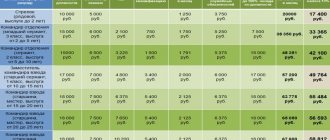
What travel expenses are reimbursed to employees?
In Russia, according to the law, there are several types of compensation to employees for expenses incurred in the performance of their official duties. Article 165 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation explains in what cases the expenses for travel of employees to and from work are compensated, and contains an exhaustive list of compensation payments, among which transportation costs are separately highlighted.
What compensation is provided for transportation costs:
- reimbursement of expenses for operating an employee’s personal car;
- compensation for travel to and from work, including by public transport and taxi;
- payment of travel expenses in terms of purchasing tickets (air, railway, land, water and other types of transport);
- payment for tickets to and from the employee’s place of rest;
- reimbursement of travel expenses to the place of work when moving to another area.
There are no restrictions on amounts for each type of compensatory additional payments, and employers independently set standards for employees. These norms should not contradict the current provisions of labor legislation and are fixed by local orders for the organization.
We will analyze the features of providing each type of compensation payments and the procedure for how to apply for compensation for travel to and from work correctly.
Reimbursement of travel expenses by force of law
All company expenses, including transportation, subject to reimbursement to the employee, must satisfy the conditions of Art. 252 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation: to be economically justified and supported by correctly executed documents. Moreover, the employer can compensate them only on the condition that they were carried out with his knowledge and permission (letter of the Ministry of Finance dated September 10, 2015 No. 03-03-07/52139). Let's consider what documents need to be prepared in each specific case.
- Local acts of the company
The amount and algorithm for reimbursement of expenses for traveling employees must be specified in the collective agreement and the corresponding additional agreements with them (Article 168.1 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). The condition regarding the traveling nature of the work must also be fixed in the employment contract (Article 57 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
To justify business trips for both office and traveling workers, you can draw up a single regulatory act of the company, for example, a provision on compensation for travel costs for employees, which specifies all positions and the procedure for paying compensation. Such a document will justify the travel of both the cashier and the sales agent, etc.
- Documents for registration and payment of compensation for the use of a personal car for business purposes
Expenses for the use of a car by an employee for work purposes are also subject to reimbursement (Article 188 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). To justify payment of compensation, the employee must provide the employer with a copy of the title, a statement listing the job functions for which the car is required, and an indication of how often it is used.
The amount of this payment is specified in the additional agreement with the employee. And the basis for including these costs when calculating income tax is the order of the head (letter of the Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation for Moscow dated January 13, 2012 No. 20-15 / [email protected] ). In this case, the profit expenses can include the amount of compensation within the limits provided for by Government Decree No. 92 dated 02/08/2002: no more than 1,200 rubles. per month for a car with an engine capacity of up to 2,000 m3 and 1,500 rubles. – over 2,000 m3.
If the amount of compensation is more than the norm, then the difference is not included in the expenses that reduce the profit base (subclause 11, clause 1, article 264 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation), and a discrepancy arises between accounting and tax accounting.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ytaboutru
IMPORTANT! If the employee does not own the vehicle, then the tax authorities may require personal income tax and insurance premiums to be calculated from the compensation amounts (letter of the Ministry of Finance dated February 21, 2012 No. 03-04-06/3-42).
If an employee uses his own car for work purposes, then to justify the cost of fuel and lubricants, tax authorities require a waybill (letter of the Federal Tax Service dated June 2, 2004 No. 04-2-06 / [email protected] ).
For the algorithm for preparing a waybill, see the material “What is the procedure for filling out waybills (sample, form)?”
However, the Ministry of Finance believes that tax authorities do not have the right to oblige taxpayers to use any forms for tax accounting (letter of the Ministry of Finance dated November 1, 2013 No. 03-03-06/1/46664).
- Documents when renting a car from an employee
The employing company can also enter into a car rental agreement with an employee and set a certain amount of its cost. Such costs are included in other costs on the basis of clause. 10 p. 1 art. 264 Tax Code of the Russian Federation. Car maintenance costs, such as fuel, insurance, repairs, maintenance, etc.
