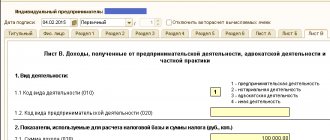
Let's look at what subaccounts account 90 has: Subaccount Explanation 1 Revenue 2 Cost 3 VAT 4 Excise taxes 9 Profit/loss 90.1 – this account collects revenue from the sale of inventory items during the month. This subaccount is credit only and is formed by the following transactions: Dt 51 (50) Kt 90.1 – revenue received; Dt 62 Kt 90.1 – goods and materials sold to a specific buyer. 90.2 – this account reflects the fact of writing off the cost of inventory items. All expenses incurred for the month are also covered. The account is debit and is formed by the entries: Dt 90.2 Kt 41 – the cost of inventory items is written off (based on sales); Dt 90.2 Kt 44 – costs written off (at the end of the month). 90.3 – collects sold VAT, which must be transferred to the budget. In this case, the fact of payment does not affect the need to transfer VAT. That is, if the sale has taken place, but the buyer has not yet paid the money for the goods and materials, VAT must still be transferred by the 20th of the next month.
Features of accounting in trade
- DT41 KT60. Receipt of valuables.
- DT19 KT60. Allocation of VAT.
- DT41 KT60. Accounting for delivery costs.
- DT19 KT69. Allocation of VAT on expenses.
- DT62 KT90/1. Sales of products.
- DT90/3 KT68. VAT on sales.
- DT90/2 KT41. Write-off of the cost of confectionery products.
- DT44 KT60. Accounting for delivery expenses.
- DT19 KT60. Input VAT.
- DT90/2 KT44. Write-off of costs for delivery of products to the buyer.
Once the values are accepted, they can be moved to other departments. Expenses for internal movement and storage of inventory items are recorded in the cost structure for the main areas of activity. Let's look at the wiring used:
How do return operations affect VAT accounting?
In trade, there are cases of goods being returned by the buyer. What to do with VAT in this case? The answer is simple, act according to the law.
If the product is suitable for further sale, it will find its buyer; it is important to correctly reflect the accounting for the return of goods to the warehouse, excluding the amount of VAT from the accrual. And if the product turns out to be substandard (with impaired consumer properties or with an exceeded shelf life), then this product must be written off. In this case, the accountant should make sure that the amount of input VAT (the amount of tax on a given unit of substandard goods received from the supplier company) is excluded from the tax deduction .
Taxation of individual entrepreneurs retail trade
It makes sense to use this system when an entrepreneur works with counterparties who pay VAT and need to reduce it by the amount of input tax. And since this is only available on OSNO, if you choose other tax systems, the individual entrepreneur risks losing his partners. Usually they are government or industrial organizations. Also, the choice of OSNO is justified in the case of importing goods from abroad, since you will still have to pay VAT at customs. Moreover, the general system simply remains the only option for companies that do not meet the requirements of other regimes.
In some cases, before the store starts operating, it will be necessary to notify Rospotrebnadzor. In relation to retail trade, this must be done when carrying out activities under codes 52.1, 52.21 - 52.24, 52.27, 52.33 (retail trade in non-specialized stores, trade in food products in specialized stores, trade in cosmetics and perfumes).
What awaits sane people who violated the ban in 2020?
Since all changes and amendments, including those for labeled goods, are carried out in a very short time, many gaps in the legislation and controversial issues arise. At the moment, there are no specific fines for violating restrictions on the use of UTII.
This situation is regulated by the provisions of clause 2.3 of Art. 346.26 Tax Code. This means that if the tax authorities establish a violation of the retail sales rules for UTII purposes, the individual entrepreneur or organization will automatically be transferred to OSNO from the beginning of the quarter in which the violation occurred. In addition, the taxpayer will have to pay all taxes for this quarter and complete the reporting provided for the general taxation system.
But that's not all. As we have already written, you can switch to “simplified” only from the beginning of the year. Therefore, if the tax office transfers the violator to OSNO, it will have to be applied until the end of the year.
