What is a balance?
Balance is the difference between income and expenses calculated for the reporting period.
The balance can be positive, that is, greater than zero. This indicates that the enterprise's income exceeds its expenses. The balance can also be negative - less than zero. This indicates that expenses exceed income.
Balance is used in many areas. Its characteristics differ from the area in which it is used. The balance is relevant when calculating the following indicators:
- Trade balance.
- State balance of payments.
However, the indicator is mainly used in accounting. Its total value must be reflected in the amount of the funds balance at the beginning and end of the period that is the reporting period.
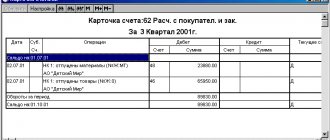
Key points when forming SALT on a count of 10
2 methods of analytical accounting of materials are discussed in great detail in Chapter. VII section 2 Methodological guidelines for accounting of industrial production, approved by order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated December 28, 2001 No. 119n. This document lays out the foundations on which you need to rely when organizing materials accounting. At the same time, it is necessary to make modern adjustments to the development of software products for accounting.
The main thing that must be taken into account when forming OSV:
- SALT is a summary report that should indicate:
- opening balance in quantitative and monetary terms;
- income in quantitative and value terms;
- consumption in quantitative and monetary terms;
- ending balance in quantitative and monetary terms.
- The SALT is first generated for each warehouse, then all statements for warehouses are collected into a consolidated SALT for the organization as a whole. Then, based on the summary report, synthetic accounting data is obtained, which is reflected in the reporting.
- Despite automated accounting, warehouse cards for materials accounting must be required. The posting of receipts and disposals in them is carried out by the financially responsible person in quantitative terms. A card is created for each item number.
- Primary documents on the movement of materials must be on paper, and they must have “live” signatures.
Functions
The balance is extremely important for analyzing the activities of an enterprise. It is required to find out the current financial condition of the company. Based on the indicator, the following points can be determined:
- profitability of the enterprise;
- stable functioning of the company;
- analysis of the organization's profitability for different periods.
For example, an enterprise recorded balance indicators throughout the entire period of its activity. The company has opened a new direction. Previously, the balance was closer to zero, but after the introduction of the new direction it began to grow sharply. This indicates that the innovation increased the profitability of the enterprise.
Example
On March 30, the organization received 500,000 rubles. On the same day, funds were spent on renting premises in the amount of 100,000 rubles. The opening balance on April 1 will be 400,000 rubles.
Accounting balance
The account balance will be the indicator under consideration. The difference between debit and credit will be the balance of the following types:
- Debit balance . Formed in a situation where the debit is greater than the credit. Displayed in the balance sheet asset.
- Credit balance . Formed in a situation where credit exceeds debit. Records the status of the sources through which funds are received. Displayed on the passive.
The difference between debit and credit (that is, between income and expense) can be zero. In this case, the account will be closed. In some cases, accounting has accounts that have both debit and credit balances.
When considering accounting for the reporting period, the following can be noted:
- Opening balance . Another name for it is incoming. This is the account balance. Calculated at the beginning of the reporting time. The calculation is made based on those transactions that were performed by the enterprise before the time in question.
- Debit and credit turnover . For calculations, only those operations that were performed at the time in question are taken.
- Balance for the period . It represents the total result of the enterprise’s actions during the reporting period.
- Closing balance . The second name is outgoing. Represents the balance available in accounts at the end of the month or other reporting time.
The reflection of the balance depends on its type. Calculations must be made regularly. This is important for tracking dynamics.
What is a balance?
Balance is a term that is used in accounting, economics, banking, as well as foreign economic activity. The word "balance" translated from Italian means remainder, final result, total or calculation.
In accounting, the balance is the total amount for each account . It is calculated as the difference between debit and credit over a certain period of time. The balance of foreign economic activity is the difference between imports and exports of goods.
Accounting balance
Accounting is an orderly system consisting of many components. The objects of accounting are all types of property of the enterprise and the sources of its formation. Each accounting object is reflected in a special accounting account.
Balance is an indicator of the balance of each account in monetary terms as of a certain date.
In particular, the balance of property accounts reflects the following information:
- the cost of the organization's fixed assets and intangible assets, minus accrued depreciation;
- the cost of materials, fuels and lubricants, spare parts, equipment, workwear and footwear, goods and packaging that are available;
- the balance of funds in ruble and foreign currency accounts of the organization, as well as in the cash desk of the enterprise;
- the amount of receivables from customers for products, goods or services shipped but not paid for;
- the amount of debt of suppliers that arose after the transfer of an advance against the upcoming delivery of goods and materials;
- the value of other assets of the enterprise.
