In the process of labor activity, such a concept as a production norm arises. It is not applicable to all sectors of the economy, but is a very important indicator when calculating employee wages. Most often used exclusively for manufacturing enterprises. Where and how the production rate is used will be discussed further.
Theoretical concepts
Rationing of labor is necessary in any case. How to set the salary amount for an employee? Based on what data and indicators? John Keynes first thought about this at the dawn of economic theory. Nowadays, standardization is carried out in any industry, and recommendations for this are indicated in regulatory documents.
In fact, the production rate determines how many units of output one person must make in the time allotted to him. The parameter is calculated in natural terms: ton, pieces, kilograms, meters, and so on. Despite the fact that there is a unified approach to the formation of production standards, for each sector of the economy it is completely different. At the state level, only practical recommendations are given, but specific indicators are established directly at the enterprise and are regulated by a collective agreement.
Next, we’ll look at how to calculate the production rate using the example of a specific industry.
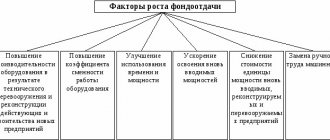
Factors increasing and decreasing
An increase or decrease in labor productivity can be associated with both the human factor and the peculiarities of the operation of equipment.
For example, wear and tear of even high-tech equipment will cause more frequent breakdowns and an increase in the duration of repair work, the same will happen when using low-quality machines and production lines.
Re-equipping with modern types of equipment leads, as a rule, to improving labor productivity at the enterprise , but this will not happen overnight. Personnel will be forced to retrain to work on more modern machines, so HP should be increased gradually.
Proper planning and organization of the work process also influence the value of production standards. Constant downtime, associated, for example, with poor performance of supply departments, will negatively affect the work of the entire enterprise as a whole, as will the purchase, for example, of materials of inadequate quality.
Training and retraining of employees is an important factor in the practical and psychological impact on NVyr . The employee gains useful skills for work, and at the same time feels like a valuable member of the team, which is a good motivation for further optimization of the functions performed.
The procedure for developing production standards for the food industry
In catering establishments, it is customary to assume that the work of any cook is assessed in the number of dishes prepared. This approach helps to objectively assess what time, resources and labor were necessary to create a particular product. In regulatory documents for the food industry, special labor intensity coefficients have been developed, without which it is impossible to calculate the production rate.
Features of calculation of output
Before calculating the level of labor productivity, it is necessary to measure labor costs and output volume.
Labor costs include one of two indicators:
- the number of workers involved in the production of a given volume of products,
- time worked, measured in man-hours (days) worked.
To calculate labor productivity, the following indicators are used:
- average hourly output, which is determined by the formula:
Hour.=Q/T
Here Q is the volume of production,
T – actual number of man-hours worked by workers.
- average daily output,
Ind.=Q/T
T – actual number of man-days.
- average monthly (quarterly, annual, etc.) production.
Int.=Q/N
N – average number of workers per month.
Labor intensity coefficient of the food industry
The labor intensity coefficient shows how much time is needed to prepare one dish in relation to the dish taken as a unit of labor intensity. In other words, there is a single parameter taken as one, and all others are equal to it.
For example, the simplest chicken soup in one serving takes 100 seconds to prepare. This is a unit. Milk soup will take 90 seconds, in which case the labor intensity coefficient will be 0.9. Timing helps set such boundaries. But in order for catering enterprises not to waste their time studying standards, government services did it all for them, and now all norms and labor intensity coefficients for the food industry can be found in regulatory documents.
What is it measured in and what does it show?
Productivity is defined as a measure of the efficiency and fruitfulness of work activity. The category under consideration is expressed in two indicators. It is determined by the labor intensity of one product and the output of one person.
Production refers to the amount of product produced by a person over a specific period of time. For example, if a mechanic processes 50 parts in 5 hours of work, then the efficiency is calculated by dividing 50/5 and equals 10 parts per hour.
Types of labor intensity
Labor intensity is the time period spent on the production of one product. If an employee processes 10 parts in one hour, then the labor intensity is determined by dividing 60/10 and it turns out that one part takes 6 minutes of working time.
Labor productivity is determined through these concepts. It is understood as the number of products created in a single period of time, or the time spent on creating one product.
The company is staffed not only by blue-collar workers who directly create products; there are also employees, technicians, engineers, and support workers.