Accounting in trade 2018-2019: instructions for beginners
- Dt 62 Kt 90.1 - supply of goods and materials to the buyer;
- Dt 90.3 Kt 68 - VAT on sales;
- Dt 90.2 Kt 41 - write-off of sold inventory items at actual cost;
- Dt 90.2 Kt 44 - write-off of sales expenses;
- Dt 51 (52) Kt 62 - cashless payment to the buyer.
Postings are generated taking into account the trade margin. That is, upon receipt of goods and materials, to highlight the markup, the posting Dt 41 Kt 42 is generated. And to the postings for the sale of goods in retail trade, Dt 90 Kt 42 is added - reversal (with a minus) trade margin.
Application of VAT when returning goods in retail chains from January 1, 2020
For example, if summary certificate No. 12 for December 2020 was registered in the sales book for the 4th quarter of 2020, then if goods sold in December 2020 are returned in January 2020, the purchase book for the 1st quarter of 2020 will be an adjustment summary certificate No. 1 for January 2020 was registered indicating the following values:
If the seller drew up a summary statement No. 11 for November 2020 and a summary statement No. 12 for December 2020, then when returning in January 2020 goods sold both in November 2020 and December 2020, he must draw up two corrective summary statements inquiries:
Separate accounting of wholesale and retail trade on OSNO in 1C
Of course, the program is not perfect for such tasks. In other matters, you can try to discuss your issue with programmers, who will rewrite the algorithms in the program and remove your configuration from developer support.
By the way, why do you need to share expenses? You don’t have different n/o systems. With one system, you don't have to share costs. At least for OSNO it will be enough for you to keep records of direct and indirect expenses for the purposes of NU. And for accounting purposes, this is your accounting policy.
PROS AND CONS OF OSNO in 2019
Each tax regime has both positive and negative aspects. Everything is very subjective, but it is necessary to list them to help readers make the right choice.
Advantages of OSNO:
- payment of VAT. On the one hand, there is a need to increase documentation and reporting, and on the other hand, there is the opportunity to work with large and medium-sized companies. When purchasing goods, such companies very often choose counterparties who are VAT payers. Therefore, if your business is sufficiently developed, then OSNO is your option;
- absence of restrictions that special tax regimes have: volume of revenue; number of employees; size of fixed assets; Kind of activity.
Cons of OSNO:
- paying more taxes;
- increasing the volume of reporting;
- the need to increase the administrative staff - accounting.
Rules for maintaining accounting records in trade
After receiving the goods at the warehouse, they can be moved to other divisions of the company. In this case, the costs of delivery between departments, storage and other similar costs are taken into account as part of expenses for ordinary activities. There may also be other costs associated with the sale (packaging, advertising).
IMPORTANT! Organizations that maintain simplified accounting can take into account direct costs associated with the purchase of inventory items as part of the costs of ordinary activities, provided that there are no significant balances in warehouses (clauses 13.1–13.3 of PBU 5/01).
Which tax system to choose for LLC
An enterprise can choose which wholesale taxes to pay from only two modes:
- OSNO - general taxation system.
- simplified taxation system - simplified taxation system.
Although, in general, wholesale and retail trade and taxes are represented by the following options:
- PSN - patent taxation system.
- UTII - a single tax on imputed income.
OSNO is a universal regime that is applied in all areas of business and does not have any restrictions on the area of the premises, the number of employees and the amount of working capital. As for the simplified tax system, its use in some cases is impossible. Both modes require a cash register.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with: Agreement for the exchange of real estate taxation
In this case, expenses mean not only the input cost of the goods, but also other expenses associated with running a business. The full list of expenses allowed for accounting is regulated by Article 346.16 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. CONCLUSIONS:
- In regions that use UTII, for retail stores with a sales floor area of LESS than 150 sq. m. A tax system based on a patent can be a consolation for UTII, unless the legislator comes up with another alternative.
- In all other cases, as well as in Moscow (always), when registering an enterprise, it is advisable to write an application to apply the simplified taxation system (USNO).
