Ways to implement a business plan
The implementation of a ready-made business plan can occur in several ways:
Opening your own enterprise “from the ground up”. When establishing a business “from scratch”, it is necessary to give your best at the initial stage: adequate preparation of a business project, attracting interested investors, authorized capital, as well as initial capital, legal registration, advertising, long waiting times for payback.
Moreover, even after going through these important stages of establishing his own business, an entrepreneur cannot be sure of the profitability of his “brainchild”. The market is developing dynamically, so it is important to adequately maintain competitiveness, otherwise there are risks of owing money to investors and suffering a fiasco at the very beginning of a given reporting period.
Purchase of a ready-made business as personal property . The main advantageous aspect of a finished business project is considered to be the promotion and recognition of the brand (production company).
When purchasing an established and operating company, you will not need the costs that are necessary for the organization itself.
The risks of failure will not leave serious consequences, since an existing business, even in a crisis, is of understandable interest to the target audience. In a ready-made business, you can more accurately calculate probable risks along with losses, calculate profits, and set the correct benchmark in a short time.
Buying a franchise . For many businessmen, buying a franchise is considered the only profitable investment that allows them to purchase a successful enterprise or brand that is widely known among consumers for the purpose of further work under its logo. This option is quite economical and allows you to quickly set up production and make a profit.
What is franchising
Franchising as a form of mutual cooperation between several enterprises has been known for a long time. The explanation for such an interaction is the sale by a known company or production of all rights to another person that in no way relate to it legally . In essence, the selling company sells the licensed right to manufacture products, sell them or provide services, to use the company's brand or logo, business technologies and various technical achievements. The company that sells the franchise is called the franchisor, and the company that buys the franchise is called the franchisee.
For many businessmen, buying a franchise is considered the only profitable investment that allows them to acquire a successful enterprise or brand.
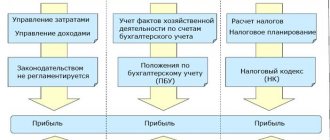
Value added tax
In accordance with paragraphs. 1 clause 1 art. 146 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the sale of services on the territory of the Russian Federation is subject to VAT.
According to paragraphs. 4 paragraphs 1 art. 148 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the place of sale of services is recognized as the territory of the Russian Federation if the buyer of services carries out activities in the territory of the Russian Federation. This applies in particular to the transfer, grant of patents, licenses, trademarks, copyrights or other similar rights.
Thus, the provision of services by a foreign copyright holder is subject to VAT, and a Russian organization, when paying royalty payments to a foreign organization, is a tax agent for VAT (clause 2 of Article 161 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
A tax agent is obliged to calculate, withhold from a foreign organization and pay the appropriate amount of VAT to the budget, regardless of whether he himself is a payer of this tax (for example, he may apply special tax regimes, in particular, a simplified taxation system, and not be a VAT payer ).
The transfer of the VAT amount to the budget is carried out simultaneously with the transfer of funds to the foreign counterparty.
In accordance with paragraph 3 of Art. 171 and paragraph 1 of Art. 172 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, a tax agent who paid the withheld VAT to the budget has the right to claim this amount as a tax deduction after the above services are registered.
According to paragraph 3 of Art. 171 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, tax amounts paid in accordance with Art. 173 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation by buyers - tax agents. The right to the specified tax deductions are available to buyers - tax agents registered with the tax authorities and acting as taxpayers, provided that the services were purchased to carry out transactions recognized as objects of taxation.
It should be noted that in accordance with paragraphs. 26 clause 2 art. 149 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the sale in the territory of the Russian Federation of exclusive rights to inventions, utility models, industrial designs, programs for electronic computers, databases, topologies of integrated circuits, production secrets (know-how), as well as rights to use the specified results of intellectual property is not subject to taxation activities on the basis of a license agreement.
