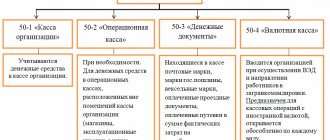
The man paid for the electrician’s work immediately after completion according to the tariffs established by the HOA. Here's what needs to be shown on the balance sheet:
- debit 50, credit 62 - receiving payment from the tenant - customer;
- debit 62, credit 90-1 – recognition of funds received as income;
- debit 90-3, credit 68 – VAT accrual on the cost of work performed;
- debit 20-2, credit 70 – calculation of piecework wages for a full-time electrician;
- debit 20-2, credit 69 – calculation of insurance premiums for the amount of labor remuneration;
- debit 90-2, credit 20-2 – write-off of the cost of work performed;
- debit 90-9, credit 99 - reflection of the financial result - profit.
In addition to the listed operations, the HOA’s balance sheet will reflect the costs of repairing common residential property and accounting for the organization’s fixed assets.
The legislative framework
All accounting in the HOA is carried out in compliance with the following acts and regulations:
- letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation No. 03-11-04/2/58;
- position No. 43n;
- position No. 34n;
- chart of accounts No. 94n;
- Order of the Ministry of Finance No. 66n;
- Tax code.
These are the main regulations necessary for carrying out accounting activities. All HOA records are kept in compliance with these documents. HOAs have their own accounting features. For example, accounting in HOAs and housing cooperatives have significant differences. The differences arise due to the fact that the HOA does not make a profit from its activities. And if income exists, then it is used only to achieve the goals set for the partnership.
The HOA accountant has many tasks, including detailed accounting of possible debts of residents, fees, additional expenses, etc. And therefore, accounting uses a huge number of different entries and subaccounts, which only a good specialist can handle.
The advantage of a homeowners' association is that it consists of residents of an apartment building, which means that they can influence the financial policy of the organization. However, in practice, one of the homeowners rarely acts as an accountant.
Responsibilities of the chief accountant
Bookkeeping is the main responsibility of an accountant working in an organization.
But besides this, there are a number of other powers that a specialist has:
- organization of accounting;
- formation of the company’s accounting policy based on the specifics of its core activities;
- preparation and approval of work plans, document forms, etc.;
- organization of internal control over the execution of business transactions;
- formation of accounting information systems;
- providing the necessary data to external and internal users;
- ensuring timely transfer of taxes to the budget;
- payment of insurance premiums;
- implementation of financial analysis and tax policy;
- control over cash and financial discipline;
- registration of documents in connection with shortages or illegal spending of funds of owners.
This is a short list of responsibilities that the chief accountant in a management company must perform. Based on this, we can conclude that they are no different from the responsibilities of such specialists in other organizations.
https://youtu.be/waXNQOKjgYg
Accounting policy of HOAs under the simplified tax system
Everything related to accounting in a partnership is the responsibility of the chief accountant.
His task is to prepare an accounting policy plan and coordinate it with the chairman of the partnership within 3 months after the creation of the association. And in the future, all activities of the specialist must be carried out in accordance with this policy.
If you need to make changes to the accounting policy, then for this you will have to change certain requirements specified in the constituent documents. Or for the organization to change the specifics of its activities. And such amendments can only be made at the beginning of the financial year.
In addition to the accountant, the chairman of the board is also responsible for the accounting policies of the organization. He is obliged, first of all, to monitor the deadlines for completing and submitting reports on the financial activities of the HOA.
If an organization uses the simplified tax system, then the following points must be recorded in the accounting policy:
- assessment of the organization's assets, as well as liabilities;
- inventory of HOA property;
- chart of accounts;
- development and implementation of primary documentation forms;
- methods used to process information;
- control of economic activities.
Under the simplified tax system, the organization must comply with the following conditions:
- the object of taxation is income;
- money received into the organization’s account is recognized as profit;
- contributions of participants and donations are not considered as income of the partnership;
- the creation of separate accounts for capital or current repairs is not considered profit.
Taxes for HOAs are based on the calculation of revenues from the services provided by the organization. All expenses incurred by the HOA to maintain or repair the property are tax deductible. The exception is those expenses that are not included in the constituent documents.