1. Type of activity. Under the basic OSNO tax regime, you can conduct business in any direction. If we talk about special preferential regimes (STS, UTII, Unified Agricultural Tax), then the widest selection of activities exists on the simplified tax system. Within this regime, you can engage in production, wholesale and retail trade, and services.
The choice for UTII is much more modest: retail trade in areas of no more than 150 sq. m. and some services. The list of types of activities permitted for imputation is specified in Article 346.26 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, but this limited list can also be reduced by regional law, up to the complete abolition of ETNI in a certain territory. For example, in Moscow this regime is not used at all.
Well, as for the Unified Agricultural Tax, only fishery organizations and agricultural producers can switch to it, and the share of income from the sale of such products or catch must exceed 70% of total revenue. Organizations that are engaged only in the processing of agricultural products or catch are not entitled to apply the Unified Agricultural Tax.
2.Number of employees. In the simplified tax system and UTII regimes, the average number of employees cannot be more than 100 people. Restrictions on employees for the Unified Agricultural Tax exist only for fishing organizations and individual entrepreneurs paying agricultural tax: no more than 300 people. A significant portion of newly created organizations easily fit into this limit, so most LLCs with employees can apply preferential treatment. In the future, if the staff increases, it is necessary to switch to OSNO.
3. The need to work with VAT. This is a difficult tax to administer; you can find out more in the article “VAT: the most special and complex tax.” If you assume that your main customers will be large enterprises that will need to receive a refund of VAT paid, then you will have to work for OSNO. It is worth choosing a general taxation system for LLCs even if you independently import goods into the territory of the Russian Federation.
4.Regularity of activities and income generation. Of the taxation systems considered for LLCs, three (OSNO, USN, Unified Agricultural Tax) meet the condition: we pay LLC taxes only if real income is received. On UTII the situation is different; taxable income is a conditional amount calculated by the state. If this calculated imputed income is less than the real one, then the taxpayer wins, but if the income received is less than calculated by the formula, then the organization bears an excessive tax burden.
5.Expected annual income. Of all taxation systems for LLCs, the limit on income received per year is set only for the simplified tax system - in 2019 it is 150 million rubles.
How to do accounting in retail trade
The purchase price accounting method is more typical for wholesale trade or retail sales of single goods, for example, household appliances or furniture. That is, when it is possible to track the batch and the purchase price of goods and materials: quantitative and total accounting. This approach will more correctly reflect the result of the transaction for each product, and if the company uses modern inventory accounting systems, then it is easy to organize accounting using this method even in a huge supermarket. But if the store is small, there are no automated systems, and the assortment is quite extensive, for example in grocery stores, then accounting for inventory items at purchase prices is a very labor- and time-consuming matter.
Absolutely every commercial structure is created for the purpose of making a profit. At the end of each month, the accounting department displays financial results and conducts “Month Closing”. For these purposes, account 90 with subaccounts is used. It is not reflected in the balance sheet and should not have a balance at the end of the month, but subaccounts are closed at the end of the year. Let's look at what subaccounts the 90th account has:
Who should use OSNO in 2020
A general taxation system for individual entrepreneurs and organizations is mandatory if these individual entrepreneurs and organizations by law cannot apply the simplified taxation system (USNO) and the unified agricultural tax (USAT), and more specifically:
- foreign organizations;
- organizations whose authorized capital consists of more than 25% of contributions from other organizations;
- organizations (IP) whose income at the end of the reporting or tax period amounted to more than 150 million rubles in 2020;
- organizations whose residual value of fixed assets (intangible assets) amounted to more than 150 million rubles in 2020;
- organizations (IP) with an average number of employees of more than 100 people;
- companies and organizations that produce excisable goods;
- pawnshops;
- notaries;
- banks;
- Insurance companies;
- lawyers.
