Why do you need a company's tax burden ratio?
The tax burden coefficient is an indicator that tax specialists use when analyzing the details of companies and choosing who to include in the on-site inspection plan. The lower the tax burden, the greater the likelihood that the organization will be suspected of violating the Tax Code of the Russian Federation and will be included in the plan.
The Order of the Federal Tax Service dated May 30, 2007 No. MM-3-06/ [email protected] “On approval of the Concept of the planning system for on-site tax audits” contains the criteria by which an organization falls into the risk zone when drawing up an audit plan. The first item on the list is that the tax burden on business is less than the industry average.
In addition, the tax burden indicator, among others, is used by banks when deciding whether to issue a loan to an organization. Banks also control the tax burden in order to comply with the “anti-money laundering” law of August 7, 2001 No. 115-FZ. Thus, according to the Methodological Recommendations of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation No. 18-R, approved in 2020, if the amount of taxes paid is less than 0.9% of the total turnover on the account, then this is a sign of a “bad” client. The bank may refuse service to such a client.
On guidelines for banks to identify “bad” clients
Tax burden by type of economic activity in 2020
The tax burden is the total amount of taxes that a company must pay to the budget. Low performance is a surefire way to get included in the on-site inspection plan. Compare your indicators with the load by type of economic activity in 2020.
One of the priorities of the financial director is to reduce the amount of taxes payable. After all, no owner wants to overpay the state and receive less earned profit.
Particularly valued are those specialists who, within the framework of legislation, using various tools, can bring the amount of taxes closer to a critical threshold - the average statistical burden on a business, determined by the fiscal service by industry.
Crossing the threshold value will result in an on-site inspection for the enterprise.
What is the tax burden of an enterprise and why calculate it
First, let's understand the terms. The tax burden in absolute terms is the total amount of payments that an enterprise must pay to the state treasury. In relative terms, this is the total amount of taxes paid by the enterprise, divided by the amount of revenue received by the enterprise for the relevant period, calculated as a percentage.
It is the second indicator that the Federal Tax Service uses to formulate a plan for on-site audits for the next year, comparing the indicator in the submitted financial statements with the industry average.
Those companies whose performance is below normal are included in the list of suspicious ones.
Inspectors have doubts whether the company did not use illegal tax schemes, because within the framework of the law it is theoretically impossible to obtain such a positive result.
How to calculate an organization's tax burden
According to the Order of the Federal Tax Service dated May 30, 2007 No. MM-3-06/ [email protected], the total burden is calculated as the ratio of all taxes paid.
In a letter dated June 29, 2018 No. BA-4-1/ [email protected] the Federal Tax Service specified the calculation procedure:
- the proceeds must be taken without VAT and excise taxes;
- the amount of taxes includes the paid personal income tax;
- Insurance premiums are not included in the calculation.
The resulting indicator must be compared with data from Appendix 3 of the same order, where the Federal Tax Service annually publishes average data by industry.
Tax burden by type of economic activity at the end of 2018 ( )
The table also shows the fiscal burden on insurance premiums for reference.
Example
According to tax returns, the construction organization paid 950 thousand rubles for 2020. taxes, including personal income tax. Insurance premiums – 430 thousand rubles. The organization’s revenue for 2020 excluding VAT amounted to 10.5 million rubles.
Total tax burden: 950,000 / 10,500,000 * 100 = 9.05 Tax burden on insurance premiums: 430,000 / 10,500,000 = 4.1
Let's compare the obtained coefficients with the average load by industry for 2020. For construction, the average value of the total load is 10.4, for insurance premiums - 4.4.
The company in our example has indicators below the industry average, which means it falls into the risk zone and will most likely be included in the inspection plan.
Grounds for an on-site tax audit: how to find out whether there will be an audit
It happens that when calculating the tax burden, incompetent inspectors do not take all indicators, for example, only income tax, but compare them with the industry average burden from the specified letter. So they get an incorrect picture with an underestimated tax burden and ask the organization for an explanation. In such a situation, send your calculation to the tax office, taking into account all taxes, and an explanation of the calculation.