The balance on the accounts for accounting sources of property formation shows:
- the amount of the organization’s own capital (authorized, additional, reserve capital and retained earnings);
- the amount of long-term loans and borrowings whose repayment period is more than 1 year;
- the amount of short-term loans and loans with a repayment period of less than 1 year;
- the amount of debt to counterparties for work, services and inventory;
- the amount of wages owed to the company's employees;
- debt on taxes and fees;
- other types of short-term debt.
Each account consists of analytical data. For example, the materials accounting account is divided into subaccounts: basic materials, fuels and lubricants, spare parts, household and production equipment, clothing and special equipment, containers. In turn, each subaccount consists of individual specific items of materials. The balance is displayed for each item.
Balance in foreign trade relations
The indicator is calculated based on relationships with foreign companies. The calculations take into account the following operations:
- Export indicators.
- Import amount.
- Cash receipts from foreign structures.
- Payments to foreign structures.
The trade balance is distinguished, as well as a similar indicator of the balance of payments.
Trade balance
Export and import are the basis of foreign trade. The difference between exports and imports is considered the balance. It must be calculated within the established time frame. The trade balance is divided into different types:
- Positive . This is relevant if the state sells more than it acquires. The balance will be positive if exports are greater than imports.
- Negative . This is relevant when imports are greater than imports. The balance will be negative if the government acquires more than it sells.
Let's take a closer look at the negative balance in the context of the state. This indicator means that the country has a lot of foreign products, but few goods of domestic producers.
Balance of payments
Typically this term is used in trade transactions between states. Almost all countries trade with each other. Relationships involve monetary transactions. The balance of payments is the difference between remittances received from abroad. Payments sent to other countries are also included in the calculation.
The balance can be either positive or negative. Let's consider the features of two varieties:
- Positive . The balance can be called positive if there is an excess of payments received from other countries over payments sent to other states.
- Negative . The indicator is called negative if there is an excess of payments from the state over receipts to the state.
That is, the division of the balance into positive and negative is accepted regardless of its type. Determining the type of balance occurs after deducting expenses from income.
Definition of the term
This concept characterizes the account balance at the end of the billing period (day, month, quarter, etc.). The value in question cannot be negative. Even in cases where the result of the equation has a minus sign, the final balance is not entered in the column, it (the sign) is not entered, and in such cases we are talking about debt. When considering active-passive accounts, the balance is read as a debit or credit and is recorded without a negative sign.
Example 1
The opening balance as of August 1, 2020 is 5,000 rubles. During the month, expenditure transactions amounting to 10,000 rubles were carried out, and a profit of 3,000 rubles was received. Thus the ending balance is:
- 5000-10000+3000 = -2000.
In fact, a negative balance was received, which is a violation of the rules; the value must be documented without it in the columns: debt or credit balance. Accordingly, the equation is missing one variable that reflects the organization’s interaction with the creditor.
How to determine the balance?
An accountant is required to keep records of the receipts and expenditures of funds at the enterprise. The specialist also conducts appropriate accounting. This is an extremely responsible job. A small omission can lead to problems during tax audits.
Transactions are reflected through accounting entries. Indicators are recorded using the double entry method. To do this, you need to open a special account.
Accounting accounts are distinguished by two columns: debit or credit. Double entry allows you to track the movement of funds.
There is a certain law of the balance sheet. The sum of all indicators in the accounts is equal to zero. That is, the difference between debit and credit indicators is zero.
As a result. Balance is a term that is relevant for any organization. Balance displays the remaining balance after deducting all expenses. That is, this indicator allows you to determine the unprofitability or profitability of the enterprise. The balance is used both in domestic trade operations and in foreign trade manipulations. When making calculations, the accounting period is important. The length of the period depends on the policy of the particular enterprise.
Lesson 4. Balance sheet and Vasya, or accounting for turnover and account balances
Today's lesson will be devoted to consolidating the material on the principle of double entry and accounting by accounts. As we already understood, an account is simply a group of funds, an accounting section. Just a convenient way to interpret and group financial information. In the last lesson, we drew up a comic balance using the example of Vasya’s creditor and the inventory value of “felt boots.” Let's take a closer look at these characters we love. We had the initial data: 100 rubles received. on loan from Vasya. Felt boots were purchased for 60 rubles. As a result, we got the balance:
In principle, it’s intuitively clear where everything came from, I think? Let us remember - Assets are means, Liabilities are the sources of their occurrence. We have felt boots and 40 rubles in our assets, they are real, you can touch them, in Passive - the source of these material benefits - that is, our beloved sponsor Vasya. However, intuition is intuition, but where does all this come from in accounting documents? Intuition is no excuse for recording in ledgers. Therefore, initially we record all business transactions with postings. Let me remind you, credit - where it came from, debit - what
appeared and
where
we put it: So where does the balance come from, which we intuitively wrote down right away?