Read about the nuances of accounting when renting a car from an employee in the article “Do I need to withhold insurance premiums from renting a car?”
- Reimbursement of transport costs for taxi
Such compensation can only be taken into account if its possibility is stipulated in the collective agreement or regulation on compensation of transport costs. In addition, it is necessary to have supporting primary documents, and for substantiation, an employee’s application for compensation with a detailed explanation of the reasons for using a taxi (for example, an early flight, etc.).
Dt 20 (23, 25, 26, 44) Kt 73 – compensation reflected;
Dt 73 Kt 50 (51) – compensation paid.
All compensation payments are accepted for tax accounting when calculating profits, with the exception of amounts exceeding the norms of subclause. 11 clause 1 art. 264 Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Example
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ytdevru
Dt 26 Kt 73 – 1,500 rub. – compensation is accrued within the norms;
Dt 91.2 Kt 73 – 5,400 rub. (6,900 – 1,500) – compensation not accepted in tax accounting.
Thus, the amount of expenses in accounting exceeds the expenses in tax accounting, and a permanent tax liability is formed, regulated by the norms of PBU 18/02.
Dt 99 Kt 68 – 1,080 rub. (5,400 × 20%) – conditional expense accrued.
We invite you to read: Appealing an arbitration court decision: instances and deadlines
There is no need to withhold personal income tax from compensation payments to the employee (letter of the Ministry of Finance dated April 11, 2013 No. 04-03-06/11996).
The taxation procedure directly depends on what type of transport you choose to transport your subordinates.
| Item no. | Kind of transport | Characteristic |
| 1 | Public | If a subordinate is compensated for travel by public transport to and from the workplace, then insurance premiums will be deducted from this compensation. |
| 2 | Official | Such an additional privilege for subordinates, such as transportation to and from work by official transport, is not subject to income tax. The main thing is to write this point in the collective agreement |
| ★ Best-selling book “Accounting from Scratch” for dummies (understand how to do accounting in 72 hours) purchased by {amp}gt; 8000 books |
Cases when the employer is obliged to pay for the travel of employees are established by the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. In accordance with Art. 168 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the employer reimburses employees for travel expenses when sent on a business trip. And in accordance with Art. 168.1 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, transportation costs associated with business trips are reimbursed to employees whose permanent work is carried out on the road or is traveling in nature.
You need to be especially careful when traveling by taxi. Such travel expenses on a business trip are subject to compensation only if their need can be justified. For example, an employee had to get from the airport to the hotel at a late time. Or it was impossible to get to the destination by other public transport.
When an employee moves, by prior agreement with the employer, to work in another area in accordance with Art. 169 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, an employee is entitled to compensation for travel to his place of work and new place of residence not only for himself, but also for his family members. And on the basis of Art. 325 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, some of our fellow citizens can even go on vacation for free.
Such compensation for travel to a place of rest and back within the Russian Federation is provided once every two years to persons working in organizations located in the regions of the Far North and equivalent areas, and annually to employees of federal government bodies and institutions. To receive such compensation, the employee must submit an application to the employer.
If an employee uses a personal car to travel on behalf of the company, the employer is obliged to compensate him for the cost of fuel and depreciation of the car. For this purpose, payment of compensation may be provided for in the employment contract. But it should be remembered that compensation can be included in expenses when calculating income tax only within the limits of the following standards:
- 1200 rub. per month - with an engine of 2000 cm³ or less;
- 1500 rub. - with an engine volume of more than 2000 cm³.
The amount of compensation paid can be stipulated by order of the manager.
Another option is to enter into a vehicle rental agreement. This method will allow you to reflect the entire amount of employee expenses on a vehicle in tax accounting. For compensation to be valid, the employee must confirm that he is the owner of the car.
Travel from home to work in a personal vehicle is not eligible for compensation.
