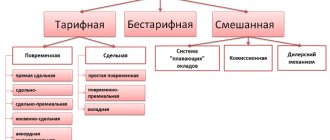
Type of bank account
Each type of bank account opened in a credit institution for legal entities or individual entrepreneurs when conducting business activities has its own purpose.
Table 1. Type of bank account
| View | Purpose |
| Calculated | Opens for current operations related to business activities |
| Credit | Information is recorded on the flow of funds and the accrual of interest on loans provided by the bank to legal entities and individual entrepreneurs |
| Deposit | Free funds deposited into the bank are taken into account to generate additional income in the form of accrued interest. |
| Budget | For funds received from all levels of the Russian budget. Note! Finance can be provided in the form of subsidies, subventions, subsidies, etc. |
| Transit | To account for currency transactions |
| Foreign exchange | To make payments in foreign currency |
| Collateral | The funds credited to it are aimed at repaying the obligations of the pledgor to the pledgee |
| Trust management | Bankruptcy proceedings in case of declaring a legal entity or individual entrepreneur bankrupt |
| Supplier invoice | To account for transactions of suppliers accepting payments through payment agents |
Note! Each account has a unique balance number according to the Chart of Accounts of the Bank of Russia.
Example of a chart of accounts according to IFRS
Different countries have different versions of the chart of accounts, but their general essence remains the same. Thus, in the USA and England there is no strict numbering of accounts, but there is a certain order of distribution on the balance sheet. In assets, liquidity decreases from top to bottom, and in liabilities, balance sheet items are arranged according to the debt period, starting from the shortest. Equity closes the right side of the balance sheet, and in IFRS the balance sheet is based on increasing liquidity. In some European countries, North Africa and Turkey, the chart of accounts has a rigid order, which is similar to the Russian type, the account itself can contain up to 10 digits in the number, and sub-accounts can act as accounts. According to the above principles, the international chart of accounts can be constructed, for example, like this:
— 1ХХХ — Non-current assets; — 2ХХХ — Current assets; — 3ХХХ — Capital; — 4ХХХ — Long-term liabilities; — 5ХХХ — Short-term liabilities; — 6ХХХ — Income; — 7ХХХ — Expenses; — 8ХХХ — Management accounting accounts; — 9ХХХ — Off-balance sheet accounts.
Typical sample.
Accounts 1-5 are balance sheet accounts that follow the order of the IFRS balance sheet. Accounts 6-7 are income and expense accounts, accounts from 8 are temporary accounts that are used to collect analytical information. Off-balance sheet accounts - from 9. The entire chart of accounts contains 5 elements of financial statements: assets, liabilities, capital, income and expenses.
Checking account
Chart of accounts of a credit institution:
- for legal entities – 40702;
- for individuals (individual entrepreneurs) – 40802.
This type is intended for all operations related to business activities:
- payment for goods and services from suppliers;
- receipt of payments from customers for work performed, goods, services rendered;
- settlements with personnel regarding wages;
- transfer of taxes and contributions to regulatory authorities;
- settlements on loans and borrowings with counterparties, etc.
Control of operations is recorded by a bank statement provided at the client’s request (can be issued electronically or when authorized persons contact the bank). The balance according to the daily statement must coincide with the internal reporting of the enterprise.
A current account can be opened:
- legal entities;
- individual entrepreneurs;
- persons engaged in private practice in accordance with the established procedure;
- representative offices of credit institutions;
- non-profit enterprises for operations for the purposes for which they were formed.
Note! According to current legislation, you can have an unlimited number of current accounts in various banks. Opening of sub-accounts is provided for separate divisions.
The basis for opening is the conclusion of an agreement with the bank.
The list of basic documentation of legal entities provided to enter into an agreement with a credit institution is as follows:
- Constituent documents – charter and standard provisions. For authorities – legislative acts on creation and legal status. For individual entrepreneurs - an identity document.
- Licenses and permits granted to a given legal entity in cases where they affect the legal capacity of the company to enter into contracts.