TAXATION OF SERVICES OF A FOREIGN ORGANIZATION FROM A RUSSIAN CONTRACTOR
Lump sum fee in franchising
Many beginning entrepreneurs often ask the question: “What is a lump sum payment? What is its essence? What determines the lump sum payment? What is this in simple words? The word "lump sum" has Austrian roots and means "on the whole" or "on the whole."
In other words, a lump sum fee is a one-time entrance fee, regulated in Russia by the law on making fixed one-time payments. The company purchasing the franchise (franchisee) pays a one-time fee, which is fixed in a special commercial agreement.
The expediency of a lump sum fee is determined by the need for the franchisee to simultaneously use all the licensed rights of a well-known organization.
The requirement to make a lump sum contribution also applies if the buyer is not known to the modern market and monitoring his activities presents certain difficulties.
The lump sum fee will vary significantly depending on the scope of the license.
How is it paid?
The one-time payment is calculated from the approximate values of the franchisee's potential profit under the license and the likelihood of economic efficiency.
The lump-sum payment can be paid either as a one-time payment in the amount of the entire amount, or in short-term installments using the payments established in the contract.
The size of the one-time fee is fixed and represents the cost of purchasing licensed rights. Thus, the lump-sum contribution fully covers all expenses of the selling company for the implementation of a new business project . In addition, the payment represents a kind of financial support from the copyright holder at the beginning of a new business:
- professional calculation of profitability;
- advisory activities on the selection, legal registration and equipment of premises;
- marketing and advertising campaign;
- training of full-time employees for the purchasing company.
Lump sum contribution: calculation criteria
Each franchise has its own characteristics, differences and specifics, so the size of the lump-sum fee will vary significantly depending on the particular scope of the license . There are a number of factors that are key in the formation of a fixed lump sum contribution:
- expenses for the project of retail and administrative space (for example, for a new store);
- costs for equipment and technical equipment of the premises;
- the need to invest in initial sales and training of employees of the new company.
Training of employees, including administrative and management staff, is an expense item on which it is not customary to save. Competent employees with a professional and highly qualified approach to any business become the most valuable resource of any enterprise. You should also not save on technical equipment, computer programs, or accounting.
According to statistical business data, the highest lump-sum contribution amounts are noted in the restaurant and hotel business, varying in the range of 3-4 million rubles.
Royalty or franchise system payment
Royalty exemptions involve the transfer of a trademark or brand on a license basis.
System payments in franchising – what is it? Royalties are regular payments for the use of licensing rights in franchising. Royalties are calculated by determining a percentage of gross revenue. Royalties can be in the form of fixed payments, paid annually, quarterly or monthly.
In general, the form, payment procedure, amount and period are prescribed when drawing up the contractual relationship of a commercial concession. If the payment of royalties is established from the total sales volume of the enterprise, then this form may indicate some interest of the company selling the license in the profitability of its franchisee.
If an agreement on fixed payments is established between the franchisor and the franchisee, then this, rather, indicates the difficulties of monitoring the activities of the new company by the franchisor.
Royalty in a franchise - what is it?
Royalty is the amount paid during the entire period of formation, development and conduct of business activities under the license of the true copyright holder.
When paying regular contributions, the franchisee receives the following benefits :
- organization of financial support from the franchisor;
- personnel training and qualified preparation for work activities;
- assistance during the management of the enterprise;
- accounting.
This happens when the royalty agreement specifies zero values . Here events can go in two directions:
- The franchisor is not interested in supporting the franchisee in the future;
- The franchisor included royalties in the amount for the purchase of goods or consumables.
The form, payment procedure, amount and period are prescribed when drawing up the contractual relationship.
A way to avoid regular payments
The royalty waiver method involves the transfer of a trademark or brand on a license basis to a third interested party . The method consists of calculating the value of the licensed trademark, which takes into account the amount of all royalties. The amount of the royalty itself, in this case, is determined from the percentage of the potential revenue of the new enterprise under the trademark.
