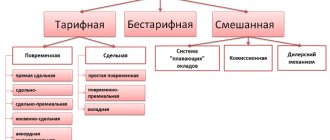
What is the tariff system of remuneration. Differences from the tariff-free system
The tariff system includes a number of provisions, norms, rules and regulations that make up a unified method of calculation, as well as the calculation of employee wages. The form of remuneration under consideration differs significantly from the non-tariff form.
The tariff system takes into account the complexity of the work, its intensity, working conditions, qualifications of certain categories of personnel; only if the specified components are available and analyzed, the employee will be paid a salary.
The non-tariff system has fundamental differences: the wages of all employees of the enterprise depend on the results of the work of the entire enterprise and on the amount of money allocated by the employer to pay for the labor process.
A fundamentally important element of the non-tariff system is the coefficient that takes into account the individual contribution of each employee to the overall final result. The tariff-free system is distinguished by the fact that the salary of each member of the work team is part of the general wage fund.
The tariff system of remuneration includes the main elements:
- tariff schedules;
- tariff directories;
- tariff rates.
Definition
A tariff rate is a monetary payment to an employee for completing tasks of a certain complexity within a specified time frame.
This amount is fixed in the employment contract and is the minimum guaranteed wage, below which the employee cannot receive provided that all duties are performed.
The enterprise can develop tariff wage rates, tariff schedules and staffing schedules, on the basis of which the employee’s salary is determined. The rules by which the calculation is carried out are presented in labor legislation.
The first step is to familiarize yourself with the tariff and qualification directory of a specific industry to find out the size of the tariff rate, the number of categories provided, and the availability of additional payments. The formula for calculation is as follows:
- Rate = 1st category rate x Increasing coefficient.
In the calculations, monthly rates are used only if the actual payment coincides with the norms, daily rates - if the number of days of actual attendance at work during the week differs from 5. The employee’s hourly tariff rate is necessarily used when calculating payment:
- in dangerous, difficult and harmful conditions;
- for excess production;
- on night shifts;
- on weekends.
It is calculated by dividing the salary by the number of hours worked in a month (or the average monthly number of working hours for the year). The exact calculation algorithm is specified in the Collective Agreement.
Payment schemes
The payment system is the ratio of the measure of labor and the reward for it. This also includes the conditions and procedure for calculating incentive payments and bonuses. The approved system is fixed in the Collective Agreement.
Time system
With a time-based system, regulatory tasks are developed and the amount of time required to complete them is established. To calculate earnings, the amount of time worked should be multiplied by the rate. It can be hourly or monthly.
Example 1
The hourly wage rate for a worker is 75 rubles. In a month he worked 160 hours against the norm of 168 hours. The employee's salary is: 75 x 160 = 12 thousand rubles.
Information for calculations is taken from the “Time Sheet” and the employee’s personal card. Most often, the hourly rate is used when calculating wages for industrial workers, and monthly salaries are set for specialists and managers.
Example 2
An accountant in an organization has a salary of 15 thousand rubles. During the month he worked 17 days out of the required 20. His salary is: 15,000: 20 X 17 = 12.75 thousand rubles.
Forms of payment are established:
- Simple time-based - provides payment for the amount of time spent on completing a task.
- Time-based bonus system - provides additional payments for product quality.
The salary amount may depend on the quantity of products manufactured. In this case, prices are determined by multiplying the rate by the category and the production rate. Let's take a closer look at the forms of remuneration.
Direct piecework
In this system, the salary is directly proportional to the number of products manufactured based on established prices. The calculation procedure will depend on the type of norm.
Example 3
The tariff rate for a mechanic is 180 rubles/hour with a production rate of 3 pieces/hour. 480 parts were produced in a month. Salary: 180: 3 x 480 = 28.8 thousand rubles.
Example 4
The turner's tariff rate is 100 rubles/hour with a time limit of 1 hour/piece. 150 parts were produced in a month. Salary: (100: 1) x 150 = 15 thousand rubles.
Example 5
A team of three workers completed the specified amount of work in 360 hours. According to the terms of the contract, she is entitled to a payment of 16 thousand rubles. The tariff rates of team members and the actual time spent are presented in the table.
| FULL NAME | Tariff rate (RUB/hour) | Output (hours) |
| Alexandrov A. A. | 60 | 100 |
| Voronov V.V. | 45 | 120 |
| Karpov K.K. | 45 | 140 |
Alexandrov: 60 x 100 = 6000. Voronov: 45 x 120 = 5400.
