most difficult situation, when an organization acts as an agent in the sale of the principal's goods, while the principal also provides services for the delivery of goods to customers. In addition, the organization also provides its own services to protect goods during transportation. The agent submits documents on his own behalf.
First of all, the document Receipt of goods and services is drawn up, with the help of which the fact of transfer of goods by the principal to the agent is registered. In this case, the document is drawn up in the usual way, using the transaction type Purchase, commission. Account 004 “Goods accepted on commission” is used as an accounting account.
Thus, an accounting entry is made to the Debit of account 004.1 for the cost of the transferred goods - see Fig. 2.
Rice. 2
Then we register the sale of goods to the buyer, but at the same time we also reflect the fact of the sale of the principal’s service and our own service.
To do this, on the Goods tab of the Sales of Goods and Services document, we indicate the list of the principal's goods being sold, on the Services tab, the service for protecting goods provided to the buyer on our own, and on the Agency Services tab, the principal's service for the delivery of goods.
It should be noted that on the Agency services tab of the document, columns with information about the principal, the agreement with him, within the framework of which the service is implemented, and the settlement account (in our case 76.09) must be filled in.
In case of mistaken entry of information about agency services into the services table and vice versa, the data in these tables can be mutually supplemented using the Transfer to “Services” and Transfer to “Agency Services” buttons.
When posting the document, the necessary entries will be made - see fig. 3.
Rice. 3
As can be seen from the entries, VAT on goods and services sold under an agency agreement is not reflected by the agent. It must subsequently be reflected to the principal.
The agent issues an invoice to the buyer for the total amount of the transaction, but only the cost of his own service should be included in the agent's sales book from this amount.
The buyer transfers payment for goods and services to the agent. This operation is formalized in the usual way using the document Receipt to the current account with the transaction type Payment from the buyer.
Debit 51 Credit 62.01
In our case, the entire payment amount is transferred upon the provision of services, but even in the case of an advance, this operation does not have any special features, compared to a similar operation under an agreement with the buyer.
After this, the agent draws up a report to the principal; for this, the document Report to the principal (principal) on sales is used.
This document is filled out with a list of goods and services sold in accordance with the agency agreement. The program implements the ability to automatically fill the table of goods and services with one of three possible algorithms:
The header of the document indicates the procedure for calculating the agency fee; information about it is inherited from the agency agreement (remember, at the very beginning we said that it is desirable, but not necessary, to indicate this information in the agreement). If the agreement does not specify the procedure for calculating remuneration, it can be indicated directly in the header of the report to the principal.
https://www.youtube.com/watch{q}v=ytcopyrightru
The amount of the agency fee is indicated for each product or service from the table of the same name in the document. For each line, the amount of VAT remuneration is also calculated.
The procedure for reflecting the sale of intermediary services in accounting is indicated on the Remuneration tab. The Withhold commission flag allows you to regulate the mechanism for paying agent commissions:
- if the flag is set, then the amount of remuneration is withheld from funds received from buyers as payment for the goods and services of the principal;
- if the flag is not set, then when posting a document in the usual way, either an offset to the advance payment (if the principal paid for agency services was made earlier) or the principal’s debt is registered.
We suggest you read: FMS Taganrog what documents are needed to deregister at the place of residence
On the Settlement Accounts tab, set the account for settlements with the counterparty (to reflect mutual settlements for the provision of agency services - by default account 62.01) and, depending on the selected method of payment for the agency fee, either the account for settlements with the principal or the account for settlement of advances.
When deducting the amount of remuneration from customer payments, the default settlement account with the principal is 76.09. If the payment of the agency fee is made in a separate payment from the principal, then here you need to indicate another account - settlements for advances 62.02.
On the Cash tab, the user manually enters information about funds received from the buyer.
Debit 62.01 Credit 90.01.1 – for the amount of agency fees – revenue is reflected; Debit 90.01.1 Credit 68.02 – for the amount of VAT on remuneration – VAT is reflected.
