Every organization must carry out periodic inspections of material assets and various liabilities, that is, recording the presence and analyzing the condition. The actual quantity, value and condition of tangible assets must correspond to the figures entered in the accounting records. Inventory of property funds, goods, and other assets is an indispensable procedure for all business owners.
We will describe below what rules this operation is carried out and what nuances are typical for its documentation.
Inventory and its objective importance
Periodic accounting of material assets by comparing actual objective information obtained after a personal inspection with the information reflected in accounting is called inventory .
A discrepancy between the actual and documented state or number of inventory assets is possible for a number of reasons:
- natural influences on certain material assets that can affect changes in their quantity, weight, volume, residual value (shrinkage, losses during transportation, spoilage due to storage, evaporation, etc.);
- identification of abuses in the accounting of material resources (incorrect measurements, allowance of body kits, theft, etc.);
- problems that arose when making entries in accounting documentation (slips, errors, blots, corrections, inaccuracies and other ambiguities).
Therefore, regular inventory taking is of utmost importance for any enterprise.
https://youtu.be/TT6yxHqJzZs
What is technical inventory?
The inspection of buildings and structures, storage and provision of information about them to all interested parties is called technical inventory. This work is performed by employees of a special organization who have the necessary qualifications for this.
Information of this kind is necessary for planning development, maintaining the safety of citizens, maintaining residential and public buildings, infrastructure and other structures in order and in good condition. The results of the technical inventory are entered into a technical passport, which is prepared for each object.
Required by law
The mandatory nature of this procedure is approved by the federal legislation of our country. Entrepreneurs are required to regularly take inventory of their own, stored or leased property and their financial obligations by two regulatory documents:
- Federal Law of December 6, 2011 No. 402-FZ “On Accounting”;
- Methodological recommendations for inventory of property and financial obligations (approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated June 13, 1995 No. 49).
Inventory: step-by-step instructions
How to take inventory? We bring to your attention step-by-step instructions for conducting this key event.
Preparing and conducting an inventory requires compliance with the provisions of Federal Law dated December 6, 2011 No. 402-FZ “On Accounting” (hereinafter referred to as the Accounting Law), as well as the Regulations on Accounting and Financial Reporting in the Russian Federation (approved by order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated July 29 .1998 No. 34n, hereinafter referred to as Regulation No. 34n).
The procedure for conducting an inventory of property and financial obligations of an organization and recording its results are defined in the Guidelines for the inventory of property and financial obligations (approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated June 13, 1995 No. 49, hereinafter referred to as the Guidelines for Inventory).
Unified forms of documents for registration of inventory results were approved by the State Statistics Committee (Resolution of the State Statistics Committee of Russia dated August 18, 1998 No. 88, dated March 27, 2000 No. 26).
The use of these regulations will allow you to correctly draw up all the documentation necessary as part of the inventory and comply with all the requirements of current legislation.
Inventory. Frequency
Inventory must be carried out (clause 3 of article 11 of the law on accounting, clause 27 of regulation No. 34n):
- before drawing up annual financial statements, excluding property, the inventory of which was carried out starting from October 1 of the reporting year. An inventory of fixed assets (FPE) can be carried out once every three years;
- when changing financially responsible persons. In this case, an inventory of the property that was entrusted to this person is carried out;
- when facts of theft or damage to property are revealed;
- if there was a natural disaster, fire, or other emergency situation;
- during liquidation or reorganization.
Inventory. "Road map"
Here are the necessary inventory steps:
Step No. 1. Create an inventory commission.
Step No. 2. We receive current incoming and outgoing documents.
Step No. 3. We receive receipts from financially responsible persons.
Step No. 4. We check and document the existence, condition and valuation of assets and liabilities.
Step No. 5. We reconcile the data in inventory records (acts) with accounting data.
Step No. 6. Summarize the results of the inventory.
Step No. 7. Approve the inventory results.
Step No. 8. Reflection of inventory results in accounting.
Step No. 1. How to create an inventory commission
The creation of an inventory commission is formalized by order (resolution, resolution) of the head of the organization (clause 2.3 of the guidelines for inventory).