Labor Productivity Measurement
The listed persons do not independently produce the product, but create the conditions for its production and productive operation of the enterprise. When determining the productive level in the company as a whole, the labor of the listed employees is subject to accounting.
The concept of productivity is used as a generalizing characteristic of the company's production level. In practice, the expression of output in monetary terms is widely used. Using this indicator, it is possible to calculate the efficiency of the country as a whole, in the industry, and in an individual company.
The organization employs 200 people, with a total production volume of 400,000 rubles. Output for one person is calculated by dividing 400,000/200.
Output must be measured in physical form, which are pieces, meters, liters and other quantities. Indicators related to natural ones are applicable in organizations producing products of a homogeneous type. An example is stone mining, brick production, etc.
Improvement of production and its growth are mainly associated with increased productivity. A number of factors influence increased productivity levels.
First of all, the development of scientific and technological progress is reflected. Progression in the technical field affects the reduction of labor costs for the production of one product. Refers to a situation where old equipment is replaced with new equipment, improving the production sector.
The physical and emotional burden of work also affects productivity, so when new automated technologies are introduced into the work process, it is possible to significantly increase the level of production.
Example
The following initial parameters are given:
In total, one cook spends 25,220 rubles on making a cottage cheese cake. Preparatory time takes 1260 s, preparation of the workplace and necessary materials costs 1008 s. During breaks for rest and personal needs, 1260 s are spent. According to the timing specified in the regulatory documents, it should take 32.39 seconds to make one unit of cottage cheese cake. Find the production rate.
We substitute the data into our formula and get the result:
Hb = (25220 - (1260+1008+1260)) / 32.39 = 671 pcs.
Thus, one cook can produce 671 units of cottage cheese cake in one work shift. The results obtained serve as an assessment of labor productivity and are the main data for calculating wages.
Output per 1 employee: formula, standards and calculations
The output formula is of great importance, since the calculated indicator is used when calculating labor productivity at the enterprise.
Output is an indicator directly proportional to labor productivity, so the more products are produced for each unit of labor input, the higher the level of productivity will be.
B = Q / T
Here B is the production indicator,
Q – volume of products produced;
T – labor costs for a given volume of production.
The daily production rate helps to improve labor productivity, increase the amount of profit received by the enterprise and reduce costs. Moreover, the type of organization does not matter: production, warehouse complex or construction teams.
Typical optimization of the work process of each department is one of the key points in the effective operation of the entire company as a whole. Failure to comply with technical conditions leads to a reduction in wages for piecework. How to calculate the completion rate or percentage of overfulfillment, how many hours per month or per year are spent on producing a unit of product.
Terminology
To study issues related to establishing a workflow, it is customary to use certain terms.
Labor standards
A specific task that an employee (or team) must complete in the allotted working time is called a labor standard (NTr). As stated in the second article of the Labor Code, every employee is obliged to comply with this standard.
Scientific and technical progress can be individual and collective. In the second case, the total work is calculated for a group of employees united into a single team, for example, this applies to:
- brigades;
- production sites;
- departments;
- workshops
Scientific and technical standards can be specified in employment contracts, but are determined by the planning departments of enterprises. If the employer decides to change labor standards, then he is obliged to notify employees about this no later than 1 month in advance, according to Article 103, Part 2 of the Labor Code.
Important! Violation of this rule leads to the cancellation of the introduced changes, and wages must be calculated at the old rates.
Labor legislation obliges the employer to provide employees with appropriate conditions that will allow them to fulfill the relevant scientific and technical requirements, namely:
- Provide working equipment and devices necessary for work.
- Ensure timely access to up-to-date technical documentation.
- Deliver materials and tools needed to complete the plan on time and of acceptable quality.
- Monitor the uninterrupted supply of electricity, gas, and other energy sources.
- Comply with technical safety rules at the enterprise. This includes requirements for lighting, space heating, ventilation, and elimination of harmful factors (vibration, radiation).
It should be noted that with the improvement of work methods and technical re-equipment of the enterprise, scientific and technological progress can be revised. At the same time, if an employee or team was able to independently achieve increased output through the use of new production methods or independent improvement of workplaces, then there is no reason to increase scientific and technological progress.
Standard time
The period of time required to create one unit of product to perform one or more specific work operations is called standard time (NTr).
When calculating this parameter, the item produced (an object produced by an employee) is considered as:
- one piece;
- one product;
- one production operation;
- one cycle of production operations;
- one type of any service.