- Card of signatures of persons authorized to manage the company’s finances (usually the general director and chief accountant).
- Documents confirming the rights of the sole executive body of the organization (order of appointment, meeting of shareholders, etc.).
Note:
- when opening sub-accounts for separate divisions - the provision on creation;
- for enterprises created under the laws of foreign states - documents confirming the legal status, a certificate of registration with the Federal Tax Service;
- for an individual entrepreneur - a foreign citizen - an additional migration card or documents confirming the right to reside and carry out activities in the territory of the Russian Federation are provided.
Termination of a bank account agreement is carried out on the basis of an application. When closing an account, the credit institution is obliged to issue the account balance in cash to the client within 7 days or transfer funds to the details specified in the application at closing. The customer must return unused cash check books with counterfoils.
Note! If the client does not show up to receive the balance or does not receive the details for transferring funds within 60 days, the bank is obliged to credit these funds to a special account with the Central Bank of the Russian Federation.
Types of bank accounts for individuals
Modern Russian banks offer Russian citizens a wide range of financial services that take into account a variety of needs. Thus, the types of Sberbank accounts for individuals include current, deposit, card and currency deposit options. This significantly expands the client’s ability to choose different banking products for their purposes.
Current accounts
This bank account for individuals is designed to service the owner’s daily needs - wages are transferred here, and services or goods in stores are paid for from here. Using such an account has several features:
- It must not be used for commercial purposes.
- Service is possible only at bank branches (by linking a debit card to your account, you can significantly expand the functionality using ATMs and payment terminals).
- Interest on the remaining amount is not accrued here or is of a purely symbolic nature.
If necessary, the client can have several bank balances at once, for example, to make payments with different currencies. To open such an account, you must provide the bank with the following package of documents:
- client application and questionnaire,
- passport (other identity document),
- agreement,
- TIN.
The cost of service depends on the specific bank, but often it is symbolic (for example, in Russian Standard - 50 rubles per year). When planning to stop using the services of a financial institution, the client should write a closure application, after which the remaining funds are issued in cash through the cash desk or transferred to the specified details.
Deposit
This account is created in accordance with the instructions of the Bank of Russia for long-term storage of funds with interest income. The determining factor here is the amount of the deposit and the period for which the money is placed. Depending on the mode of use of finance, deposits are of two types:
- Poste restante. Partial or full withdrawal of money is allowed, so the interest rate is not very high - up to 1%.
- Urgent. They have a shelf life of one year and a higher interest rate than “on demand”, but withdrawing money from them before the end of the agreement with the bank will be problematic. Time deposits are divided into savings, savings and settlement, differing in the nuances of replenishment and withdrawal of funds.
The interest rate on a term deposit in the country's leading financial institutions (Sberbank, BTB 24, etc.) is 7-10%. Small financial organizations (Loko-Bank, YAR-Bank, Riabank) can offer higher rates, over 13%, but this only happens as part of special promotions and for deposits over 300,000 rubles, so not everyone can take advantage of these offers.
Deposit services are opened in a bank with the same package of documents as for the current balance, but in some cases a military ID or pension certificate may be required. Closing a bank deposit implies the expiration of the agreement, the accrual of the stipulated interest and the issuance of money to the client or transfer to another account.
- Proper use of soda to cleanse the body
- Birth control pills that don't make you fat - a list of the best non-hormonal drugs for women
- Anticoagulants - what they are and a list of drugs. The use of direct and indirect anticoagulants
Loan accounts
To service the loan taken, a loan account is opened, which reflects the movement of funds for payments. It may have a negative balance and on its basis, cash receipts are kept for repaying debts by credit institutions. If the borrower is an individual, then no opening or servicing fees are allowed. Currently, the following types of interest payments on loans are used in banking practice:
- The annuity method involves a fixed monthly payment. This form of payment is very convenient for the creditor, because he knows in advance exactly what his expected receipts are, but for a debtor who plans to repay the loan ahead of schedule, it is not suitable.