Justified and documented travel expenses for employees are included in the costs of the enterprise in both accounting and tax accounting. In accounting they are reflected in the debit of expense accounts (26, 25, 44). In tax accounting - included in expenses based on:
- pp. 11 clause 1 art. 264 - compensation for the use of personal transport within the limits of the norm;
- pp. 12 clause 1 art. 264 — travel expenses.
Employees often use their personal vehicles to perform official duties: transporting goods, delivering reports, distributing goods. But the fact that the employee arrived at the office in his own car in the morning does not constitute grounds for assigning compensation.
The conditions for calculating and paying compensation for the use of a personal car must be discussed with your superiors and the agreements must be formalized in a special document - a contract or agreement on the use of a subordinate’s personal transport. Without a contract, you cannot claim compensation payments.
The amount of compensation is established by agreement (Article 188 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). There are no maximum or minimum restrictions by law; the employer and his subordinate can agree on almost any amount of compensation payment.
The employer should be aware of tax risks in terms of compensation for transportation costs. According to the current edition of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the costs of operating an employee’s personal transport can be taken into account as part of other expenses within the approved standards (subclause 11, clause 1, article 264 of the Tax Code, clause 1 of Resolution No. 92 of 08.02.
2002, Letter of the Ministry of Finance No. 03-03-06/1/465 dated 08/09/2011). This means that only the compensation standard can be legally ignored by the organization when paying income tax, and everything above will increase its tax base. That is why in most organizations the amount of compensation for a personal car does not exceed this standard established by law.
Compensation for personal transport
Employees often use personal vehicles to perform official duties: transporting goods, delivering reports, distributing goods. But the fact that the employee arrived at the office in his own car in the morning does not constitute grounds for assigning compensation.
The conditions for calculating and paying compensation for the use of a personal car must be discussed with your superiors and the agreements must be formalized in a special document - a contract or agreement on the use of a subordinate’s personal transport. Without a contract, you cannot claim compensation payments.
How much compensation for travel expenses to the place of work and back is a matter of agreement (Article 188 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). There are no maximum or minimum restrictions by law; the employer and his subordinate have the opportunity to agree on almost any amount of compensation payment.
The employer should be aware of tax risks in terms of compensation for transportation costs. In the current version of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the costs of operating an employee’s personal transport are taken into account as part of other expenses within the approved standards (subclause 11, clause 1, article 264 of the Tax Code, clause 1 of Resolution No. 92 of 02/08/2002, Letter of the Ministry of Finance No. 03-03- 06/1/465 dated 08/09/2011). This means that only the compensation standard can be legally ignored by the organization when paying income tax, and everything above will increase its tax base. Therefore, in most organizations, reimbursement for travel to the place of work by personal car does not exceed this standard established by law.
Examples of amounts:
- for a passenger car with an engine capacity of 2000 cm³ or less, the amount of compensation should not exceed 1200 rubles per month;
- if the engine volume is more than 2000 cm³, then compensation is due up to 1500 rubles per month;
- for a motorcycle, only 600 rubles are reimbursed. per month, regardless of the brand of motorcycle.
What is compensation, and what personnel expenses are classified as transportation?
Most companies have employees whose functions are related to travel. These could be drivers, couriers, sales agents, managers, and office workers. For example, a cashier periodically needs to hand over funds to the bank, and an accountant needs to submit documents to the inspectorate. Such costs must be compensated by the employer.
Compensation is a monetary payment that is associated with reimbursement to an employee of expenses incurred during the performance of his work duties (Article 164 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
Transportation costs that are subject to reimbursement to employees include:
- Compensation for the use of personal vehicles.
- Payment for rental property (such as a car or an employee's computer) and the cost of maintaining it.
- Compensation for public and other transport tickets, as well as taxi services, etc.
If the employee’s work is of a traveling nature, then the employer must reimburse the costs of renting residential premises, travel costs, daily allowance and other costs provided for in Art. 168.1 Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
Payment for tickets to and from your holiday destination
Workers in the Far North and equivalent areas are provided with compensation for travel to and from their holiday destination. This norm is enshrined in Art. 325 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation and is provided once every two years.