To avoid confusion, it is necessary to separate different types of income and expenses. The form of such accounting is approved by the chairman of the HOA.
As for HOA insurance premiums, with “simplification” the organization has the right to receive benefits (Federal Law No. 212). At the same time, income from the management of common property (taken into account under the simplified tax system) must be at least 70%. If the activities of the partnership are financed only by membership fees, then insurance premiums will have to be paid in full.
How to do accounting in an HOA: step-by-step instructions
All issues that the chief accountant of the HOA must resolve are divided into three conditional groups:
- performing basic work;
- formation of plans and budget of the organization;
- making report.
Instructions for maintaining accounting consist of the following steps:
- drawing up accounting policies;
- determination of the estimate;
- keeping records of business activities;
- determining the budget.
Chart of accounts
Charts of accounts are an important component of accounting in any enterprise. They are necessary for detailing information on profit and expense items. The specialist must maintain such accounts in accordance with established rules.
For example, indicate:
- wages and taxes;
- overhead expenses;
- MKD maintenance costs;
- expenses for major repairs, creation of a reserve fund, etc.
Very often the following question arises: “We keep records in the HOA, what should we include in income under the simplified tax system?”
As for income, in the HOA this includes:
- cash receipts from partnership participants (contributions);
- Payment of utility services;
- subsidies that are allocated to organizations for the maintenance of common property;
- various types of donations;
- income that the HOA receives from renting out common property.
These are standard items that a partnership’s income and expense budget should include.
Accounting for business transactions in HOAs
All activities of the partnership are aimed at achieving specific goals. But the specificity of accounting is that all activities must be divided into those that are subject to taxation and those that are not. Naturally, if the accountant uses the simplified tax system.
Business activities, income from which are subject to certain taxes, include:
- performing work of members of the organization that does not relate to the maintenance of apartment buildings;
- provision of premises for rent;
- sale of services;
- other income taken into account in Articles 249, 250 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Article 249. Income from sales
- For the purposes of this chapter, income from sales includes proceeds from the sale of goods (works, services) both of one’s own production and those previously acquired, and proceeds from the sale of property rights.
- Sales proceeds are determined based on all receipts associated with payments for goods (work, services) sold or property rights expressed in cash and (or) in kind. Depending on the method of recognition of income and expenses chosen by the taxpayer, receipts related to payments for sold goods (work, services) or property rights are recognized for the purposes of this chapter in accordance with Article 271 or Article 273 of this Code.
- The specifics of determining sales income for certain categories of taxpayers or sales income received in connection with special circumstances are established by the provisions of this chapter.
Income is taken into account regardless of the form in which it was received - in kind or in cash.
Payments for utilities provided by the HOA are also subject to taxes.
If the organization’s constituent documents indicate that it has the right, on behalf of residents, to enter into contracts with suppliers for the receipt of utility services, then intermediary fees are taken into account as income.
How to fill out a book of business transactions?
All business transactions must be registered. For this purpose, there is an accounting book consisting of certain tables.
An example of filling out a book of accounting of business transactions of an HOA:
If the HOA uses the simplified tax system, then all expenses of the organization are indicated in the “Debit” column. As an example, you can use the membership fees paid by all members of the association. The accountant carries out the operation using subaccount 01-1. The balance is zero, as is the account 86.
Then he makes payments to suppliers. The debit position is 60, and the credit position is 51. This means that the payment was made and credited to the bank. At the end of the table, the transfer of funds 86-1 to account 60 (Suppliers) is also indicated.
How accounting is carried out in HOAs and what is regulated, accounting policies under a simplified taxation system.
An accountant in a homeowners' association is one of the main positions, since accounting is the responsibility of the organization.
Otherwise, the partnership simply will not be able to fulfill its functions.
In this article we will talk in detail about how to keep accounting records in an HOA?
How are financial receipts processed?
Calculation of payments:
- Receipt of account 76 “Settlements with various creditors and debtors” subsection “Settlements with residents” credit of account 86 “Targeted financing” - payment by residents of membership fees (aka rent).
- Receipt of nominal account 76 sub-account “Settlements with tenants” credit of account 76 sub-account “Settlements for utility bills” – calculation of payment for utility bills.