You can check a company’s tax burden and compare it with industry averages using a special service on the Federal Tax Service website. It is suitable for those who pay taxes according to the general taxation system. The service allows you to compare your tax burden, including individual taxes, with industry averages by region. The service also contains information on the average salary level, calculated on the basis of 2-NDFL certificates.
Any organization wants to pay less taxes. This is normal and not prohibited, as long as you do not use illegal optimization methods. On the other hand, if a company reduces payments and deviates from industry averages, they come to check it. 1C-WiseAdvice carefully ensures that the load always remains in the safe zone and does not deviate from the reference values by more than 10%. This allows you not to attract the attention of the Federal Tax Service and reduce the risk of an on-site tax audit to almost zero.
The tax optimization options that we offer are developed individually, taking into account the business structure and characteristics of your company’s activities. They are absolutely legal and safe.
More details
Calculation of tax burden in 2019
All individual entrepreneurs face the obligation to pay taxes. The size of the tax base is provided for by law, but it can be reduced in certain ways.
The value is calculated independently or using a calculator - this is necessary by order of the Federal Tax Service during their unscheduled inspections. If the income tax burden is too low, then in most cases there may be an error in the calculations. To avoid this, a calculator was created.
When is it necessary to calculate the tax burden?
The total amount includes all types of payments, including VAT, personal income tax, insurance premiums, which are expressed as a certain percentage of all income or in established amounts expressed in rubles. The assessment of the total tax burden occurs according to the requirements of specialized inspections or according to the needs of the taxpayer in the following situations:
- When the load indicator is less than the average payments for a long time. They depend on the type of activity, but if the fiscal service suspects that payments are not being transferred in full, an unexpected check will be sent.
- If the amount significantly exceeds the level of tax burden, then the development of the organization is at risk. If deductions show obligatory payments that are beyond the company’s capacity, then it would be correct to switch to other taxation systems - the simplified tax system or the unified income tax.
In order to calculate the workload, the accounting department must estimate the amount of mandatory payments to the state and compare the obtained figures with the total profit. The result is expressed as a percentage. It is compared with the average indicators of the Federal Tax Service.
Normal load indicator
These values are relevant in 2020. They depend on the type of activity of the organization or individual entrepreneur. Thus, the load for trading companies is less than 1%, and for manufacturing companies no more than 3%. It happens that over the past few years there has been a violation in the dynamics of changes in interest rates, then it is necessary to calculate the tax burden using a calculator.
Deviations from the norm are always disadvantageous for taxpayers, because when an error is discovered, penalties are issued from the state. If a deficiency is detected, the company must identify the reasons for the low load. Among them may be:
- incorrect activity type code;
- making the necessary investments;
- temporarily problematic implementation;
- increased equipment or supplier costs;
- making an export.
These arguments are provided to the Federal Service. This way the company is protected from penalties. For the fiscal authorities, the legal entity prepares documents explaining the reasons, which are reviewed within three days.
If an organization evades warnings and instructions from the fiscal service, it has the right to take more severe punitive measures.
During an on-site inspection, she freezes the production account or opens a criminal case on the fact of non-payment of obligatory funds to the state.
The principle of calculating the tax burden
Tax burden is the ratio of all payments withdrawn from organizations to the amount of income received for the reporting period.
Tax burden calculation formula
Calculations occur according to the following formula:
- Tax burden = Amount of taxes accrued for the calendar year / Amount of annual revenue * 100%.
The amount of all taxes can be found in the relevant declarations. There are some recommendations for getting an error-free result.
- Import value added tax (VAT) is excluded from the total calculation.
- Customs duties are also not taken into account.
- The calculation includes all fiscal payments made during the billing period.
- Insurance premiums transferred to the state from the company.
