Who is called to the commission
Features of the selection of subjects are set out in the letter of the Federal Tax Service dated July 17, 2013 N AS-4-2/12722. It states that the choice is made on the basis of the economic activity of the organization, the specifics of taxation during reorganization, liquidation, and bankruptcy. A company is selected for a commission call based on the following criteria:
- Information set forth by the taxpayer in a statement of loss. Suspicion may be raised by the indication of a negative loss for the last 3 years or the lack of information about losses.
- Reduced taxation for individual entrepreneurs for excise taxes, simplified taxation system, personal income tax. You need to divide the tax amount by the amount of all income of the enterprise. If the result is a number less than 3, the load is considered light. For trade entities this number will be less than 1.
- Reduced tax burden for VAT. To determine the low load, you need to divide the VAT to be reimbursed by a similar indicator to be paid. If the calculation result is more than 89%, this indicates a reduced indicator.
- Arrears on personal income tax. To detect arrears, information from 2-NDFL certificates is compared with actual payments. RSV-1 PFR can also be used to obtain information.
- Companies that paid personal income tax less by 10% compared to the previous tax period. This item is identified on the basis of payment cards, the dynamics of received payments, the number of company employees (according to data submitted to the Pension Fund), and the amount of payments by branches.
- Low salaries for employees relative to sector salaries. The information is analyzed based on the 2-NDFL certificate, all company payments to its employees, the average number of employees. A candidate for consideration by the commission is an organization that pays wages less than the minimum wage.
- Application for a professional deduction equal to more than 95% of the enterprise's income. This paragraph applies to individual entrepreneurs. 3-NDFL declarations are checked. In the process, line 120 indicators are divided by 110 indicators.
- Individual entrepreneurs who recorded a certain amount of revenue in the VAT return, but entered 0 in the 3-NDFL declaration or did not fill out the form in question at all. Inconsistency between information from two documents may raise suspicions.
Let's consider additional criteria:
- Receipt of data on the income of residents of the Russian Federation from foreign countries.
- Receipt of data on concealment of income from the Department of Internal Affairs, the prosecutor's office, individuals and legal entities.
- Application of tax breaks and reduced rates without proper justification.
- Providing VAT refund.
- Various violations of the law in the field of tax law.
After compiling a list of companies subject to control, the order of invitation to the commission is determined. First in line are companies with a larger amount of taxes to potentially be refunded. Once the priority is determined, notifications are sent to companies. They contain recommendations for eliminating the offense. If a legal entity or individual entrepreneur has not followed the recommendations, a letter is sent calling the commission.
Object of taxation of insurance premiums
^Back to top of page
In accordance with Article 420 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, for payers - organizations and individual entrepreneurs making payments and rewards in favor of individuals, payments and other rewards in favor of individuals who are subject to compulsory social insurance in accordance with federal laws on specific types of compulsory social insurance (except for remunerations paid to individual entrepreneurs, lawyers, notaries, etc.):
- within the framework of labor relations and under civil law contracts, the subject of which is the performance of work and the provision of services;
- under copyright contracts in favor of the authors of works;
- under agreements on the alienation of the exclusive right to works of science, literature, art, publishing license agreements, license agreements on granting the right to use works of science, literature, art, including remunerations accrued by organizations for managing rights on a collective basis in favor of the authors of works under agreements , concluded with users.
For payers of individuals who make payments and remunerations in favor of individuals, the object of taxation with insurance premiums is payments and other remuneration under employment agreements (contracts) and under civil law contracts, the subject of which is the performance of work, the provision of services in favor of individuals (for excluding remunerations paid to individual entrepreneurs, lawyers, notaries, etc.).
The object of taxation with insurance contributions for payers who do not make payments and other remuneration to individuals is the minimum wage established at the beginning of the corresponding billing period, and if the amount of income of such a payer for the billing period exceeds 300,000 rubles, the object of taxation with insurance contributions its income is also recognized.
Main features of commissions
Control of a company by a commission is a pre-trial method of resolving tax disputes. The event can also be called a pre-verification action. Let's consider the goals of the commission:
- Improved tax revenues.
- Increase in the collection of income tax, as well as insurance premiums.
- Identification of incorrect data in accounting and tax reporting.
- Detecting the issuance of unofficial salaries to employees.
- Prevention of late transfer of income tax and insurance contributions.
- Identification of companies paying wages below the minimum wage.
- Identification of organizations that do not officially employ employees in order to reduce the tax base.