Inflow of funds:
- Receipt of account 51 “Current accounts” credit of nominal account 76 sub-item “Settlements with tenants” – funds credited to the account;
In order to pay utility providers, money is spent as follows:
- Receipt of account 86 debt of account 60 “Settlements with service providers and contractors”;
If there is a need to pay for the services provided by other organizations, then the entry is made as follows:
- Income of nominal account 60 debt of account 51;
We should not forget that proceeds also go to pay for business needs:
- Salaries for electricians, mechanics and other workers;
- Purchase of household materials;
Then the wiring should look like this:
- Receipt of invoice 86 credit of invoice 70 “Settlements with personnel for wages” - salaries to employees.
- Receipt of account 50 “Cash” debt of account 51 – receipt of money from the bank.
- Receipt of nominal account 10 “Materials” credit of account 50 – purchase of household supplies for cash.
The legislative framework
All accounting in the HOA is carried out in compliance with the following acts and regulations:
- letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation No. 03-11-04/2/58;
- position No. 43n;
- position No. 34n;
- chart of accounts No. 94n;
- Order of the Ministry of Finance No. 66n;
- Tax code.
These are the main regulations necessary for carrying out accounting activities. All HOA records are kept in compliance with these documents. HOAs have their own accounting features. For example, accounting in HOAs and housing cooperatives have significant differences. The differences arise due to the fact that the HOA does not make a profit from its activities. And if income exists, then it is used only to achieve the goals set for the partnership.
The HOA accountant has many tasks, including detailed accounting of possible debts of residents, fees, additional expenses, etc. And therefore, accounting uses a huge number of different entries and subaccounts, which only a good specialist can handle.
The advantage of a homeowners' association is that it consists of residents of an apartment building, which means that they can influence the financial policy of the organization. However, in practice, one of the homeowners rarely acts as an accountant.
Postings under the simplified tax system
If the company uses a simplified system, then there will be no postings D68 K19 and D90/3 K68 (these are postings for the deduction and calculation of VAT ). This rule applies if, under OSNO, the management company has VAT benefits.
The main advantage of accounting in a management company using the simplified tax system is that organizations do not pay VAT and income tax . Instead, they pay a separate fee to use the simplified system. Its size depends on the subject of taxation and is 5% or 15%.
When using OSNO UK, it also has VAT benefits. For example, an organization is exempt from payment when providing utilities, carrying out work on the maintenance and repair of apartment buildings with the involvement of relevant organizations.
Accounting policy of HOAs under the simplified tax system
Everything related to accounting in a partnership is the responsibility of the chief accountant.
His task is to prepare an accounting policy plan and coordinate it with the chairman of the partnership within 3 months after the creation of the association. And in the future, all activities of the specialist must be carried out in accordance with this policy.
If you need to make changes to the accounting policy, then for this you will have to change certain requirements specified in the constituent documents. Or for the organization to change the specifics of its activities. And such amendments can only be made at the beginning of the financial year.
In addition to the accountant, the chairman of the board is also responsible for the accounting policies of the organization. He is obliged, first of all, to monitor the deadlines for completing and submitting reports on the financial activities of the HOA.
If an organization uses the simplified tax system, then the following points must be recorded in the accounting policy:
- assessment of the organization's assets, as well as liabilities;
- inventory of HOA property;
- chart of accounts;
- development and implementation of primary documentation forms;
- methods used to process information;
- control of economic activities.
Under the simplified tax system, the organization must comply with the following conditions:
- the object of taxation is income;
- money received into the organization’s account is recognized as profit;
- contributions of participants and donations are not considered as income of the partnership;
- the creation of separate accounts for capital or current repairs is not considered profit.
Taxes for HOAs are based on the calculation of revenues from the services provided by the organization. All expenses incurred by the HOA to maintain or repair the property are tax deductible. The exception is those expenses that are not included in the constituent documents.
To avoid confusion, it is necessary to separate different types of income and expenses. The form of such accounting is approved by the chairman of the HOA.
As for HOA insurance premiums, with “simplification” the organization has the right to receive benefits (Federal Law No. 212). At the same time, income from the management of common property (taken into account under the simplified tax system) must be at least 70%. If the activities of the partnership are financed only by membership fees, then insurance premiums will have to be paid in full.