Legislation has issued documents regulating the relationship between taxpayers and state regulatory authorities. The regulations can be found in the order of the Federal Tax Service “On the approval of planning systems for on-site tax audits”, as well as in the letter “On the work of tax authorities’ commissions on the legalization of the tax base.” All data can be found on the official website of the Federal Service.
https://youtu.be/KTjLgeBmtRo
It is better to calculate the load using an online calculator. It uses a generally accepted formula, but differs from manual counting in speed and detailed display of the sequence of actions. It is enough to enter the taxpayer’s information in the appropriate fields. To do this, you only need to know the tax amounts and the amount of annual revenues.
The service is free, so anyone can calculate their tax burden. The calculator can be used by both taxpayers themselves and the federal tax service.
Users receive correct calculations in a short time. There is no need to worry about the possibility of errors or omissions.
The algorithm of actions is clearly established for everyone; you just need to correctly indicate the initial information.
Source: https://AktBuh.ru/raschet-nalogovoy-nagruzki.html
Calculation formulas for individual taxes and types of taxation
In the letter dated July 25, 2017 No. ED-4-15/ [email protected] “On the work of the commission on the legalization of the tax base and the base for insurance premiums” (Appendix 7, table 1), the Federal Tax Service of Russia provides a methodology for calculating the tax burden by type of taxation.
For LLC on OSNO
For individual entrepreneurs on OSNO
For individual entrepreneurs and LLCs on the simplified tax system
For individual entrepreneurs and LLCs on the Unified Agricultural Tax
If a company reports on mineral extraction tax, excise taxes, water tax, payments for the use of natural resources, property tax, transport and land taxes, then payments for these taxes must be included in the calculation.
In Table 2 of the same Appendix 7, tax officials analyze the obtained indicators, compare the level of burden with the indicators of similar taxpayers, the average indicators for the type of economic activity and decide whether to call the head of the company for a commission to the Federal Tax Service.
From 1.3 to 45.4% - the spread of the tax burden by industry
How can you find out what the industry average pays? To do this, you need to focus on the indicators of the tax burden by type of activity for the previous year, which the Federal Tax Service makes publicly available. The difference in industry indicators is impressive: the spread is 44.1%. The tax burden is low for agriculture, energy workers, low for transport workers, average for construction workers and public catering, above average for manufacturers of computers, drinks, tobacco, communications specialists, IT specialists, the highest in the field of mining.
But what about narrow niche areas that do not fall into the general industry list, and for which the average figure has not been determined? That’s when you need to focus on the Russian average tax burden for the previous year. In 2018, when calculating, you need to be equal to the 2020 figure, which was 10.8%. It was this that was indicated by the Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation in letter dated August 22, 2020 No. GD-3-1/5806.
In the summer of 2020, the Federal Tax Service received a written request on how to calculate the tax burden for an enterprise engaged in sanatorium and resort activities. The question arose due to the fact that the federal list of average industry indicators does not include the tax burden of this industry. The response letter from the Federal Tax Service states that the tax burden of sanatorium and resort organizations should be compared with the average level of tax burden in the Russian Federation - due to the lack of values for the industry, that is, with an indicator of 10.8%.
Tax burden by industry. Data for 2017.
Personal income tax burden
Letter of the Federal Tax Service dated July 25, 2017 No. ED-4-15/ [email protected] defines the tax burden of individual entrepreneurs for personal income tax as the ratio of the calculated personal income tax from business activities to the total amount of income from this activity.
If the personal income tax burden is low, the entrepreneur will be called to a commission at the tax office. But the letter does not say what is considered a low tax burden.
But in the same letter there is another criterion - the share of professional deductions for calculating personal income tax. If this share exceeds 95%, the individual entrepreneur becomes a candidate for a commission.
As for organizations, tax specialists analyze not the relative burden of personal income tax, but the dynamics of the amounts paid. Inspectors analyze the indicators of 6-NDFL reports and call for a commission if:
- personal income tax receipts decreased by more than 10 percent compared to the previous quarter or year;
- Based on personal income tax amounts, they concluded that the organization pays wages below the average level in the region for this type of activity.
