Who is entitled to maternity benefits?
According to the Order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of the Russian Federation of December 23, 2009 No. 1012n “On approval of the Procedure and conditions for the appointment and payment of state benefits to citizens with children,” the following categories of citizens have the right to receive maternity benefits - the so-called maternity payments :
- women subject to compulsory social insurance in case of temporary disability and in connection with maternity, including women from among the civilian personnel of military formations of the Russian Federation located on the territories of foreign states, in cases provided for by international treaties of the Russian Federation;
- women dismissed due to the liquidation of organizations, termination of activities by individuals as individual entrepreneurs, termination of powers by notaries engaged in private practice, and termination of the status of a lawyer, as well as in connection with the termination of activities by other individuals whose professional activities are in accordance with federal laws subject to state registration and (or) licensing during the twelve months preceding the day they are recognized as unemployed in the prescribed manner;
- women studying full-time on a paid or free basis in professional educational organizations, educational organizations of higher education, educational organizations of additional professional education and scientific organizations (hereinafter referred to as full-time students in educational organizations);
- women performing military service under a contract, serving as privates and commanding officers in internal affairs bodies, in the State Fire Service, in institutions and bodies of the penal system, in agencies for control of the circulation of narcotic drugs and psychotropic substances, in customs authorities ;
- the women mentioned above when they adopt a child (children) under the age of three months.
State support
Of course, improving the demographic situation in the country is one of the primary tasks. That is why the state is trying to create the most favorable conditions for this. Having one child is quite energy- and financially costly. And when there are two or even three children, this turns into a real challenge. Because of this, support from the state is extremely important.
There are several material ways to support various families, based on their condition. Let's look at specific examples:
- The first can be allocated to benefits for pregnancy and subsequent childbirth.
- There is also one-time financial support for women who register with a medical institution in the early stages of pregnancy.
- Another one-time benefit can be received directly after giving birth to a child.
- It is possible for parents to apply for a child care allowance, which is paid monthly.
Such a wide range of financial support options really stimulates fertility. Often the amounts that parents receive are sufficient for the purposes for which they are allocated. Let's talk in more detail about the first benefit.
Who is not entitled to maternity benefits?
Maternity benefits (maternity benefits) are not provided:
- citizens of the Russian Federation, stateless persons, citizens of foreign states whose children are fully supported by the state;
- citizens of the Russian Federation, stateless persons, citizens of foreign states deprived of parental rights;
- citizens of the Russian Federation who have decided to permanently reside outside the Russian Federation;
- a woman who refused maternity leave and, accordingly, did not receive a certificate of temporary incapacity for work;
- unemployed women who are not registered with the employment center;
- correspondence students who do not have an employment relationship and are not registered with the employment center.
Is personal income tax withheld and paid on sick leave?
The basis for the absence of personal income tax is that these benefits are state compensation. They are paid to the Social Insurance Fund. Since 2020, control over benefit payments has been transferred to the Federal Tax Service.
IMPORTANT! Any entrepreneur must make payments for labor and child care. This also applies to individual entrepreneurs who have chosen a special taxation regime: imputation, simplified.
Let's look at the various features of calculating benefits:
- If an employee works in several places part-time, each company must pay her money. Benefits are issued in a standard manner.
- The funds in question are not subject to personal income tax or insurance premiums. That is, the woman receives payments in full.
- Benefits will be paid only if the woman is officially employed. If she works unofficially, then only the employer makes the decision on payments. If he doesn’t pay anything, the employee won’t even be able to sue him.
The amount of benefits is determined individually in each case, depending on the worker’s salary.
To receive payments, the employee must provide the employer with a corresponding application, as well as a certificate of incapacity for work. Papers must be submitted no later than six months from the date of the end of the leave under the BiR. If an employee wants to go on maternity leave later than the date specified in the certificate of incapacity for work, the employer must provide it from the date specified in the application.
IMPORTANT! It is not recommended to make payments under B&R for the period during which the employee actually worked. This is due to the fact that the Social Insurance Fund is unlikely to reimburse these expenses to the entrepreneur.
FOR YOUR INFORMATION! Tax exemption is due to the fact that the entrepreneur, when issuing benefits, does not spend the funds of his company. All expenses are reimbursed by the state. This is a measure to protect pregnant women, one of the social benefits.