How to do accounting in an HOA: step-by-step instructions
All issues that the chief accountant of the HOA must resolve are divided into three conditional groups:
- performing basic work;
- formation of plans and budget of the organization;
- making report.
Instructions for maintaining accounting consist of the following steps:
- drawing up accounting policies;
- determination of the estimate;
- keeping records of business activities;
- determining the budget.
Chart of accounts
Charts of accounts are an important component of accounting in any enterprise. They are necessary for detailing information on profit and expense items. The specialist must maintain such accounts in accordance with established rules.
For example, indicate:
- wages and taxes;
- overhead expenses;
- MKD maintenance costs;
- expenses for major repairs, creation of a reserve fund, etc.
Very often the following question arises: “We keep records in the HOA, what should we include in income under the simplified tax system?”
As for income, in the HOA this includes:
- cash receipts from partnership participants (contributions);
- Payment of utility services;
- subsidies that are allocated to organizations for the maintenance of common property;
- various types of donations;
- income that the HOA receives from renting out common property.
These are standard items that a partnership’s income and expense budget should include.
Accounting for business transactions in HOAs
All activities of the partnership are aimed at achieving specific goals. But the specificity of accounting is that all activities must be divided into those that are subject to taxation and those that are not. Naturally, if the accountant uses the simplified tax system.
Business activities, income from which are subject to certain taxes, include:
- performing work of members of the organization that does not relate to the maintenance of apartment buildings;
- provision of premises for rent;
- sale of services;
- other income taken into account in Articles 249, 250 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Article 249. Income from sales
- For the purposes of this chapter, income from sales includes proceeds from the sale of goods (works, services) both of one’s own production and those previously acquired, and proceeds from the sale of property rights.
- Sales proceeds are determined based on all receipts associated with payments for goods (work, services) sold or property rights expressed in cash and (or) in kind. Depending on the method of recognition of income and expenses chosen by the taxpayer, receipts related to payments for sold goods (work, services) or property rights are recognized for the purposes of this chapter in accordance with Article 271 or Article 273 of this Code.
- The specifics of determining sales income for certain categories of taxpayers or sales income received in connection with special circumstances are established by the provisions of this chapter.
Income is taken into account regardless of the form in which it was received - in kind or in cash.
Payments for utilities provided by the HOA are also subject to taxes.
If the organization’s constituent documents indicate that it has the right, on behalf of residents, to enter into contracts with suppliers for the receipt of utility services, then intermediary fees are taken into account as income.
How to fill out a book of business transactions?
All business transactions must be registered. For this purpose, there is an accounting book consisting of certain tables.
An example of filling out a book of accounting of business transactions of an HOA:
If the HOA uses the simplified tax system, then all expenses of the organization are indicated in the “Debit” column. As an example, you can use the membership fees paid by all members of the association. The accountant carries out the operation using subaccount 01-1. The balance is zero, as is the account 86.
Then he makes payments to suppliers. The debit position is 60, and the credit position is 51. This means that the payment was made and credited to the bank. At the end of the table, the transfer of funds 86-1 to account 60 (Suppliers) is also indicated.
Step-by-step instructions on how to keep accounting records in a homeowners' association.
The partnership's financial statements for the year include:
- balance;
- income statement;
- report on the intended use of funds.
The responsibility for accounting and reporting remains with the HOA, even if it does not conduct commercial activities and applies the simplified tax system. In addition to the above forms, the HOA is required to maintain a register of members of the partnership. Tax accounting for a homeowners' association. Features of accounting under the simplified tax system. In most cases, the HOA prefers a simplified system. The main advantage of the simplification for HOAs is a reduction in insurance premiums (20% rate). The HOA accountant must distinguish between receipts that are classified as income and amounts that do not fall under this definition and, accordingly, under taxation.
Operations that correspond
Accounting for utility bills
Accounting for funds when calculating rent is the main problem when maintaining accounting records for a housing association using the simplified tax system.
If a separate article in the activities of the HOA specifies the service of providing members of the partnership with housing and communal services resources and on behalf of the organization contracts are concluded with suppliers of housing and communal services resources, then utility payments are not taken into account in income, but only the amount for intermediary services of the HOA.