To more accurately determine HBP, clear timing of each operation should be used, while observing all technological standards.
НВр = Вр_пз Вр_з Вр_about Вр_отл Вр_тВр_пз – preparation for the work process; Вр_з – main time; Вр_ов – period of caring for the workplace; Вр_тл – time for personal needs;
Vr_pt – technological breaks.
The unit of measurement for HBP is usually considered to be the man-hour. For example, a miner needs 3 hours of working time to obtain 1 ton of minerals, therefore, the labor force for this industry is 3 man-hours.
Production rate
The number of products, operations, services performed per unit of working time is called the production rate (NPr). The time period is selected depending on the characteristics of the enterprise. This could be the length of a shift (for example, 8 or 12 hours), one working hour, or any others.
It is customary to indicate the НВр parameter in units characteristic of a given industry: number of products, liters of products, tons of goods, etc.
НВр = Вр_см x Х/ НрВр_см – shift duration; Х – number of team;
Nvr – standard time per unit of production, operation.
The production rate is an appropriate coefficient if we are talking about constant work of the same type. For example, laying parquet, painting work, etc.
Number of people
Attention! The number of workers of a certain qualification required to carry out a cycle of production or other volumes of work is called the norm of strength (NChis).
NChis = НВр x В / Вр_смНВр – standard time per unit of production or cycle of operations; В – planned volume of work per shift;
Time_cm – duration of one shift.
The parameter helps to estimate labor costs for a number of professions, specialties, individual cycles of operations throughout the enterprise or for its individual divisions (sites, workshops, etc.).
Standard of service
The number of objects that an employee (group of employees) is able to service during one time unit (shift, hour) is called the standard of service (NOb). The calculation can be made if the standard of time (NVR) is known:
- NOB = Time_cm x K / НВрВр_cm – duration of the time period under consideration;
- K – degree of use of working time, expressed as a coefficient;
- НВр – service time.
The calculations are useful for assessing the activities of repairmen, production maintenance personnel, warehouse workers, etc.
The amount of work that an employee or team must complete in a certain period of time is called a standardized task (NT). Like the production rate (NR), this parameter determines the calculated result of the actions of an employee or a joint group for a specific time, being essentially a more general case.
The units of measurement can be standard hours or standard rubles. The work order must take into account the qualifications of a particular specialist, the specifics of working conditions, the degree of harmfulness and other points.
Groups of workers should be distinguished by the actions they perform:
- the same cycle of work at a permanent place;
- various works performed;
- work carried out at different sites or objects.
The first group includes, for example, assembly line workers; their work order is determined according to the specific standards of piece workers.
For reference. The second type of employee is engaged, for example, in various repair or adjustment work within the enterprise. The work order must be consistent with the schedule or plan of technical activities of the production enterprise.
The third group, whose activities may be related to travel, is supplied with individual assignments, for example, this could be an application for car repair or maintenance.
Calculating the HBP per person will allow you to optimally organize the work process of the entire team. At large enterprises, this is done by specialist timekeepers. At small production sites and other enterprises, calculations fall on the shoulders of production managers.
Without HBP, it is impossible to predict product output, which may cause a delay in the expected delivery dates, and as a result, penalties on the part of the customer. As an example, you can use the formula HVyr = Time_cm x H/Nvr, where H (number of employees) will be equal to one.
If automated equipment is used in production, then a different formula should be used.
NVyr = NVyr_ter * KpvNVyr_ter – theoretical value of the indicator;
Kpv – useful coefficient for one shift of time;
NVyr = Time_cm / Time_unit_time_cm – shift duration;
Vr_ed is the period during which one product is created.
These calculations of NVyr are made every quarter in the planning and economic department of the enterprise.
Different industries are characterized by individual characteristics that must be taken into account when analyzing production processes.
NVRs are characterized by the peculiarities of time periods (time of year) for field work, as well as the climate characteristics of a given area, the availability of mechanization means at the enterprise, and the volume of areas on which agricultural activities should be carried out.
To study the process and calculate NVyr, they resort to phototiming; this is the actual recording of the working day with the participation of photo or video equipment, further analysis of the data obtained to obtain an objective picture.
Features in the determination of HP are considered to be the calculation of the balance between the capabilities of production lines and manual operations.
