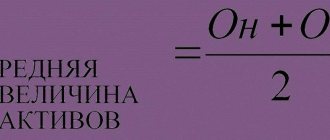HOLDING: CONCEPT, STRUCTURE, TYPES OF INTEGRATION
A holding is a corporation that regulates the activities of independent organizations. The purpose of creating a holding is to increase the efficiency of joint economic activities of the merged enterprises.
The holding consists of a parent (management) company and subsidiaries.
Types of integration
In the economic sphere, there are five main ways to build the potential of large enterprises, that is, types of integration:
- vertical;
- horizontal;
- independent;
- mixed;
- partial vertical.
Vertical integration
This is the accession to the holding of enterprises whose main activity fits into a single technological chain of production of finished products of the existing holding, which makes it possible to create a closed production cycle (Fig. 1).
The main advantage of vertical integration is significant cost savings, which for the most part consists of profits included in the price of suppliers of raw materials, materials and components necessary for the production of the holding's main products.
In the event of the merger of supplier enterprises or companies replacing previous suppliers, profits and invoices previously included in the purchase price remain in the holding. In addition, effective management, optimization, rationing and strict control of resource consumption in the process of economic activities of companies merged into a holding can bring additional savings.
Horizontal integration
This type of integration involves the accession to an existing holding or a company creating a new holding of enterprises that produce products similar to those produced in the holding (Fig. 2).
The main advantage of horizontal integration is the growth of the holding’s share in its market segment. This means that the main purpose of creating a holding company with horizontal integration is to reduce the level of competition . In this case, the opportunity to set your own prices on the market increases and thus ensure an increase in profits and an increase in the profitability of production and sales.
At the same time, we must not forget about the requirements of the Federal Law of July 26, 2006 No. 135-FZ (as amended on July 4, 2016) “On the Protection of Competition.” In addition, a horizontally integrated holding company can afford to purchase raw materials and supplies at significant discounts by increasing purchase volumes.
Independent Integration
Independent integration means joining the holding of enterprises that produce products (provide services) for consumption in various markets. The production facilities, products or services of the enterprises that are part of such a holding are in no way connected with each other. A holding with independent integration may include metallurgical enterprises, construction organizations, and companies providing services to the public (Fig. 3).
Independent integration allows you to reduce the risks of a significant decrease in sales volumes and demand in one of the consumption markets for products produced in the holding. Risks may be caused by seasonality of production or demand, economic crises and increased competition.
When choosing the areas of activity of enterprises integrated into the holding, it should be taken into account that when the demand for any product decreases, the need for other products of the holding in the consumer markets during this period should remain stable or increase . If, for example, one of the holding companies produces expensive, highly profitable products, then it is necessary to integrate into the holding enterprises that produce low-price goods that are constantly in demand regardless of economic crises. The integration of enterprises producing seasonal goods into the holding is structured in a similar way.
The presence of risks may also be associated with the emergence of one large or several competitors in one of the markets. These risks are mitigated due to the chosen holding structure with an independent integration method. Such a holding is created as if for the purpose of mutual assistance of the enterprises included in the holding.
Blended Integration
The most successful activities are those of holdings with mixed integration (Fig. 4). This holding structure combines all the advantages of various integrations.
An example of such a holding would be UMMC Holding . There is a wide list of market areas in which UMMC Holding LLC occupies leading positions not only in the Urals and the Sverdlovsk region, but also in Russia and abroad. The holding includes:
- non-ferrous metallurgy enterprises;
- mining industry enterprises;
- ferrous metallurgy enterprises;
- enterprises for the enrichment of raw materials for metallurgical production;
- machine-building enterprises;
- aircraft manufacturing enterprises;
- scientific organizations;
- construction enterprises engaged in civil and industrial construction;
- construction industry enterprises;
- enterprises producing cable products;
- service sector enterprises;
- food industry enterprises.
Vertical integration by industry of some groups of enterprises included in UMMC Holding LLC makes it possible to significantly reduce production costs and increase management efficiency. The multidirectional nature of the holding’s activities makes it possible to smooth out the consequences of a drop in demand in a particular sales market, and the high level of concentration of the holding’s resources allows directing cash flows in the directions necessary for the successful activities of the holding.
Partial vertical integration
Partial vertical integration means the unification within a holding of a part of enterprises whose total production activities do not form an integral closed production cycle, but at the same time part (parts) of the technological chain for the production of finished products is within the holding (Fig. 5).