Karpov: 45 x 140 = 6300.
The tariff salary of the entire team is 17.7 thousand rubles.
16 : 17,6 = 0,91.
3. The actual salary of workers is shown in the following table.
| FULL NAME | Tariff (rub.) | Coefficient | Salary (RUB) |
| Alexandrov A. A. | 6000 | 0,91 | 5460 |
| Voronov V.V. | 5400 | 0,91 | 4804 |
| Karpov K.K. | 6300 | 0,91 | 5736 |
| Total | 17700 | 16000 |
This scheme provides bonuses for production in excess of the established norm. Such additional payments are considered part of actual earnings and are set in relation to the salary.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=t1OZVOKMdRs
Example 6
6000 x 0.1 = 600 rub. – bonus.6000 600 = 6600 rub. - accrued salary.
The salary of employees servicing equipment is calculated using indirect piece rates and depends on the quantity of products manufactured.
Chord system
In this case, the deadlines for completing a set of works are estimated. The salary depends on the calculation of each type of work and the total amount of payments. The system provides bonuses for early completion of a task. It is used to calculate the salaries of employees involved in eliminating the consequences of accidents and other urgent tasks.
Example 7
(6 x (1.1-1) : 1) x 1.5 = 0.9 thousand rubles. – bonus.6 0.9 = 6.9 thousand rubles. - accrued salary.
The considered remuneration systems depend on the quantity of manufactured products. But according to the requirements of labor legislation, the salary should also depend on the quality of the work performed.
Therefore, in practice, the considered wage systems are differentiated depending on the quality of manufactured products, that is, combined systems are used.
For example, the tariff rate is calculated according to a direct piece-rate system, and bonuses are paid when work is performed in excess of the norm. To calculate salaries according to differentiated systems, the following are used:
- Tariff reference books of professions.
- Qualification characteristics.
- Workplace assessment report.
- Tariff rate.
- Tariff schedule.
- Coefficients of payment of allowances.
The tariff rate of remuneration in government agencies depends on the results of certification of tariffs from the “Unified Directory of Positions” (USD). It presents job characteristics and skill level requirements. It is used to rate work and assign categories to workers.
The directory presents tariff rates per unit of time depending on the category of worker.
The 1st category rate represents remuneration for low-skilled labor. Its size cannot be lower than the minimum wage, and the increasing coefficient is “1”. The calculation of the tariff rate of the 2nd category is carried out by multiplying the rate of the 1st category by the corresponding coefficient, etc. All these indicators, supplemented by regional coefficients of additional payments and allowances, are grouped into a tariff schedule.
Additional payment is monetary compensation for non-standard work hours, working conditions and labor intensity. A bonus is a payment that encourages an employee to improve their qualifications and skill level. The legislation provides for the following types of incentive payments:
- for working on a day off;
- overtime and night work;
- multi-shift mode;
- combination of positions;
- increase in the volume of work, etc.
To calculate each type of additional payment, an algorithm must be developed to determine deviations of actual working conditions from standard ones. That is, it is necessary to specify in the employment contract the night work schedule, instructions for each employee, etc. Then, by comparing the actual working conditions with the normative ones, calculate the amount of the bonus and make payments.
Unified tariff and qualification reference books
These reference books are necessary to regulate the work of representatives of the main working professions, management positions, employees and specialists within the enterprise. Using the provisions of a single directory, you can determine the suitability of an employee for the position held.
The document contains requirements for personnel categories, descriptions for each type of activity, a listing of the employee’s skills and knowledge, and a list of professions related to each type of work.
The unified directory of positions for managers, employees, and specialists contains requirements for the qualifications, knowledge and education of these categories of workers and explains their main job responsibilities.
Using the provisions of the directory, various types of professional activities are compared according to the complexity of their components. In addition, categories and qualifications are determined. This process is generalized into the concept of “tariffication”.
Salary in Belarus is derived from two indicators: salary and additional payments
Salary is the amount specified in the contract (“salary from... BYN”). It is derived from the tariff rate of the first category, additional payments for the position, professional level and promotion under the contract.