Important! Reducing manipulations carried out directly by employees to the necessary minimum greatly increases the production rate. However, the complexity of the mechanisms does not eliminate the need for maintenance and adjustment of equipment, so the performance of repair teams should be optimized.
In construction
Highly specialized work is easier to calculate, but it is necessary to proceed from the qualifications of the craftsmen or teams. The average value is 1 cu. m. per hour.
NVyr is also influenced by the structural complexity and requirements imposed by SNiP II-22-81. It is believed that about 20% of the duration of a mason’s entire work shift is preparatory work and cleaning at the end of the day.
The productivity of this type of work depends on the type of equipment, driver qualifications, and the characteristics of the working premises. When making calculations regarding road construction work, the volume of buckets and the average speed of equipment for various types of objects (flat area, rough terrain) are also taken into account.
An increase or decrease in labor productivity can be associated with both the human factor and the peculiarities of the operation of equipment.
Performance standards for cleaners of non-industrial premises
Let's look at another example. Cleaning of industrial premises is carried out approximately according to the same plan, so data from a real existing enterprise, for example, the beer and soft drinks industry, is taken as a basis.
Calculation of the production rate is carried out taking into account the following points:
- basic operations: washing and sweeping floors, washing and wiping walls, windows, doors;
- cleaning premises: technological workshops and auxiliary areas;
- characteristics of cleaning objects: material of manufacture, labor intensity during work;
- The optimal working time is an 8-hour shift.
Formula
On average, production per month or per year in a company is calculated using the formula:
Calculation of average annual or average monthly output
To make the calculation, you first need to determine the indicators used in the formula. An indicator of product production over a period of time or labor intensity can be used. Production relative to one product over a time period is calculated as follows:
Calculation of average output of one product
Indicators regarding labor intensity are subject to calculation:
Calculation of labor costs per unit of production
The method used to calculate performance is then defined:
- cost;
- natural;
- labor.
The natural method is applicable to determining the amount of output and products produced by the organization. Measurements are made in quantities, meters, cubes and other quantities.
The company employs 100 workers. 100,000 products are produced in one month. The output per employee is equal to one thousand products (at the rate of 100,000/100).
The labor method is associated with measurement in standard hours. This type of method is not used in small and medium-sized businesses, as it is not entirely convenient.
Calculation formula for cleaning industrial premises
Directly at the enterprise, they carry out their own time measurements when calculating production standards. This is done in order to most accurately understand how many minutes or hours it takes to wipe windows, say, measuring 1 by 1 m or 2 by 3 m. The same goes for floors. The tiled covering, without chips and cracks, can be removed much faster than its concrete counterpart. Let's look at how the production rate (formula) for industrial premises is calculated:
You need to know the following parameters:
Nv - production rate;
Tcm — duration of one shift, min;
Tobs - time required to service the workplace during a shift, min;
Totd - time spent on rest, min;
Tln - time for a break for personal needs, min;
Top - calculated time for cleaning 1 square. m area, sec;
k is a coefficient that is taken into account when cleaning several rooms. It shows how much time a worker spends moving from one hall to another. It is actually set by a stopwatch.
Production and labor intensity
Labor productivity is characterized by two important indicators.
- Output is the amount of labor performed by one person. This way you can measure not only the number of things produced, but also the provision of services, sales of goods and other types of work. Average output can be calculated by taking the ratio of output produced to the total number of workers. Output is calculated using the following formula:
V = V / TWhere:
- B – output;
V – volume of production (in money, standard hours or in kind);
- T is the time taken to produce a given volume of products.
- Labor intensity is the costs and associated efforts that accompany the production of goods. They can be of various types:
- technological – labor costs for the production process itself;
servicing – expenses for equipment repairs and production services;
- managerial – labor costs for managing the production process and its protection.
NOTE! The totality of technological and maintenance labor costs constitutes production labor intensity. And if we add management to production, then we can talk about full labor intensity.
To calculate labor intensity, you need to apply the following formula:
TP = T/V
The term “labor intensity” usually refers to the ratio of resources and time spent on their production. Typically measured in man-hours. Sometimes the word “production” is used as a synonym for the concept. Calculating this coefficient allows you to achieve the following goals:
- Calculate how much labor and time is needed to create a unit of finished product.
- Identify in which areas resources are being used productively and in which areas need optimization.
- Identify weak links in the technological process.