Partial vertical integration of a holding can take place at the beginning of its formation, when the holding’s management seeks to unite enterprises whose production capacities make it possible to organize a closed production and technological cycle. In some cases, creating holdings with complete vertical integration is not practical due to the variety of material resources required to create the final product.
An example of holdings with partial vertical integration would be construction holdings . Creating a closed production cycle, starting from the production of all building materials and ending with the construction of facilities, is practically inaccessible due to the high total cost of production necessary to form a continuous technological chain for the production of building materials and the construction of facilities.
In the production of many building materials, expensive complex technologies are used, non-standard and far from cheap equipment is used. And the management of such a complex should be at the appropriate level. Therefore, organizing a holding company that includes enterprises that produce all the materials and products necessary for construction is an almost impossible task.
At the same time, you need to understand that by purchasing products from third parties, a construction company gives a significant share of its profits to its suppliers. We also have to put up with endless, sometimes unreasonable increases in prices from suppliers. The price of materials also includes the supplier’s overhead costs, which the company that purchases the products pays out of its own pocket.
IT IS IMPORTANT
When forming a holding, overhead costs for production can be significantly reduced through the correct formation of the organizational structure of the holding. This will be an additional cost saving relative to the situation in which materials are purchased externally.
A successfully developing construction company should definitely think about providing itself with at least a basic production base .
If the activity of the enterprise is quite effective, which is expressed in the presence of a certain amount of free financial resources, then they must be invested in the construction of their factories for the production of building materials or look for ways and opportunities to acquire controlling stakes in enterprises operating on the market that produce products in demand in construction . Otherwise, the amount of profit given to suppliers will increase, since the increase in supplier prices is not always adequate to the increase in production costs (often produced as if on schedule and without any economic justification for increasing sales prices).
Organizational leadership - what is it?
Before considering directly the question of what it is - the management team of an organization, it is necessary to become familiar with the basic principles of forming the personnel structure of an enterprise. In general, the company’s personnel are divided into:
- Administrative and management personnel (AUP). These employees include employees who are not directly involved in the production process and the provision of services to customers. Moreover, this category includes the heads of individual structural divisions and the enterprise as a whole. However, in addition to the management of the organization, the concept of administrative and managerial personnel is broader, because it also includes employees engaged in servicing the activities of the enterprise itself. For example, accountants, personnel department workers and other specialists.
- Production personnel. Production personnel generally include workers who provide direct economic benefit to the organization with their labor. However, there is no actual requirement for participation specifically in production, as in the creation of material assets, to classify employees as production personnel. This also includes employees who provide services to the organization’s clients. In addition, production personnel also include support personnel - workers who are not directly involved in economic activities, but also do not have any direct administrative function of the enterprise. For example, security guards, cleaners and other employees whose activities consist primarily of serving the organization itself.
The concept of management is directly related to the concept of subordination at work. Accordingly, in order to effectively distribute duties and responsibilities within the production process, the employer should carefully regulate the labor regulations of the hierarchical structure of the enterprise using local regulations.
From the point of view of legislation, issues of division of labor and the creation of job descriptions and internal labor regulations largely rest with the employer. However, a large number of management professions are mentioned in unified qualification reference books or even have generally accepted professional standards, in accordance with which their activities can be regulated. Also, the management staff of budgetary institutions may have special legal regulation - in this case, their activities may be considered by the provisions of individual regulations directly related to this area of labor.
HOW TO MAKE THE RIGHT CHOICE IN FAVOR OF INTEGRATION OF A CONSTRUCTION HOLDING?
If a construction company strives to develop, but its financial resources are somewhat limited, it is important to make the right choice in favor of integrating a particular enterprise.
Basic principles of selection :
- current and future financial capabilities of a construction organization or holding company;
- construction prospects in terms of types of objects, volumes and methods of construction;
- direction of activity of the integrated enterprise;
- compliance of the production capacity of the integrated enterprise with the needs of the holding;
- the level of costs for the construction and organization of a new enterprise or the value of a controlling stake in the acquired enterprise;
- comparison of financial capabilities and the cost of integrating a new enterprise into the holding;
- the complexity of managing the production and technological process of an integrated enterprise and the ability to ensure uninterrupted operation of knowledge-intensive, innovative or high-tech production;
- economic efficiency of integration.
Given the huge list of raw materials, materials, components and services consumed in the construction of civil and industrial facilities, the most important issue is the choice of an enterprise with the most useful line of activity for the holding, taking into account current or future construction methods.
The construction method determines which materials are primarily used in the construction of buildings and structures.