If remuneration is withheld from customer payments, a posting will also be made
Debit 76.09 Credit 62.01
– for the amount of agent’s remuneration.
The agent issues an invoice to the principal for the amount of remuneration, which is registered in the program directly from the Report to the Principal document.
https://www.youtube.com/watch{q}v=upload
Based on the report, the principal can register the document Write-off from the current account, with the help of which the fact of transferring funds to the principal for goods and services sold is formalized. If the amount of the agency fee was withheld from funds received from buyers, then the amount of receipts minus the amount of the agent fee will automatically be entered in the bank document.
Otherwise, the document will contain the full amount of payments made by buyers for goods and services of the principal from the current report to the principal.
Also, based on the report, the principal can enter the document Receipt to the current account, reflecting the fact that the principal has transferred the agency fee. This document is entered when the Withhold agent fee flag is not selected.
We also need to mention invoices. In our example, based on the results of the operation, two invoices should be included in the sales book: an invoice issued to the buyer, but only for the cost of the services provided by us for the protection of goods; an invoice issued to the principal for the amount of the agency fee (see Fig. 4).
Rice. 4
Let's now look at the same example from the principal's point of view.
When transferring goods to commission, a document Sales of goods and services is drawn up with the transaction type Sale, commission. Based on this document, you can subsequently register the document Report of the commission agent (agent) on sales. The document will be automatically filled in with the goods transferred to the commission; then you will also need to add a list of services sold under the agency agreement.
On the Remuneration tab, in a manner similar to the document Report to the principal (principal), the fact of offset of the agency fee from the cost of goods and services paid by buyers is drawn up.
From the principal's report, you can issue an issued invoice for goods sold and register the received invoice for the agency fee - see fig. 5.
Rice. 5
Debit 90.02.1 Credit 45.01 – sale of goods transferred on commission; Debit 62.01 Credit 90.01.1 – sale of goods transferred on commission; Debit 90.03 Credit 68.02 – VAT on sales of goods; Debit 62.01 Credit 91.01 – sale of delivery services; Debit 90.03 Credit 68.02 – VAT on the sale of delivery services; Debit 76.09 Credit 60.01 – for the amount of the commission agent’s remuneration; Debit 19.04 Credit 60.01 – VAT on the commission agent’s remuneration. Debit 60.01 Credit 62.01 – offset of agency fees against receipts from buyers.
Thus, we have illustrated that in the 1C: Accounting 8 program (rev. 2.0) the most complex version of the operation under an agency agreement is fully automated.
https://youtu.be/uM0Dj0CJdqQ
Features of re-invoicing
An invoice is both confirmation of acceptance of products and the basis for deduction for VAT. The corresponding provision is stipulated in Article 169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. It is necessary to take into account the specifics of the procedure in which an agency agreement is present. In this case, an additional link is formed between the seller and the consumer - an agent. It works in the interests of the consumer (Article 1005 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
Initial SFs are issued to the agent. For the principal to use the deduction, you need to re-issue the SF to him. That is, the agent needs to provide the principal with the SF when transferring authority for the products.
The Federation Council is drawn up in a certain form. All the nuances of its preparation are specified in Government Decree No. 1137 of December 26, 2011. Re-listing of paper is carried out by an agent who acts on his own behalf.
The agent is considered to be directly involved in the re-registration if these conditions are met:
- Execution of instructions under agreement.
- Working on your own behalf.
Re-listing must be carried out on the basis of the law.
kak_perevystavit_schet-fakturu_po_agentskomu_dogovoru.jpg
Related publications
An intermediary working under an agency agreement always acts in the interests and at the expense of the customer, and, based on the conditions specified in the contract, on his own behalf or on behalf of the principal. Upon fulfillment of obligations or after the expiration of a certain agreed period, the agent must provide the customer with a report accompanied by documentary evidence of the costs incurred (Article 1008 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation). For goods purchased for the customer or services provided that are subject to VAT, the agent receives invoices, which he also attaches to the report.