All payments from apartment owners who are not members of the HOA are fully taxed unless a special agreement has been concluded with them. With the “income minus expenses” accounting scheme, an organization can take into account the amounts of utility services provided in the Expenses item.
If the supply of utilities is not specified in the activities of the partnership, then agency agreements should be concluded with the property owners. And with companies that supply HOAs with resources, contracts for the provision of services are mandatory.
Important! First, an agreement is concluded with residents, and then with service providers!
Example:
If utilities are not included in the organization’s charter, then the accrual of payments for utilities will be accounted for in accounts No. 62 Settlements with buyers and customers, No. 76 Settlements with debtors and creditors and No. 90 Sales. And the receipt of payment from residents will go through accounts No. 50 Cash, No. 51 Current accounts, No. 62 Settlement with buyers and customers, and No. 76.
If services are provided under agency agreements, then payments for services will be charged to accounts No. 76 and No. 60. The organization's income in the form of agency fees is accounted for in accounts No. 76 and No. 90, and fees from residents and agency fees are accounted for in accounts No. 50, No. 51 and No. 76.
Carrying out repairs
Contributions from members of the association for major repairs will not be considered income , while payments from homeowners who are not members of the HOA are income.
Business operations to create a repair fund are carried out on accounts No. 86, No. 20, and No. 96. Contributions from members of the housing association for major repairs are taken into account in accounts No. 55 and No. 76.
Example:
A plumber, employed by the HOA on a piecework basis, performed a number of works for one of the residents. The customer paid only for the work of the master. In accounting entries it should look like this:
- Receiving payment from customer No. 50 No. 62.
- Funds received from a tenant are recognized as income No. 62 No. 90-1.
- VAT accrual No. 90-3 No. 68.
- Calculation of wages for foreman No. 20-2 No. 70.
- Insurance accrual for the amount of payment there No. 20-2 No. 69.
- Write-off of the cost of work No. 90-2 No. 20-2.
- Reflection of profit No. 90-9 No. 99.
Improvement of the local area
Accounting for funds allocated for improvement of the territory takes place in accounts No. 26, No. 51, No. 60, No. 84, No. 86. Example : The HOA received a profit from commercial activities in the amount of 5,000 rubles, and it was decided to use it to install a fountain in the yard, in this case the wiring will look like this:
- Profit is included in target financing, accounts No. 84 and No. 86.
- Costs for improvement using contract No. 26 and No. 60.
- Payment to contractor No. 60 and No. 51.
- Write-off of targeted financing for purposes No. 86 and No. 26.
- The building was registered No. 012.
Renting out non-residential premises
The rental of premises is carried out according to accounts No. 76 and No. 91 . Income from the rental of premises is determined at the time of accrual; the costs of the facility are covered by the rent and are not charged to the customer. VAT is calculated on rent in accounts No. 91 and No. 68.
Expenses for renting premises are considered only those expenses that are not specified in the charter and arose in connection with the rental.
Example:
The homeowners association leases office space.
- The tenant was issued an invoice: No. 62 No. 90.01.
- Received rent from the tenant: No. 51 No. 62.
Check out other useful materials about HOA funds and their accounting. Learn how to properly prepare an estimate and the nuances of working as an accountant in an HOA.
Accounting and tax accounting in homeowners' associations (tsn): postings, documents, benefits
Features of creating an HOA The main purpose of creating an HOA is the following:
- effective management of real estate, which legally belongs to the participants of the partnership;
- timely repair and maintenance of utilities;
- calculation of utilities according to real and not inflated tariffs;
- improvement of the area adjacent to apartment buildings, etc.
Federal law does not prohibit property owners' associations from engaging in commercial activities whose purpose is to generate income.
How can a homeowners’ association on a simplified street keep records of income and expenses (Zhuravleva V.V.)
Answers to pressing questions Question No. 1. How are the amounts received in payment of utility bills from the residents of the house reflected in the HOA's accounting? If the obligation to provide utility services to residents is specified in the charter of the partnership, then receipt of payment for this is reflected in the following entries:
- Dt62, 76 Kt 90 – the amount of payment for utilities has been accrued;
- Dt 50, 51 Kt 62, 76 – utility payments received at the cash desk or on account.