Travel expenses are reimbursed not only for the employee himself, but also for his family members, but only for vacations in Russia. There will be no compensation for travel abroad, and they will not reimburse the actual costs, but only the amount calculated based on the lowest cost of travel, and the shortest route (there is a special calculation method).
Not only northerners, but also contract military personnel receive payment for the road to their vacation spot. Commercial organizations that are not required by law to reimburse employees for travel expenses are not prohibited from doing so on their own initiative.
If a shift worker travels from Ukraine
All of the above applies to organizations that employ Ukrainian citizens on a rotational basis.
The main thing is that the employee has time to arrive at the collection point on the day indicated in the schedule. After all, it reflects the time spent on the road from the gathering place to the place of work for the watch test. 301 Labor Code of the Russian Federation. The shift work schedule should be:
- agreed with the trade union (if there is one in the organization) as LNAst. 372 Labor Code of the Russian Federation;
- brought to the attention of employees no later than 2 months before its entry into force.
It should also be noted that there is some risk for those organizations that pay for the travel of rotation workers in a roundabout way (Ukraine - Moldova - Russia or Ukraine - Belarus - Russia). If the cost of a roundabout route differs significantly from the cost of a direct route, then tax authorities may pay attention to this nuance during an on-site audit.
As a rule, in such cases, inspectors need at least some document justifying why the employee did not take a direct flight, but a detour (certificate of canceled flights, closure of air or rail traffic, etc.) If there is no such document, then the cost of travel can be excluded from “profitable” expenses (based on the economic inexpediency of paragraph 1 of Article 252 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). In this regard, we can recommend the following:
- Each time, take written statements from employees explaining why they left Ukraine in this particular way. But there is no need to show them to the tax authorities for the time being, only if questions arise;
- record information about the cost of tickets “directly” - in case the inspectors cannot be convinced of the justification of the costs. Then insist that only the difference be deducted from the expenses, and not the entire amount of the fare.
If you use the rotation method, remember that the procedure for its use in the organization must be regulated by local regulations. And be sure to specify all types of compensation for shift workers in a collective or employment agreement.
Before you deal with reimbursement of travel costs, you should find out on what basis tickets are paid. To do this, we need to consider individual “geographical” concepts. When talking about compensation for travel, terms such as place of residence, place of assembly and place of shift work are mentioned.
The law requires employers to transport employees in an organized manner from the location of the company or from the place of assembly to the place of work and back by economically feasible modes of transport. The legislator does not say anything specific about collection points, and therefore the collection point is determined by the employer independently.
For example, for a trip to an enterprise in Yakutia to work on a rotational basis, the company’s office located in Moscow can be approved as the collection point.
Paying for travel on a business trip
When traveling to another location, compensation for travel to and from work is required, along with payment for accommodation and daily allowance. The basis for payment will be a business trip order, official assignment and other documents confirming expenses (checks, receipts).
Compensation for travel to the place of work during a business trip has no legal restrictions. The employer is obliged to reimburse all costs after the fact, but he has the right to set individual requirements regarding the rational and economical use of the company's budget: prohibit employees from using taxis instead of public transport to travel to the place of business or purchasing luxury, business, or first class tickets. Such restrictions are common in the public sector.
Upon return, the posted worker confirms the expenses incurred with documents, providing checks, receipts, tickets, statements and other payment documents confirming the fact of payment for the carrier’s services. Commissions, insurance and other additional payments collected by transport companies when selling tickets are also compensated.
Compensation for travel to the place of work from the first watch
The rotation method of labor organization is used in cases where the place of work is significantly removed from the place of residence of workers and (or) the location of the organization. 297 Labor Code of the Russian Federation. Workers engaged in such work cannot return home every day. During the shift period (usually a month), they live near the site where they work, in a specially created rotation camp, provided dormitory, etc., and employers pay for their travel to the place of work.