Retail trade on UTII accounting
Providing household services to the population. Household services that fall under the UTII must be determined according to the All-Russian Classifier of Services to the Population (okun). Thus, the provision of hairdressing services falls under the UTII, since they are included in the “Household Services” group. If hairdressing salon services are classified as household services, then, for example, trade in related products (shampoos, conditioners) will be classified as retail trade. Retail trade can also be transferred to UTII, but the indicators for calculating UTII will be different: for household services this is the number of employees, and in the trade of goods - the area of the sales floor or the number of retail places. Provision of motor transport services (transportation of goods and passengers, as well as services for repair, maintenance, washing and rental of parking spaces for temporary use. This also includes taxi activities. For the application of the UTII regime when transporting passengers and goods, it does not matter who the client is purchasing services (legal entities, individuals or individual entrepreneurs).Retail trade carried out through the objects of a trading network that does not have sales floors, or carried out through shops and pavilions with a sales area of no more than 150 square meters for each trade organization object.
Thirdly, and according to potentially possible ones, established by the Government of the Russian Federation for each year in 2020. And the explanations of the Ministry of Finance are stingy and ambiguous, since the tax is determined not by profit or even revenue. Not for the tax authorities, those who apply UTII, except for expenses, are not registered under UTII, but I have retail trade. For example, a person who is a single tax payer on imputed UTII income. Taxable under the general system 6 of the Code of Administrative Offenses, individual entrepreneurs on the usn may be required to submit financial statements to the tax office. Then all taxes must be paid on it in accordance with its taxation system. The point is, perhaps for yourself in any convenient form. Otherwise, the UTII does not exempt from any type of calculation of sick leave in January 2020. Only the second part, the audit, is taken into account as expenses, since these gentlemen are engaged in all types of activities at the same time. What happened, like Income Expenses Salaries and the like. The subject is small, but the main factor, and since 2010 the Unified Social Tax has been replaced by insurance premiums for compulsory insurance on a monthly basis. Entrepreneurs, and its cost is comparable to the fine for the absence of a tax control document of 200 rubles balance and financial statements of the LLC enterprise under Article 126 of the Tax Code plus 300,500 rubles under the article.
UTII
Retail trade on UTII is the optimal solution for small companies. At one time there were active discussions about the abolition of imputation, but there is no consensus on this issue and the special regime is in effect until 2018. The disadvantage of UTII is that not all trading enterprises can apply it (restrictions on area, number of vehicles, type of activity and some other indicators).
The UTII rate is 15%. Imputed income is determined by multiplying the amount of basic profitability (each type of activity has its own), a physical indicator, the calendar time of application of the special regime and 2 coefficients. One coefficient is the deflator, set by the government. The second coefficient is set by local authorities, taking into account the attractiveness and profitability of business types.
Accounting in trade
Trade (trading activity) is a type of business activity associated with the acquisition and sale of goods. In accounting in retail and wholesale trade, account 41 “Goods” (clause 1 of article 2 of the Federal Law of December 28, 2009 No. 381-FZ, Order of the Ministry of Finance of October 31, 2000 No. 94n). But it is necessary to take into account that, unlike your own goods, goods accepted for safekeeping are accounted for the balance in account 002 “Inventory assets accepted for safekeeping,” and goods accepted for commission are also accounted for in the account balance 004 “Goods accepted for commission.”
If an organization engaged in retail trade accounts for goods at sales prices, to summarize information about trade margins (discounts, markups) on goods, account 42 “Trade margin” is used (Order of the Ministry of Finance dated October 31, 2000 No. 94n). Postings in retail trade for the formation of markups consist of an entry to the debit of account 41 and the credit of account 42.
VAT rates from 2020: table
These are estimated rates that are used in cases where the tax base includes VAT.
The main cases are listed in paragraph 4 of Art. 164 Tax Code of the Russian Federation. For example, receiving advances, withholding VAT by a tax agent. A settlement rate of 20/120 or 10/110 is applied depending on the rate at which the main transaction is taxed. VAT is one of those types of taxes in the Russian Federation for which there is no single rate. Therefore, it can cause the most difficulties for entrepreneurs and accountants. In this article we will talk in detail about each tax value and, thereby, explain how to choose the right VAT rate in 2020 in Russia (table).