The unified form of this order (form No. INV-22) was approved by Decree of the State Statistics Committee of Russia dated August 18, 1998 No. 88.
Any employee of the organization can be included in the inventory commission. As a rule, the members of the commission are:
- representatives of the organization's administration;
- accounting service employees (for example, chief accountant, deputy chief accountant, site accountants);
- other specialists - employees of technical (for example, an engineer), financial (for example, the head of a financial department), legal (for example, a lawyer) and other services.
Attention: financially responsible persons cannot be members of the inventory commission. At the same time, their presence when checking the actual availability of property is mandatory.
The commission must have at least two people.
The order, in addition to the composition of the inventory commission, must indicate the timing and reasons for conducting the inventory, the property being inspected and obligations.
The order is approved by the general director, after which the document must be signed by the chairman and members of the inventory commission.
The order to carry out an inventory is registered in the journal for monitoring the implementation of orders (decrees, instructions) to carry out an inventory, which can be drawn up in form No. INV-23 (clause 2.3 of the guidelines for inventory).
Step 2. We receive current incoming and outgoing documents
Before checking the actual availability of property, the inventory commission must obtain current receipts and expenditure documents, the latest on the day of the inventory.
The received documents are certified by the chairman of the inventory commission with the indication “before the inventory on “__” __________ 201_.” This is the basis for the accounting department to determine the balance of property at the beginning of the inventory according to accounting data (clause 2.4 of the guidelines for inventory).
Step 3. We receive receipts from financially responsible persons
A receipt issued by the financially responsible person before the start of the inventory is provided to the inventory commission on the day of the inspection. This document confirms that:
- by the beginning of the inventory, all expenditure and receipt documents for the property were handed over by the financially responsible person to the accounting department or transferred to the commission;
- all assets received under their responsibility are capitalized, and those disposed of are written off.
Step No. 4. We check and document the existence, condition and valuation of assets and liabilities
The inventory commission determines:
- names and quantities of property (fixed assets, inventories, cash on hand, documentary securities) available in the organization, including leased property, by physical counting (clause 2.7 of the inventory guidelines). At the same time, the condition of these objects is checked (whether they can be used for their intended purpose);
- types of assets that do not have a tangible form (for example, intangible assets, financial investments) - by reconciling documents confirming the organization’s rights to these assets (clauses 3.8, 3.14, 3.43 of the inventory guidelines);
- composition of receivables and payables - by reconciling with counterparties and checking documents confirming the existence of an obligation or claim (clause 3.44 of the inventory guidelines).
The inventory commission enters the received data into inventory records (acts).
After this, financially responsible persons must sign in the inventory records (acts) that they were present during the inventory (clauses 2.4, 2.5, 2.9 - 2.11 of the guidelines for inventory).
Step 5. Reconciliation of data in inventory records (acts) with accounting data
The received data in inventory records (acts) is verified with accounting data.
It happens that during the inventory, surpluses or shortages are identified. In this case, a matching statement is drawn up, which indicates the discrepancies (surplus, shortage) identified during the inventory. A matching statement is compiled only for those assets for which deviations from the accounting data have been identified.
To document the conduct and results of the inventory, you can use the following forms of documents:
- for OS - Inventory list of OS (form No. INV-1) and Comparison sheet of inventory of OS (form No. INV-18);
- for goods and materials - Inventory list of inventory items (form No. INV-3), Inventory report of shipped inventory items (form No. INV-4) and Comparison sheet of inventory results of inventory items (form No. INV-19);
- for Deferred Expenses - Inventory report of deferred expenses (Form No. INV-11);
- at the cash desk - Cash Inventory Report (Form No. INV-15);
- for securities and BSO - Inventory list of securities and forms of strict reporting documents (form No. INV-16);
- for settlements with buyers, suppliers and other debtors and creditors - Inventory report of settlements with buyers, suppliers and other debtors and creditors (form No. INV-17).