The answer to the question of whether sick leave is subject to personal income tax is contained in paragraph 1 of Art. 217 Tax Code of the Russian Federation. Temporary disability benefits are excluded from the list of payments not subject to personal income tax. Since the document confirming the employee’s incapacity for work is a certificate of incapacity for work, personal income tax is calculated from the sick leave.
Let us recall payments that are not subject to personal income tax (Clause 1, Article 217 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation):
- lump sum maternity benefit;
- monthly allowance for child care up to 1.5 years;
- monthly compensation for child care up to 3 years old.
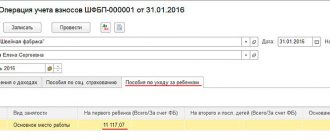
How is maternity benefit calculated?
Maternity benefits (maternity benefits) are accrued to women on so-called maternity leave, which amounts to:
- 140 days – for uncomplicated pregnancy;
- 156 days – in case of severe labor;
- 194 days – for multiple pregnancy.
The start of maternity leave depends on the number of babies the expectant mother is expecting:
| Pregnancy | Start of maternity leave |
| Singleton pregnancy | 30 weeks pregnant |
| Multiple pregnancy | 28 weeks pregnant |
To calculate maternity benefits, the following are taken as a basis:
- average daily earnings of a pregnant woman;
- duration of vacation.
To calculate the average daily earnings, a woman’s earnings are taken for 2 years (730 days) preceding the year when maternity leave was granted (Federal Law of December 29, 2006 No. 255-FZ “On compulsory insurance in case of temporary disability and in connection with with motherhood"). All employee income that is subject to calculation when paying insurance premiums to the Federal Social Insurance Fund of the Russian Federation and the Federal Compulsory Medical Insurance Fund is taken into account.
Thus, the formula for calculating average daily earnings will be as follows:
SDZ = ZP2 / (730 – ID*)
SDZ – average daily earnings
ZP2 – earnings for 2 years
ID* – excluded days
* In accordance with clause 3.1 of Article 14 of the Federal Law of December 29, 2006 No. 255-FZ, when calculating the average daily earnings for calculating maternity benefits, days that fell in the following periods are excluded from the number of days for the specified period:
- period of temporary disability, maternity leave, parental leave;
- the period of release of the employee from work with full or partial retention of wages in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation, if insurance contributions to the Federal Social Insurance Fund of the Russian Federation and the Federal Compulsory Medical Insurance Fund were not accrued on this wage.
After calculating the average daily earnings, it is necessary to determine the amount of the daily benefit, which depends on the length of service of the pregnant woman (Article 11 of the Federal Law of December 29, 2006 No. 255-FZ):
| Experience of a pregnant woman | Benefit amount |
| 6 months or more | 100% of average earnings |
| up to 6 months | Does not exceed the minimum wage for a full calendar month, taking into account the regional coefficient |
After calculating the amount of daily earnings, you can begin to calculate maternity benefits:
PBiR = DP * KDDO
PBiR - maternity benefit
DP – daily allowance (average daily earnings)
KDDO - number of days of maternity leave
When calculating maternity benefits, there is a maximum threshold limited by the maximum amount of income subject to calculation of insurance premiums. This limit threshold is determined by clause 3.2 of Art. 14 of the Federal Law of December 29, 2006 No. 255-FZ and amounts to:
- 2017 – 755,000 rubles;
- 2020 – 815,000 rubles.
Thus, the maximum average daily earnings will be (755,000 + 815,000) / 730 = 2,150.68 rubles .
Example 1:
Pregnant employee Matveeva M.M. On May 10, 2020, she provided a certificate of temporary incapacity for work, which indicated the duration of maternity leave as 140 days. Experience of Matveeva M.M. 3 years 8 months. There were no periods of temporary disability, maternity leave, or parental leave over the previous 2 years.
Income amounted to:
2017 – 550,000 rubles
2020 – 620,000 rubles
Average daily earnings (550,000 + 620,000) / 730 = 1,602.74 rubles.
The daily allowance will be 1602.74 rubles.
The benefit amount is 1602.74 * 140 = 224383.60 rubles.