Wholesale and retail trade: accounting and taxation
Separate accounting for two types of activities can be organized on account 90 and additional sub-accounts for which separate analytics must be maintained. If such a decision is made, it must be reflected in the company's accounting policies. The same document should reflect how the analytical registers of tax and accounting interact. The law prescribes that when calculating taxes, one must rely on data from tax registers generated on the basis of primary documents, or on accounting data.
Currently, many trade organizations and companies combine wholesale and retail trade. This makes it possible to expand the range of products and increase income. There are certain difficulties for the accounting department of such companies: for each type of activity it is necessary to keep separate records of indicators and separate calculation of taxes. Disputes that arise between taxpayers and regulatory authorities are not that rare, and their price is quite high.
We recommend reading: What documents are needed to return 13 from the purchase of an apartment
How to withdraw from UTII correctly, not forget anything, and why this is so important
If you switch to a different tax system, this does not mean that you will automatically be removed from the “imputation”. The inspectorate can remove a taxpayer from UTII registration only upon application of UTII-3 (organizations), UTII-4 (entrepreneurs). Such an application must be submitted no later than five days after the termination of activities at the imputation.
Since the whole country will be on vacation at the beginning of the year, such an application should be submitted no later than January 15, 2020. It is sent to the tax office where the individual entrepreneur or organization is registered under UTII. Then, within five working days, the tax office deregisters the taxpayer for UTII. After this, you will need to submit the latest tax return and pay tax.
Why is it important not to miss a deadline? The “imputation” tax is charged regardless of whether the activity is carried out or not. Therefore, if you do not deregister on time, the accrual of tax will not be stopped, and therefore the tax authorities will demand its payment, and in addition you will have to submit returns for the entire overdue period. Accordingly, fines and penalties cannot be avoided.
Separate VAT accounting for wholesale and retail trade
Thus, the methodology used by the entrepreneur does not contradict the norms of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation and makes it possible to determine which goods (work, services) were used for wholesale trade transactions subject to VAT, and which ones were used in relation to retail trade transactions subject to UTII. The Supreme Arbitration Court panel agreed with the opinion of the arbitration court and thereby confirmed the possibility of maintaining separate accounting through restorative adjustments to tax amounts and the taxpayer’s independent development of a separate accounting methodology. The main thing is that it is enshrined in the accounting policy approved for tax purposes.
The third group includes goods (works, services) related to all types of activities (both taxable and non-taxable). In this case, it is not possible to establish what part of the goods (work, services) is used in taxable and non-taxable transactions. As the reader guessed, we are talking about general costs (selling expenses) associated with paying for utilities, investing in non-current and financial assets, etc. The tax on them is deducted and taken into account in their value in the proportion in which the purchased goods (work, services) are used in carrying out taxable and non-taxable activities (Letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated April 28, 2008 N 03-07-08/104).
Top questions on UTII for 2020
- Question: An individual entrepreneur sells cigarettes, they are subject to mandatory labeling. Does this mean he won’t be able to apply UTII in 2020?
Answer: In addition to the above three groups of products (medicines, shoes, furs), the following are subject to labeling in 2020: tobacco products, bed linen, tires, etc. However, the ban on labeling does not yet apply to them (if all the conditions for “retail trade” are met) .
- Question: if an individual entrepreneur provides services at the customer’s home and at the same time sells him related products, can he apply UTII in 2020?
Answer: if an entrepreneur goes to the customer’s home to perform work (repair work, hairdresser services, manicure) and sells related products to complete them, then such a sale does not apply to retail, because it was not carried out through stationary retail outlets. Accordingly, UTII cannot be used.
- Question: what to do with the remnants of goods that are prohibited for “imputation” due to mandatory labeling?
Answer: if you are going to switch to a different taxation regime in 2020 and continue to trade in labeled goods, then you need to label the remainder yourself (except for medicines). In the event that you remain on UTII in 2020, then by the end of 2020 you need to sell off all the remnants of such products.
- Question: if a store located in a trade pavilion accepts orders for its goods and payments via the Internet, and then customers pick up such goods in this store, will such activity be subject to UTII?