Step No. 6. Summarize the inventory results
At the meeting following the inventory, the commission:
- analyzes identified discrepancies;
- offers ways to resolve detected discrepancies in the actual availability of values and accounting data (clause 5.4 of the guidelines for inventory).
The meeting of the inventory commission is documented in minutes.
If the results of the inventory do not reveal any discrepancies, then this fact should also be reflected in the minutes of the meeting of the inventory commission.
Following the meeting, the inventory commission summarizes the results of the inventory, using
For this purpose, the unified form No. INV-26 “Record of results identified by inventory” can be used (approved by Resolution of the State Statistics Committee of Russia dated March 27, 2000 No. 26). It reflects all identified surpluses and shortages, and also indicates the method of reflecting them in accounting (clause 5.6 of the inventory guidelines).
The minutes of the meeting of the inventory commission, together with the results record sheet, are submitted for consideration to the head of the organization, who makes the final decision.
Step No. 7. Approve the inventory results
The inventory commission submits to the head of the organization the minutes of the meeting of the inventory commission and a record of the results identified by the inventory.
Matching statements and inventory lists (acts) may be attached to these documents.
After reviewing the documents, the head of the organization makes a final decision, which is formalized by an order approving the inventory results (clause 5.4 of the inventory guidelines).
A mandatory part of the order is an instruction on the procedure for eliminating discrepancies identified by the inventory.
After this, the documentation on the inventory results is transferred by the inventory commission to the accounting service.
Step 8. Reflection of inventory results in accounting
Discrepancies identified during the inventory between the actual availability of objects and the data of the accounting registers should be reflected in the accounting records in the reporting period to which the date as of which the inventory was carried out (Part 4, Article 11 of the Accounting Law).
In the case of an annual inventory, the specified results must be reflected in the annual financial statements (clause 5.5 of the guidelines for inventory).
If, as a result of an inventory, property is identified that is not subject to further use due to obsolescence and (or) damage, such property must be written off from the register.
Also, debts with an expired statute of limitations are written off from the balance sheet.
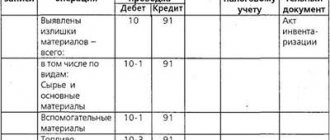
Based on the results of the inventory, a shortage was identified
In accounting, shortages are reflected on the date as of which the inventory was taken (Clause 4, Article 11 of the Accounting Law).
The cost of acquiring missing inventories is attributed to costs associated with production or sale, within the limits of natural loss rates (subparagraph “b”, paragraph 28 of regulation No. 34n). The postings will be like this:
Debit 94 Credit 10 (41, 43)
— the cost of lost property is written off;
Debit 20 (25, 26, 44) Credit 94
— the shortage is written off within the limits of natural loss norms.
The cost of shortages of inventories in excess of the norms of natural loss and shortages of inventories for which such norms are not approved, as well as shortages of fixed assets, tools, money and monetary documents (BSO, etc.) (subparagraph “b” of paragraph 28 of Regulation No. 34n) or recovered from the guilty person (if such a person is identified), or written off as other expenses (if the guilty person is not identified).
Debit 94 Credit 01 (10, 41, 43, 50)
— the cost of lost property is written off;
Debit 73 (76) Credit 94
— the cost of shortages is attributed to the guilty parties;
Debit 50 (51, 70) Credit 73 (76)
— the cost of the shortage has been recovered from the guilty party;
Debit 91 Credit 94
— excess shortages are written off as expenses.
For income tax purposes, the cost of acquiring missing inventories is taken into account in material costs during the period when the shortage is identified within the approved norms of natural loss (subclause 2, clause 7, article 254 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
The procedure for accounting for shortages of inventories in excess of the norms of natural loss and shortages of inventories for which such norms are not approved, as well as shortages of fixed assets, instruments, money and monetary documents (BSO, etc.) depends on the situation.
Situation 1: the person responsible for the shortage has been identified
In this case, the cost of the shortage is taken into account in expenses for one of the following dates (subclause 8, clause 7, article 272 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation):
- or recognition of the amount of damage as guilty (for example, on the date of concluding an agreement with the employee on voluntary compensation for damage);
- or the entry into force of a court decision to recover the amount of damage from the perpetrator.