- Determine whether there are reserves for improving productivity.
The term “labor intensity” usually refers to the ratio of resources and time spent on their production.
How to calculate labor intensity? To do this, you need to use the following formula: the working time for producing a certain number of products divided by the number of goods manufactured. Let's look at the formula and calculation example in more detail.
- To begin the calculation, you need to establish the exact amount of time that was used to produce a certain volume of products. This information is taken from time sheets. This document reveals the number of man-hours - units corresponding to one hour of working time of one person. To calculate the number of man-hours, you need to add up all the hours worked by all employees. Let’s say that an enterprise employs 5 people, their working day is 8 hours. For one shift the number of man-hours is 40 (5 people x 8 hours), for a working week - 40 x 5 = 200.
- Next, you need to determine the total cost of all goods produced (services provided, etc.) during the specified time. This number must also be taken from the documentation.
- To calculate labor intensity, you need to divide the number of man-hours (first point) by the total cost of goods or services (second point). The resulting value is the labor intensity of a unit of production.
Let's look at the calculations using a specific example. During an 8-hour working day, 5 employees produced 100 units of goods, costing 80 rubles per unit. We count step by step.
- Number of man-hours: 5 people x 8 hours = 40 man-hours.
- The total cost of all products: 100 units of product x 80 = 8,000 rubles.
- Product labor intensity coefficient: 40 / 8,000 = 0.005.
Now you know how to find the labor intensity factor.
Calculating labor intensity is only half the battle. What to do with this value? It needs to be interpreted correctly.
Here are some recommendations:
- The lower the value of the labor intensity coefficient, the higher the labor productivity.
- This indicator needs to be monitored over time - it should decrease, that is, labor productivity should increase. If it takes less time to produce the same volume of products, it means the technological process has been optimized and the professional skills of workers have improved.
- If, on the contrary, the value of the indicator has increased, you need to find the reason that complicates production. These could be problems with equipment, new raw materials, a new employee, or even a general decrease in motivation in the workforce.
- You need to compare the coefficient value not only with previous values, but also with planned ones. That is, based on the data obtained, you need to prepare a plan and include in it an equal or slightly reduced value of labor intensity for a similar reporting period.
Calculating labor intensity is only half the battle. It needs to be interpreted correctly.
So, we looked at how to calculate labor costs. The man-hour formula presupposes access to primary documentation, namely a time sheet recording hours worked and acts recording the number of products produced.
The value of this indicator is influenced by a very significant number of factors. To competently analyze the data obtained, you need to know and take into account all influencing factors.
Each individual production has its own list, but the most common are:
- Professionalism of the staff.
- Streamlined technological process, comfortable working conditions.
- Timely supply of raw materials.
- No problems with infrastructure and communications (no power outages, access roads are cleared, etc.).
- Motivation of workers, mood in the team and decent wages.
Specific labor intensity is a value showing how much time is spent on producing one unit of product (good, service). Let's look at how this coefficient is calculated. It is in inverse proportion to labor productivity and is calculated by dividing the number of workers by the amount of work in monetary terms.
Example: 5 workers produced 100 units of product in 1 shift at 80 rubles per unit. We already know that the labor intensity coefficient will be equal to 0.005. What will be the specific labor intensity? 5 / 8,000 = 0.000625.
The labor intensity of a production program is an important coefficient that will show how many man-hours will have to be spent to complete the entire production plan. It can be either planned - that is, calculated before the start of the program, or final - to estimate how many man-hours it took to produce a given amount of products in fact.
It is not difficult to calculate this coefficient - you need to multiply the amount of production provided for by the plan by the time spent (in man-hours) to produce one unit of goods. For example, a production program involves the production of 1000 units of products, at a cost of 2.5 man-hours per unit. 1000 x 2.5 = 2500 man-hours.
Economists distinguish several types of labor intensity.
Above are the two most common types of output in practice: production and specific. However, economists identify several more types of labor intensity:
- Technological labor intensity implies an assessment of the time costs of all workers.
- Maintenance - on the contrary, shows how much time was spent on auxiliary workers.
- Production - is the sum of the values of technological labor intensity and maintenance, that is, the time costs of main and auxiliary workers.
- Management - records the time spent by process managers.
- Construction of an object is a special case of labor intensity; it shows how many man-hours will be spent on the entire process of constructing the object.