- The differentiated method involves calculating the minimum contribution, which the client can exceed at his discretion. In this case, the payment amounts are periodically recalculated, and the overpayment on the loan is reduced. This method is not very profitable for financial institutions, so it is not used so often in lending.
Card
Accounts (SCS) can be used to service plastic cards, allowing you to use ATMs to receive cash and terminals to make non-cash payments. The procedure for opening such a card is not complicated - the only documents required are often a passport. Issue and annual maintenance require payment (for example, Zenit Bank Standard card – 600 rubles per year), but if the card is related to salary projects, then the services will be free for the client. The card number consists of 16 digits (there are twenty in a regular balance).
Credit account
Chart of accounts of a credit institution:
- for legal entities – 452 (for example, 45201 for overdraft);
- for individuals (individual entrepreneurs) – 454 (45406 for loans for a period of 181 days to a year).
Opens when a credit institution applies for a loan. It displays transactions for transferring funds to the borrower on the basis of a loan agreement, and also records information about debt repayment.
The account is divided into several types:
- Simple: borrowed funds are credited one-time according to the loan agreement, a legal entity or individual entrepreneur deposits money into the account as debt repayment.
- Line of credit – borrowed funds are provided in partial amounts within a certain limit as needed. The credit limit is determined based on the financial statements of the company submitted to the bank.
- Overdraft is a separately connected service to the client’s current account: an additional reserve of funds, the use of which is provided in the absence of own funds in the account.
Current currency and transit accounts
Chart of accounts of a credit organization: transit - 40911, currency ones have the same structure as settlement ones, but the 3rd order numbers change depending on the currency code.
These types of accounts are used when carrying out transactions in foreign currency.
Transit is a temporary account into which the organization's export proceeds, expressed in foreign currency, are initially received. To access funds and the right to use them, you must submit documents confirming the legality of the transaction:
- certificate of currency transactions;
- document basis for crediting funds (contract, invoice, etc.).
Note! The opening of a current foreign currency account and a transit account is carried out at the same time.
Bank selection
In order to choose a banking or credit institution to open an account, you need to pay attention to the following basic criteria:
- stability (political and economic) of the state where the bank is located;
- bank rating, its reputation, prestige and reliability;
- packages of services provided;
- the degree of state control of banking operations;
- cost of bank services;
- minimum deposit amount;
- interest;
- location of the banking institution and its branches;
- availability of investment programs;
- the opportunity to get a credit card;
- convenience when servicing remote depositors.
List of documents required to open and use an account:
- application in the prescribed form (provided by the banking institution);
- notarized copies of documents confirming the status of the enterprise (memorandum of association, charter, minutes of the decision on creation);
- notarized certificate of state registration;
- two cards with a seal and signatures (one notarized);
- a copy of the certificate of registration with the tax authorities;
- a copy of a certificate stating that the company is registered with the Social Insurance Fund;
- a copy of a certificate from the statistical authorities on classification criteria and assignment of the OKPO code;
- copies of documents confirming the election and appointment of authorized persons, which are indicated on the bank card (protocols of election, orders for taking office and appointment, and so on).
If, when concluding a contract, the client provided unreliable (invalid) information, this is fraught with serious consequences, including litigation.
Deposit
Chart of accounts of a credit institution:
- for legal entities - 421 (for example, 42107 for deposits for a period of more than 3 years);
- for individuals (individual entrepreneurs) – 423.
The main purpose of the deposit is the opportunity to receive additional income from depositing temporarily free funds. Income is accrued in the form of interest. According to the banking service agreement, the credit institution undertakes to return the deposit amount and pay interest accrued on it in the manner specified in the agreement.
Standard deposit types:
- without early closure and replenishment;
- with the possibility of replenishment;
- with the possibility of partial removal.
Note! Some banks provide for the accrual of income in the form of interest for the minimum balance of the company's current accounts - the amount in rubles or foreign currency that must be in the balance at the beginning of the banking day for a pre-agreed period.