At the same time, the income must take into account the amount of damage found guilty or awarded by the court (clause 3 of Article 250, subclause 4 of clause 4 of Article 271 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Situation 2 The person responsible for the shortage has not been identified
Then the cost of shortages is taken into account in expenses on the date of drawing up one of the following documents (subclauses 5, 6, clause 2, article 265 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation):
- or a decision to suspend the preliminary investigation in a criminal case due to the fact that the person to be charged as an accused has not been identified;
- or a document from the competent authority confirming that the shortage was caused by an emergency.
For example, in the event of a fire, such documents will be a certificate from the fire service (EMERCOM), a fire report and a protocol for examining the scene of the incident.
If the inventory reveals surplus
The market value of surplus property identified as a result of the inventory is included in accounting and tax accounting as part of income as of the date on which the inventory was carried out:
The market value of such property can be confirmed by one of the following documents:
- or a certificate compiled by the organization itself based on available information on prices for the same property (for example, from the media);
- or a report from an independent appraiser.
The accounting entry will be as follows:
Debit 01 (10, 41, 43, 50) Credit 91
— surpluses identified during inventory are reflected.
Audit Department of RIGHT WAYS LLC
Reasons for assigning an inventory
In accordance with legislative documents, an inventory must be carried out by organizations, regardless of their form of ownership, in the following circumstances:
- when selling, purchasing or leasing tangible property;
- if the organization is reorganized or officially liquidated;
- when a person bearing financial responsibility changes in a particular area;
- in cases where a municipal organization or state-owned enterprise is transformed into another form of ownership;
- when establishing facts of theft (theft), violation of conditions of storage, movement and release of goods, identification of abuses, etc.;
- after the end of sudden extreme conditions - accidents, natural disasters, catastrophes, and other emergency situations;
- under any circumstances, at least once a year before drawing up the annual accounting report (if the inventory was carried out after October 1 of the current year, this is enough).
FOR YOUR INFORMATION! If financial responsibility is borne not by an individual, but by a group, for example, a brigade, then the reason for the inventory may be a change in the leader of this group (foreman) or more than half of its composition, or a request from any member of the group.
Accounting
Identified surpluses of fixed assets are reflected in the accounting records as follows:
DEBIT 01 CREDIT 91-1
– the fixed asset has been capitalized.
If there is a shortage of fixed assets, the entries look like this (if the culprit is not identified):
DEBIT 02 CREDIT 01
– depreciation on missing fixed assets is written off;
DEBIT 94 CREDIT 01
– the residual value of the fixed assets is written off;
DEBIT 91-2 CREDIT 94
– the shortage is reflected in other expenses. If the culprits are identified in the event of a shortage, the postings will be as follows:
DEBIT 73 CREDIT 94
– the shortage is written off at the expense of the guilty parties;
DEBIT 50 CREDIT 73
– the employee has repaid the amount of debt.
Example
B, selling computer office equipment, due to the dismissal of warehouse manager I.I.
Ivanova carried out an inventory. As a result of the actions taken, the following was discovered: – surplus – a laptop worth 45,000 rubles; – shortage – a printer worth 45,000 rubles. How to fill out the inventory list of fixed assets (form No. INV-1) and the comparison sheet of the results of inventory of fixed assets and intangible assets (form No. INV-18) ()
Yu.L. Ternovka, expert editor
Practical accounting
A universal berator that contains complete and reliable information about accounting rules. Comprehensive information about the work of the company from creation to distribution of profits. Find out more >>
Who sets the procedure?
In addition to the legal requirements set out in the Methodological Recommendations, all other nuances of the inventory remain the responsibility of the organization’s management. Naturally, they must be recorded in the local documentation of the enterprise. The Directorate needs to clarify the following issues:
- how many inventories need to be carried out during the working year;
- at what time should this be done;
- listing the types of assets subject to inspection;
- appointment of the head and members of the inventory commission;
- possibility of selective (sudden) inventory.
What exactly is being checked?