Labor costs are the entire amount of money payable to employees for the reporting period. The formula for labor costs is quite simple. It is necessary to multiply the average annual number of employees by the average salary per employee.
For example, let’s calculate monthly labor costs for an enterprise with 15 employees and an average salary of 27 thousand rubles. 15 x 27,000 = 405 thousand rubles. If you need to get the value for the year, then the monthly costs need to be multiplied by 12: 405,000 x 12 = 4,860,000 rubles.
The main result of calculating output should be an analysis that will show which components of the technological process need to be improved. Of course, each individual enterprise will have its own optimization paths, but in general the following options can be mentioned:
- increasing the professionalism of employees, retraining;
- introduction of modern technologies and innovations;
- improving logistics;
- analysis and improvement of the technological process;
- use of higher quality raw materials.
General requirements for production workshops before starting cleaning
The above production standards will make sense if a number of requirements for production premises are met. As we understand, in a workshop where work is in full swing all day, everything must be in order by the end of the shift. This time is taken into account by the worker standing at the machine, and not by the cleaning lady. So, here are the general requirements for production premises:
- At the entrance there must be special floor gratings or mats that collect dirt from the street;
- floors must be promptly repaired when cracks and potholes appear;
- all transport carts must have rubber wheels that do not damage the floor;
- the walls must be made in accordance with the standards adopted by government services (painted or covered with light tiles);
- garbage and broken containers must be removed by the employee into appropriate containers;
- special attention is paid to the distance standards between equipment;
- All employees must maintain their work area and keep it clean.
What it is?
The labor intensity in the calculation for one product is represented by the total amount of time spent on its production. Based on this, labor efficiency is defined as the amount of product produced by a company employee per calculated unit of time.
Also, the definition of this concept is the time spent by a person on the production of one product. The production characteristics are compiled after analyzing the concept under consideration.
Sample of filling out production characteristics
Indicators are calculated for individual employees and for the entire organization. Production and production of products at individual employee locations and areas where products are manufactured must be measured in kind.
The volume of products manufactured over a certain period of time is taken into account. An example is the number of printed publications that were sorted by one person in an hour, the number of certificates issued per day by an employee, etc.
Dimensions relative to output at individual worker locations are often subject to standardization. A separate planned task or production norm is developed for the employee.
Methods for measuring labor efficiency
The productivity of employees involved in servicing various communications media can be characterized through production. This is because they are involved in adjustments and troubleshooting.
The work of such employees often involves performing duties at the workplace. Determine the required labor intensity, namely the amount of time spent on eliminating damage.
If we are talking about an enterprise that provides communication services, then the labor productivity of all employees is characterized through average output indicators. In general, it will not be possible to calculate production in kind for such a company. This is due to the provision of various services and works, and therefore the measurement is made in money.
Labor efficiency analysis
The volume of products sold by an enterprise providing communication services is reflected in the profit received. Therefore, when calculating the productivity of the entire company, sales revenue is used.
Labor efficiency is influenced by:
How to achieve accuracy in estimating labor costs
There are two ways. The first is classic, when, when carrying out labor standardization work, time measurements for an operation are made immediately or sequentially for several workers working in different shifts and at different workplaces. This is quite labor-intensive and also time-consuming. Or measurements are taken of the “correct” employee. But where to get it, and how to understand that it is correct?
There is another way. Assessment of labor efficiency directly during timing work. Efficiency assessment was carried out for each labor movement for each time measurement for an operation, or its element, by setting the efficiency coefficient of labor movements. At one time, back in the USSR, there were several centers for the development of standardization in the country, and one of them was the Volga Center , the peculiarity of which was the study of the effectiveness of labor movements, and the development, if you like, even training of engineers for the organization and standardization of labor for the correct assessment of these movements. I am just an example of such a “trained” engineer in organizing and rationing work.
What is the essence of the method and how were we “trained”? Basic, elementary movements were taken as a basis, such as arm movement, body rotation, bending, walking, etc., based on the example of microelement rationing (I won’t talk about microelement rationing, this is a separate big topic), and the operation was divided into such elements. The result is certain tables, such as Table 1.