In fact, in order to get a balance, you first need to calculate the turnover and balances for each individual account. In this case, we have the following accounts: Vasya Valenki Wallet
and
Seller
. We do not have any initial account balances, i.e. At first, according to the conditions of the problem, there was no money, no debts, no felt boots. In working accounting, order journals, statements and other documents are used to record turnover and account balances (if you use an accounting program, and you will use the program, since we live in the 21st century)) - the program will generate such journals and statements automatically , as soon as you demand it from her). In training, a certain layout of the order magazine is used, called an “airplane”.
A little different, of course, but there is a similarity. “Airplane” is the simplest sign of two columns - “wings”. You can already guess what is in each of the columns, I know! Certainly! In the left column - DEBIT In the right column - CREDIT Next, three large line sections: Opening balance (balances at the beginning) Turnovers for the period (there can be many sublines, as many transactions as there are as many lines) Final balance (balances at the end of the period) Here So:
“Airplane” is the simplest sign of two columns - “wings”. You can already guess what is in each of the columns, I know! Certainly! In the left column - DEBIT In the right column - CREDIT Next, three large line sections: Opening balance (balances at the beginning) Turnovers for the period (there can be many sublines, as many transactions as there are as many lines) Final balance (balances at the end of the period) Here So:
Something like a glider with numbers on the wings and tail. Is it clear where the turnover on the credit to the “Vasya” account came from?
Is it clear where the turnover on the credit to the “Vasya” account came from?
Of course, from the posting D——————K
Wallet——-Vasya——100 rub.
100 rubles were posted to the credit of the “Vasya” account. We sent them on the plane. Where do balances come from? Initial balances are taken from the problem conditions; for us they are equal to 0 for all accounts. The final balance in this example is calculated using the formula: Final balance = Initial loan balance + Credit turnover - debit turnover. Those. since the initial balance was equal to zero, the final balance was formed from the loan turnover. They borrowed 100 rubles, but haven’t returned anything yet - that means 100 rubles. We still owe money, and Vasya is our creditor. Now let's take another account: “Wallet”. The wallet was involved in as many as two business transactions - the receipt of money from Vasya and the payment for felt boots to the Seller. When money was received from Vasya, 100 rubles passed through the wallet account. by debit, and when paying to the seller - 60 rubles were spent. from a loan. These are the postings: Debit——————Credit
Wallet—————-Vasya———100 rub. — borrowed from Vasily Seller—————Wallet——60 rub. — we paid for the felt boots. Now let’s put them on the airplane.
Those. 100 rubles, received in the debit of the account, 60 rubles. left from the account credit, 40 rubles. left. In this case, the final balance is calculated using the formula: Final balance = Initial debit balance + Debit turnover - Credit turnover Let’s stop here, because Most likely, the formula for calculating the balance was a little confusing for everyone. Why are they slightly different, these formulas, for calculating the balance on the “Wallet” account and on the “Vasya” account? Why, in the case of Vasya, did we sum up the turnover on the loan, and in the case of the wallet, we sum up the debit, subtracting the loan? Because these accounts are different in meaning. Generally speaking, all accounts are divided into: ACTIVE PASSIVE ACTIVE-PASSIVE Active accounts are used to account for assets and only assets. These accounts take into account what can be touched, touched, spent, sold, etc. Money, materials, goods, other valuables. Passive accounts are used to record liabilities, i.e. SOURCES of assets. These are either loans and debts, or profits and other funds. Yes, yes, profit is a liability. For some reason, everyone is very surprised by this fact. Apparently, everyone thinks according to the principle - assets are good, so profit should be an asset :))) So, this is wrong. Money in accounts and in the cash register, felt boots and other valuables in warehouses - these are our assets. And profit is just a term; it can only be calculated, but cannot be spent. If we didn’t know how to count, we wouldn’t even know about its existence! But assets can be noticed even without knowing how to count. There are also active-passive accounts, i.e.