Payment by the employer for travel from the place of residence was once provided for by regulation. 2.5 Basic provisions. Now this provision is not in effect. Decision of the Supreme Court of December 17, 1999 No. GKPI 99-924. However, in the opinion of the SAC, this does not mean that the employer does not have the right to compensate for travel expenses from the place of residence voluntarily; Resolution of the Presidium of the SAC dated 04/08/2014 No. 16954/13;
Let us now consider how road payments are taken into account for tax purposes.
Compensation for travel at the place of work on a rotational basis can be paid differently, depending on the place of assembly and the location of the enterprise. So, travel can be paid:
- From the place where employees gather to the place where work is performed and back - such payment for travel is mandatory, established at the legislative level.
- From the employee’s place of residence to the gathering place and back. This procedure for payment of compensation can be approved by the employer at will - the conditions are fixed in the employment contract and reported in the vacancy. Typically, applicants are primarily interested in this type of travel payment option.
- From the employee’s place of residence to the place of shift. As a rule, this procedure for travel compensation is offered to residents of the regions who want to get a shift job in the capital as cleaners, security guards and workers.
It happens that recruitment of employees is carried out by an agency or, for example, a student union. Then it is the sender who deals with travel compensation. If workers take on shift work on their own, as a rule, they buy tickets with their own funds and then receive compensation.
When an employee arrives at an enterprise, he presents the purchased tickets to the enterprise’s accounting department or its financial department, and a company employee assigns him a compensation amount in the amount of the full cost of travel. Moreover, if the travel from the place of assembly to the place of employment is paid, the employee arriving on duty has the right to demand payment at the daily tariff rate for each day spent on the road. Moreover, if he was forced to stay somewhere through no fault of his own, this time will also be paid for.
Depending on the procedure for making payments at the enterprise, money for travel can be issued in person according to the salary slip or transferred to the employee’s bank card.
Since it is not known in advance whether a potential employee overestimates his strength, and whether he is really ready to perform hard work on a rotational basis, employers refuse compensation for travel before the first shift. Jobs usually offer “travel after first watch” and this is based on the law.
Paying for travel on public transport
Some employers reimburse their employees not only for travel and vacation expenses on tickets, but also for daily trips by public transport to their place of work, when the place of work is outside the city or remote from the residential sector. Some organize transportation, while others pay for travel.
Payment for travel to the place of work in public transport is established on an individual basis. The law does not tell us anything on this topic; the norms and amounts are the prerogative of a particular employer.
Payments of compensation for travel (except for business trips) should be classified as payments in terms of remuneration for labor. This means that the employer will have to calculate and pay insurance premiums. This opinion was expressed by officials in Letters of the Ministry of Finance dated March 13, 2018 No. 03-15-06/15287 (clause 1) and the Federal Tax Service dated October 30, 2017 No. GD-4-11/ [email protected]
How to make it easier for employees to pay for travel
It is more convenient and profitable to buy travel tickets centrally and distribute them to employees.
Legal entities and individual entrepreneurs can buy travel passes for employees via the Internet by bank transfer through the Troika Business service (ORC LLC, agent of Mosgortrans). There will be no commission for this.
If you suddenly don’t know what “Troika” is. This is an electronic refillable plastic transport card of Moscow, which can be used to pay for travel on all public transport.
Do I need to collect Troika cards from employees in order to use the service?
No, it is enough to know the card number.
You can add tickets to your card immediately after paying the bill:
- through the Troika Business mobile application,
- in the terminals of the Moscow Credit Bank.
If employees do not have cards, they can be purchased through the service with delivery. For orders over 30,000 rubles, card delivery is free..
In general, you don’t need to travel anywhere; you can arrange everything through the website.
Payment amounts
The law has not established specific amounts of compensation payments. Amounts are determined on an individual basis.
The amounts of payments are fixed by orders, regulations or resolutions in the organization. Without this they are impossible.
The norms for compensation for travel are prescribed:
- in the employment contract with the employee;
- in the vehicle operating agreement;
- in a collective agreement;
- in certain regulations and standards, for example, in the regulations on the posting of an employee.