Classification of bank accounts
A certain problem is the current situation when the current legislation, although it determines the type of bank account, does not contain a complete and clear classification. In such a situation, the optimal solution would be to resort to special legal literature, where the issue of the types of bank accounts has been studied in great detail.
By subject composition
The division into types of bank accounts by subject composition provided for by law has two categories:
- Client - opened by the bank for individuals or legal entities, and can be settlement, current, deposit, etc.
- Interbank - opened for another bank on the basis of correspondent relations, when settlement occurs using funds and on behalf of another credit institution that is part of the federal payment system.
By purpose
In accordance with this division, the following main types of accounts are distinguished, the purpose of which is already clear from the name:
- settlement – for use as the main balance sheet of a legal entity;
- current – for individuals or organizations that are not legal entities;
- budgetary – for enterprises and organizations financed from the federal budget;
- deposit - for storing funds and making a profit through interest charges;
- loan – for servicing credit cards and operations to fulfill financial obligations.
By currency type
Current legislation divides bank payments as follows:
- Ruble – carried out in Russian monetary units (rubles).
- Currency – which are opened in the monetary units of other countries. Such accounts may require a currency license from the Bank of Russia.
- Foreign currency – foreign currency deposits of residents of the Russian Federation outside the country.
- Multicurrency – in this case, by concluding one agreement with the bank, several different currency deposits are made (with the possibility of converting funds between them).
By validity period
For transactions with foreign currency, according to Russian legislation, it is necessary to have two types of bank accounts:
- Permanent – for making all current currency payments.
- Transit – funds from export transactions with non-residents and other earnings in foreign currency come here. These funds can be used only after a number of mandatory procedures (identification of the received amount, etc.).
Possibility of replenishing or withdrawing funds
According to this possibility, there are three types of bank accounts:
- No replenishment. Money is credited here once and there are no additional contributions.
- With the possibility of replenishment. It is allowed to deposit new amounts during the deposit period.
- With the possibility of partial withdrawal of funds. You can use money from your deposit, but there is a limit that must remain.
By purpose of use
Depending on the purpose of the funds, the law provides for several types of bank accounts:
- Current – implying the owner’s freedom of disposal regarding the expenditure of funds stored in a financial institution (including through payment orders and other payment documents).
- Targeted – their purpose is determined by agreement or directly stated by law. For example, these could be investment funds from the federal budget intended to finance specific projects.
By volume of settlement transactions
There are three types of bank accounts depending on the number of settlement transactions allowed for them:
- Without restrictions on operations - when all operations can be performed on this account.
- With a limited range of transactions - for example, an account with trust management, you cannot add your own funds.
- Temporary or cumulative – for which settlement transactions are generally excluded. This could be, for example, a court deposit opened by a bank to a client for crediting funds, but not for the purpose of extracting commercial benefits.
Budget
Chart of accounts of a credit organization: 401 for funds of the Federal budget and 402 for budgets of constituent entities of the Russian Federation
The main purpose is to use funds allocated by the state within the framework of the current legislation of the Russian Federation.
Note! Budgetary funds are funds for a designated purpose; operations with these revenues must be aimed at achieving the goal that is financed by the state.
Special accounts
Special accounts are opened when their use is mandatory under current legislation.
Trust account
Opens on the basis of bankruptcy proceedings when a legal entity or individual entrepreneur is declared bankrupt. Must be maintained at all times during the trustee's employment to conduct financial management operations.
The procedure for closing a debtor's bank account during bankruptcy proceedings is as follows.
- The bankruptcy trustee presents an identification document and a copy of the court decision on the appointment of a financial manager in the bankruptcy case of a legal entity (individual entrepreneur).
- The bankruptcy trustee fills out an application to close a bank account, indicating the details of the bank account to which the balance of the account will be transferred.
Collateral
The purpose of opening is to place finances that are intended to repay the obligations of the mortgagor to the mortgagee. The subject of the pledge is the rights to funds under the pledge agreement.
Opening is carried out in accordance with the bank’s standard rules for legal entities and individual entrepreneurs.