Differences in indicators
The minimum wage is a fixed indicator that reflects the minimum wage for Russian citizens. It is approved by the government of the country. The minimum wage is the same for the entire state; wages cannot be paid below this figure. But the law also explains possible exceptions that may arise in certain situations. The subsistence minimum is the minimum amount of earnings that a citizen will need to meet the minimum level of needs.
The federal minimum wage is established for the entire territory of the Russian Federation. Employers are required to pay wages to employees in an amount not less than a fixed amount. Since the territory of Russia is large and located in different climatic conditions, the standard of living differs by region. Therefore, local authorities can set the minimum wage in a larger amount than the basic indicator for the country, but not less.
Regional levels are used for specific regions - the Far North and territories that are equivalent to it, including highlands and deserts. The minimum wage also differs for capital districts. The minimum wage in the Russian Federation is regulated by Law No. 82, adopted in 2000.
Many other payments to citizens depend on the monthly salary and the minimum wage:
- earnings;
- compensation for sick leave;
- pensions;
- payments to pregnant women;
- child care payments;
- compensation.
What the minimum wage and the living wage have in common is that both indicators are designed to guarantee citizens a normal existence and satisfaction of basic needs.
The main differences between the minimum wage and the PM:
- The minimum wage is a minimum fixed indicator of income for performing labor activities.
- With the help of PM, the standard of living in different cities and regions of Russia is assessed through the consumer basket. That is, how much food can you buy in a certain area for the same amount. Or how much the same set of products will cost in each region.
The living wage is based on the consumer basket - the monetary value of all goods and services that are needed for a normal life. It includes:
- food, utilities, non-food products;
- other mandatory payments to the government or essential service providers.
Therefore, the concepts of minimum wage and minimum wage rather complement each other.
Legal documents
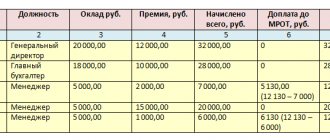
The minimum wage has been enshrined in federal law since 2000; before that, a new legislative act was issued each time. Since then, annual changes in the law concern only the amount of the lowest income for working Russians. For 2020, the minimum wage was 11,280 rubles, and from January 1, 2020 it will be increased to 12,130 rubles. The cost of living in 2020 was higher than the minimum wage. For 2020, the cost of living is 11,185 rubles, that is, it is 95 rubles lower than the federal minimum wage.
The size of the regional minimum wage is determined on the basis of Article 133 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, and the indexation of the indicator is supported by Article 421. Wages are not the same thing as the minimum wage. The salary consists of salary, bonus payments, allowances, and regional coefficients. If all these payments in total exceed the minimum wage, then the employer can legally reduce the salary.
The minimum wage may be less than salary in such situations:
- When the employee is not on full-time work. In this case, the salary is proportional to the time worked.
- If a citizen works part-time in several organizations. Moreover, his total income with full-time work cannot be less than the minimum income level.
The cost of living is regulated by Federal Law No. 134. The indicator is used to assess the lives of citizens and for statistics on the number of poor people in the country. The PM serves as the basis for the formation of the minimum wage.
Where can an employee complain about low wages?
In all other situations, when the employee fully fulfills all the duties assigned to him and works a full month, the salary must exceed the minimum wage . If this is not the case, then you can prepare a complaint against the employer to the appropriate authorities.
contact various places, in particular, the following statement will be accepted:
- trade union organization;
- Labor and Employment Inspectorate;
- prosecutor's office;
- judicial authorities.
But first you will need to obtain a certificate of salary from the accounting department of the employing company.
You can also write a written request directly to the company’s management to clarify why the amount of payments does not reach the legally established minimum wage (how is the minimum wage established?).
The employer can only explain this by non-compliance with the provisions of paragraph 3 of Art. 133 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, and if there are no grounds for understating wages, then you will have to bear some responsibility for the violation.
When the minimum wage may not reach the subsistence level
The Decree “On National Goals and Strategic Objectives of the Development of the Russian Federation until 2024” defines ways to combat poverty in the Russian Federation. The minimum wage is set for the next year based on the cost of living calculated for the second quarter of the previous year.
Since the minimum wage has been equalized with the minimum wage, employers cannot set wages for their employees that are less than the subsistence level. The monthly minimum income must now include the monetary size of the consumer basket. If for some reason the employee’s salary is less than the minimum wage, the employer must pay the missing amount through bonuses, allowances, or increase the salary by an additional agreement.
To form the minimum wage, the subsistence level of the second quarter of the current year is chosen for the following reasons:
- In the second half of the year, the inflation rate decreases. Because of this, the cost of living also decreases.
- According to statistics, it is the second quarter that reflects the average PM level for the year.
- After the second quarter, there are still 6 months left to distribute finances for the next year and wages to citizens of the Russian Federation who receive funding from the budget.