Briefly
- Payment for travel on public transport for employees is carried out at the expense of the company: by purchasing travel cards, issuing money on account, or paying a fixed amount.
- All expenses must be economically justified, recorded in the employment contract, LNA, and supported by documents. In accounting entries, standard accounts 70, 71, 73 are used in correspondence with the cost accounts of the corresponding departments.
- Travel cards purchased by the organization are received through account 50/3. Amounts are not subject to personal income tax, contributions, or VAT (except for taxis). They are included in profit expenses under the OSNO, and organizations using the simplified tax system can include travel costs in the calculation only if they prove that they are part of the remuneration.
- The use of account 70 and other accounting accents indicating that the payment is part of wages and not compensation can lead to additional assessment of personal income tax and contributions.
How to write an application for reimbursement of travel expenses
To receive compensation, the employee writes a statement justifying the need for payment. Supporting documents (receipts from gas stations, tickets, statements, etc.) are attached to the application. When traveling on business, money is issued in advance, and supporting documents should be attached to the advance report.
Typically, an application for travel compensation is made in writing. There is no unified form. Write your full name in the header of the document. and the position of the manager, indicate the name of the organization. Then your own full name, position in the company.
In the text of the application, describe in detail the circumstances that are the basis for payment: with dates, references to regulations or legislative acts. Sign the application, indicate the date of preparation and submit it to the accounting department for review.
Answers to common questions about who is entitled to compensation for travel to work
Question No. 1: Should I return the compensation transferred to me for paying for my own travel to the place of work on a rotational basis if I could not stay for the entire period of work?
Answer: No, you do not need to return the compensation, but many employers stipulate in advance the terms of its payment in the employment contract, so it is unlikely that it will be possible to avoid financial losses for refusing to follow the agreement.
Question No. 2: Is the employer obliged to pay for my travel from my place of residence to my place of assembly if I am ready to get a job on a rotational basis?
Answer: No, this payment procedure is at the discretion of the employer; the law obliges him to pay only for travel to the place of work.
Issuance of travel cards
Situation: how to issue travel tickets to employees?
Travel tickets must be received at the box office. The cashier is responsible for their safety. As necessary, employees who have the right to use travel tickets receive them against signature, and upon returning from a trip (at the end of their validity period) they hand them back. The movement of travel tickets must be reflected in a special statement, which the organization develops independently (Part 1, 4, Article 9 of the Law of December 6, 2011 No. 402-FZ). It must be borne in mind that the primary document must contain the mandatory details established by Part 2 of Article 9 of the Law of December 6, 2011 No. 402-FZ.
The list of employees who have the right to use travel tickets must be approved by order of the manager (another local act of the organization, for example Labor Regulations) or established in an employment (collective) agreement. This procedure follows from Part 3 of Article 57 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
Situation: should an organization assign a public transport ticket purchased by it to a specific employee?
Answer: no, you shouldn't.
An organization has the right to purchase one or more travel tickets without assigning them to specific employees. In this case, the ticket is issued to employees as needed and then returned. The order for the organization may not specify the positions and names of employees who have the right to use such a travel ticket. But you need to specify the rules for its storage and use. In addition, provide in the order the procedure for confirming the official nature of the trips.
Travel expenses for employees in the employment contract
One of the legal options for compensating employees for travel expenses is to indicate this compensation in the employment contract. In this case, this will be considered one of the items of labor costs. The legality of reflecting compensation in an employment contract can be expressed in several aspects:
- In the case of concluding an employment contract, regardless of what is stated in it, any citizen has the right to count on all those compensations and preferences provided for by labor legislation. In addition to labor legislation, the employee is also protected by specific laws, which may also apply to labor relations.
- In case of changes in the terms of the agreement, the citizen has the right to refuse to sign a new additional agreement if this infringes on his rights. A citizen has the right to express all his claims regarding disagreement with the new provisions and if the employer is not ready for dialogue, he can appeal to the trade union, the labor inspectorate, and, in extreme cases, to the court.