Basic methods of building construction:
- monolithic;
- frame;
- brick;
- small-piece;
- monolithic brick.
For an initial assessment of the rationality and feasibility of integrating an enterprise - a manufacturer and supplier of building materials into a holding company, you need to know:
- what products and materials are used in the construction process using the existing or planned method of house construction;
- what is their share in value terms in the total cost of the constructed building.
Own capital: compliance with the section “Capital and reserves”
It can be noted that the main components of equity capital in the appropriate interpretation (authorized, reserve, additional capital, retained earnings and amounts for repurchase of shares) are almost completely reflected in the structure of the balance sheet approved by order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated July 2, 2010 No. 66n, namely in section “Capital and reserves” of the relevant document.
It can also be noted that in paragraph 66 of the Order of the Ministry of Finance dated July 29, 1998 No. 34n, there is a rule according to which the authorized capital , additional capital, reserve capital, retained earnings and other reserves should be taken into account in the composition of equity capital. The legislator does not explain what exactly these reserves are, and therefore economists understand this definition of the concept of “equity capital” as subject to a fairly free interpretation.
If you adhere to the considered concept of understanding the essence of equity capital , then calculating it as a whole is easier than using the formula from the Ministry of Finance discussed above. All you need to do is add up the figures in lines 1310–1370 of the balance sheet.
ANALYSIS OF THE INTEGRATION OF A CONSTRUCTION MATERIALS SUPPLIER AS PART OF A HOLDING
The list of the range of raw materials, materials and components used in construction is huge, so initially it is possible to calculate the share of costs for the purchase of materials for each enlarged group of materials used in performing certain types of construction and installation work (CEM).
For the calculation, let’s take a typical 18-story residential building as an example. As a source of information, we use a consolidated local estimate for the facility in 2001 prices. We will not be tied to the cost, since this is an unstable value, unlike the cost structure as a percentage.
The share of construction and installation work as a percentage of the total estimated cost of construction is determined as the result of dividing the estimated cost of production of each type of work by the final estimated cost of the construction project (Table 1).
In terms of the cost of construction work, the largest share is occupied by external finishing work (11.48% of the total cost of construction and installation work). Next comes the installation of the heating system (10.54%).
We will use the estimates on the basis of which the local estimate was drawn up. The estimate numbers in the summary local calculation must be indicated. Such work will not take much time, since at the bottom of each estimate there is a final summary of the estimated costs for each type of work. It is enough to copy the data into a separate table and then calculate the share of each cost item in the estimate by type of work (Table 2).
Let's calculate the share occupied by enlarged groups of materials for each type of construction and installation work in the total estimated cost (Table 3).
As can be seen from the data in table. 3, the maximum share in the total estimated cost of the facility is occupied by materials used in the installation of heating systems (9.17%).
When performing several types of work, the same groups of materials are used. Let's group them and calculate the share of the total need for materials of one group (Table 4).
Now we will determine the groups of materials with the maximum share in the total volume of construction and installation work (Table 5).
The largest share in the cost of construction and installation work among other groups of materials is occupied by the “ Reinforced Concrete ” group, which includes concrete, reinforcement and other materials for performing monolithic work (15.66%). This does not take into account other works, the production of which also uses concrete and reinforcement.
Such an analysis does not provide a complete answer to which manufacturers of which groups of materials should be integrated into the holding, but it can become a guide in the choice. At the same time, the picture of priority groups of materials according to the principle of the share of consumption during the construction of different types of objects can be radically different even with the monolithic construction method. For example, the Reinforced Concrete group, when constructing shopping and entertainment complexes, may not occupy the first place in terms of material consumption in value terms.
In this example, we will consider options for joining a holding company:
- concrete plant;
- valve production plant.
The production capacities of these enterprises can be completely different, as well as the cost of these plants. For example, to produce fittings it is not at all necessary to integrate a large metallurgical plant into the holding. For small and medium-sized construction volumes, you can pay attention to mini-factories for the production of construction reinforcement , specializing in the processing of scrap ferrous metals, capable of producing not only construction reinforcement, but also channels, angles, etc.
Such enterprises, due to the absence of blast furnaces, can significantly reduce energy costs. In addition, the mini-plant can be located as close as possible to the construction site or to workshops for the production of reinforced concrete products, which significantly reduces transportation costs. The profitability of such plants is 40% or more . It is only necessary to ensure the high quality of the products produced at such factories.
a concrete plant into the holding , this promising business direction requires further study of the issue of joining the holding of such mining industry enterprises as sand and crushed stone quarries. Vertical integration of a group of enterprises producing inert materials and concrete will bring a significant economic effect in the form of high marginal profits remaining at the disposal of the holding. In addition, the concrete plant can produce masonry mortars and floor screed mortars. Subject to the acquisition of additional equipment, all kinds of reinforced concrete products can be produced from concrete and mortars.