The tariff rate is indicated in the Unified Tariff Schedule (UTS); for 2019 it is 41 BYN. There you will also find coefficients that correspond to each position and profession in Belarus. According to the UTS, salaries are calculated for public sector employees. Commercial organizations and individual entrepreneurs can set their own tariff rates and pay salaries, but they often use the specified document.
It all depends on where you will work. For example, a teacher is traditionally considered a public sector employee, but if he gets a job not in a public school, but in a private educational center, he will be a representative of the commercial sector
An increase under a contract is a “bun” that is paid by the director as motivation for employees. The maximum amount is 50% of the salary, but the director is not obliged to pay exactly that much: even an increase of 0.5% is considered compliance with the terms of the contract.
Don't forget that taxes are deducted from your salary every month. The Population Social Protection Fund (SPSF) collects money (35% of salary) to finance social insurance benefits. With the help of the collected money, pensions, various types of benefits, and treatment costs for adults and children are paid. To insure workers against accidents at work and against occupational diseases, compulsory insurance has been introduced in Belarus since 2004 (0.5% in 2020). Income tax is also deducted from the salary - income tax (13%).
From the above figures, the “bare salary” is derived - the amount you will receive monthly. This is usually what young professionals receive. Next, let's talk about additional payments.
Tariffing procedure
Tariffication occurs by comparing the work performed at the enterprise with the list and examples of work contained in a single directory. For pricing purposes, an enterprise can develop and introduce internal lists of work, and use them along with the main ones.
Depending on the rank, the salary of an employee of an enterprise varies. To transfer an employee from rank to rank, in accordance with the internal regulations of the organization, a qualification commission is formed and convened, and its chairman is elected.
The employee, in the presence of members of the commission, passes a qualification exam, which includes testing theoretical knowledge and, in some cases, practical skills. If the exam is passed successfully, the employee receives a certain rank or moves from one to another, which is recorded in his work book. To rate the salaries of managers, as well as employees and specialists, a single directory of the specified positions is used.
Salary
This is the name given to that part of earnings that remains unchanged and is paid to an employee who has worked fully for a month, without temporary sick leave (sick leave), vacation days, or compensatory days. In other words, it can be called a stable part of the salary. And it will be accrued to the employee even with zero results of his activities.
The salary amount is specified in the employment contract; it remains unchanged until an additional agreement is signed with the employee, by which any changes can be made to the contract, including those related to salary changes.
The salary system has been successfully used in a wide variety of areas for a long time.
The official salary evokes associations with the state, which is completely understandable. It is used in the public sector. The salary is assigned to teachers and doctors, civil servants and military personnel, etc. This form can be considered very convenient and predictable when calculating wages. Experience and qualifications, living conditions and area, and other factors are taken into account, due to which, even with a small salary, earnings can increase significantly.
Institutions and organizations usually develop staffing schedules that reflect the range of salaries for employees of certain professions with different qualifications.
In part, this scheme is applicable in the field of sales, when a certain constant amount is established as part of the earnings, and depending on the results achieved, bonuses are paid, such as a percentage of a transaction or contract.
But the employee must understand that the salary specified in the contract is not the money that he will receive in person. After all, taxes are still withheld from this amount.
Tariff rates
The tariff rate is understood as a payment to an employee measured in monetary terms, taking into account his qualifications, nature and standards of work performed. Calculation of tariffs occurs both for time-based and piecework wages.
The tariff rate is a guarantee that the employee will receive money for work, provided that it is performed in good faith. Additional payments, bonuses, compensations are not included in the concept of “tariff rate”. Consequently, the tariff rate is the minimum wage for an employee, to which, in the process of wage formation and calculations, other components of wages are added.
Official salary and wage rate: what is the difference
The concept of official salary
For work performed, each employee receives a monetary reward. At the legislative level, it is determined that wages consist of at least three main components:
- the main part, formed on the basis of the salary (rate);
- compensation payments due to an employee for performing actions under certain conditions;
- incentive part, which is awarded as various additional cash bonuses in order to increase interest in the work performed.
As a rule, the most “weighty” part of the remuneration is the official salary (tariff rate), which, depending on the employee’s field of activity, ranges from 40 to 90% of the total level of all remuneration due.