Depending on which assets are included in the inventory list, one or another form is distinguished:
- complete inventory - the entire property fund corresponding to the company’s property rights, material assets leased and/or taken for safekeeping, plus possible unaccounted for assets and business liabilities;
- selective (sudden) inventory - a specified share of property is subject to re-registration (for example, only assets under the control of a specific person bearing financial responsibility, or those combined geographically).
The following groups of material assets and commercial obligations are recognized as inventory objects in one or another combination.
- Fixed assets of the company.
- Goods.
- Intangible property.
- Cash investments.
- Unfinished production.
- Planned expenses.
- Cash, valuable documents, strict reporting forms.
- Calculations.
- Reserves.
- Animals, plants, seed, etc. (in the relevant field of entrepreneurship).
Registration of inventory results
As a result of the entire check, an inventory report is drawn up, which shows the actual inventory balances in the warehouse in actual and monetary terms.
To display all available information, the accountant fills out a statement using the INV-26 form, where data on mismatches, surpluses, and shortages is entered in specific columns. The document is signed by all members of the commission. Based on it, you can subsequently recover losses from financially responsible persons. The results of the warehouse inventory are included in the reporting of the month in which it was carried out (usually carried out at the close of the month).
Body carrying out inspection and accounting
Since inventory is recognized by law as a mandatory and regular action, it is advisable to have a permanent inventory commission at the enterprise, which has the following responsibilities:
- preventive measures aimed at preserving material assets;
- participation in resolving problems related to the management of storage issues and possible damage to property funds;
- control of documentary support of the dynamics of material assets;
- ensuring the inventory process in all its aspects (instructing commission members, carrying out the inspection itself, preparing relevant documentation);
- registration of inventory results.
The composition of the commission is approved by the management of the organization, registered in accordance with the order and recorded in the Logbook for monitoring the implementation of orders (decrees, instructions) to conduct an inventory (form No. INV-23). It can include:
- administrative workers;
- accounting employees;
- internal auditors or independent experts;
- representatives of any specialty working at the enterprise.
If the volume of property assets is small, then the function of the inventory commission can be assigned to the audit commission in cases where it operates at the enterprise.
IMPORTANT! If during the actual inspection the absence of even one member of the commission is recorded, then the inventory is not considered valid.
The procedure for carrying out inventory in production
Before the start of the inspection, an inventory commission is appointed by order or instruction of the manager. If the volume of property being verified is large, then there may be several commissions. They include employees from administration, accounting, and other services of the enterprise. Internal audit staff or independent auditors may be included.
note
The inspection must be carried out in the presence of all members of the commission and the financially responsible person. If someone from the commission is absent, this may become a reason to challenge the results.
Before starting an inventory, the head of the commission receives accounting data about the property being inspected.
During the reconciliation, inventory lists are filled out, where accounting and actual availability data are entered. A sample inventory is available in Order No. 49 of the Ministry of Finance.
If the volume of property being inspected is large and the inventory takes several days, at the end of each working day the room where the valuables are located is sealed by the head of the inspection.
note
If at the time of the inventory there is a need to release or capitalize inventory items, this operation is carried out in the presence of a commission that carries out the reconciliation. For such operations, a separate inventory is drawn up “Inventory items issued (received) during inventory counting.”
On each page (below) the number of entries about values on the page and the overall result of their measurement in physical terms are written.
If there is an error or typo in the inventory, the correction is endorsed by everyone present during the reconciliation.
The inventories and acts drawn up during the inspection are signed by the members of the commission and the mat. responsible person. There, the employee being inspected makes a note indicating that there were no comments regarding the inspection process.
After the inventory, a control test is sometimes prescribed to check whether it was carried out correctly.
If, during the reconciliation of property with accounting data, a discrepancy (extra or missing) is revealed, after the inventory, a matching statement is drawn up, in which all deviations are entered.
Discrepancies found between the fact and the information in the accounting. reports are subject to settlement by:
- capitalization of surplus;
- write-offs for expenses (within the limits of natural loss standards);
- compensation for the person responsible for the shortage;
- offset of shortages and surpluses for the same type of property.