In the same way, they analyze calculations for insurance premiums and see whether the amount of contributions has decreased with the same number of employees.
How to calculate the burden of insurance premiums
To compare a company’s workload with the average for a specific type of activity, it must be calculated. Calculate the company's contribution burden using the formula.
Load of contributions = Amount of contributions : Revenue x 100%
Federal Tax Service specialists recommended that when calculating, take the amount of contributions that the company accrued in 2020 and paid in the same year. And contributions that the company accrued in 2020, but transferred in 2020, should not be taken into account, since the company calculated them under Law No. 212-FZ, and the Federal Tax Service in its data only takes into account contributions under Chapter 34 of the Tax Code. Take the revenue from line 2110 of the income statement.
Income tax burden
The current documents do not contain a methodology for calculating the burden separately for income tax. It was stated in the letter of the Federal Tax Service dated July 17, 2013 No. AS-4-2/12722, which has now been cancelled. But it is possible that tax authorities can still use the same methodology when analyzing the burden of taxpayers.
The calculation formula looks like this:
In the mentioned letter, low is understood as the tax burden:
- less than 3% – for manufacturing enterprises;
- less than 1% – for trade enterprises.
If the tax burden is low
As we see, it is in the interests of the taxpayer to know how to calculate the tax burden. Having discovered deviations from generally accepted load indicators in the direction of underestimation during independent calculations, it is better to prepare in advance for explanations with the tax office.
A low level of tax burden does not always indicate a company’s “avoidance” of taxes and the presence of violations of tax legislation. If the formula is used correctly when calculating the tax burden and there are no other errors, then the reasons may be quite objective, for example, an increase in costs due to rising prices of suppliers.
How to calculate correctly using the formula
It is necessary to pay attention to the fact that the established formula for calculating the tax burden in a company that conducts official business activities in Russia is quite simple.
However, it is inaccurate. Representatives of the tax authority, who generate static data, calculate the indicator under consideration on a fairly average basis.
In this case, the possibility of several options for calculating the tax burden is allowed. In 2020, tax officials use the following formula:
Bn = (Cn x 100%)/Bv
| Vn | The required tax burden indicator |
| Sn | The total number of all taxes, without exception, that were subject to transfer to the state during the tax reporting period in question |
| Bv | Established amount of accounting revenue |
The Ministry of Finance uses a similar formula during calculations, which ultimately produces similar values.
At the same time, you need to pay attention to the fact that the format of this option is slightly different from that used by the structural divisions of the tax authority.
In addition, the possibility of other calculation options is provided, which are indicated in economics textbooks.
At the same time, it is worth remembering that there are difficulties in applying them in practice, which is why representatives of the tax authority and the Ministry of Finance use the most simplified calculation methods in their work. Only through this can the likelihood of making mistakes be significantly reduced.
How to derive a relative indicator of the tax burden?
But when analyzing different projects that require different amounts of investment and have different implementation deadlines, it is incorrect to compare the tax burden by total indicators. It is unreasonable to compare, for example, 220 thousand rubles. taxes for the conditional period of a small retail store and 3 million rubles. large manufacturing enterprise. Such heterogeneous basic factors can only be compared in terms of relative values.
This indicator is often called the tax burden coefficient, an indicator of the effectiveness of tax planning, since its value is often influenced by methods of legal optimization of the tax burden.
But regardless of the name used, the relative value of the tax burden as an economic category reflects the ratio of the total amount of taxes and fees paid by an enterprise to the fiscal authorities with the indicators of its activities.
The tax burden coefficient (Knn) can be calculated using the formula:
Knn = ∑N / B,
where B is the comparison base selected at the enterprise.
For your information
There have been heated debates regarding the basis of comparison for many years. Each of the experts defends their proposed indicators. And each of the proposals has its own advantages and disadvantages.
Various authors suggest using: gross profit, net profit, market value of the business, revenue.
In search of a methodology, the main idea is to make the tax burden coefficient a universal indicator that allows one to compare the level of taxation in different sectors of the national economy.