This procedure is relevant in a situation where the agent performs all operations on behalf of the principal, therefore, the customer will appear as the buyer in the invoices. If the intermediary acts on his own behalf, then in the invoices that he receives, his name is indicated as the acquirer, although this distorts the essence of intermediary activity, because the purchased assets are intended for the principal. To correct this “distortion,” the agent will have to reissue similar invoices (IF) to the customer. Let's consider the mechanism of this operation.
Legislative justification
Re-issuance of the SF is a procedure that is regulated by these regulations:
- Article 169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation . It states that invoices can be issued by agents selling goods/services on their own behalf.
- Articles 171, 172, 169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation . These articles indicate the conditions for deducting VAT. In particular, these are the following circumstances: acceptance of products for registration, use in work subject to VAT or use for resale, receipt of an invoice from the supplier.
- Article 1011 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation . The SF is first filled out for the agent.
When filling out, you must take into account the provisions of Government Decree No. 1137 of December 26, 2011.
Accounting Features
To use the deduction, you must take into account the provided SF. Receipt from the SF agent must be reflected in these documents:
- Logbook.
- Book of sales and purchases.
SF purchased from an agent are recorded under the number 01.
NOTE! Invoices received by or reissued by the agent do not need to be recorded in the purchases and sales ledger. They should be taken into account only in the Invoice Log (Clause 3.1 of Article 169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
If the agent does not need to provide VAT returns, then the tax office must check the logbook provided by him once a quarter. The deadline for this is the 20th day of the month following the end of the quarter.
If the agent is a VAT payer, he does not need to submit the Journal - the tax authorities will receive all the information necessary for control from the VAT return, and specifically from sections 10 and 11.
Selling products by agent
The agent may, on his own behalf, sell the principal's products subject to the latter's instructions. In this case, you need to do the following:
- Filling out two SFs.
- One paper is sent to the acquirer.
- The second paper is registered in the SF accounting journal.
- There is no need to register the document in the sales ledger.
- The SF values are sent to the principal.
The principal, when receiving values from the agent, performs these actions:
- Issuance in the name of the SF agent.
- Registering an account in the sales ledger.
All this information must be recorded in part 2 of the Federation Council journal.
sf.png
The agent reissues the invoice in accordance with the current rules:
line 1 is dated by the date of the invoice received from the supplier, and the document number is entered chronologically in the agent's invoice journal;
lines 2, 3, 4 remain unchanged;
line 5 adds information about the details of the payment order to receive funds for the purchase from the principal;
Lines 6, 6a and 6b indicate the name, details and address of the buyer, i.e. the principal under the agency agreement.
Changes in the document are highlighted in red.
Sample of a reissued invoice under an agency agreement:
Features of re-issuance of invoices when purchasing products
If products are purchased for a principal, the procedure for creating invoices will be different:
- The SF in the name of the agent is issued by the supplier.
- The document is registered in the sales book.
- The agent enters the account in the second part of the SF accounting journal.
- The agent, on his own behalf, fills out the SF with the same meanings addressed to the principal. The “seller” line records the actual supplier.
- The agent enters the SF in part 1 of the accounting journal.
The last step is the registration by the principal of the SF previously issued by the agent. A purchase ledger is used for registration.
If an agent makes purchases (purchases goods, pays for work or services) for several principals at once and receives a common invoice for the purchase he made, then when re-issuing it needs to be “sorted”. Each specific principal should receive not a single list, but an invoice relating only to his order. This requirement is stated in the letter of the Federal Tax Service No. GD-4-3 / [email protected] dated April 18, 2014.
If the agent has received from sellers for the same principal several invoices of the same date, he is allowed to combine them into a single one when reissuing. In this case, all data must be given using the “;” sign. This is permitted in paragraphs. “c” clause 1 of the Rules for filling out an invoice, approved by Government Decree No. 1137 of December 26, 2011.
Supporting documents for the agency agreement
What documents should the agent provide to the customer (the agent makes purchases){q} In whose name the documents should be drawn up if the agent acts on his own behalf{q}
Regardless of on whose behalf the intermediary acts, when carrying out the instructions of his customer, he must report to the principal for the work performed.