FOR YOUR INFORMATION! It is assumed that the work of the commission encourages companies to independently clarify the exact amount of taxes and contributions due for payment and to avoid violations of tax law.
Federal Tax Service as an administrator of insurance payments: main tasks
If the organization does not have the right to apply reduced tariffs, then in relation to payments it must charge insurance premiums at general rates. This is provided for in Article Art. 426 Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
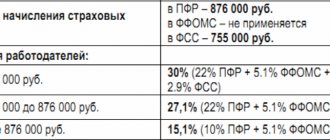
The total amount of insurance premiums in 2020 is 30 percent:
Such tariffs must be applied to payments and rewards in favor of:
- Russian citizens;
- foreigners permanently or temporarily residing in Russia who are not highly qualified specialists (HQS);
- permanently or temporarily residing citizens of the EAEU.
Author of the article: Philip Soloviev
Hello! I'm Philip, I've been practicing law for over 12 years. I believe that I am a professional in my field and I want to tell all site visitors how to solve various problems. All materials for the site have been collected and carefully processed in order to convey all the necessary information as accessible as possible. However, in order to apply everything described on the site, consultation with specialists is always necessary.
✔
About me
✉
Feedback
Since July 25, 2020, monitoring of taxes, the base for them, as well as insurance premiums of the legalization commission is carried out on the basis of a new procedure. It is confirmed by letter of the Federal Tax Service of Russia No. ED-4-15/14490. At the same time, the previous regulations ceased to apply (approved by letter of the Federal Tax Service dated July 17, 2013 No. AS-4-2/12722).
For more information about this, see “New regulations for the work of commissions on the legalization of the tax base from 2020.”
Note that the Federal Tax Service already has experience in collecting such payments. From 2001 to 2009, the department administered the Unified Social Tax (UST), which was later replaced by contributions to the Pension Fund, Social Insurance Fund and Federal Compulsory Medical Insurance Fund. It is noteworthy that until 2001, extra-budgetary funds were also responsible for collecting contributions.
The procedure for interaction of the new administrator of the corresponding contributions with taxpayers has not fundamentally changed in comparison with the work of the Pension Fund and the Social Insurance Fund. The names of contributions, the principles of their calculation, the use of benefits, and the terms of payment remain the same.
However, the main regulatory normative act within the framework of these legal relations has become the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. It introduced a new Chapter 34, which replaced the previously existing federal laws under which the administration of insurance premiums by state funds was carried out.
In turn, the legislator made a noticeable adjustment to the KBK in terms of contributions that it collects in accordance with the received powers of the Federal Tax Service.
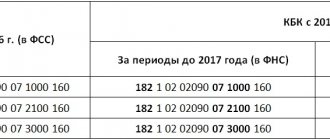
If the employer has not transferred insurance payments to state funds on time for periods before 2020, then the Federal Tax Service will expect their transfer using the BCC:
- for contributions to the Pension Fund - 182 (Federal Tax Code) 10202010061000160;
- for contributions to the FFOMS - (Federal Tax Code) 10202101081011160;
- for contributions to the Social Insurance Fund - (Federal Tax Code) 10202090071000160.
In turn, when paying insurance premiums to the Federal Tax Service from 2020, the employer will accordingly apply the following codes:
- for pension contributions - (Federal Tax Code) 10202010061010160;
- for medical contributions - (Federal Tax Code) 10202101081013160;
- for contributions for sick leave and maternity leave - (Federal Tax Code) 10202090071010160.
Individual entrepreneurs with debts for periods before 2020 must apply the KBK:
- for contributions to the Pension Fund - (Federal Tax Code) 10202140061100160;
- for contributions to the Pension Fund from incomes of more than 300,000 rubles. — (Federal Tax Code) 10202140061200160;
- for contributions to the FFOMS - (Federal Tax Code) 10202103081011160.
When filling out payments for periods starting from 2020, the individual entrepreneur will use the KBC:
- for contributions to the Pension Fund - (Federal Tax Code) 10202140061110160;
- for contributions to the FFOMS - (Federal Tax Code) 10202103081013160.
BCC for individual entrepreneur contributions for income over 300,000 rubles. for 2020: 18210202140061200160. For payments in 2020, there is no separate BCC for 1% in the Pension Fund - see “Which BCC should an entrepreneur pay contributions on income over 300,000 rubles?”