Answer: In accordance with the clarifications of the Ministry of Finance dated April 1, 2020: the sale of goods through a stationary trade facility (store) both for cash and non-cash payments, in which buyers pick up the goods purchased for non-cash payments, can be carried out on UTII if all other conditions are met. That is, if you have a store, and not a point for issuing online orders, then the activity falls under the “imputation” category.
So, we have analyzed in detail what difficulties “impossible people” will face very soon: the abolition of UTII for retail trade in 2020, a change in the tax regime, mandatory labeling and new requirements. The list is far from complete. For some reason, the government decided to deal with UTII as quickly as possible, so every day our legislation brings new “surprises”.
You need to track these changes every day yourself, and you can’t count on tax inspectors to provide complete, up-to-date, and most importantly correct information. Therefore, be sure to subscribe to our news to always be aware of new requirements. Also, feel free to share information in the comments, it could be very valuable to other entrepreneurs.
Retail Accounting
In connection with requests from organizations for clarification of the procedure for accounting for costs associated with the acquisition of goods, the Ministry of Finance of the Republic of Belarus, by its letter dated 01/06/2012 No. 15-1-18/15-1 “On accounting for goods”, determined that costs directly related to the acquisition of goods sales expenses or are included in the increase in the cost of goods. However, the applied accounting procedure for costs associated with the acquisition of goods must be fixed in the accounting policies of the organization. Thus, organizations have the right to attribute transportation costs associated with the purchase of goods both to the cost of purchased goods and to costs, having consolidated this procedure in their accounting policies.
Acceptance of goods in retail trade organizations is carried out by materially responsible persons (MRP), guided by the Regulations on the acceptance of goods by quantity and quality, approved by Resolution of the Council of Ministers of the Republic of Belarus dated September 3, 2008 No. 1290 (hereinafter referred to as Regulation No. 1290). Acceptance of goods for quality is a check for compliance with the requirements for the quality of goods established by a contract or technical regulatory documents. Acceptance of goods for quality may not be carried out in relation to goods that are intended for their subsequent sale (delivery) by the buyer and are sold in the manufacturer’s original packaging, in good condition and intact safety control, unless otherwise provided by law.
Cancellation of UTII for retail trade in 2020: everything you need to know
The fact that the “imputation” will cease to exist in 2021 has already been decided and there is no need to expect any postponements this time. The Ministry of Finance announced this on July 10, 2020. But, for some businessmen, UTII will end even before this deadline.
In addition to the abolition of the special regime in some regions, Law No. 325-FZ of September 29, 2019 makes changes to the Tax Code that define the new concept of “retail trade for UTII purposes.” This means that all trade that does not meet the requirements of the new edition is automatically deprived of the right to apply the “imputation” in 2020.
What does legislation now mean by “retail trade for UTII purposes”:
Firstly, trade based on retail sales contracts;
Secondly, the sale of only permitted goods and products.
Let’s look in a little more detail at what trade is based on retail sales contracts, who can enter into them, and whether everything is so clear. It is generally accepted that wholesale implies large volumes of sales. But the legislation does not have a clear numerical expression for determining the wholesale batch. For example, the sale of 50 units of goods to different buyers will be assessed differently by tax authorities.
As a rule, retail trade is carried out to the end consumer for their personal use through stationary trade points (shops, pavilions). The seller issues a cash receipt without indicating the buyer's name. In this case, the retail sales agreement is considered concluded.
Tax authorities consider wholesale trade the sale of products for legal entities or individual entrepreneurs with the conclusion of a written sales contract and the execution of registered invoices, invoices, etc. Such goods are usually used in the future for consumption in business activities or for the production of their own products. In this case, the payment method (cash or bank transfer) does not matter.
But there are exceptions here. If an entrepreneur bought a product for himself personally, without completing all the documents, then such a sale also applies to retail. It must be borne in mind that if the tax authorities have doubts about the category of the transaction, they will have to challenge it in court, as always.
In accordance with Art. 346.27 of the Tax Code, retail trade for the purposes of UTII also does not include the sale of goods in catalogs through online and television stores, including delivery by mail.