Official salaries are displayed in the company's remuneration system. Their formation is carried out taking into account the hierarchy of positions, the complexity of the work performed in a certain area, the specifics of the functions assigned to the employee, the necessary skills and qualifications.
As a rule, the remuneration system provides for a range of official salaries for each position in order to be able to set the level of basic income for a new specialist, taking into account his professionalism.
Considering that the range of official salaries usually provides a gap of 5 to 20% between the upper and lower levels, you should be interested in the size of the basic remuneration during the job interview process.
The remuneration system is one of the most important elements of the relationship between employee and employer. Typically, tariff rate and salary are used. What is the difference? Many people who work for hire do not distinguish this concept, which can lead to conflict with the management of the organization.
What is salary
This is a fixed amount of remuneration per calendar month. If a person worked in accordance with the approved schedule for a month, he cannot be paid less than his salary. The amount is negotiated with each hired employee individually.
This is the amount of money that an employee will receive if he fulfills a certain labor standard. The rate depends on several factors:
- level of qualification of a particular specialist;
- working conditions, workplace equipment;
- duration of the time period (1 hour, day or month);
- provided equipment and tools.
Salary is the minimum amount an employee can receive
Difference between concepts
You can understand how a tariff rate differs from a salary by comparing these concepts according to a number of parameters:
- For the item that is being paid for. The salary is set if the amount of work, the time it takes to complete it and the complexity are difficult to calculate. The tariff rate is approved for the performance of strictly defined work. This can be the production of a given number of parts in accordance with technological conditions.
- By area of use. The salary is typical for the service industry. It is installed for economists, lawyers, managers, marketers, etc. Tariff rates are used to calculate income in the production sector - they are set for turners, mechanics, millers, etc.
- In most cases, the salary includes incentive payments for doing a good job. To receive more than the approved rate, the employee must exceed the norm.
- The salary is set for a calendar month. The rate can be hourly, daily or monthly.
- To size. The salary depends on how valuable the employee is to the company. If remuneration is calculated at the tariff rate, then payment is proportional to the work performed.
- The difference between salary and rate also lies in the procedure for establishing the amount of remuneration for an employee. The salary is fixed in the employment contract - the employee knows how much he will receive at the end of the month.
- Salary increase. If the organization uses tariff rates, then the indexation of payments affects all employees. An increase in salary is possible if the employee individually agrees with the head of the organization.
In most cases, the employee does not know the difference between the tariff rate and the salary. The employee is obliged to work in accordance with established standards throughout the entire working day. If the employer's demands are not met, the employee may be fired.
Payment at the tariff rate can be calculated for a certain time
Small commercial organizations set salaries for employees. When hiring, the applicant for the position and the company representative agree on the salary level and fix it in the contract. There is no single system for organization.
Large manufacturing companies introduce tariff schedules.
The base rate is approved, the salary of workers in various professions and positions is several of these values, as coefficients are applied.
For example, a worker can receive up to 6 tariff rates, a leading specialist - up to 15, and an enterprise director - up to 30. Wage differentiation is achieved through bonuses and personal allowances.
For some professions, piecework wages are introduced - remuneration depends solely on the results of work that can be physically measured.
The concepts considered do not include:
- bonuses;
- compensation payments (for example, for the use of your own equipment and tools);
- remuneration based on the results of the quarter or year;
- bonuses for working on weekends;
- compensation for harmful working conditions.
The amount of remuneration depends on the amount of remuneration fixed in the contract with the employer. A person should not focus on the salaries or tariff rates approved by the company, since such nuances concern accountants and managers more.
Tariff schedule and tariff category
The tariff schedule represents the ratio of tariff rates in accordance with the category. Designed in the form of a table for entering data. For different categories of work, tariff scales with different numbers of categories are provided.
Enterprises, as a rule, use a six-digit grid, where the first digit is the lowest and the sixth is the highest.
An enterprise, in accordance with its internal situation, can change the tariff scale towards increasing or decreasing its range. The instrument in question is used not only in relation to blue-collar professions. The tariff schedule is typical for calculating wages of public sector workers.
The tariff category shows the level of qualifications and skills of the employee and characterizes the complexity of the work he performs. The composition and size of an employee’s salary largely depends on the tariff category.