Individual entrepreneurs pay a fixed fee for themselves according to the formula
VZS = VZS (PFR) VZS (FFOMS),
VZS (PFR) - individual entrepreneur’s contribution for himself to the Pension Fund;
VZS (FFOMS) - individual entrepreneur’s contribution for himself to the FFOMS;
VZS (PFR) = minimum wage × 12 × 0.26 D300 × 0.01,
D300 - income exceeding 300,000 rubles;
VZS (FFOMS) = minimum wage × 12 × 0.051.
In this case, the maximum value of the indicator VZS (PFR) is determined by the formula
VZS-GEN (PFR) = 8 × minimum wage × 12 × 0.26,
VZS-OBSHCH (PFR) - the maximum possible contribution of an individual entrepreneur for himself to the Pension Fund.
Employers can transfer insurance payments to the Federal Tax Service (depending on their status, organizational and legal form and other grounds):
- using reduced rates for contributions to the Pension Fund, Social Insurance Fund and Federal Compulsory Medical Insurance Fund in 2017–2019 and other periods;
- in the Pension Fund of the Russian Federation - at a reduced rate, and in the Social Insurance Fund and the Federal Compulsory Medical Insurance Fund - at a zero rate;
- don't pay any fees at all.
Let's consider what criteria determine the possibility of using these benefits by employer firms.
1. Rates established from 2020 to 2020:
- for contributions to the Pension Fund - 8% in 2020, 13% in 2018 and 20% in 2019;
- for contributions to the Social Insurance Fund - 2%, 2.9% and 2.9%, respectively;
- for contributions to the FFOMS - 4%, 5.1% and 5.1%.
The following have the right to pay contributions at the given rates (subject to compliance with other criteria established by Article 427 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation):
- enterprises on the simplified tax system that are engaged in intellectual development;
- enterprises operating in special economic zones.
2. Rates established for IT enterprises operating outside special economic zones, from 2020 to 2023:
- for contributions to the Pension Fund - 8%;
- for contributions to the Social Insurance Fund - 2%, for foreigners and stateless persons with the status of temporarily staying in the Russian Federation - 1.8%;
- for contributions to the FFOMS - 4%.
At the same time, the tariffs for temporarily staying citizens of the EAEU countries are the same as for Russians, and for temporarily staying highly qualified specialists (who are not citizens of the EAEU countries) who receive their status according to the law “On the Legal Status of Foreign Citizens” dated July 25, 2002 No. 115- Federal Law, you do not need to pay contributions to the Social Insurance Fund.
3. Rates established for companies in Sevastopol, Crimea, residents of the free port in Vladivostok:
- for contributions to the Pension Fund - 6%;
- for contributions to the Social Insurance Fund - 1.5%;
- for contributions to the FFOMS - 0.1%.
Entrepreneurs in Crimea and Vladivostok can use these rates for 10 years after acquiring their preferential status.
- enterprises on the simplified tax system that carry out the types of activities specified in subparagraph. 5 p. 1 art. 427 Tax Code of the Russian Federation;
- pharmaceutical organizations and individual entrepreneurs (with a license) for UTII;
- charitable organizations, NPOs;
- Individual entrepreneur on PSN (with some restrictions on types of activities).
These business entities have the right to use the corresponding benefits in 2020 and 2020.
^Back to top of page
The base for calculating insurance premiums is defined as the amount of payments and other remunerations that are subject to taxation, accrued by payers of insurance premiums for the billing period in favor of individuals, with the exception of amounts not subject to insurance premiums (for example, benefits, compensation, financial assistance, etc. ).
In this case, the base for calculating insurance premiums is determined separately for each individual at the end of each calendar month from the beginning of the billing period on an accrual basis.
The base for calculating insurance contributions for compulsory pension insurance and the base for calculating insurance contributions for compulsory social insurance in case of temporary disability and in connection with maternity have a limit value, after which insurance contributions are not charged. The exception is insurance premiums paid by the main category of payers when applying the tariff of insurance premiums for compulsory pension insurance in the amount of 22%, in this case, insurance premiums are also levied on payments in excess of the established maximum value of the base of insurance contributions for compulsory pension insurance in the amount of 10% in excess of the specified amount.
The maximum value of the base for calculating insurance premiums is subject to annual indexation from January 1 of the corresponding year based on the growth of average wages in the Russian Federation.
in 2020 - 1.9;
in 2020 - 2.0;
in 2020 - 2.1;
in 2020 - 2.2;
in 2021 - 2.3.
^Back to top of page
Payers-employers calculate and pay insurance premiums on a monthly basis. The deadline for payment of insurance premiums is no later than the 15th following calendar month in which payments were made in favor of individuals.
