At any manufacturing enterprise there are products that have not completely gone through the manufacturing cycle and are not ready, and therefore they are in the work-in-progress stage. However, such goods are the property of the enterprise, and therefore must be subject to inventory, like any other material assets. In the article we will look at how the inventory of work in progress (WIP) takes place in construction and production and how accounting (postings) is carried out.
The essence of work in progress inventory
Inventory of work in progress involves determining the volume of such products at the enterprise and its actual cost, as well as the correspondence of this information to accounting data. At the same time, objects of work in progress are understood as goods that are only partially finished, that is, they have not gone through the entire manufacturing cycle, and therefore cannot be considered finished products and, accordingly, cannot be sold to consumers.
Work in progress items should include:
- products sent into the production process;
- defective items of goods;
- manufactured goods that have not passed tests (if this item is mandatory);
- incomplete products;
- work or services performed that were not accepted by the customer;
- semi-finished products of own production, not considered finished products.
| ★ Best-selling book “Accounting from scratch” for dummies (understand how to do accounting in 72 hours) > 8,000 books purchased |
Determining the actual cost of work in progress items can be carried out using several methods, namely:
| Method | Cost calculation |
| Simple (process-based) | Used for homogeneous products and involves the summation of all costs incurred divided by the number of units produced |
| Custom | Cost is determined in terms of costs incurred for each specific order |
| Lateral non-semi-finished | It is used in production, where products go through several stages of processing and are not sold until they are ready. Cost is calculated as the sum of all costs incurred at each stage of processing |
| Lateral semi-finished | It is used in production, where products undergo several stages of processing and can be sold at any of them. Cost is defined as the amount of costs incurred at past stages |
| Normative | The method is based on the use of standard cost, adjusted by indexes of changes in standards depending on deviations recorded at the final stage of production |
Types and methods of conducting inventory in production
Russian legislation, which regulates accounting issues, stipulates circumstances when an audit is mandatory. In addition, the director or owner of the company can order a reconciliation of the actual availability of various valuables with accounting data independently.
The inventory procedure, its timing and order of appointment is regulated by the Law “On Accounting” N 402-FZ dated 06.12.2011, the order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation “On approval of guidelines for the inventory of property and financial liabilities” No. 49 dated 06.13.1995 (Order of the Ministry of Finance N 49).
Cases in which reconciliation is required:
if the property is alienated, for example, by sale or conclusion of a lease agreement;- there is a transformation of an enterprise that is owned by the state or municipality;
- annually before the date of reporting for the year, carried out in the last quarter of the reporting year, with the exception of fixed assets and library collections (they are checked every three and five years, respectively);
- transmission from one mat. responsible person to another;
- detection of theft or damage to property;
- after eliminating the consequences of an emergency situation caused by a man-made or natural disaster;
- if the company is reorganized or liquidated;
- other circumstances provided for in the legal acts, for example, when a collective agreement has been concluded. responsibility, reconciliation can be assigned by the manager at the request of one or more employees responsible for the property.
In addition to mandatory inspections, the director or owner of the company can appoint additional ones, approve the timing in which they are carried out and the list of property to be reconciled.
Inventory can be planned or unscheduled, complete or partial. It can be carried out using natural and documentary methods. When reconciling property in kind, a visual inspection, weighing, counting, and measurements are carried out.
Documentary inventory is carried out to control intangible assets and various liabilities of the enterprise. During such an audit, accounting data is compared with documents confirming the existence, ownership or possession of property, rights to intangible assets, financial obligations to creditors, etc.
A full (continuous) check combines both methods. As a rule, it is carried out before the preparation of annual reports.
Important
If at the time of reconciliation, fixed assets are not at the enterprise (for example, transport on a voyage), they are checked before the start of the inventory.
The purpose and objectives of inventory of work in progress
The main purpose of the inventory of work in progress is considered to be to determine the actual presence of objects of work in progress, identifying unaccounted for defects, determining the completeness of products, determining the balances of canceled or suspended orders and calculating the cost of products that are in the stage of work in progress. In addition, the purpose of the inventory is to compare actual data with accounting indicators and identify factors influencing discrepancies in information.
In accordance with the goal, the following tasks should be solved during the inventory of work in progress:
- determination of the composition, structure and quantity of work in progress;
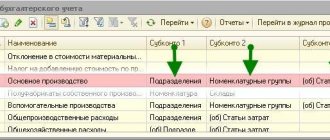
- drawing up inventory lists that will contain all the necessary information, including the name of the object or product, its quantity, degree of readiness and completeness, stage of production;
- identifying unaccounted for defects in production and determining its percentage of manufactured products;
- study and analysis of maps for the release of materials into production in order to identify the irrational use of the enterprise’s material resources;
- calculation of the cost of work in progress according to the method specified in the accounting policy and used in the organization.
| ★ Best-selling book “Accounting from scratch” for dummies (understand how to do accounting in 72 hours) > 8,000 books purchased |
Capital construction
For unfinished capital construction, the inventories indicate the name of the object and the volume of work performed on it - for each individual type of work, structural elements, equipment, etc.