How to use coefficients to calculate salary
Application of coefficients when calculating salaries
In the process of forming basic remuneration, many companies use a system of coefficients that take into account the individual characteristics of the employee’s work, his level of workload, responsibility, and the complexity of the final result. The application of coefficients may vary. Let's look at the most common ways to calculate salary using coefficients.
The remuneration system is based on coefficients. In some cases, in order not to recalculate the entire salary grid, employers introduce a system of coefficients for each position.
In this case, the actual calculation of the official salary is based on the minimum salary of an unskilled worker of the company, which is initially charged at a coefficient of 1.0. In the future, when wages rise, the level of the base salary simply changes, and all other salaries are simply recalculated by mathematically multiplying this indicator by coefficients.
Individual coefficients for employees. Sometimes employers introduce individual increases for the most qualified employees in order to increase their remuneration level. This is done by order of the enterprise; further calculation of all remuneration is carried out based on the salary multiplied by the individual coefficient.
Regional odds. They are established at the legislative level (for the conditions of the Far North) or at the level of local constituent entities of the Federation (for example, Moscow, St. Petersburg).
The coefficient is calculated on the base level of remuneration. If other types of coefficients that increase his salary are applied to an employee, then the regional one is applied last. In other words, initially you multiply the base salary by all individual increasing coefficients, and then also multiply by the regional allowance.
If an employee's income level increases, the employer is not required to inform the employee about such changes. At the same time, if the employee’s remuneration level is to be reduced, he will have to be notified of this at least two months in advance. And if the employee does not agree with such changes, he may be fired as he refused to continue working under the new conditions.
The use of tariff systems for time-based and piecework wages
The main types of payroll calculation include:
- time payment;
- piece-work payment.
When calculating wages, the employer takes into account the following elements:
- grade of work;
- its characteristics;
- the standard time allotted for its implementation;
- tariff rate.
Calculation of piecework payment is made on the basis of the provisions of the unified tariff and qualification reference books. The most important component of work with piecework payment is production. One of the main disadvantages of piecework payment is the high probability that, in an effort to produce more products, the employee will not pay due attention to the quality of the finished product.
When calculating time wages, the amount of money an employee receives monthly depends on his rank. Also, when calculating time-based wages, the amount of time worked plays a significant role, which fundamentally distinguishes this form of payment from piecework.
Time-based payment requires mandatory staff pricing and clear timekeeping of the time spent by the employee on work. Today, most enterprises produce time-based wages, recognizing it as a more convenient type of payment for the parties to labor relations than piecework wages.
How to calculate your bet
Since calculating the cost of a working day means predicting the upcoming salary payment, it is necessary to understand the features of payment at an hourly rate. There are 2 main ways to calculate the tariff rate based on payment at an hourly rate:
- In order for an employer to be able to pay labor at an hourly rate, the monthly rate (or salary) must be divided by the number of hours spent at the workplace during a calendar month.
- The second option, how to calculate the hourly tariff rate from the salary, involves dividing the salary portion by the average monthly number of hours during the year (according to the calendar).
When the work schedule completely coincides with working days on the production calendar, information about the monthly rate, which has little difference from the salary, is taken into account.
Since calculating the cost of one working day is often required to determine standards and plan working time and costs, calculated rates are used in conditions of the possibility of rationing work and time to complete a given volume.
Since the tariff rate can be calculated taking into account information about the standards and volumes expected from each employee, if it is impossible to mathematically calculate the workload and digitize the results of labor, they often resort to salaries. This is how the issue of defining and accounting for the work of an office worker, an employee of the enterprise administration, and persons occupying management positions at the middle and senior level is resolved.
The issue of calculating payment according to the tariff rate or salary is resolved individually at each enterprise, taking into account the characteristics of work and areas of activity. If it is impossible to determine the monthly production rate, they resort to salary calculations. If the work schedule differs from the generally accepted 5-day workweek with an 8-hour day, and it is possible to determine a person’s production standards, they are inclined to pay at the tariff rate.
2020 zakon-dostupno.ru
Procedure for establishing tariff systems
Russian labor law in its provisions determines the procedure for establishing tariff systems. Regardless of the legal form of the organization and the type of its activity, the tariff payment system is established by local regulations, provisions of collective agreements, and agreements.