The amount of insurance premiums is determined in rubles and kopecks and is calculated separately in relation to insurance premiums for compulsory pension insurance, insurance premiums for compulsory social insurance in case of temporary disability and in connection with maternity, and insurance premiums for compulsory medical insurance.
The billing period is the calendar year, the reporting periods are the first quarter, six months, and nine months of the calendar year.
In addition, from January 1, 2020, the offset principle of spending compulsory social insurance funds in the event of temporary disability and in connection with maternity is preserved. In this regard, after January 1, 2020, the payer can reduce the amount of insurance contributions for compulsory social insurance in case of temporary disability and in connection with maternity by the amount of expenses incurred by him for the payment of compulsory insurance coverage for the specified type of compulsory social insurance.
Moreover, if, at the end of the settlement (reporting) period, the amount of expenses incurred by the payer for the payment of insurance coverage for compulsory social insurance in case of temporary disability and in connection with maternity (minus the funds allocated to the FSS policyholder in this period) exceeds the total amount of calculated insurance contributions for this type of insurance, then from January 1, 2020, the difference received is subject to offset by the tax authority against upcoming payments for compulsory social insurance in case of temporary disability and in connection with maternity on the basis of confirmation received from the Social Insurance Fund of the expenses declared by the payer for the payment of insurance coverage for the corresponding settlement ( reporting) period or compensation to the Social Insurance Fund in the prescribed manner.
Features of the conduct and organization of the commission
Each company is considered by the commission individually. After the control event, the following documents are drawn up:
- The minutes of the meeting, which must be signed by the secretary, as well as the chairman of the commission. The taxpayer's representative gets acquainted with the protocol against signature. A person may request a copy of the protocol.
- Recommendations that reflect the actual amount of taxes, the amount of additional payment, etc. The period for eliminating violations is 10 days.
The company is obliged to comply with all instructions of the commission. The fact that violations have been eliminated is verified by the Federal Tax Service inspectorate. If the company has not taken any action, a decision is made to conduct an on-site inspection.
How to behave at the legalization commission
The peculiarities of behavior at the commission are determined by what questions the representatives of the regulatory body will ask. Let's take a closer look at these questions:
- What activities does the company specialize in?
- What suppliers, contractors and customers does the company cooperate with?
- Does the company have a security service that checks counterparties for reliability?
- Compliance of the company with the legal address, existence of a lease agreement, amount of lease payments.
- The number of employees in the company and their specialization.
- Cooperation with shell companies to create fictitious document flow.
If a company representative cannot answer these questions, the company's activities are called into question.
What to say at the commission
Before the commission, you need to build a certain line of defense. It will depend on what exactly the taxpayer is accused of. It is very important to prepare arguments to justify yourself. Explanations may be provided in writing. It is advisable to support each argument with documents. Let's look at an example of a line of defense. The company is charged with large amounts of damage. In this case, the suspicious phenomenon can be explained by the following facts:
- The sector in which the company operates involves large losses for all firms.
- The cost of raw materials has increased.
- Fluctuations in currency rates.
- Demand for the company's products fell sharply.
- Financial crisis.
- The company operates in a new sector.
If the commission considers the low salaries of employees, you can present these arguments:
- Some employees work in other regions where salaries are relatively low.
- The company introduced a floating schedule and part-time employment.
All arguments must be logical and justified. They can be strengthened by providing supporting documents (for example, statistics).
Arguments for a small salary
What will be a convincing argument in favor of a small salary depends on the characteristics of the company. You know them, but you are used to them, so you may not immediately remember them. To avoid missing anything, ask yourself questions and think through your answers. We've written a list for tips.
What do employees get in exchange for a small salary? For example, flexible hours, early career and experience, the only opportunity to get a job.
The company has a call center, the salary of specialists is twenty thousand rubles. The salary is small, but you can work from home and have a flexible schedule. Students and mothers on maternity leave work in the call center; they need part-time work, and the work schedule suits them.
“Look at the year of birth of employees. They are all from the first or second year. I give them experience that helps them get decent positions in large companies.
This type of work is not often offered to students, so I always have employees who are willing to work for a small salary. True, because of students there is a high turnover: they work for a year, gain experience and go where they pay more.”
It would be great to explain about students who started with a small salary, they liked working in the company, so they stayed and are now working in a higher position with a good salary. The turnover and career growth of students must be supported by personnel documents.
There are companies that explain low salaries by friendship in the team and a good atmosphere. Like, the company is so good that employees are willing to earn less than they could. We believe that this can happen, but it is not a fact that the tax office will believe it.