Norm of time spent on simple movements
| Types of movements | Times/min. | |
| Finger movement (clench, unclench) | 90 | |
| Rotates the body at an angle of 45-90 degrees | 90 | |
| Sit on a chair, get up from it | 20 | |
| Walking with a stride length of 750 mm | 88 | |
| Complex movements of the hand and forearm (screwdriver work) | 90 degrees | 180 degrees |
| — With a force of up to 1 kg | 150 | 90 |
| — With a force of up to 5 kg | 120 | 70 |
| — With a force of over 5 kg | 80 | 45 |
Table 1
Physiological studies have shown that if a worker works throughout the day at the pace provided for by these standards, then the degree of his fatigue will not exceed acceptable limits, since he performs work at a normal pace, for which the coefficient of labor movements is set to 1.
Next, based on these tables, the different pace and rationality of the worker’s movements were calculated and assessed. As a result, the pace and rationality of the worker’s movements in its various manifestations was recreated. The range of fluctuations of the coefficient was compiled with an interval of fixed values ± 0.05.
0.65 <= Kef <= 1.25
1 was taken as the normal/optimal coefficient. That is, one corresponds to the work that is performed by the employee in a rational way at a normal pace. If, during timekeeping, a specialist determines that the employee performs work with a coefficient above 1.25, or below 0.65, then it is not recommended to carry out timekeeping. In the first case, the employee will not be able to maintain such a pace for a long time, and in the second case, there is clearly no desire to work, so it is inappropriate to use the data obtained to calculate time standards. Then, from these movements, the operation was “assembled” back together.
Based on this, a video sequence was recorded in which workers moved with varying efficiency. During the training of the profession, the engineer for the organization and regulation of labor, thanks to hundreds of views of video sequences, developed the skill of determining an accurate assessment of the effectiveness of labor movements.
labor efficiency coefficients is to adjust the time expenditure recorded during timing, that is, to bring the time for an operation to the optimal value. The application of the coefficient is shown in table No. 2, where five workers perform the same operation.
Relativity of labor productivity
Labor productivity as an economic indicator carries direct information about the degree of efficiency of workers' labor invested in the products produced.
When working, a person spends time and energy, time is measured in hours, and energy is measured in calories. In any case, such work can be both mental and physical. If the result of labor is a thing, product or service created by a person, then the labor invested in it takes on a different form - “frozen”, that is, materialized, it can no longer be measured by the usual indicators, because it reflects past labor investments and costs.
Assessing labor productivity means determining how effectively a worker (or group of workers) invested their labor in creating a unit of output in a specified time period.
Formula for average annual output per worker
Formula for calculating output per worker Availability of resources The number of employed people in an enterprise is of great importance. When analyzing the supply of labor resources, the actual number is compared with the planned number and indicators for the previous period for each group of workers. A positive trend is one in which average annual output grows against the backdrop of a change (decrease) in the number of any of the groups of employed employees. The reduction of support personnel is achieved by increasing the level of specialization of those involved in setting up and repairing equipment, increasing mechanization and improving labor. The number of personnel is determined according to industry standards and the rational use of working time necessary to perform certain functions: 1. Workers: H = Labor intensity: (Annual working time * Standards fulfillment rate).2.
The working process
The production process is associated with the organization of the employees' working day. For optimization, management constantly takes measures aimed at improving the working conditions of subordinates.
The begining of the work day
The mornings of employees of any company begin with the fact that they wake up. Then there is a meal, a shower, a choice of a suit to wear and a direction to the workplace.
The human brain is designed in such a way that in the sequence of performing the listed actions, it prepares the person for work.
This suggests that it is necessary to establish a schedule for completing work duties, which ensures success in production.
Often the working day starts at 09:00 and ends at 18:00, however, this schedule is not mandatory, and each employer has the right to apply his own.
In addition to setting the time for work, you need to remember to communicate with customers, thereby proving the professionalism and organization of workers. Clients are given special attention and their wishes are taken into account.
Eliminating extraneous sounds
Often, while performing work functions, a person listens to music. However, it has been proven that such sounds can distract the employee’s attention and, as a result, reduce efficiency.
For this reason, the employer is taking measures to eliminate unnecessary sounds during the labor process. The person himself may claim that music is not distracting, but in reality this is not the case.
Organization of work space
When a person performs labor functions at home, it is enough to sit down at the computer and start working. If an employee has a permanent place in the company where he works, then to improve productivity this place should be properly organized and optimized if possible.
Blocking sites that distract you from work
Upon arrival to work, the employee must block all sites and places that can distract from the performance of functions. Access to sites that are not used for work can be blocked or not opened during the work process.