100 rubles, received in the debit of the account, 60 rubles. left from the account credit, 40 rubles. left. In this case, the final balance is calculated using the formula: Final balance = Initial debit balance + Debit turnover - Credit turnover Let’s stop here, because Most likely, the formula for calculating the balance was a little confusing for everyone. Why are they slightly different, these formulas, for calculating the balance on the “Wallet” account and on the “Vasya” account? Why, in the case of Vasya, did we sum up the turnover on the loan, and in the case of the wallet, we sum up the debit, subtracting the loan? Because these accounts are different in meaning. Generally speaking, all accounts are divided into: ACTIVE PASSIVE ACTIVE-PASSIVE Active accounts are used to account for assets and only assets. These accounts take into account what can be touched, touched, spent, sold, etc. Money, materials, goods, other valuables. Passive accounts are used to record liabilities, i.e. SOURCES of assets. These are either loans and debts, or profits and other funds. Yes, yes, profit is a liability. For some reason, everyone is very surprised by this fact. Apparently, everyone thinks according to the principle - assets are good, so profit should be an asset :))) So, this is wrong. Money in accounts and in the cash register, felt boots and other valuables in warehouses - these are our assets. And profit is just a term; it can only be calculated, but cannot be spent. If we didn’t know how to count, we wouldn’t even know about its existence! But assets can be noticed even without knowing how to count. There are also active-passive accounts, i.e. those that can take into account both assets and liabilities - for example, accounts with customers, suppliers, employees and others. If we owe them, then the account will have a credit balance, in other words, a liability. If they owe us, it will be our asset, the debit balance. Therefore, when calculating balances, credit is summed up with credit, debit is summed up with debit, then we look at whether the amount is greater - debit or credit, and subtract the smaller from the larger, so we get the final balance. In the example with “Wallet” - debit turnover is 100 rubles. on loan - 60 rubles. 100 is more than 60, so we subtract 60 from 100, and not vice versa. And in general, it is logical that a wallet cannot have a negative amount of money, right? That is, we repeat again - the balance is the remainder. We all know how to count the balances of our own funds in our wallets. From an accounting point of view, this is an inventory. If we decide to start planning and maintaining a family budget and take into account expenses, then we can also calculate the remaining money.
those that can take into account both assets and liabilities - for example, accounts with customers, suppliers, employees and others. If we owe them, then the account will have a credit balance, in other words, a liability. If they owe us, it will be our asset, the debit balance. Therefore, when calculating balances, credit is summed up with credit, debit is summed up with debit, then we look at whether the amount is greater - debit or credit, and subtract the smaller from the larger, so we get the final balance. In the example with “Wallet” - debit turnover is 100 rubles. on loan - 60 rubles. 100 is more than 60, so we subtract 60 from 100, and not vice versa. And in general, it is logical that a wallet cannot have a negative amount of money, right? That is, we repeat again - the balance is the remainder. We all know how to count the balances of our own funds in our wallets. From an accounting point of view, this is an inventory. If we decide to start planning and maintaining a family budget and take into account expenses, then we can also calculate the remaining money.
How? The amount that was at the beginning + The amount that we received - The amount that we spent = Balance (Final balance on the debit of the account) For active accounts there cannot be a credit balance. It cannot be -1000
rubles.
at the cash register or on your account. It cannot be - 5000
goods. If this happens, it’s immediately an error. How to calculate the credit balance using a real-life example? The simplest and most obvious example is a credit card. Credit card debt is the same liability, i.e. credit balance, the source of part of the money we spend. For example, we bought a TV for 20 thousand on credit. Consider that the liability is 20 thousand, according to the “Credit Card” account. They paid 5 thousand in a month. At the end of the month, the balance of the debt is already 15 thousand. That is. in life, calculating such processes using familiar methods is not a problem for us, and we will also get used to the principle of double entry ;)) However, let’s try our example. There are still accounts “Seller” and “Valenki”. The Valenki account is, of course, active, the Seller is “active-passive”. We look at the wiring and make up the planes:
With the “Seller”, our debit and credit turnovers mutually destroyed each other, i.e., as much as we received from the seller, we paid him as much, the balance is zero. Now let's collect what we got, all the leftovers, from the very beginning. We look at the planes and write out the final balance: Account “Wallet” - Final balance = 40 rubles. (D) Account "Valenki" - Final balance = 60 rubles (D) Account "Vasya" - Final balance = 100 rubles. (K) Account “Seller” - Final balance = 0 Let’s write it down as an asset and a liability. Debit is an asset, credit is a liability.
That's how we got those same 100 rubles.
in the balance sheet, describing the turnover for each account. Girls, if you are unaccustomed to this, this may be difficult, but don’t worry - we will reinforce and explain until we completely understand. If it’s completely unclear, try to rest, and then re-read with a fresh mind, perhaps it will suddenly dawn on you and a ray of light will dawn :)) I give you five whole days to master this lesson, because it is very important!!! If you understand this topic, you can consider that you are already an accountant :)) Because the main thing is to understand the principle, and the rest is details, details can be studied endlessly. Homework: 1. Copy into your notes an example from the lecture, starting from postings and ending with the balance sheet. Get into it. 2. In the last lesson, I gave you the task of describing some expenses and processes in your life in comic entries. Now try, based on the postings that you wrote, to create comic balance sheets. In order for your balances to come together, be very careful when performing.