- Before concluding an employment contract, the employee has the right to discuss all his wishes and expectations. The employee states in advance what he would like to receive for performing work duties in this organization. The employer, in turn, can accept these conditions and include them in the contract. Or offer a compromise option and your own terms of relationship.
- In general terms, the cost of travel to the place of work falls entirely on the employee. When applying for employment, he must independently assess his economic benefits from such a transaction. But if the location is difficult to access, the employer can bear these costs. Moreover, this measure can be individual or general for all employees.
Taxation of travel expenses
When determining the amount of income tax, one should take into account the fact that only amounts of travel costs that are part of earnings and incurred based on production needs can be accepted as expenses. However, there is no direct indication that these two conditions must be met simultaneously.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with Preparation of a civil case for compensation for damage caused
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=upload
Thus, if there is a production need, travel costs for employees can be accepted as expenses for income tax in the following cases:
- The work process is continuous, it is not possible to stop it. This provision is enshrined in the resolution of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the Moscow Region dated June 17, 2009
- If work at the enterprise involves several shifts, for example, three shifts. The position is confirmed by letter of the Ministry of Finance No. 03-03-06/1/449 dated 08/31/2012
- If it is very difficult to get to your place of work
| IMPORTANT! The nearest transport stop should not be more than 300-500 meters away. In industrial zones, stops should be located no more than 400 meters from the entrance of the enterprise (clause 11.15 of the Code of Town Planning Rules) |
Accounting for travel expenses reflected in the employment contract when calculating income tax is carried out on the basis of paragraph 25 of Article 255 and paragraph 26 of Article 270 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, as well as letters of the Ministry of Finance No. 03-03-06/14664 dated March 18, 2015 and No. 03-03-06/1/449 dated 08/31/2012 and No. 03-03-07/26913 dated 04/16/2019.
In addition, it should be remembered that such expenses must be justified. In order to prove, for example, that the place of work is difficult to access, you can attach traffic diagrams indicating stops or receive information in writing from the Administration about how transport services in this direction are organized.
Travel expenses related to other situations do not reduce the income tax base.
| ★ Best-selling book “Accounting from Scratch” for dummies (understand how to do accounting in 72 hours) purchased by {amp}gt; 8000 books |
Income tax
The Tax Code directly states that the costs of transporting shift workers from their place of residence (recruitment) to their place of work and back are taken into account as part of other costs associated with the production and sale of subsection. 12.1 clause 1 art. 264 Tax Code of the Russian Federation. It does not matter whether the organization buys the tickets itself or compensates the costs to employees.
But what if there is no collective agreement in the organization? After all, its presence is not necessary. Then the procedure for paying delivery costs must be reflected in the employment contract with the shift worker. Letter from the Ministry of Finance dated July 12, 2005 No. 03-05-02-04/135.
Thus, the organization can take into account travel costs in “profitable” expenses under any option.
Personal income tax and contributions
Payment of travel expenses to the place of work can be considered as compensation for costs associated with the performance of work duties. 164 Labor Code of the Russian Federation. It is mandatory for the employer:
- in the part “collection point - watch” - by virtue of the regulatory act. 2.5 Fundamentals; Art. 423 Labor Code of the Russian Federation;
- in the part “house - collection point” or “house - shift” - by virtue of a local regulatory act, collective or labor agreement.
Therefore, personal income tax and insurance premiums (including “accidents”) should not exist here. 3 tbsp. 217 Tax Code of the Russian Federation; subp. “and” clause 2, part 1, art. 9 of the Law of July 24, 2009 No. 212-FZ (hereinafter referred to as Law No. 212-FZ); subp. 2 p. 1 art. 20.2 of Law No. 125-FZ dated July 24, 1998 (hereinafter referred to as Law No. 125-FZ).
However, the Ministry of Finance expressed a different opinion. He considered it possible not to tax only the payment for travel from the collection point, and even then on the condition that workers do not have the opportunity to get to their destination on their own (due to the inaccessibility of the facility). And payment for the road from the place of residence to the place of collection (or directly from the place of residence to work) is the employee’s income in kind. Letters from the Ministry of Finance dated 02.26.2013 No. 03-04-06/5379, dated 04.24.2008 No. 03-04-06- 02/41.