If such calculations are carried out under agency agreements, then:
- Dt 76 Kt 60 - the amount of payment for utilities has been accrued;
- Dt 76 Kt 90 – for the amount of remuneration under the agency agreement;
- Dt 50, 51 Kt 76 - utility bills received at the cash desk or on account.
Analytical accounting for accounts 62 and 76 is carried out for each property owner individually.
How do those who have not joined the HOA pay for utilities?
One of these controversial issues is the payment of utilities by those residents of apartment buildings who have not expressed a desire to join the HOA. Many defend the right to independently conclude an agreement with service and resource companies, according to which the conditions for the provision of services and their payment will be determined. But such a right is not provided for by law.
Even if the homeowners in an apartment building are not members of the partnership, they are required to make appropriate payments for utilities on the same terms as members of the HOA.
Basic rules for accounting in a homeowners' association (nuances)
Kt 90 subaccount “Revenue” - debt of the owner of the premises who is not a member of the HOA (under the same items). HOA expenses: Dt 26 Kt 70, 69, 71, 01, 10 - the costs of maintaining the HOA are recognized; Dt 26 Kt 68 - income tax is charged under OSNO or on income or income-expenses under the simplified tax system; Dt 26 Kt 60 - costs for maintaining the common property of apartment buildings (according to the accounts of resource supply organizations and for services, work of other third-party organizations (removal of solid household waste, etc.); Dt 86, 20 Kt 26 - distributed among the owners of the premises ( members of the HOA and persons who are not such) costs for the maintenance of the HOA and the maintenance of the common property of the apartment building (proportional to the area of the premises); Dt 86, 20 Kt 60 - debt of premises owners for individual consumption of utility resources; Dt 90 subaccount "cost of sales" Kt 20 - costs associated with servicing “non-members” of the HOA were written off.
Accounting in housing and communal services for beginners: from A to Z
Working as an accountant has a number of nuances, and a person needs to undergo training to become a specialist in this field. When working in a management company, it is important to understand the basic things that an employee will have to constantly deal with.
Accounting policy
The accounting policy includes accounting for salaries, company expenses, income, taxes, and also contains information about settlements with organizations that supply resources. A policy is being developed in accordance with the tax code and accounting regulations. Nuances that are not regulated by law are developed independently by management companies. A prerequisite for developing an accounting policy is to indicate the taxation system in it.
Income accounting
A housing and communal services management company, like other commercial organizations, has certain income for which it is necessary to keep accounting records. These include:
- funds received into the company's account from consumers of housing and communal services;
- payment from enterprises or organizations that received services;
- government subsidies for citizens in need of support;
- subsidies;
- refund according to the benefits provided.
Expense accounting
In addition to funds received into accounts, the company also has expenses. These include:
- funds spent on wages to employees;
- costs of maintaining the territory and apartment building;
- office expenses.
Report to the tax office
Management organizations can independently choose the method of paying taxes. This can be done either in the usual manner or using a simplified system. Companies pay two taxes: value added and profit.
Attention! Only small organizations with a staff of no more than 100 people can submit a report using the simplified system.
The legislation does not provide for special rules for accounting accounting of housing and communal services. Management companies have the right to independently decide how accounting will be carried out. The rights and responsibilities of an employee are specified in the job description, which may vary slightly in different organizations.
How to keep accounting records in a homeowners' association using the usn system? step by step instructions and wiring
The decision to create an HOA is made at a general meeting of owners by a majority vote (Article 135 of the Housing Code of the Russian Federation). The number of votes that each owner of the premises has is proportional to his share in the ownership of common property in a given house (Clause 3 of Article 48
Housing Complex of the Russian Federation). To ensure its activities, the partnership has hired personnel - at least a board headed by the chairman of the board. According to the Federal Law of 05.05.2014 No. 99-FZ, from September 1, 2014, HOAs are classified as partnerships of real estate owners.
(TSN) Homeowners' association does not apply to small businesses.
How is accounting carried out in a homeowners' association?
According to the protocol of the owners' decision, the funds were used to improve the adjacent territory of the apartment building and build a children's playground. A contract for landscaping work in the amount of RUB 417,300 was concluded between the Lazurny HOA and Remont Plus LLC.