In this case they check:
- whether equipment transferred for installation, but not actually started by installation, is included in the capital construction in progress;
- condition of mothballed and temporarily stopped construction facilities.
For these objects, it is necessary to identify the reasons and basis for their conservation.
For completed construction projects, actually put into operation in whole or in part, the acceptance and commissioning of which are not documented with the appropriate documents, special inventories are drawn up.
Separate inventories are also compiled for objects that are completed, but for some reason not put into operation. The inventories indicate the reasons for the delay in registration of commissioning.
For objects that have been stopped under construction, as well as for design and survey work for construction that has not been completed, inventories are drawn up, which include:
- data on the nature of the work performed and its cost;
- reasons for stopping construction.
To do this, you need to use the appropriate technical documentation (drawings, estimates, financial estimates), certificates of completion of work, stages, logs of work performed at construction sites, etc.
As a result, the inventory commission, based on documents, establishes the amount that must be reflected in the deferred expenses account and attributed to production and distribution costs (or to the appropriate sources of funds of the organization) within a documented period in accordance with the calculations and accounting policies developed in the organization.
Preparatory activities
Before carrying out an inventory of work in progress, it is necessary to carry out a number of preparatory procedures in order for the process to produce effective results. Storekeepers need to sort work-in-process items according to their nomenclature, as well as separate defective items to make it more convenient to carry out direct counting.
Accounting employees should post all available documents on the movement of materials and work-in-progress items into synthetic and analytical accounting accounts. In addition, you need to prepare a scheme according to which the cost will be calculated, as well as identify orders that were canceled or suspended for some reason.
The director of the organization is obliged to issue an inventory order, which will specify the timing of the event and the composition of the working audit commission. In addition, the document indicates the reason for which the inventory is carried out and the list of property being inspected. As for the reasons, there may be several of them, for example, the dismissal of a storekeeper or other financially responsible person, the preparation of annual reports, suspicion of embezzlement or theft.
The main preparatory activities can be presented in the following table:
| Event | Description |
| Issuance of an order | The order is issued by the director of the organization. It indicates all the essential aspects of the inventory, including the period of conduct, objects of inspection, the reason for the audit and the composition of the working commission |
| Delivery and preparation of documentation | Materially responsible persons are obliged to submit to the accounting department all documentation on the movement of work in progress objects, and the accountant is obliged to enter documents into the program and process them in accordance with all established rules |
| Identifying groups of objects or individual units | The audit commission, together with accounting and economists, must develop a nomenclature according to which the inventory will be carried out. In addition, a scheme should be prepared according to which the cost of work in progress items will be assessed |
Organization of inspection
The procedure for taking inventory of work in progress must be reflected in the company's accounting policies.
First of all, the director of the organization must issue an order indicating the following information:
- the reasons for the inspection;
- types of property that fall under the inventory;
- composition of the commission that carries out the inspection;
- start and end date of the inspection;
- deadlines within which all necessary documents must be submitted to the accounting department.
We can say that this order is an assignment for the inventory commission.
The commission for inventory of unfinished construction objects may include accounting employees, administration employees and other employees. During the inspection, workers carrying the mat must be present. responsibility.
How to determine the frequency and scale of inventory of work in progress
Inventory work in progress in full at the end of each month, quarter and year, if one of the conditions is met:
1. The cost of finished products at the enterprise is calculated based on data on the cost of work in progress.
2. The number of inventory items for each production unit does not exceed 1000 units, and one day is allocated for inventory.
Inventory procedure
At the time of the inventory of work in progress, the audit commission receives documents that serve as the basis for the movement of material assets and checks that they are filled out correctly. Then a direct complete census of work-in-progress items is carried out into the inventory list. A separate inventory is drawn up for rejected products, since such items cannot be included in the general inventory list for work in progress. It is necessary to take into account that the absence of a financially responsible person or one of the commission members during the audit is considered unlawful, and therefore the results of the audit are considered invalid.
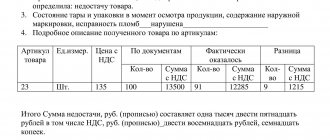
Upon completion of the inventory, all compiled documents are signed by members of the inspection commission and transferred to the accounting department for processing. In this case, the discrepancy between the actual and accounting indicators must be documented using a reconciliation sheet, and the results - surplus or shortage - are attributed to the appropriate accounts of synthetic and analytical accounting.