They must sign the report. What minimum package of documents (instructions, regulations, regulations, etc.) should be present in the company in terms of personnel documentation and labor protection{q}
(Staff 14 people) Please clarify what features exist when concluding an agreement with an external part-time worker. ✒ When concluding an employment contract with a part-time worker, the same rules apply as when hiring an employee for the main job….
- Agent's invoice to the buyer Good afternoon, please tell me.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with: Title documents for a land plotOur supplier delivered the goods to our buyer by rail. in the documents issued to us for railway services, it is not our supplier, but the owner of the cars, who is...
- Payment by corporate card - postings Good afternoon.
We are your client. Contract 49825. Two related issues. A corporate card was issued directly to the current account. The employee withdrew cash from an ATM and deposited it into the organization’s cash desk.….
Features of invoice design
Let's consider a scheme for filling the SF with intermediaries (they could be, for example, developers, freight forwarders):
- Line 1 – date of creation of the SF by the agent.
- Page 1a – number of the correction included in the Federation Council.
- Page 2 – name of the selling company.
- Page 2a – address of the seller, contained in the Unified State Register of Legal Entities, address of the forwarder.
- Page 2b – TIN and checkpoint of the seller.
- Page 3 – name of the shipper (must correspond to the information recorded in the constituent documentation).
- Page 4 – name of the consignee of the cargo (if the invoice is drawn up for services, a dash is placed in the lines).
- Page 5 – details of payment papers on the transfer of money by the agent to the seller.
- Page 6 – name of the buyer.
- Page 6a – buyer’s address recorded in the Unified State Register of Legal Entities.
- Page 6b – TIN and KPP of the acquirers.
- Page 7 – name of the currency that appears in the transaction.
- Page 8 – this line needs to be filled out only when issuing a SF when working on a government contract.
- Column 1 – name of goods.
- Gr. 1a – product type code.
- Gr. 2 – unit of measurement (if it is not there, a dash is added).
- Gr. 3 – volume of production.
- Gr. 4 – product price.
- Gr. 5 – cost of all products.
- Gr. 6 – excise tax amounts, if these are excisable products.
- Gr. 7 – tax rate.
- Gr. 8 – VAT.
- Gr. 9 – price of all products.
- Gr. 10 – state in which the product was manufactured (you must indicate the code and short name).
- Gr. 11 – this column is filled in when the country of origin of the product is not Russia.
FOR YOUR INFORMATION! The agent is the element between the principal and the merchant. He is obliged to re-expose the Federation Council. An agent trading on his own behalf registers himself as a seller in the Federation Council. Based on the invoice, the buyer has the right to claim a VAT deduction. If the agent buys products at the behest of the principal, when re-listing, you need to write down information about the supplier in lines 2, 2a and 2b.
Invoices: new for 2020
This year there are some differences in the management of invoices that need to be taken into account, especially for VAT payers.
The main innovation is a new form, which was approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation No. 981 of August 19, 2020. There are a few things that look different now, including:
- a new column in the header of the form, which needs to be filled out only if such data is available (“Identifier of the government contract, contract (agreement)”);
- a new column “Product Type Code” in the plate, information is entered into it only when sending goods to countries that are members of the Eurasian Economic Union;
- the column on the customs declaration has changed its name slightly - before the word “number” the clarification “registration” has been added;
- The signature field has been supplemented - now not only the individual entrepreneur himself, but also “another person” has the right to leave an autograph there, of course, with a executed power of attorney.
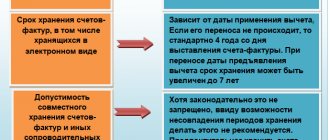
Another important innovation is permission from tax services to store second copies of invoices in electronic form (confirmed by Letter of the Federal Tax Service No. SD-4-3 / [email protected] of Russia dated September 6, 2017). This is convenient, and the permit is valid even if the purchase copy was in paper form.