Also, when establishing tariff systems, the data of the unified tariff and qualification reference book are fundamentally taken into account, taking into account all the requirements of the labor legislation of the Russian Federation and other regulations mandatory for execution on the territory of the Russian Federation. The employer, when introducing tariff systems to the enterprise, must respect the rights of the employee and create decent working conditions.
Construction system and functions
So, the tariff rate is used to calculate the wages due to an employee for fulfilling labor standards. In practice, this value performs several functions:
- Allows you to equalize wages with the nature of work.
- Makes it possible to calculate the amount due to each employee, regardless of the work schedule and the labor organization system as a whole.
- Allocates a minimum portion of each employee's compensation.
- Systematizes payment for work activities in specific conditions (for example, in hazardous production or if the employee has a long work history, regular overtime, etc.).
The created tariff grid allows you to systematize all available positions and specialties, and then calculate the corresponding minimum wage for each of them. Plus, it allows you to justify why this employee is entitled to remuneration in this particular amount.
The employee’s length of service, his specific skills and other parameters necessary for his position will be taken into account.
When using the tariff system, several categories apply. On their basis, a tariff schedule for the enterprise is drawn up, according to which wages are paid to employees with different qualifications and job functions. The exact calculation procedure is fixed in the collective agreement of the organization, as well as in the regulations on remuneration.
Among other factors, market prices for a specific type of labor activity are also taken into account. Low-skilled work is valued much lower than highly qualified, intellectual work associated with increased responsibility.
Therefore, the amount of the tariff rate is first calculated based on the average salary for a specific type of work, and only then based on the financial capabilities of the organization. The state and municipal authorities are responsible for the current minimum wage indicator.
Based on the tariff schedule, it is determined which coefficient should be applied to each employee. The base category is the 1st category of the tariff rate - on its basis the amount that an unqualified employee will receive for work within a specified period of time is calculated. It is always equal to one.
An employee cannot receive remuneration less than the minimum wage established by law. It may increase at the discretion of the enterprise management.
Then there are 2, 3, etc. categories based on:
- Qualifications required to perform job duties in a specific position.
- Levels of professional suitability of employees.
The tariff coefficient demonstrates how many times the tariff rate of an employee of a particular category exceeds the minimum. Accordingly, with 2 digits the amount doubles, etc.
Salary elements
Salary is a combination of three elements:
- The fixed part is the salary (we will touch on this concept a little later).
- The variable part is modified in relation to the actions of a particular employee, the type and class of enterprise, and even geographic location. For example, residents of the northern regions must receive a special allowance due to the harsh living conditions. The variable part represents a certain portion of the salary (from 15 to 100%) based on their residence in a particular region.
- Additional payments are related to the season, production characteristics or performance of work that is not specified in the employee’s employment contract.
For example, employees of some enterprises are paid monetary compensation for food. Covering the cost of travel to your vacation destination is also an additional payment, because this happens extremely rarely.
Salary consists of three elements:
- fixed part;
- variable part;
- additional payments.
The fixed part is the salary, which will be discussed below.
Varies depending on the actions of a particular employee, type of business, or even geographic location. For example, residents of the northern regions receive a premium for harsh living conditions. In this case, the variable part each month will be a certain proportion of the salary, depending on the specific region: from 15 to 100%.
Additional payments may be associated with production features, seasonality, or the employee’s performance of work not specified in his employment contract.
For example, employees of some enterprises receive cash payments to pay for food. Covering the cost of travel to the vacation destination will also be an additional payment, since it rarely occurs.
Salary is a fixed amount of remuneration based on the assumption that the employee worked the entire calendar month (did not take sick leave or vacation). The salary is described in the employment contract, which the candidate is familiar with when applying for a job.
The salary does not include bonuses, allowances and compensation; it is taken as the basis for subsequent calculations of other indicators of remuneration.
For example, remuneration for overtime on official weekends, overtime in the evening, high performance indicators, harmful and dangerous working conditions, length of service, and others.
Salary and salary are different concepts.
The main difference between the amount of salary and salary is that salary is a fixed amount of remuneration for a specific position according to the work schedule. The salary amount is unchanged provided that the hired employee goes to work on all days of the calendar month.