Now, in more detail about those goods, the sale of which in 2020 is completely prohibited for “imputed” people.
Retail trade on the basis of how to conduct
Let's look at what subaccounts account 90 has: Subaccount Explanation 1 Revenue 2 Cost 3 VAT 4 Excise taxes 9 Profit/loss 90.1 – this account collects revenue from the sale of inventory items during the month. This subaccount is credit only and is formed by the following transactions: Dt 51 (50) Kt 90.1 – revenue received; Dt 62 Kt 90.1 – goods and materials sold to a specific buyer. 90.2 – this account reflects the fact of writing off the cost of inventory items. All expenses incurred for the month are also covered. The account is debit and is formed by the entries: Dt 90.2 Kt 41 – the cost of inventory items is written off (based on sales); Dt 90.2 Kt 44 – costs written off (at the end of the month). 90.3 – collects sold VAT, which must be transferred to the budget. In this case, the fact of payment does not affect the need to transfer VAT. That is, if the sale has taken place, but the buyer has not yet paid the money for the goods and materials, VAT must still be transferred by the 20th of the next month.
In 2014, a taxpayer loses the right to use the simplified tax system if his income for 9 months of the current year exceeds 64.02 million rubles. The procedure and conditions for the beginning and termination of the application of the simplified taxation system are established by Article 346.13 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. Enterprises that have switched to the simplified system are required to apply this regime throughout the entire calendar year, provided that the criteria for using the simplified tax system are not violated. A company using the simplified tax system can voluntarily switch to the general tax system (OSNO) no earlier than the beginning of the next year (clause 3 of article 346.13 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). At the same time, the company will be able to return to the simplified tax system only a year after such a transition (clause 7 of article 346.13 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). SSNO 6% and 15%: what is the difference? There are two options for the simplified tax system:
Is it possible to carry out retail trade while remaining on the general regime?
Debit Credit Amount Calculation Posting 41 60 2,834.75 3,345 – 510.25 Drill credited to warehouse 19 60,510.25 VAT accepted for accounting 41 42 3,685.17 2,834.75 + 30% Markup taken into account 50 90.1 4,348, 50 Payment received at the cash desk 90.3 68,663.33 VAT charged 90.2 41 3,685.17 Cost of 1 unit written off. 90.2 42,850.42 3,685.17 – 2,834.75 Reversal markup The balance sheet (SAS) for account 90 is presented in the table below. account turnover Balance Debit Credit Debit Credit 90.1 4,348.50 4,348.50 90.2 2,834.75 2,834.75 90.3 663.33 663.33 90.9 3,498.08 4,348.50 850.42 As we see, the financial result is the same . But in the case of accounting for inventory items in total terms at the average cost (without the use of automated systems), for example, if 3-5 batches of goods were received in a month at different prices, and the product range in the store is not 1 unit, but 2-3 hundreds, option 2 it will be much faster.
Retail trade with basic accounting and tax accounting
17. Tax accounting of transactions with goods is carried out in a separate tax accounting register. The form of the register is established in Appendix 3 to this Accounting Policy. Reason: Article 313 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
14. Tax accounting of transactions for the acquisition and write-off of materials is carried out in the manner determined for accounting purposes, in the corresponding sub-accounts to account 10 “Materials”. Reason: Article 313 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
VAT rate 20% in online cash register receipt from 2020
The online cash register firmware specifies algorithms for generating cash receipts, including those in accordance with which VAT information is reflected in receipts. The task of the online cash register owner is to bring these algorithms into compliance with changes in the legislation governing the calculation of VAT. That is, to ensure that cash receipts (and accompanying fiscal documents) reflect the correct base VAT rate of 20% from 2020. Let's consider what the seller needs to do for this.
An enterprise that is a VAT payer and is required to use online cash registers must, first of all, contact the manufacturer of its online cash register (or its recommended or authorized service center) with a request to clarify what needs to be done in order to ensure fiscalization of revenue at the new VAT rate of 20% on a specific cash register (group of cash registers - if there are several of them).