Example 2:
Pregnant employee Zaitseva Z.Z. On May 10, 2020, she provided a certificate of temporary incapacity for work, which indicated the duration of maternity leave as 194 days. Experience of Zaitseva Z.Z. was 4 months. There were no periods of temporary disability. The average daily earnings will be calculated based on the current minimum wage. In accordance with Art. 133 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation from 01/01/2020, the minimum wage is 11,290 rubles.
The average daily earnings will be 11,290 / 30 = 376.33 rubles.
The daily allowance will be 376.33 rubles.
The amount of maternity benefit is 376.33 * 194 = 73008.02 rubles.
Reflections of benefits in certificate 2-NDFL
For a pregnant employee, receiving B&R benefits is income. But should the tax agent-employer include such amounts in the certificate in Form 2-NDFL? Since maternity benefits are excluded from payments subject to income tax, there is no need to enter information about B&R benefits in 2-NDFL.
If a pregnant woman does not receive any other types of payments from the organization in the reporting year, with the exception of maternity benefits, there is no need to submit certificates to the Federal Tax Service to the accounting service. But if an employee works part-time, she needs to make a choice between salary and benefits, since social insurance requirements prohibit the simultaneous receipt of wages and maternity benefits.
The 2-NDFL certificate indicates only those payments that are taxable. If the benefit is exempt from personal income tax, then it does not need to be taken into account in the certificate. That is, the document does not need to indicate information about:
- B&R benefits;
- benefits for caring for a child up to 1.5 years old.
If the employer pays the woman a certain amount above the established level of benefits, it must appear in the certificate, since it is taxed.
Is maternity benefit subject to personal income tax?
Maternity benefits are tax-free benefits. At the same time, the calculation of this benefit is quite clear, established by the legislation of the Russian Federation. At the same time, some employers express a desire to support the expectant mother and make additional payments to the specified benefit. These payments can no longer be considered as a state benefit, but as additional income for a pregnant woman, which is necessarily subject to taxation.
Example:
Pregnant employee Mamaeva M.M. On May 10, 2020, she provided a certificate of temporary incapacity for work, which indicated the duration of maternity leave as 194 days. Experience Mamaeva M.M. was 4 months. There were no periods of temporary disability. The average daily earnings will be calculated based on the current minimum wage. In accordance with Art. 133 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation from 01/01/2020, the minimum wage is 11,290 rubles.
The average daily earnings will be 11,290 / 30 = 376.33 rubles.
The daily allowance will be 376.33 rubles.
The amount of maternity benefit is 376.33 * 194 = 73008.02 rubles.
This amount is not subject to personal income tax.
Employer Mamaeva M.M. All pregnant employees receive additional payments in the amount of 50,000 rubles. This payment will be subject to personal income tax.
Thus, to pay Mamaeva M.M. the following amount is due:
73008.02+(50000 – (50000*13%))=116508.02 rubles.
What period and date of personal income tax withholding are established for sick leave and vacation pay?
The deadline for paying sick leave tax from 2020 is no later than the last day of the month in which the benefit was paid.
By the way, a similar procedure and payment deadline is provided for personal income tax on vacation pay: the tax should be withheld and transferred to the budget no later than the last day of the month when the vacation pay was issued.
By law, any monetary income is taxed. Is the income of individuals (abbreviated as personal income tax) paid as maternity leave taxed? Employees and their employers are certainly interested in the question: will certain tax levies be made on maternity benefits?
DETAILS: Is sick leave paid on maternity leave?
Of course, no one wants this money to be deducted by the authorities. Women want to receive all payments without any deductions that reduce the total amount of vacation pay. In this regard, the question arises: “If tax levies cannot be circumvented, how can they be reduced?”
Such questions are best answered by a qualified lawyer, but in this case you can delve into some of the subtleties on your own, especially since the legislative norms quite clearly state what happens to vacation pay, whether they are taxed or not. In any case, the answer to the question of whether they are taxed is clear - withholding personal income tax from maternity leave is unacceptable. Maternity benefits are not taxed because it is against the law.
Despite the fact that it is illegal to collect personal income tax from maternity leave, there are cases when taxation of cash payments received on maternity leave still occurs. If, despite all this, the accountant at the enterprise withheld a certain amount as tax, it must subsequently be returned to the employee.