We emphasize that no indicator will be universal for all taxes and fees: for property tax, the basis for calculation is the value of the taxable property, insurance premiums are calculated according to the general condition from the wage fund, and transport tax depends on engine power.
In our opinion, taking into account the diversity of practice and everyday situations, the creation of one universal indicator is a utopian task.
Why should there be just one indicator? We believe that we are talking about choosing not a single, universal indicator, but about choosing the most information-rich base on the basis of which it will be possible to draw correct analytical conclusions.
For example, business value is an interesting, but more theoretical than a practical tool for this calculation. The value of such an indicator as the tax burden coefficient lies in the comparative simplicity and efficiency of obtaining data. And with such a basic indicator as the cost of a business, there can be no talk of any simplicity and speed of calculation. Business value is a complex, subjective and controversial indicator that in no way simplifies or makes calculations more accurate.
Perhaps it was previously interesting as a type of accurate management information that eliminated shortcomings and inaccuracies in accounting, but now, in our opinion, this basis is irrelevant for such calculations.
It seems more realistic and information-intensive to use gross profit, net profit and revenue as a basis for calculating indicators. Although, again, there are differences of opinion regarding some approaches.
For example, when comparing the tax burden with the revenue indicator, should other income be included in the revenue volume? In our opinion, other income should also be included in the assessment of the tax burden.
Comparing the tax burden indicator with a certain base will allow you to get an answer to the question of how many kopecks go to the budget from each ruble of revenue, gross profit (added value), net profit, which, in turn, will answer the question about the efficiency of the generation enterprise through indicator of revenue, gross and net profit.
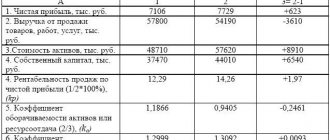
Example 2
Completing the analysis of taxation systems for Elba LLC, we will calculate the tax burden coefficients when applying different taxation systems, using the gross profit indicator (calculation results are in Table 4).
The indicator of the tax burden at an enterprise can be taken not as a general indicator, but to assess the impact of individual taxes for each type of tax:
Kn1 = N1 (N2, N3, …, Nn) / V,
where Kn1 is the tax burden coefficient for each tax;
N1, N2, N3, …, Nn - taxes and fees paid by the taxpayer.
Some authors offer a comparison with the source of funds for paying taxes. It is difficult to agree with the validity of this approach, because in this case, in fact, we will only receive a tax rate expressed as a coefficient.
Back in 1996, the Department of Tax Policy of the Ministry of Finance of Russia tried to introduce a unified methodology for determining the tax burden on an enterprise - by letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated August 13, 1996 No. 04-01-15, a program was proposed for studying the tax burden at individual enterprises in organizations of various forms of ownership, size and types of activities.
This baton was later picked up by the tax authorities. Acting in fiscal interests, they continued the initiatives of the Ministry of Finance and combined the calculation of the relative tax burden with the company’s revenue.
Tax officials, based on statistical data, have calculated and summarized the tax burden by industry, inviting taxpayers to compare them with the data they provide.
For example, at the end of 2020, for wholesale trade, except for wholesale trade of motor vehicles and motorcycles, the tax burden is 3.1%, and the burden on insurance premiums is 0.9%. For retail trade, excluding trade in motor vehicles and motorcycles, these figures are respectively 3.6 and 2.2%.
Moreover, in order to more quickly check these values, tax authorities have launched the online service “Transparent Business” (https://pb.nalog.ru/calculator.html) for organizations under the general taxation regime, using which you can compare the tax burden of an organization with the average industry indicator.
The indicator of the tax burden at an enterprise is one of the criteria for assessing a taxpayer for the purpose of conducting an on-site tax audit.
So, for fiscal purposes, regulatory organizations propose using revenue as a base indicator. But we emphasize once again that this methodology cannot be considered universal and for its analytical purposes the company can make calculations in relation to other information indicators.