We turned to the officials with questions, and this is what they explained to us.
FROM AUTHENTIC SOURCES
Department of Social Insurance Development of the Ministry of Labor of Russia
“Insurance contributions to funds (including “injury”) are not subject to only the payment for the shift worker’s travel from the collection point to the place of work. Since such expenses are recognized as compensation payments established by Art. 302 Labor Code of the Russian Federation subp. “and” clause 2, part 1, art. 9 of Law No. 212-FZ; subp. 2 p. 1 art. 20.2 of Law No. 125-FZ. And if an organization pays shift workers for travel from their place of residence to work and back, then insurance premiums must be added to the cost of travel. 1 tbsp. 7 of Law No. 212-FZ; clause 1 art. 20.1 of Law No. 125-FZ, since such compensation is not provided for in the Labor Code and this payment will be considered as a payment in favor of the employee within the framework of labor relations.”
Let us remind you that direct payment of travel from the collection point is provided for by Soviet rules. 2.5 Basic provisions. A Art. 302 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation regulates the procedure for paying bonuses and other guarantees for work on a rotational basis.
FROM AUTHENTIC SOURCES
STELMAKH Nikolay Nikolaevich
Advisor to the State Civil Service of the Russian Federation, 1st class
“The law does not oblige the employer to provide and pay for the travel of shift workers from their place of residence to the place of assembly or from their place of residence to the place of work. Consequently, such payment or reimbursement to employees of the cost of travel is recognized as the employee’s income received in kind, sub. 1 item 2 art. 211 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. Compensation payment not subject to personal income tax is only payment for travel from the place of collection to the place where work is performed. 3 tbsp. 217 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.”
Nevertheless, VAS recently came out in defense of employers. Resolution of the Presidium of the Supreme Arbitration Court dated 04/08/2014 No. 16954/13: additional guarantees and compensations established in the organization become mandatory for the employer. Therefore, payments provided for, for example, by a collective agreement to reimburse the travel costs of shift workers from home to the collection point and back are compensatory, are not included in the wage system and should not be subject to insurance contributions.
This dispute concerned arrears in insurance premiums in relation to payment for travel of shift workers to their place of work in the Far North. However, the formulated position is, in fact, universal; you can refer to it in the case of claims from the Social Insurance Fund for contributions “for injuries”, as well as claims from tax authorities for personal income tax.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with How to re-register OSAGO for a new owner in 2020
Single tax calculation
Many companies strive to retain their highly qualified personnel and offer various additional benefits to their subordinates. This may include a social package, pension provision and travel by road. The company can buy travel passes for subordinates, reimburse transportation costs incurred by them, or organize a special route. Simplified people often wonder about the procedure for taxation of fares in order to calculate the amount of the single tax, personal income tax, and insurance contributions for compulsory pension insurance. We'll talk about this further.
The downside to the norms of the laws and the code for simplifiers is that, by reducing the base, the list of costs that can be considered is quite small and should be comparable to the criteria under the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. When considering accounting for expenses, use income tax criteria to be sure whether they can be taken into account or not. You have the right to consider travel expenses attributable to wages. The Code stipulates this possibility and believes that such expenses can be counted among those included in wages according to the collective agreement. But this is not directly stated there, so we will have to look for a point where we can increase our costs.
The costs of traveling by special transport are taken into account when calculating tax in the following moments:
- This is required for the production purposes of the company. Subordinates cannot get to work due to the lack of public transport or irregular flights. That is, if a person is late at work, he will no longer be able to get home.
- These expenses are specified in the employment contract, that is, a priori they are considered as expenses for wages. This requirement is determined by the code and any additional benefits not specified in the collective agreement are subject to taxation.
- Even when expenses are not related to production needs, but they are spelled out in the contract and there is an appropriate reference to it, then such expenses can be considered justified.