The only exception is taxes aimed at subsidies for temporary inability to carry out labor activities. That is, the exception is when you are on forced sick leave with a sick child. Unlike other payments, maternity benefits are not subject to any taxes also because these benefits are fully provided by the state.
Questions and answers
- Do I understand correctly that if we decide to make an additional payment to a pregnant employee on the occasion of maternity leave, then we will pay personal income tax on this amount?
Answer: Yes, that’s right - personal income tax is not paid for maternity benefits, but tax will have to be paid on additional payments made by the employer.
- We want to give a gift to an employee who is going on maternity leave. Will there be a question of paying personal income tax on a gift?
Answer: Yes, the issue of paying personal income tax will arise if the value of the gift exceeds 4,000 rubles.
Is sick leave subject to personal income tax in Russia in 2020?
But personal income tax will not be charged on sick leave that was opened due to the adoption of a child.
An employer who makes an additional payment to the transferred amounts must understand that the bonus will already be taxed, but up to an amount of 50 thousand rubles can be processed as financial assistance, with which personal income tax also does not need to be paid. Among employees, there are two types of labor cooperation with the employer.
There are relationships based on an employment contract, which is considered official employment, as well as with the conclusion of a civil law contract, which is not. In the first case, tax is withheld from the benefit, and the second point implies that the employee cannot receive temporary disability benefits, and accordingly, it will not be possible to collect tax from him. Also, the amounts differ according to the source of payments, because the first three days are paid by the employer, and all other days are financed from the Social Insurance Fund.
What is income tax?
Personal income tax is a burden that falls on the shoulders of individuals. In particular, many payments that an employer provides to its employees are subject to this tax.
After calculating the amount of benefits due for payment, tax is calculated from it at a rate of 13 percent . The calculated tax amount is paid by the employer for the employee to the budget. The worker is given the difference between the accrued and withheld personal income tax. That is, the employee experiences monetary losses, but the company does not incur losses.
Not all amounts assigned by the employer are subject to personal income tax; certain amounts are exempt from this burden. Their list is given in Russian tax legislation, which also contains explanations regarding the imposition of maternity income tax.
azbukaprav.com
Social guarantees of the state
Art. 255 of the Code regulates that women may be granted maternity leave of the following duration:
| When provided | For how many days |
| Before childbirth | 70 calendars days (if two or more children are born - 84 calendar days) |
| After childbirth | In general - 70 days, if the birth is considered complicated - 86 days, if two or more children are born - 110 days |
The grounds for a woman to go on maternity leave are:
- her written statement addressed to the head of the organization;
- a certificate of incapacity for work issued in accordance with the procedure approved by law.
The procedure for issuing sick leave for maternity leave is stated in Order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development No. 624n.
Order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of Russia dated June 29, 2011 N 624n
Paragraph 46 of this Order states that a sick leave certificate is issued by an obstetrician-gynecologist or a general practitioner; in the absence of the latter, a medical assistant can issue a sick leave certificate.
The sheet is issued in one document at once and confirms the woman’s right to leave for a total duration of 70 days before the birth occurs and 70 days after the birth (in general).
General information about personal income tax
The term “personal income tax” is an abbreviation for the concept of “personal income tax.” In accounting practice, this tax is taken from all income received, which will be the object of such a taxation procedure. It is calculated for each reporting period and paid to the state budget. Calculations and payments must be made by the personal income tax payer, who is the tax agent or the employee himself.
Let's look at what basic profit the personal income tax is taken from:
- Wage.
- Various types of rewards.
- Gifts (including prizes).
- Payments due for temporary disability (sick leave).
- Sold property.
Nuances of personal income tax payments
What nuances should you know in order to accurately calculate and make personal income tax payments? Experts advise paying attention to the following points:
- The tax reporting period is 1 year - Tax Code, Article No. 216 and Article No. 55, paragraph 1.
- After the end of the reporting period, to calculate personal income tax, it is necessary to determine:
- tax base;
- the amount of tax to be paid.
- Payers have every right to apply tax deductions - Tax Code, articles No. 218-221.
- For those who carry out calculations on their own, it is mandatory to submit declaration documentation to the local tax service - Tax Code, articles No. 227-229.
- For tax agents, special document forms have been developed in which all the necessary information about workers and their income is entered - Tax Code, Articles No. 24 (clause 4) and No. 230 (clause 2).