The salary, in turn, may vary depending on the availability of bonuses and allowances, which add up to the salary amount. Thus, when calculating the salary, all compensations, bonuses are added to the salary amount and fines, if any, are subtracted.
The amount of the required salary is in the employment contract, but the salary is not indicated in any document when applying for the desired job.
In most cases, its amount may change in each subsequent month.
The salary amount is specified in the employment contract.
There are various forms and systems of remuneration for employees of enterprises. Why can’t we come up with one universal way to determine the amount of wages for the entire team?
Due to the fact that there are a large number of types of work performed, tasks set by higher management and sales standards for each individual profession, an equally large number of methods have been invented for calculating the amount of remuneration for workers. This is due to the fact that each enterprise has its own operating characteristics.
For example, an employee of a metallurgical plant works at a fixed rate, which can only change based on variations in the amount of time worked by the employee (if there were weekend days off and evening production hours).
The seller receives a well-deserved increase in income, directing more and more efforts and efforts towards increasing the customer base and increasing the sales of goods or useful services provided to them.
But there are also types of work in which we cannot measure the strength and applied professional efforts of each individual person. Then his income is stable and changes only when taking annual vacations, unexpected sick leave, and time off for family matters.
There are cases when an employer deliberately sets a low salary in order to force an employee to perform more standard operations, thereby increasing the size of the bonus and monthly income.
Workers who repair equipment, machines, replace outdated parts with new ones, receive an incentive to perform a higher quality work, receiving an additional payment to their income for the absence of frequent breakdowns of equipment important for the organization.
https://youtu.be/oLHsT0RxNlk
Distributors and employees in the field of network marketing and direct sales receive income based on the difference between the purchase price of products and the price of their sale to customers potentially interested in the product.
Allowances are taken into account when calculating the salary.
The minimum wage is set at the legislative level by the state. An employer will not be able to arbitrarily pay its workers less than the minimum wage.
This basic indicator is constantly and rapidly changing and is taken as the main basis when determining the final amount of fines, taxes levied, and mandatory payments.
Thus, it became extremely clear that salary and salary are completely different economic terms and concepts. The accountant’s salary consists of the amount of the salary and all kinds of bonuses, special incentive bonuses and mandatory compensation provided by the enterprise.
In this video you will learn about the difference between salary and compensation.
Select it and press Ctrl Enter to let us know.
Financial analyst practicing in the field of banking products and services. Loans, deposits, plastic cards - this is what I am interested in dealing with.
By occupying a work position and performing his duties day by day, a person receives a reward for his work. But there are different methods for calculating and paying salaries. Financial remuneration can be divided into parts, such as salary, advance, allowances, etc. It is necessary to understand that salary and salary are not the same thing. How do these concepts differ?
Go to Pay on holidays with a shift work schedule
Salary and wages... Concepts related to one economic category - employee remuneration. Are there differences between them or are they identical to each other? It is necessary to understand this issue in more detail.
Definition
The salary represents the amount of money that the employer initially offers to calculate the final amount. This indicator is reflected in the employee’s employment contract and is indicated in the order upon admission to work. Salary is the basic characteristic for the subsequent calculation of other indicators.
Salary is the amount of money that an employee receives after calculating the necessary allowances and withholding personal income tax. To calculate it, the salary amount is used, to which interest stipulated by the contract, bonuses and compensation, for example, for hazardous production, are added, and personal income tax is withheld.
Comparison
Why do they share? The most significant difference between them is that one indicator is calculated based on the other.
In other words, there is an established base salary for a certain position according to the staffing table, to which all interest and bonuses for quality work done are added and from which personal income tax, deductions for property damage or compensation for material damage caused are deducted.
https://youtu.be/O6FZf9GLhQU
The salary, according to current legislation, must be indicated in the employment contract, while wages are a calculated indicator that is not written down in any documents other than the salary payment sheet.
conclusions
- The salary amount is indicated in the documents when a person is hired; the salary is calculated after he has worked for a month at the enterprise or upon his dismissal from his position.
- Salary is a fixed figure in the staffing table of employees, which is used to calculate wages, and the salary indicator in no way affects the amount of salary.
- Salary is a basic, constant unit, and the salary consists of the salary and those percentages, bonuses and deductions that are provided for by law and the terms of the employee’s employment contract.
articles