Reflection of inventory results
Acts and inventories of inspections are submitted within the prescribed period to the accounting department. Inconsistencies discovered during the inventory between the data of primary documents and the actual availability of property must be reflected in the accounting accounts.
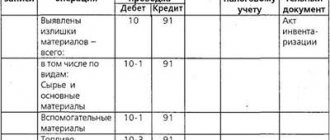
If excess work in progress is discovered, it should be capitalized at market value on the date of the inspection. Work in progress in accounting is listed on accounts 20–29. The amount is recorded in the debit of the account in which the surplus was discovered: Dt “Auxiliary production” Ct “Other income”.
Shortages or damage to work in progress are shown in the credit of production cost accounts. The accounting entries look like this: Dt “Shortages” Cht “Main production”, Dr. “Losses from damage to valuables” Cht “Main production”. If the detected shortage does not exceed the norm of natural loss, then its amount is attributed to distribution costs: Dr. “Main production” Ch. “Shortages”. Such write-off is carried out on the basis of the calculation recommended by the accounting policy.
How is WIP inventory carried out in production?
At industrial enterprises, inventory of work in progress can be carried out both for individual objects and for their totality. The main points to pay attention to when taking inventory are the following:
- it is necessary to determine the actual quantity of all items in the nomenclature;
- it is necessary to establish the completeness of all work in progress items;
- you need to determine the balance of work in progress that relates to canceled or suspended orders.
The production process in a large enterprise involves a variety of operations, for which different areas of work can be organized. Accordingly, an inventory of work in progress should be carried out in the context of these areas, and for each of them a corresponding inventory list should be compiled, and then all the data obtained should be compiled into a general inventory sheet.
OBJECTIVES OF WIP INVENTORY
The objectives of conducting an inventory of work in progress are as follows:
- check the actual presence of work in progress and assess its condition;
- compare the actual availability of work in progress with accounting data;
- check data on operational accounting of the movement of components and parts between departments and the total amount of costs in work in progress;
- control the completeness and timeliness of delivery of finished products to the warehouse and documentation of such delivery;
- check the completeness of the necessary technical documentation for finished products;
- check the correct distribution of costs by type of product and clarify the cost of manufactured products;
- determine the actual completeness of the backlog, the availability of assembly parts;
- prevent theft, concealment of marriage and other abuses;
- check the correctness of registration of output and calculation of piecework wages.
How is the inventory of work in progress carried out in construction?
If the inventory is carried out on unfinished construction projects, then the inventory list indicates the buildings, the stage of their production, as well as the volume of certain work on them or individual structural elements. Objects that are currently under conservation are also subject to inventory, and the inventory list must indicate the reasons for their conservation.
It must be taken into account that buildings that are completely constructed, but not put into operation and do not have the appropriate documentation, are also considered work in progress, and therefore they must be recorded in a separate statement. This document reflects the reasons why the buildings were not put into operation and the delivery documents were not properly completed.
Drawing up inventories
Inventories are compiled separately for each separate division (workshop, site, department) indicating:
- names of backlogs;
- stage or degree of their readiness;
- quantity or volume.
And for construction and installation work - indicating the scope of work:
- for unfinished objects;
- their queues;
- launch complexes;
- structural elements and types of work, calculations for which occur after their complete completion.
Raw materials, materials and purchased semi-finished products located at workplaces that have not been processed are not included in the inventory of work in progress, but are inventoried and recorded in separate inventories.
Rejected parts are not included in the inventory of work in progress, but separate inventories are compiled for them.
Also see Inventory List.
Typical entries for inventory of work in progress
When conducting an inventory, the commission can receive several results, and for each of them the corresponding entries are generated. The most common ones are:
- if a surplus of work in progress items is identified
Debit 20 Credit 91/1 market value of surplus accepted for accounting
- if a shortage is identified
Debit 94 Credit 20 reflects the cost of the shortage
- shortages according to the norm and in excess of it are allocated to different accounts
Debit 20 Credit 94 shortage within normal limits attributed to production
Debit 73 Credit 94 shortage in excess of the norm is attributed to the culprit, if he is identified
Debit 91/2 Credit 94 shortfall in excess of the norm is charged to other expenses if the culprit is not identified
Frequency of inventory of rolled metal and WIP balances in production
There are two types of inventory checks - sudden and planned. Most enterprises prefer the second control method. The frequency of scheduled inspections is determined in the company's accounting documents. However, there are situations in which inventory accounting is a mandatory activity. These include:
- submission of financial statements for the year;
- sale, purchase, lease of an enterprise;
- change in the composition of persons responsible for material assets;
- force majeure circumstances, after which it is necessary to assess the extent of damage.
The inspection can be carried out on the initiative of an employee of the company who provides arguments in favor of its implementation.