The criterion determining the choice may be the simplicity of the production technology of both concrete and building reinforcement, relative to most items included in other groups of materials (see Table 5).
To make a final decision, you need to most accurately determine how beneficial it is to integrate into the holding of enterprises whose main profile is the production of a particular product. Therefore, you need to develop detailed business plans , which should reflect:
- all costs of integration;
- direct and overhead costs for production;
- planned profit;
- integration payback period, etc.
As the holding develops, you should return to the analysis and selection of new business areas. After all, a high share of a particular material in the estimated cost of construction does not always mean that the production of materials will bring the greatest profit to the holding. Let's look at why.
Let us accept as a condition that for the group of materials “ Concrete ” the marginal income (MI) from the sale of products corresponds to the average statistical level of marginal income from the sale of concrete, subject to the purchase of inert and cement from third parties and is 14%. Then we calculate the share of marginal income for this group as a percentage of the estimated cost of the object (Table 6).
We will also determine what the level of marginal income from the sale of other groups of materials should be so that the share of marginal income for these groups is 1.46% of the estimated cost of construction (column 6 of Table 6), similar to the MD of the group of materials “Concrete” (Table 7).
To achieve the share of marginal income of the group of materials “Concrete”, which is 1.46% in the total estimated cost of the object, for the group of materials “Plastic and aluminum double-glazed windows” it is necessary to receive a marginal income from the sale of products of this category to the outside in the amount of 22.23% . This is not only a completely achievable level for products that are in demand, but rather even low. That is, this means that the integration of an enterprise for the production of double-glazed windows can bring the holding a higher marginal income than a concrete production plant .
The calculation results (see Table 7) indicate that other groups of materials should also not be ignored during the development of the holding. We need to think about an independent method of integration, that is, the inclusion in the holding of enterprises that do not produce materials for construction, but produce highly profitable products that are clearly in demand on the market during periods of crisis and beyond. This is necessary to reduce the risks associated with a drop in demand for real estate caused by a decrease in the level of real income of the population.
Formula for the cost of an organization's equity capital: the Ministry of Finance method
The equity formula , which is based on the provisions of Order No. 84n of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation, involves the use of:
- balance sheet indicators, namely those recorded in lines 1400, 1500, 1600;
- data from accounting accounts: Dt 75 – Kt 80, Kt 98.
At the same time, in the credit of account 98 it is necessary to take into account only those future incomes that are related to assistance from the state, as well as the gratuitous receipt of property.
The formula for determining the net assets and at the same time equity capital of a company is as follows:
- we add up the numbers on lines 1400 and 1500, and then subtract from them the indicators for the credit of account 98 (let’s conventionally call this indicator “DBP” - deferred income);
- subtract from the figure on line 1600 the values corresponding to the debit of account 75, as well as the credit of account 80 (let's call these values “DUO” - debts of the founders of the company);
- subtract from the figure obtained in point 2 the one determined in point 1.
Thus, the final formula will look like this:
SK = (line 1600 – DUO) – ((line 1400 + line 1500) – DBP).
equity is calculated within the framework of the method by which it is identified with net assets. But there is another approach to interpreting the essence of equity capital . Let's study its features.
Construction materials
Metallurgical and chemical complexes supply structural materials necessary for industry and construction.
Construction materials are a variety of materials that are used to make finished products or construction.
Based on the time of their origin, construction materials are divided into traditional ones, which humanity has been using for a long time, and new ones, which began to be used in the 20th century.
By origin they are classified as metallic, non-metallic and composite.
Increasing the number of comrades
In order to attract additional working capital, the founders of a general partnership have the right to increase the number of participants. This is done through a joint decision. There are certain requirements for potential applicants. An organization conducting commercial activities or an individual entrepreneur is considered for:
- availability of free capital (acceptable in kind and cash equivalent), commensurate with the amount established by the founding agreement;
- legal capacity;
- absence of participation in another partnership of the corresponding form.
A collective positive decision on a specific candidate presupposes the entry of a unit into the membership of the general partnership. A new member of the company is assigned the same responsibilities as the other shareholders, regardless of their affiliation with the founders. A comrade who has newly joined the company is liable for obligations that arose even before he became a member of the enterprise.