Upon completion of the work, the following entries were made in the accounting of the Lazurny HOA: Dt Kt Description Amount Document 84 86 Landscaping Retained earnings of the Lazurny HOA were recognized as a means of targeted financing RUB 417,300. Minutes of the owners' decision 10 60 Costs for the arrangement of the local area and the construction of a children's playground are taken into account: RUB 417,300.
Certificate of completion of work 60 51 Funds were transferred in favor of Repair Plus LLC as payment under the contract 417,300 rubles. Payment order 86 Landscaping 10 Targeted funds written off as used for their intended purpose RUB 417,300.
Accounting, tax accounting and reporting in homeowners' associations
The following income does not count as partnership income under the simplified tax system:
- contributions;
- from the owners for the maintenance of the property;
- from the budget for real estate repairs, including capital ones.
According to the charter of the HOA, the main purpose of its creation is the maintenance of common real estate and the provision of utilities to members of the partnership. Therefore, all funds received by the partnership for such purposes are not included in the income of the organization.
It is necessary to take into account that funds received for these purposes from HOA members are not considered income. But funds received for the same purposes from persons who are not members of the partnership are considered income and are subject to taxation. Cash receipts that are subject to and non-taxable must be accounted for separately.
Accounting in a homeowners' association: procedure and features
Amounts of payments for housing and communal services (electricity, water supply, etc.) received into the account of the HOA are revenue from the sale of work (services) and, accordingly, must be taken into account as part of income when calculating income tax in accordance with Article 249 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation ( letters of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated November 18, 2015 No. 03-11-06/2/669/7, dated June 29, 2011 No. 03-01-11/3-189). Taxation in HOAs regarding income-generating activities does not differ from the rules for commercial organizations. VAT benefit Homeowners' associations are VAT payers. The objects of taxation are transactions involving the sale of goods, products, works and services (Article 146 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). An exception is remuneration for work and services of an individual nature (subclause 4, clause 1, article 137 of the Housing Code of the Russian Federation). Accounting in the HOA (TSN) The common property in the HOA (clause 1 of Article 36 of the Housing Code of the Russian Federation) is accepted for off-balance sheet accounting.
A special account is opened for this purpose. The HOA, represented by the board, is obliged to maintain accounting records and prepare financial statements. (Law of January 12, 1996 No. 7-FZ; Article 148 of the Housing Code of the Russian Federation; letters of the Ministry of Construction of Russia dated April 10, 2020 No. 10407-ACh/04. HOAs can operate both under the general taxation system (OSNO) and under the simplified tax system (USN).
As part of HOA revenues
- taxable
- non-taxable amounts.
When receiving target revenues, the HOA is obliged to keep separate records of expenses incurred within the framework of the target revenues (clause 2 of Article 251 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation); it is necessary to ensure the distribution of indirect costs in the HOA.
Accounting for homeowners associations and housing and communal services. Generating transactions
In the last article we looked at the activities and accounting in HOAs, in this article we will pay attention to the following questions: what is the main activity of the Management Company (MC) and what are the features of accounting in the Management Company? The management company buys housing and communal services from suppliers and sells them to the public. Let's look at how accounting is organized in the Management Company.
A management company is a legal entity that, in accordance with an agreement concluded with a Homeowners Association or housing cooperative, manages apartment buildings. Her responsibilities include:
- provide utility services to home owners;
- monitor the condition of the entrusted object and carry out its repairs;
- perform other work related to building management.
The HOA on OSNO is obliged to accrue and pay to the budget all taxes and fees provided for by law, as well as submit the relevant declarations to the regulatory authorities. For late submission of reports, the responsible persons of the partnership will be subject to penalties and interest.
To jointly manage the common property of an apartment building, the owners of premises can unite into homeowners' associations (HOAs) (Article 135 of the Housing Code of the Russian Federation). We will tell you how to keep accounting and pay taxes for homeowners associations using the simplified tax system in our article.
Accounting in HOAs requires the mandatory generation of reports that must be submitted both to the Federal Tax Service and to statistical authorities and extra-budgetary funds. Accounting statements in such partnerships are prepared for the year (even if the HOA does not carry out commercial activities and is on the simplified tax system), and includes:
- Balance.
- Report on the intended use of funds.
- Register of members of the partnership.
- Income statement.