Consequences for employers in violation of the minimum wage law:
| Employer | Fine |
| IP | From 1 to 5 thousand rubles |
| Executive | From 10 to 20 thousand rubles |
| Legal face | From 30 to 50 thousand rubles |
Sanctions are imposed on the basis of Article 5.27 of the Code of Administrative Offenses.
Employer's liability for violation of the law
The amount of monthly profit is specified in the employment contract. When the salary is below the minimum wage due to a violation of the law by the organization’s management, the employee has the right to write a complaint.
https://youtu.be/mNVba4sU9_8
The regulatory legal act regulating labor relations between citizens of Russia defines administrative and criminal liability. Punishment is provided for the employer and the person responsible for payroll. In accordance with the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation, penalties may be applied to management:
- non-accrual of monthly income - 500 thousand rubles;
- determination of profit not in full - 120,000 rubles;
- salary is less than the minimum wage - up to 100 thousand rubles.
In case of repeated violation of the law, individual entrepreneurs or legal entities face a doubling of the fine. Understating wages is grounds for initiating a criminal case. In accordance with Art. 145.1 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation, by decision of the supervisory authorities, the head of an institution may be sentenced to imprisonment for up to 5 years, restrictions in types of activities, positions held, or a monetary penalty of up to 500 thousand rubles. Criminal prosecution is not a reason for the cancellation of administrative penalties.
Where is the PM level taken into account?
In general, in Russia a living wage is needed in order to:
- assess the standard of living of citizens of the Russian Federation when implementing a program to improve the economy in the state;
- justify the minimum wage at the federal level and the minimum pension;
- establish scholarships, social benefits and other payments assigned from the federal budget;
- form the federal budget.
The living wage for the regions of the Russian Federation serves for:
- determining the quality of life of citizens in a certain region and the success of the program to improve living conditions;
- providing financial support for low-income families;
- formation of the regional budget.
Also, the PM for the region is needed in order to identify suitable vacancies for registered unemployed persons in employment centers.
What do minimum wages and PM affect?
The minimum wage and the cost of living affect the following payments:
- Wage. In 2020, a citizen cannot receive an income per month below the established figure. If the salary is below the subsistence level, the employee has the right to file a complaint with the appropriate organization. After this, sanctions are applied to the company owner and fines are imposed. At the same time, real earnings may be lower than the minimum wage if a citizen works part-time, does not meet the time and labor standards, or works part-time.
- Benefits. Benefits for pregnancy, childbirth, child care up to 1.5 years old, and sick leave payments depend on the minimum income.
- Taxes. The amount of taxes also depends on the minimum wage. As the minimum wage increases, tax deductions increase.
- Regional coefficient . Additional payments are assigned to those citizens who work in special climatic zones.
Minimum wages can have a negative impact on small businesses. Entrepreneurs are not able to pay salaries in this amount. In addition, a number of citizens have reduced motivation to develop and improve professional skills.
If a Russian’s pension is less than the minimum subsistence level, then the payments reach the required level. The pensioner will need to contact the social protection fund at the place of residence or the Pension Fund and submit a written application.
In what cases can the salary be less?
List of circumstances when an employer legally has the right to pay an employee less than the established minimum wage:
- Without personal income tax . It is the wages accrued to the employee that must correspond to the minimum wage. Therefore, it is acceptable if after paying income tax, the actual amount received in hand will be less.
- When holding . A number of situations oblige the employer to make deductions from the income received by the employee on the basis of a writ of execution. There are no violations if, before deductions, the salary amount complied with the requirements of the law.
- Without joining a regional agreement . Payment for labor may correspond to the minimum wage operating at the federal level, but be inferior to the regional one. The situation, although procedurally costly, is legal.
- When working part-time . An employee spends no more than half of the working time spent at his main place of employment on part-time work. In case of part-time work, the salary is calculated in proportion to the time worked from the established minimum wage.
- When working part-time (reduced working day or week) . The employer has the right to pay less than the minimum wage, but accruals must be made based on the time worked by the employee in proportion to the approved minimum wage.
- With cumulative accounting of time worked . The employee’s actual working time is summed up and, if his performance is below the established monthly norm, the employer has the right to reduce his salary.
- When an employee takes sick leave . During this period, the employee is not paid for his work. Sick leave is paid at the expense of the social insurance fund.
- If the employee went on unpaid leave . Vacation is not paid by the employer, so a deviation from the minimum wage is acceptable.
- When idle . If the employer is not at fault, he has the right to pay employees only 2/3 of the standard salary due to them. Therefore, the indicator may fall below the minimum payment.
- While walking . Days on which an employee intentionally did not go to work without good reason are considered absenteeism. This period is not paid, which leads to a decrease in wages, including below the minimum wage.
- When an employee works under the terms of a civil contract . Civil Procedure Code rules apply here, so the minimum wage may not be observed.
If, due to the nature of the work, wages must be paid taking into account the coefficient, understating payments is unacceptable. Allowances and compensations here are considered mandatory and are calculated separately from the minimum wage, and then added to it. For example, if working conditions are harmful to the employee’s health.