To implement this method, it is necessary to compare the shares of all revenue by the amount of royalties, correctly assess the rate of increase in revenue over a short period of time, analyze royalty payment flows as of the assessment date, and add them up to a total amount.
Basic stages of the “liberation” method:
- compiling an analysis of sales volume to determine royalty payments;
- determining the amount of royalties based on various economic factors, prospects for the development of a new business.
What is royalty under Russian law?
Russian legislation does not contain a separate concept of “royalty”. At the same time, Part 5 of Article 1235 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation provides for payment - remuneration stipulated by the license agreement.
The Tax Code of the Russian Federation, in turn, in paragraph 37 of Article 246 provides for the attribution to expenses associated with the production and sale of periodic (current) payments for the use of rights to the results of intellectual activity and rights to means of individualization (in particular, rights arising from patents for inventions, utility models, industrial designs).
Also, for tax purposes, the Tax Code of the Russian Federation considers income from the provision for use of rights to the results of intellectual activity and rights to equivalent means of individualization (in particular, from the provision for use of rights arising from patents for inventions, utility models, industrial designs) as non-sales income from corporate income tax in accordance with the provisions of Article 250 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Buying a franchise without royalties and lump sum payment
The trade franchising segment is replete with a large number of commercial offers, where a lump sum payment when purchasing licensed rights is not expected. The basis of such cooperation lies in the desire of the copyright holder to maximally expand the boundaries of his own business by attracting new investors or partners . This economic tactic is typical for chain stores selling groceries, clothing, and household chemicals.
Buying a franchise is a fairly economical option that allows you to quickly set up production and make a profit.
If the acquisition of a trade franchise involves the sale of goods or services of the franchisor, then the lump-sum contribution will be included in the main costs of carrying out business activities. Such a franchise also has the prospect of achieving its own material wealth by expanding the horizons of its business and increasing the popularity of the brand.
Royalty rate
If the lump sum fee is determined by the franchisor, then the royalty is a certain rate. *Royalty rate* is a certain amount of remuneration to the owner for the use of his copyright. This means that the junior partner under the contract pays for a trademark, brand and name under which he conducts an independent business and receives his income from it. It should be noted that the royalty price includes advertising promotions, marketing costs, staff training, and posting information on the franchisor’s or company’s website.
There are three main types of royalty calculations:
- Percentage per stamp. This type of royalty is often used in cases where the store has different levels of markup on goods.
- Fixed calculation. Standing payment, it depends on the contract. The assigned amount depends on the area of the building, the number of clients served, and the cost of the franchisor’s services. This type of royalty is most often used by companies that find it difficult to accurately calculate the amount of income.
- Percentage of the company's turnover. Today this type of royalty is the most common. The junior partner pays a percentage of the turnover to the franchisor, which was previously agreed upon in the documents.
Summing up
The main form of financial interaction in franchising is royalties and lump sum fees, the amounts of which are determined in accordance with the commercial concession agreement.
A lump sum payment is a one-time payment that implies the use of all the resources of the seller enterprise on the basis of the purchased license.
Royalty payments are in the form of regular payments , and are calculated based on a percentage of the franchisee's gross revenue.
The essence of successful franchising is a commercial interaction that is beneficial for both parties, aimed at obtaining a stable profit and expanding one’s own business.
simplified tax system
Organizations that apply the simplification keep records of taxable income on the basis of Articles 249 and 250 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (clause 1 of Article 346.15 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
The revenue date is the day on which the entity actually receives the royalties. Including the amount received in the form of an advance, include it in simplified income immediately at the time it arrives to the organization. This procedure follows from paragraph 1 of Article 346.17 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, decision of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation dated January 20, 2006 No. 4294/05 and is explained in letters of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated December 18, 2008 No. 03-11-04/2/197, dated 21 July 2008 No. 03-11-04/2/108, dated January 25, 2006 No. 03-11-04/2/15, Ministry of Taxes of Russia dated June 11, 2003 No. SA-6-22/657.