The main difference between these systems during accounting is that for the simplified tax system the composition of reporting is significantly reduced.
The developer of accounting policies is most often the chief accountant or another authorized person.
The accounting policies of housing and communal services organizations are formed by them independently after conducting serious analytical work. The accounting policy should be formed taking into account the specifics of work in the housing and communal services sector, contractual obligations, and the competent organization of tax accounting at the enterprise.
Since the work of the management company provides for several options for making mutual settlements both with residents of apartment buildings and with resource supply companies, the nuances of their accounting are different. Let's consider the main and most common of them, enshrined in clause 6.2 of Art. 155 of the Housing Code of the Russian Federation, when the Criminal Code is a party to an agreement on the provision of paid services.
The HOA is a non-profit organization (clause 4, clause 3, article 50 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation). The funds of the HOA consist of the following (clause 2 of Article 151 of the Housing Code of the Russian Federation):
- mandatory payments, entrance and other fees of HOA members;
- payments from homeowners who are not members of the HOA;
- income from the entrepreneurial activities of the HOA, aimed at fulfilling the goals, objectives and responsibilities of the HOA (Article 152 of the Housing Code of the Russian Federation);
- subsidies for the operation of common property, carrying out current and major repairs, providing certain types of utilities and other subsidies;
- other supply.
When concluding any agreements, the management of the HOA must respect the interests of the homeowners. All proceeds received go to the current account of the partnership. After this, the funds are distributed to special funds. The HOA can spend it only in those areas that were reflected in the statutory documentation approved by all property owners.
When paying the latter, management companies have an advantage over other commercial organizations: according to the provisions of Article 149 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, utility services provided to the population and repair services provided by management companies with the involvement of third-party contractors are exempt from VAT.
However, these legislative norms in practice provide virtually no savings: in the first case, this is impossible, since utilities are paid at uniform tariffs, and management companies actually do not earn money from them (therefore, the VAT tax base is 0).
In the second case, arbitration practice is as follows: tax authorities believe that only that income from repairs is not subject to VAT, the amount of which is equal to expenses - amounts paid to third parties.
This point of view is supported by the courts, so theoretical savings in practice only result in unnecessary disputes with regulatory authorities.
The simplified taxation system for management companies can be applied in the following cases:
- the company's income for the period does not exceed 60 million rubles;
- the organization's staff should not exceed 100 people;
- the book value of the company's fixed assets is less than 100 million rubles.
Accounting for a homeowners' association, simplified posting using an example in 2020
To do this, make the following entries in accounting: Debit 62 (76) Credit 90, subaccount “Revenue” - utility fees have been charged; Debit 50 (51) Credit 62 (76) - payment for utilities received. At the same time, organize analytical accounting for accounts 62 and 76 so that settlements with each tenant are visible.
Option No. 2. An agency agreement has been concluded with the residents. If your HOA acts as an intermediary, receiving money to pay for housing and communal services, make the following entries: Debit 76 Credit 60 - utility fees have been charged; Debit 76 Credit 90, sub-account “Revenue” - agency fees accrued; Debit 60 Credit 50 (51) - payment for the services of the resource supply company is transferred; Debit 50 (51) Credit 76 - payment for utilities received from residents; Debit 50 (51) Credit 76 - intermediary fee received. HOA facilities consist of:
- mandatory payments, entrance and other contributions of members of the partnership;
- income from the economic activities of the partnership;
- subsidies for the maintenance of common property, repairs, provision of certain types of utilities,
- other income.
The HOA uses funds from mandatory payments and contributions to pay for the costs of maintaining and routine repairs of common property in an apartment building, as well as to pay for utilities. They do not generate income. The list of types of economic activities that the HOA has the right to engage in is closed.
Management companies, homeowners associations and housing cooperatives
The Moscow housing renovation program can reduce carbon dioxide emissions by 200 thousand tons due to a reduction in heat and electricity consumption, and can also reduce the consumption of heat, electricity and water by up to 40-50%, Anton Kulbachevsky is sure. The head of the environmental management department talks about this.
Addresses of houses for renovation, fighting the heat, guide dogs in the subway, the garden of the future, musicians in the subway, electric motorcycles for the police, a sports cluster, human trafficking - in a special review by REGNUM News Agency.